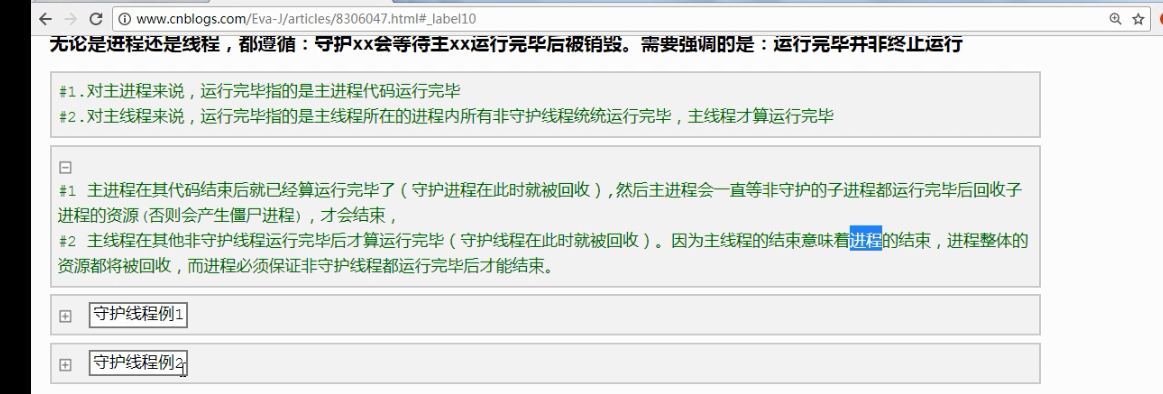
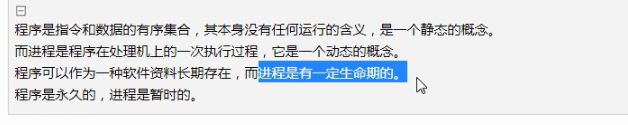
day52 进程与守护进程
http://www.cnblogs.com/Eva-J/articles/8253549.html 博客参考.








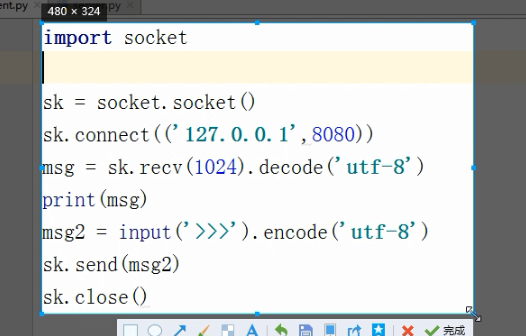
多进程聊天
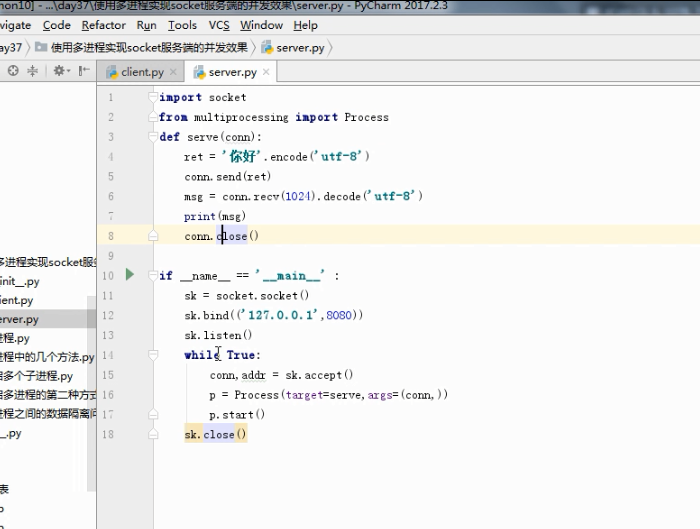
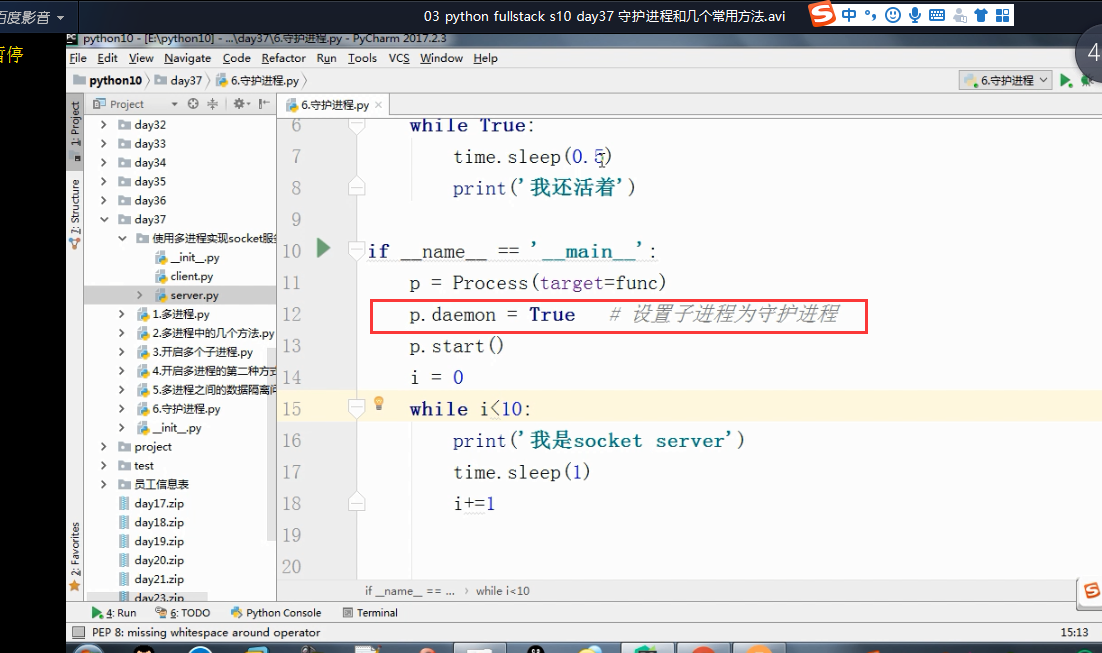
守护进程.
