jQuery实现放大镜效果
1.1.1 摘要
相信大家都见过或使用过放大镜效果,甚至实现过该效果,它一般应用于放大查看商品图片,一些电商网站(例如:凡客,京东商城,阿里巴巴等)都有类似的图片查看效果。
在接下来的博文中,我们将向大家介绍通过jQuery实现放大镜效果。
目录
1.1.2 正文
实现原理
首先,我们讲解一下放大镜效果的实现方式:
方法一:准备一张高像素的大图,当鼠标放到原图上,加载显示大图的对应位置。
方法二:对原图片进行放大,也就是调整原图的长和宽。
上面我们介绍了通过两种方式实现放大镜效果,接下来,我们将以上的两种方式应用到我们的jQuery插件中。
首先,我们需要一个img元素显示原图对象,还需要一个容器作为显示框;显示框里面存放大图对象。当鼠标移动到原图上时,通过对大图进行绝对定位来显示对应的部位,实现类似放大镜的效果。
接下来,让我们定义Index.html页面,具体实现如下:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<title>jQuery Image Zoom Demo</title>
<meta name="author" content="Jackson Huang">
</head>
<body>
<div class="magnify">
<div class="large"></div>
<img class="small" src="./img/1.jpg" width="700" />
</div>
</body>
</html>
上面,我们定义了small对象用于显示原图,而large对象作为一个显示框用来显示大图的对应位置。
mousemove事件
接下来,我们通过jQuery插件形式来实现放大镜效果,当鼠标移动到small对象上方时,就会在large对象中显示大图的对应位置,这就涉及到mousemove事件了,所以,我们需要实现mousemove事件的监听方法(如何定义jQuery插件可以参考《自定义jQuery插件Step by Step》)。
现在,让我们实现jquery.imagezoom.js插件吧!
;
(function ($) { $.fn.imageZoom = function (options) { // The native width and height of the image.
var native_width = 0,
native_height = 0,
current_width = 0,
current_height = 0,
$small = $(".small"),
$large = $(".large"); $(".magnify").mousemove(function (e) {
/* Act on the event */
if (!native_width && !native_height) {
var image_object = new Image();
image_object.src = $small.attr('src'); // Gets the image native height and width.
native_height = image_object.height;
native_width = image_object.width; // Gets the image current height and width.
current_height = $small.height();
current_width = $small.width(); } else { // Gets .maginfy offset coordinates.
var magnify_offset = $(this).offset(), // Gets coordinates within .maginfy.
mx = e.pageX - magnify_offset.left,
my = e.pageY - magnify_offset.top; // Checks the mouse within .maginfy or not.
if (mx < $(this).width() && my < $(this).height() && mx > 0 && my > 0) {
$large.fadeIn(100);
} else {
$large.fadeOut(100);
} if ($large.is(":visible")) {
/* Gets the large image coordinate by ratio
small.x / small.width = large.x / large.width
small.y / small.height = large.y / large.height
then we need to keep pointer in the centre,
so deduct the half of .large width and height.
*/
var rx = Math.round(mx / $small.width() * native_width - $large.width() / 2) * -1,
ry = Math.round(my / $small.height() * native_height - $large.height() / 2) * -1,
bgp = rx + "px " + ry + "px",
px = mx - $large.width() / 2,
py = my - $large.height() / 2;
$large.css({
left: px,
top: py,
backgroundPosition: bgp
});