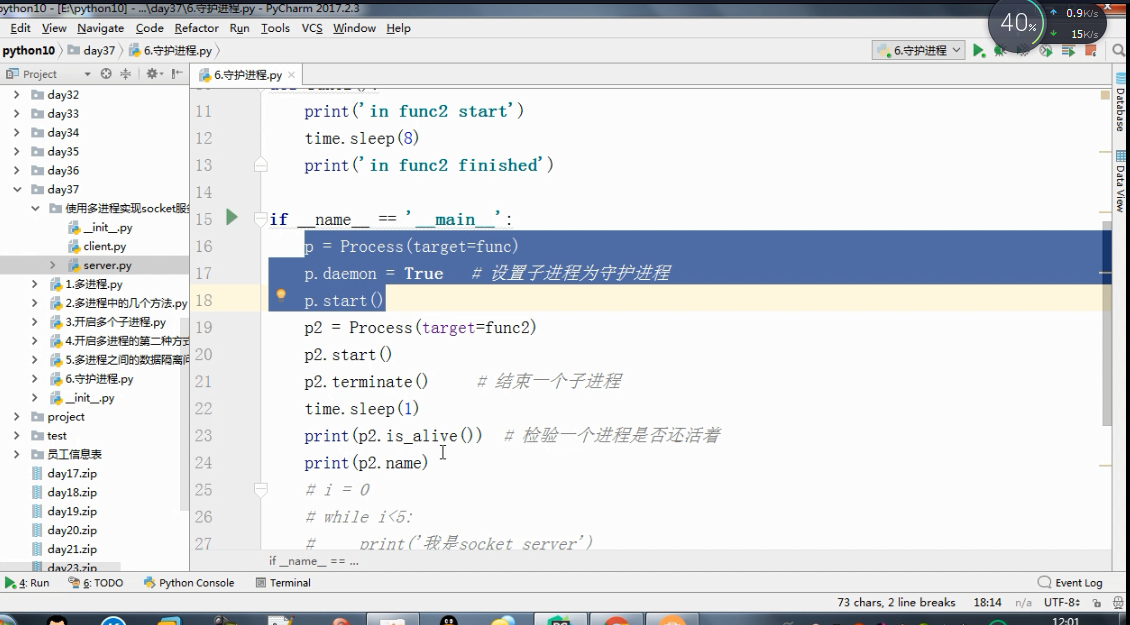
多进程
1、Unix/Linux:fork()调用实现多进程。
2、Windows没有fork(),multiprocessing模块就是跨平台版本的多进程模块。multiprocessing模块提供了一个Process类来代表一个进程对象。
#启动一个子进程并等待其结束:
from multiprocessing import Process
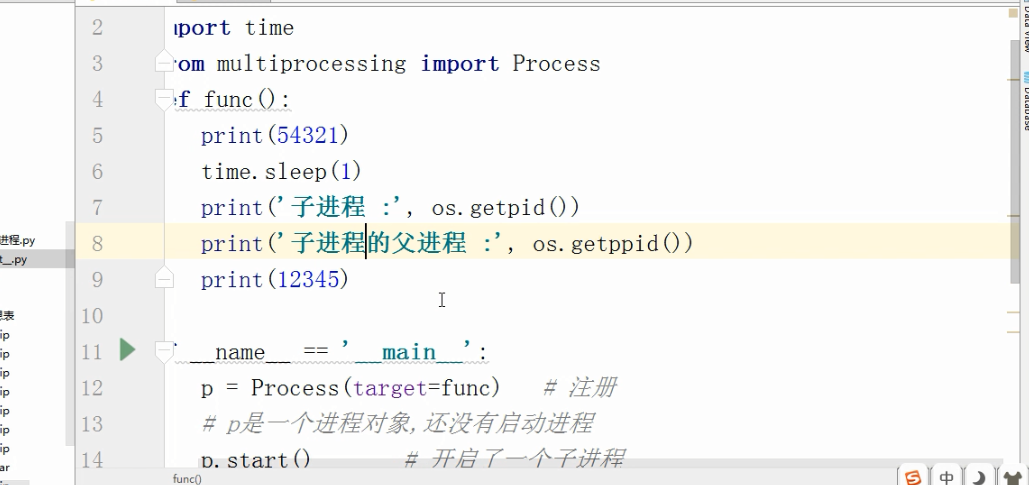
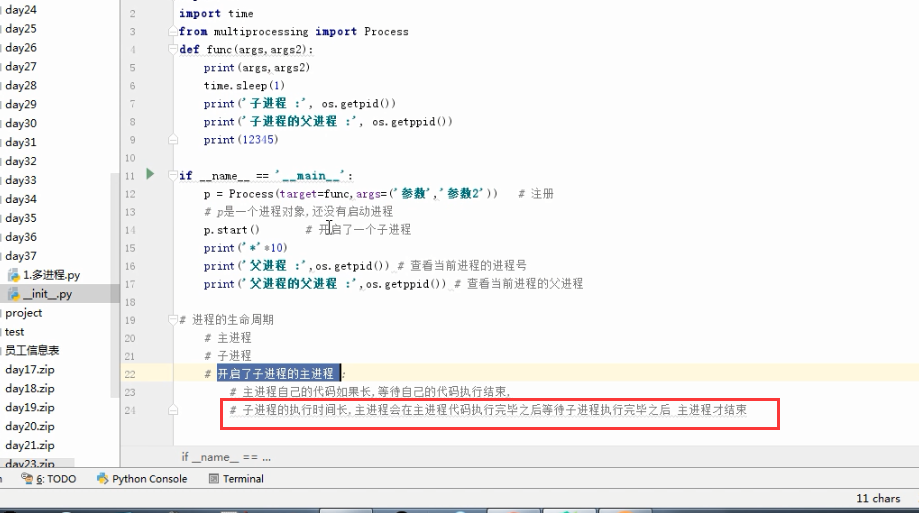
import os # 子进程要执行的代码
def run_proc(name):
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid())) #主函数
if __name__=='__main__':
print('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid()) #创建子进程时,只需要传入一个执行函数和函数的参数,
#创建一个Process实例,用start()方法启动。
p = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
print('Child process will start.')
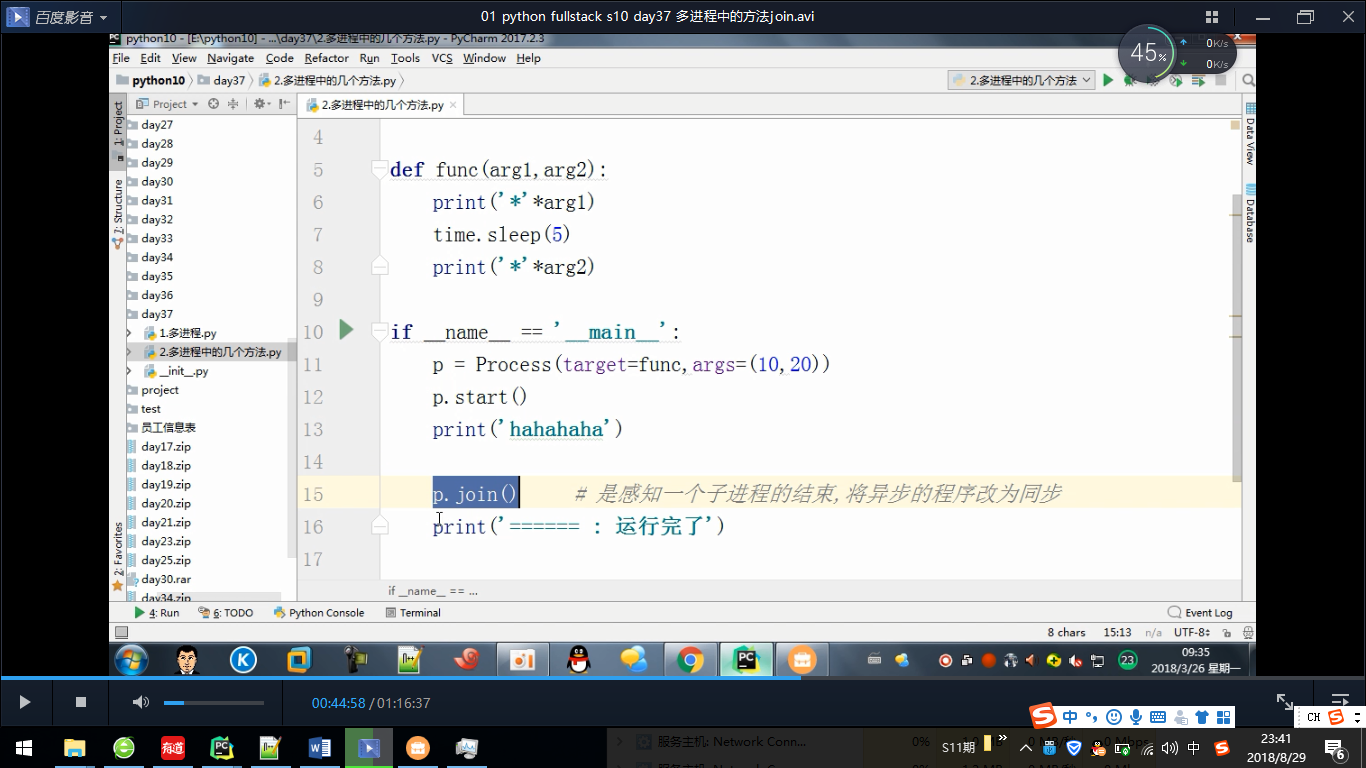
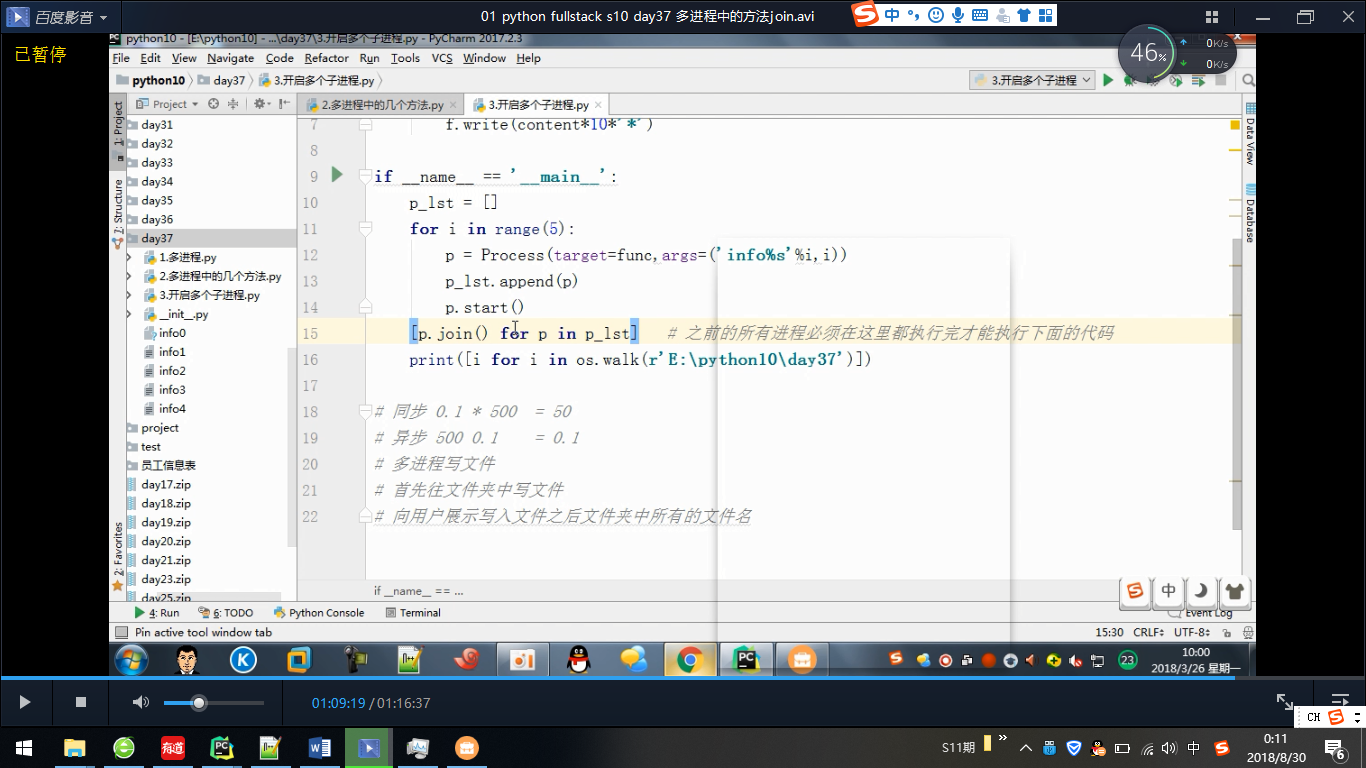
p.start() #join()可等待子进程结束后再继续往下运行,通常用于进程间的同步。
p.join()
print('Child process end.') 结果:
Parent process 928.
Process will start.
Run child process test (929)...
Process end.
进程间通信
1、Process之间肯定是需要通信的,Python的multiprocessing模块包装了底层的机制,提供了Queue、Pipes等多种方式来交换数据。
以Queue为例,在父进程中创建两个子进程,一个往Queue里写数据,一个从Queue里读数据:
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import os, time, random # 写数据进程执行的代码:
def write(q):
print('Process to write: %s' % os.getpid())
for value in ['A', 'B', 'C']:
print('Put %s to queue...' % value)
q.put(value)
time.sleep(random.random()) # 读数据进程执行的代码:
def read(q):
print('Process to read: %s' % os.getpid())
while True:
value = q.get(True)
print('Get %s from queue.' % value) if __name__=='__main__':
# 父进程创建Queue,并传给各个子进程:
q = Queue()
pw = Process(target=write, args=(q,))
pr = Process(target=read, args=(q,))
# 启动子进程pw,写入:
pw.start()
# 启动子进程pr,读取:
pr.start()
# 等待pw结束:
pw.join()
# pr进程里是死循环,无法等待其结束,只能强行终止:
pr.terminate() 结果:
Process to write: 50563
Put A to queue...
Process to read: 50564
Get A from queue.
Put B to queue...
Get B from queue.
Put C to queue...
Get C from queue.
多线程
1、Python的标准库提供了两个模块:_thread(低级模块)和threading(高级模块,对_thread进行了封装)。绝大多数情况下,我们只需要使用threading这个高级模块。
2、启动一个线程就是把一个函数传入并创建Thread实例,然后调用start()开始执行:
import time, threading # 新线程执行的代码:
def loop():
print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
n =
while n < :
n = n +
print('thread %s >>> %s' %(threading.current_thread().name, n))
time.sleep()
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name) print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
t = threading.Thread(target=loop, name='LoopThread')
t.start()
t.join()
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name) 结果:
thread MainThread is running...
thread LoopThread is running...
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread >>>
thread LoopThread ended.
thread MainThread ended.