} }
});
});
上面,我实现了mousemove事件的监听方法,当鼠标移动到magnify对象中,我们需要获取当前鼠标的相对坐标位置,下面我们通过图片讲解如何获取鼠标的相对坐标位置。
相对坐标
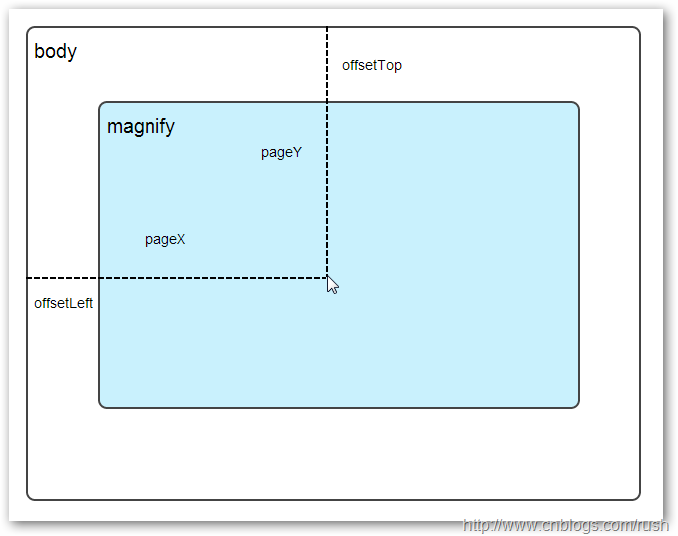
图1鼠标相对坐标位置
当鼠标移动到magnify对象中,我们需要获取鼠标在magnify中的相对坐标位置,这里我们把相对坐标定义为(mx,my),通过上图我们知道相对坐标等于(pageX - offsetLeft, pageY - offsetTop)。
现在,我们已经获取鼠标在magnify对象中的坐标值,接下来,需要获取对应大图的相应坐标,这里我们把大图的对应坐标定义为(rx,ry),我们可以通过比例关系获取(rx,ry)的值。
mx / small.width (原图的宽)= rx / native_width(大图的宽)
my / small.height (原图的长)= ry / native_height(大图的长)
通过上面的比例关系,我们知道大图的坐标(rx,ry)等于(mx/small.width*native_width, my/small.height*native_height)。
通过上述的公式,我们可以获取大图对应坐标位置,当鼠标移动到magnify对象中就显示对应位置的大图部位,接下来我们需要实现大图的加载实现了。
background-position属性
在实现大图加载显示之前,首先介绍CSS中背景定位background-position的知识。

图2 CSS background-position
上面,有一个100x100像素的图片它由四种颜色组成,而且每种颜色占50 x50像素,接下来,我们将通过修改该图片CSS的background-position属性值来显示该图片的不同位置。
我们看到在大正方形下有两行小正方形,它们显示的颜色位置都不相同,这里我们通过修改每个div元素CSS的background-position属性值实现的。
例如:第一行的蓝色方形,我们设置CSS的background-position属性为:0px -50px;这相当于原图往上移动50px,第一行的其他方形也通过左右和上下移动实现的。
但第二行的方形就显得更加奇怪了,因为它们都由四种颜色组成,而且颜色的位置都不一样,这究竟是怎样实现的呢?
例如:第二行的第一个方形,我们设置CSS的background-position属性为:25px 25px;这相当于原图向下和向右移动了25px,由于image wrap的作用它会填充剩余位置的颜色。
现在,我们已经了解到了CSS的background-position属性的作用,所以我们通过修改large对象的background-position属性来显示对应的图像部分,具体实现如下:
$large.css({
left: px,
top: py,
backgroundPosition: bgp
});
上面,我们通过加载大图的方式来实现放大镜效果,接下来,我们将介绍通过调整原图的长和宽来实现放大镜效果。
mousewheel事件
前面,我们通过mousemove事件来放大图片,这里我们将通过鼠标的滚轮事件实现图片放大效果。
由于,不同的浏览器有不同的滚轮事件。主要是有三种:onmousewheel(IE 6/7/8)、mousewheel(IE9,Chrome,Safari和Opera)和DOMMouseScroll(只有Firefox支持),关于这三个事件这里不做详细的介绍了。
由于不同浏览器之间存在着差异,为了实现浏览器之间的兼容,所以,我们需要监听以上三种滚轮事件(onmousewheel,mousewheel和DOMMouseScroll),具体实现如下:
$(".magnify").bind('DOMMouseScroll mousewheel onmousewheel', function(e) {
});
上面,我们实现了兼容不同浏览器的滚轮事件监听方法,接下来,判断滚轮向上或向下也要考虑不同浏览器的兼容性,主流的览器(IE、Opera、Safari、Firefox、Chrome)中Firefox 使用detail,其余四类使用wheelDelta;两者只在取值上不一致,代表含义一致,detail与wheelDelta只各取两个值,detail只取±3,wheelDelta只取±120,其中正数表示为向上,负数表示向下。
由于detail和wheelDelta都有两个值表示向上或向下滚动,所以不同浏览器间可以通过以下方式实现兼容,具体实现如下:
$(".magnify").bind('DOMMouseScroll mousewheel onmousewheel', function(e) {
// cross-browser wheel delta
var e = window.event || e; // old IE support.
var delta = Math.max(-1, Math.min(1, (e.wheelDelta || -e.detail)));
});
上面,我们已经处理了不同浏览器滚轮监听方法,当用户滚动滚轮时需要动态地修改原图的尺寸,这里我们定义缩放比scaling为0.3,也就是说每当用户滚动一下滚轮原图就按0.3的比例进行缩放,具体实现如下:
// Gets the image scaling height and width.
native_height += (native_height * scaling * delta);
native_width += (native_width * scaling * delta); // Update backgroud image size.