由于任何进程默认就会启动一个线程(主线程),主线程又可以启动新的线程,current_thread()永远返回当前线程的实例。主线程实例的名字叫MainThread,子线程的名字在创建时指定。名字仅仅在打印时用来显示,完全没有其他意义,如果不起名字Python就自动给线程命名为Thread-1,Thread-2……
3、
多进程:同一个变量,各自有一份拷贝存在于每个进程中,互不影响。
多线程:所有变量都由所有线程共享。所以,任何一个变量都可以被任何一个线程修改,因此,线程之间共享数据最大的危险在于多个线程同时改一个变量,把内容给改乱了。
#来看看多个线程同时操作一个变量怎么把内容给改乱了
import time, threading # 假定这是你的银行存款:
balance = def change_it(n):
# 先存后取,结果应该为0:
global balance
balance = balance + n
balance = balance - n def run_thread(n):
for i in range():
change_it(n) t1 = threading.Thread(target=run_thread, args=(,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=run_thread, args=(,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print(balance)



信号量:
Event事件
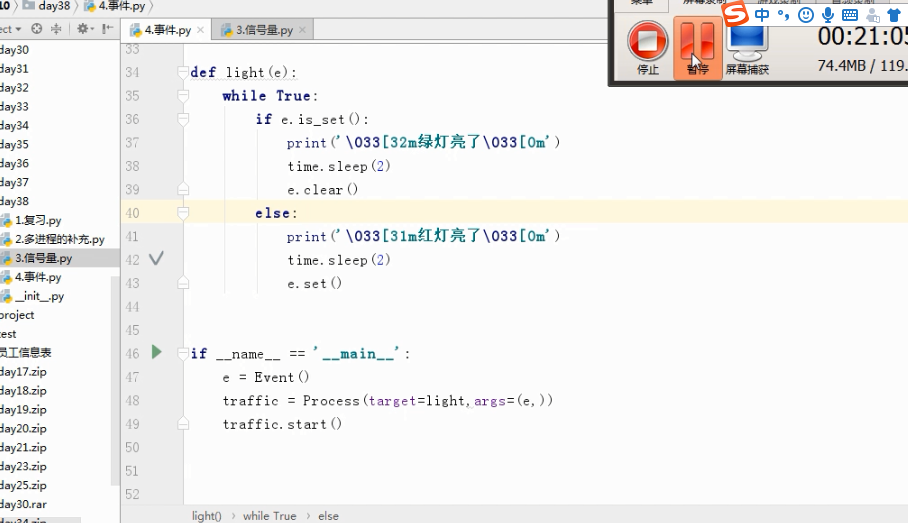

队列

线程:
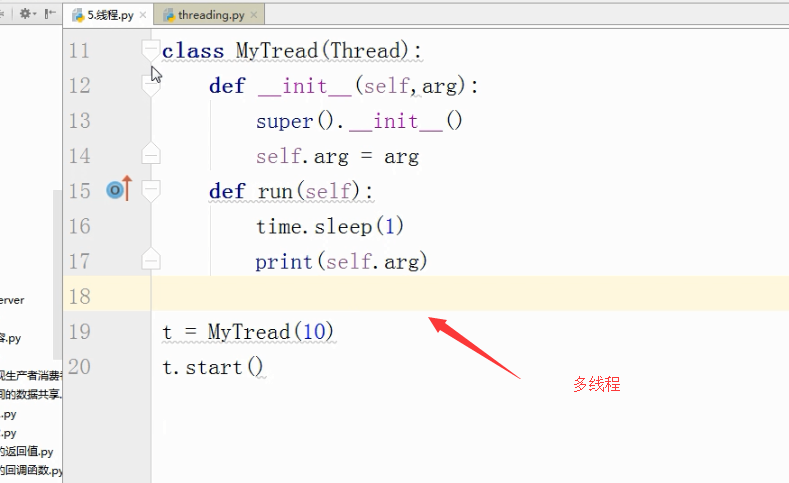

守护线程:
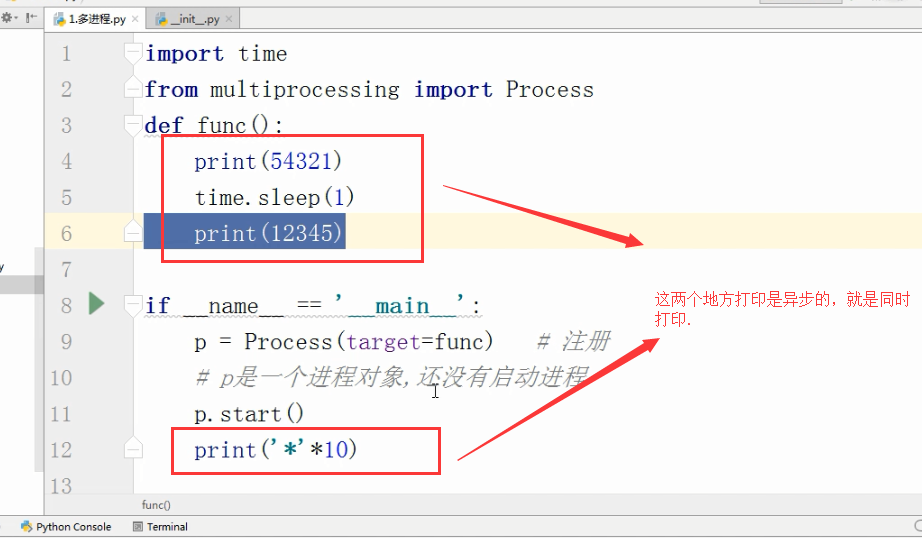
import time
from multiprocessing import Process
def func():
time.sleep()
print("func1") if __name__=="__main__":
Process(target=func).start()
print() 打印结果: func1 先打印999,打印完后等待两秒打印func1

案例2
import time
from threading import Thread
def func1():
while True:
print('*'*10)
time.sleep(1)
def func2():
print('in func2')
time.sleep(5) t = Thread(target=func1,)
t.daemon = True
t.start()
t2 = Thread(target=func2,)
t2.start()
t2.join() #join 语句的执行会等待最后打印“”主线程“”
print('主线程')
打印结果:
**********
in func2
**********
**********
**********
**********
主线程
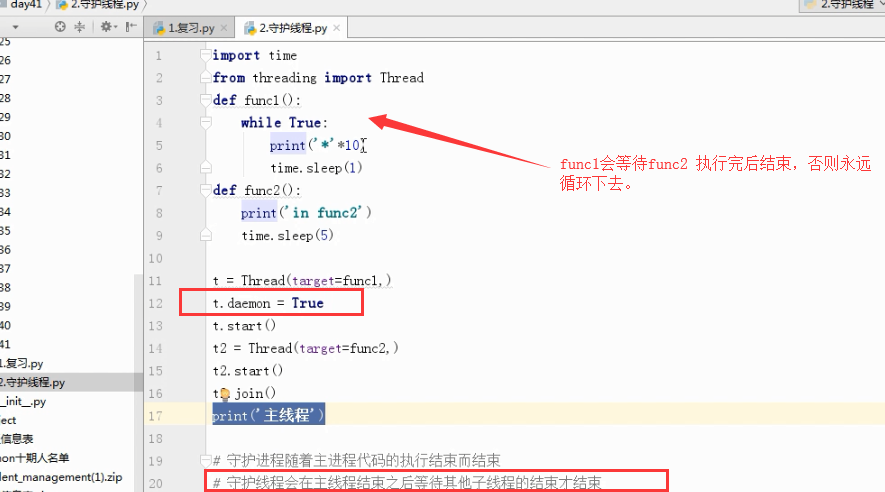
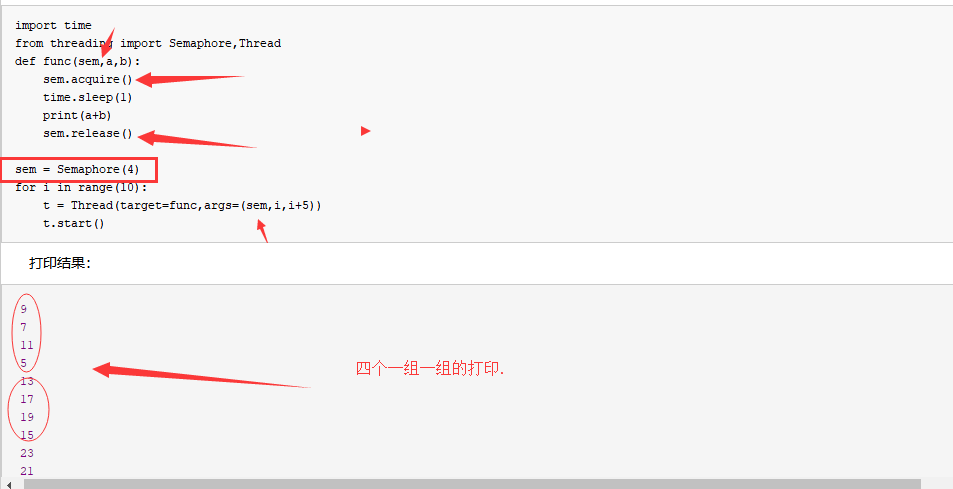
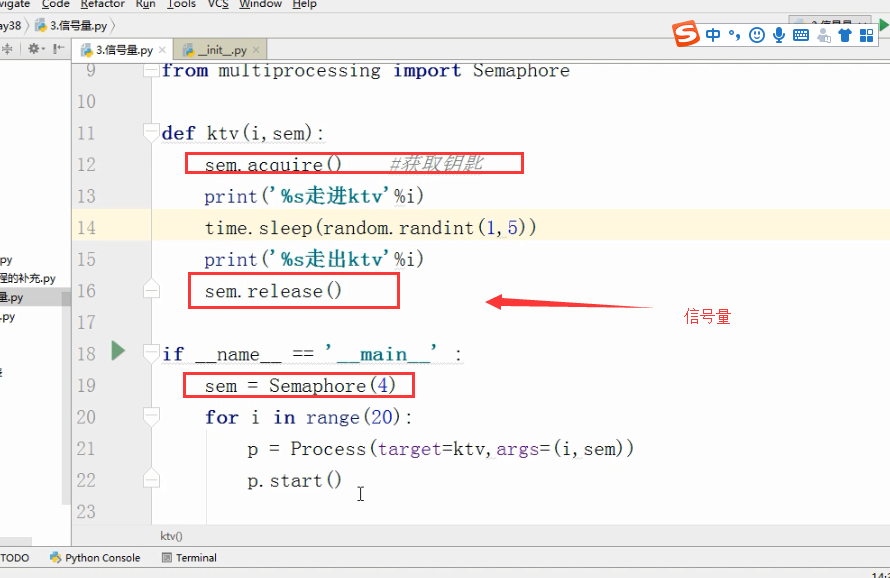
信号量 信号量
import time
from threading import Semaphore,Thread
def func(sem,a,b):
sem.acquire()
time.sleep(1)
print(a+b)
sem.release() sem = Semaphore(4)
for i in range(10):
t = Thread(target=func,args=(sem,i,i+5))
t.start()
打印结果:
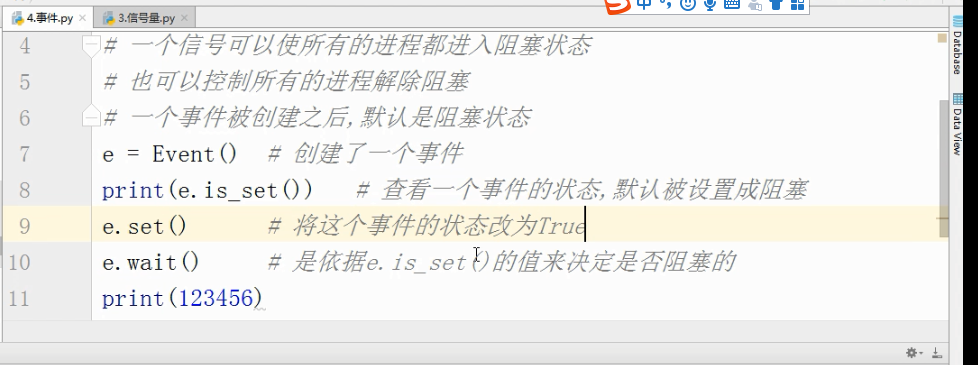
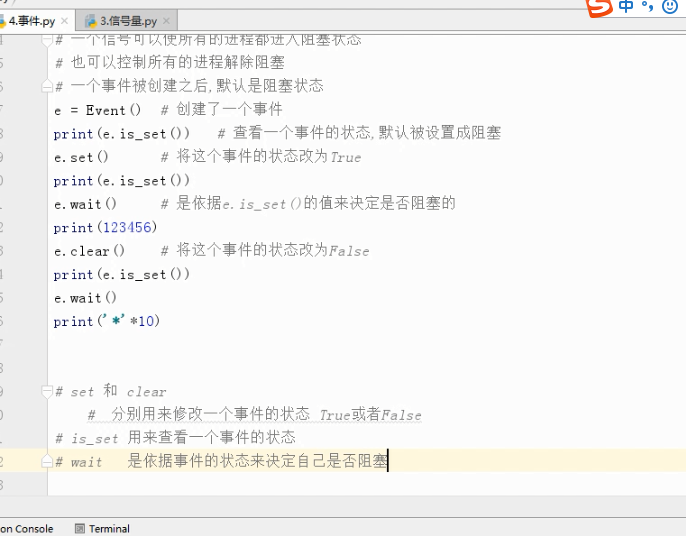
事件 :
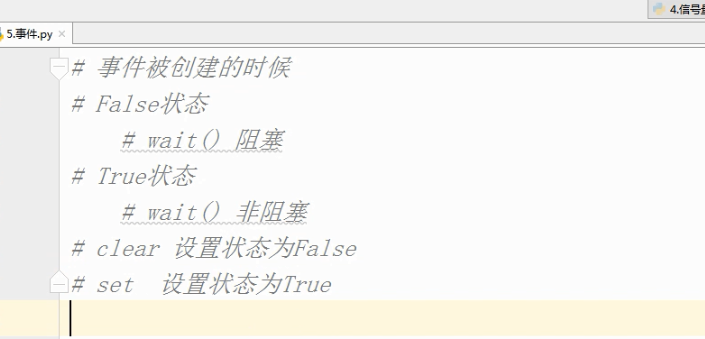
# 事件被创建的时候
# False状态
# wait() 阻塞
# True状态
# wait() 非阻塞
# clear 设置状态为False
# set 设置状态为True # 数据库 - 文件夹
# 文件夹里有好多excel表格
# .能够更方便的对数据进行增删改查
# .安全访问的机制 # 起两个线程
# 第一个线程 : 连接数据库
# 等待一个信号 告诉我我们之间的网络是通的
# 连接数据库
# 第二个线程 : 检测与数据库之间的网络是否连通
# time.sleep(,)
# 将事件的状态设置为True
import time
import random
from threading import Thread,Event
def connect_db(e):
count =
while count < :
e.wait(0.5) # 状态为False的时候,我只等待1s就结束
if e.is_set() == True:
print('连接数据库')
break
else:
count +=
print('第%s次连接失败'%count)
else:
raise TimeoutError('数据库连接超时') def check_web(e):