$large.css('background-size', native_width + "px " + native_height + "px");
现在,我们已经实现了通过滚轮对图片进行缩放查看的效果,完整的实现如下:
/***********************************
* Author: Jackson Huang
* Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/rush
* Date: 8/23/2013
* Reference:
* http://www.sitepoint.com/html5-javascript-mouse-wheel/
* http://thecodeplayer.com/walkthrough/magnifying-glass-for-images-using-jquery-and-css3
***********************************/ ;
(function($) { $.fn.imageZoom = function(options) { // The native width and height of the image.
var defaults = {
scaling: 0.3
}; // Combines object defaults and options.
options = $.extend(defaults, options),
native_width = 0,
native_height = 0,
current_width = 0,
current_height = 0,
$small = $(".small"),
$large = $(".large"); $(".magnify").mousemove(function(e) {
/* Act on the event */
if (!native_width && !native_height) {
var image_object = new Image();
image_object.src = $small.attr('src'); // Gets the image native height and width.
native_height = image_object.height;
native_width = image_object.width; // Gets the image current height and width.
current_height = $small.height();
current_width = $small.width(); } else { // Gets .maginfy offset coordinates.
var magnify_offset = $(this).offset(), // Gets coordinates within .maginfy.
mx = e.pageX - magnify_offset.left,
my = e.pageY - magnify_offset.top; // Checks the mouse within .maginfy or not.
if (mx < $(this).width() && my < $(this).height() && mx > 0 && my > 0) {
$large.fadeIn(100);
} else {
$large.fadeOut(100);
}
if ($large.is(":visible")) {
/* Gets the large image coordinate by ratio
small.x / small.width = large.x / large.width
small.y / small.height = large.y / large.height
then we need to keep pointer in the centre,
so deduct the half of .large width and height.
*/
var rx = Math.round(mx / $small.width() * native_width - $large.width() / 2) * -1,
ry = Math.round(my / $small.height() * native_height - $large.height() / 2) * -1,
bgp = rx + "px " + ry + "px",
px = mx - $large.width() / 2,
py = my - $large.height() / 2;
$large.css({
left: px,
top: py,
backgroundPosition: bgp
});
} }
}); $(".magnify").bind('DOMMouseScroll mousewheel onmousewheel', function(e) {
var image_object = new Image();
image_object.src = $large.attr('src'); // cross-browser wheel delta
e = window.event || e; // old IE support.
var delta = Math.max(-1, Math.min(1, (e.wheelDelta || -e.detail))); // Gets the image scaling height and width.
native_height += (native_height * defaults.scaling * delta);
native_width += (native_width * defaults.scaling * delta); // The image can't smaller than the original.
if (native_height < current_height) {
native_height = current_height;
} if (native_width < current_width) {
native_width = current_width;
} // console.log("native_height: " + native_height + " native_width: " + native_width); // Gets .maginfy offset coordinates.
var magnify_offset = $(this).offset(),
mx = e.pageX - magnify_offset.left,
my = e.pageY - magnify_offset.top; // Update backgroud image size.
$large.css('background-size', native_width + "px " + native_height + "px"); /* Gets the large image coordinate by ratio
small.x / small.width = large.x / large.width
small.y / small.height = large.y / large.height
then we need to keep pointer in the centre,
so deduct the half of .large width and height.
*/
var rx = Math.round(mx / $small.width() * native_width - $large.width() / 2) * -1,
ry = Math.round(my / $small.height() * native_height - $large.height() / 2) * -1,
bgp = rx + "px " + ry + "px",
px = mx - $large.width() / 2,
py = my - $large.height() / 2; $large.css({
left: px,
top: py,
backgroundPosition: bgp
});
});
};
})(jQuery);
 图3 放大镜效果
图3 放大镜效果
上面,我们实现了放大镜效果,当我们鼠标停留在图片上方会自动放大图片的相应部位,当然我们可以通过滚轮调整放大的比例。
1.1.3 总结
在本博文中,我们介绍了如何实现放大镜效果,总的来说,我们可以通过两种方式实现放大镜效果,而且在博文中都给出了详细的介绍,通过mousemove事件实现加载大图的效果,mousewheel事件实现动态修改原图的尺寸。
这只是一个简单的程序,我们还有很大的改善空间,提供一个内容丰富和功能强大的程序是我们的目标。
参考
- http://tech.pro/tutorial/681/css-tutorial-the-background-position-property
- http://www.sitepoint.com/html5-javascript-mouse-wheel/
- http://thecodeplayer.com/walkthrough/magnifying-glass-for-images-using-jquery-and-css3
jQuery实现放大镜效果的更多相关文章
- 使用jquery实现放大镜效果
原文:使用jquery实现放大镜效果 实现原理 首先,我们讲解一下放大镜效果的实现方式: 方法一:准备一张高像素的大图,当鼠标放到原图上,加载显示大图的对应位置. 方法二:对原图片进行放大,也就是调整 ...