time.sleep(random.randint(,))
e.set() e = Event()
t1 = Thread(target=connect_db,args=(e,))
t2 = Thread(target=check_web,args=(e,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
条件
# 条件
from threading import Condition # 条件
# 锁
# acquire release
# 一个条件被创建之初 默认有一个False状态
# False状态 会影响wait一直处于等待状态
# notify(int数据类型) 造钥匙
from threading import Thread,Condition
def func(con,i):
con.acquire()
con.wait() # 等钥匙
print('在第%s个循环里'%i)
con.release()
con = Condition()
for i in range():
Thread(target=func,args = (con,i)).start()
while True:
num = int(input('>>>'))
con.acquire()
con.notify(num) # 造钥匙
con.release()
定时器
https://www.jb51.net/article/139000.htm
import time
from threading import Timer
def func():
print('时间同步') #- while True:
t = Timer(,func).start() # 非阻塞的
time.sleep()
队列和栈:
队列 ,先进先出
import queue
q =queue.Queue()
q.put(100)
q.put(200)
结果:
栈,先进后出.
q = queue.LifoQueue()#栈 ,先进后出,
q.put()
q.put()
q.put()
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
打印结果:
优先级队列
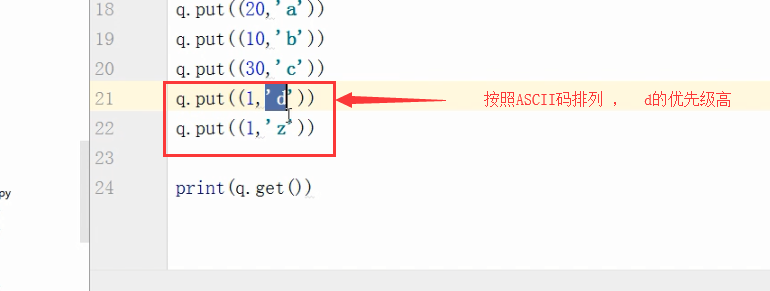
q=queue.PriorityQueue() #优先级队列
q.put((,"a"))
q.put((,"b"))
q.put((,"c"))
q.put((,"d")) print(q.get())
打印结果:
(, 'b')
优先级高的是数字最小的。
池 .concurrent.futures.