- js、jquery实现放大镜效果
在一些电商网站的商品详情页面,都会有放大镜效果,实现起来并不是很困难,今天用了两个小时,写了一个放大镜效果的实例,来分享给大家! 实现的效果大概是这个样子的 预览 先来看一下效果吧,点击下面的链接预览 ...
- 【Demo】jQuery 图片放大镜效果——模仿淘宝图片放大效果
实现功能: 模仿淘宝图片放大效果,鼠标移动到小图片的某一处,放大镜对应显示大图片的相应位置. 实现效果: 实现代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <he ...
- Jquery版放大镜效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 用JavaScript中jQuery编写放大镜效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 用jquery实现放大镜效果
----css代码--- *{margin:0;padding:0;} .showimg{position:relative;width:450px;height:420px;border:1px s ...
- 关于jQuery中实现放大镜效果
1.1.1 摘要 相信大家都见过或使用过放大镜效果,甚至实现过该效果,它一般应用于放大查看商品图片,一些电商网站(例如:凡客,京东商城,阿里巴巴等)都有类似的图片查看效果. 在接下来的博文中,我们将向 ...
- jQuery实现图片放大镜效果
实现图片放大镜的原理: 给放大镜元素一个对应的html元素为<div class='right'> 设置这个div的宽高固定为某个值(350px,350px) 设置div的css为超出部分 ...
- jquery放大镜效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8& ...
随机推荐
- Java使用Scanner接收中文并输出时出现乱码
Java中使用Scanner接收输入的中文并输出时会出现乱码现象,怎么解决此问题呢? 1.方法一 在声明Scanner时添加对应的编码格式就可以了,如下所示: Scanner sc = new Sca ...
- iOS常用公共方法
iOS常用公共方法 字数2917 阅读3070 评论45 喜欢236 1. 获取磁盘总空间大小 //磁盘总空间 + (CGFloat)diskOfAllSizeMBytes{ CGFloat si ...
- LocalDB-排序规则:中文乱码; DefaultLanguage
DefaultLanguage: Set Language 简体中文|us_english SELECT SYSTEM_USER Login SP_DefaultLanguage #Login, 简体 ...
- python中文编码
前面章节中我们已经学会了如何用 Python 输出 "Hello, World!",英文没有问题,但是如果你输出中文字符"你好,世界"就有可能会碰到中文编码问题 ...
- Accordion - 手风琴
//手风琴效果 <div style="overflow:hidden;height:400px;width:948px;"> <div class=" ...
- Good-Bye
嘛……以一种奇怪的姿势滚粗了…… 如果这个Blog能给未来的OIer们一些帮助的话,它也不枉存在了…… 我的OI之路也能以另一种形式延续下去吧…… 也许能搞ACM的话会再开?…… 不管怎么说,各位再见 ...
- Asp.net使用代码修改配置文件的节点值
使用代码修改配置文件的方法: 1.打开配置文件写入的权限 2.先按节点名称长到要修改的节点,然后删除,紧接着将有新值的节点添加回去 3.关闭配置文件写入的权限 修改Appsetting节点的值,修改其 ...
- Android volley 当用fiddler2 抓包时隔一段时间不操作,会出现 http 408错误
出现原因是由于fiddler2导致,关闭fiddler2即可...
- (转)深度分析Linux下双网卡绑定七种模式
现在一般的企业都会 使用双网卡接入,这样既能添加网络带宽,同时又能做相应的冗余,可以说是好处多多.而一般企业都会使用linux操作系统下自带的网卡绑定模式,当然现在 网卡产商也会出一些针对window ...
- 再谈CSHELL对C程序员的价值
几个礼拜前,介绍了CSHELL.http://www.cnblogs.com/hhao020/p/4974542.html今天再试着介绍下,希望能有更多C程序员留意到它,从中获益. 很多年前,我在调试 ...