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def func(n):
time.sleep()
print(n)
return n*n def call_back(m):
print('结果是 %s'%m.result()) tpool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=) # 默认 不要超过cpu个数*
for i in range():
tpool.submit(func,i).add_done_callback(call_back) # tpool.map(func,range()) # 拿不到返回值
# t_lst = []
# for i in range():
# t = tpool.submit(func,i)
# t_lst.append(t)
# tpool.shutdown() # close+join #
# print('主线程')
# for t in t_lst:print('***',t.result()) # ftp
# 并发编程
Event(事件)
Event(事件):事件处理的机制:全局定义了一个内置标志Flag,如果Flag值为 False,那么当程序执行 event.wait方法时就会阻塞,如果Flag值为True,那么event.wait 方法时便不再阻塞。
Event其实就是一个简化版的 Condition。Event没有锁,无法使线程进入同步阻塞状态。
Event()
- set(): 将标志设为True,并通知所有处于等待阻塞状态的线程恢复运行状态。
- clear(): 将标志设为False。
- wait(timeout): 如果标志为True将立即返回,否则阻塞线程至等待阻塞状态,等待其他线程调用set()。
- isSet(): 获取内置标志状态,返回True或False。
Event案例1
场景:小伙伴a和b准备就绪,当收到通知event.set()的时候,会执行a和b线程
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
# coding:utf-8import threadingimport timeevent = threading.Event()def chihuoguo(name): # 等待事件,进入等待阻塞状态 print '%s 已经启动' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 已经进入就餐状态!'%name time.sleep(1) event.wait() # 收到事件后进入运行状态 print '%s 收到通知了.' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 开始吃咯!'%name# 设置线程组threads = []# 创建新线程thread1 = threading.Thread(target=chihuoguo, args=("a", ))thread2 = threading.Thread(target=chihuoguo, args=("b", ))# 添加到线程组threads.append(thread1)threads.append(thread2)# 开启线程for thread in threads: thread.start()time.sleep(0.1)# 发送事件通知print '主线程通知小伙伴开吃咯!'event.set() |
运行结果:
Thread-1 已经启动
小伙伴 a 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-2 已经启动
小伙伴 b 已经进入就餐状态!
主线程通知小伙伴开吃咯!
Thread-1 收到通知了.
小伙伴 a 开始吃咯!
Thread-2 收到通知了.
小伙伴 b 开始吃咯!
Event案例2
场景:当小伙伴a,b,c集结完毕后,请客的人发话:开吃咯!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
# coding:utf-8import threadingimport timeevent = threading.Event()def chiHuoGuo(name): # 等待事件,进入等待阻塞状态 print '%s 已经启动' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '小伙伴 %s 已经进入就餐状态!'%name time.sleep(1) event.wait() # 收到事件后进入运行状态 print '%s 收到通知了.' % threading.currentThread().getName() print '%s 小伙伴 %s 开始吃咯!'%(time.time(), name)class myThread (threading.Thread): # 继承父类threading.Thread def __init__(self, name): '''重写threading.Thread初始化内容''' threading.Thread.__init__(self) self.people = name def run(self): # 把要执行的代码写到run函数里面 线程在创建后会直接运行run函数 '''重写run方法''' chiHuoGuo(self.people) # 执行任务 print("qq交流群:226296743") print("结束线程: %s" % threading.currentThread().getName())# 设置线程组threads = []# 创建新线程thread1 = myThread("a")thread2 = myThread("b")thread3 = myThread("c")# 添加到线程组threads.append(thread1)threads.append(thread2)threads.append(thread3)# 开启线程for thread in threads: thread.start()time.sleep(0.1)# 发送事件通知print '集合完毕,人员到齐了,开吃咯!'event.set() |
运行结果:
Thread-1 已经启动
小伙伴 a 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-2 已经启动
小伙伴 b 已经进入就餐状态!
Thread-3 已经启动
小伙伴 c 已经进入就餐状态!
集合完毕,人员到齐了,开吃咯!
Thread-1 收到通知了.
1516780957.47 小伙伴 a 开始吃咯!
qq交流群:226296743
结束线程: Thread-1
Thread-3 收到通知了.
1516780957.47 小伙伴 c 开始吃咯!Thread-2 收到通知了.
qq交流群:2262967431516780957.47 小伙伴 b 开始吃咯!结束线程: Thread-3
qq交流群:226296743
结束线程: Thread-2
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
day52 进程与守护进程的更多相关文章
- Linux 普通进程 后台进程 守护进程
一.普通进程与后台进程 默认情况下,进程是在前台运行的,这时就把shell给占据了,我们无法进行其它操作.对于那些没有交互的进程,很多时候,我们希望将其在后台启动,可以在启动参数的时候加一个'& ...
- PHP如何将进程作为守护进程
看了这篇:http://blog.codinglabs.org/articles/write-daemon-with-php.html 对里面的posix_setsid()不解 文档解释是" ...
- Linux进程学习(孤儿进程和守护进程)
孤儿进程和守护进程 通过前面的学习我们了解了如何通过fork()函数和vfork()函数来创建一个进程.现在 我们继续深入来学习两个特殊的进程:孤儿进程和守护进程 一.孤儿进程 1.什么是 孤儿进程如 ...
- UNIX基础--进程和守护进程
进程和守护进程 Processes and Daemons 进程(Processes) FreeBSD 是一个多任务操作系统. 这就意味着好像一次可以运行一个以上的程序. 每个占用一定时间运行的程序就 ...
- python进程之守护进程
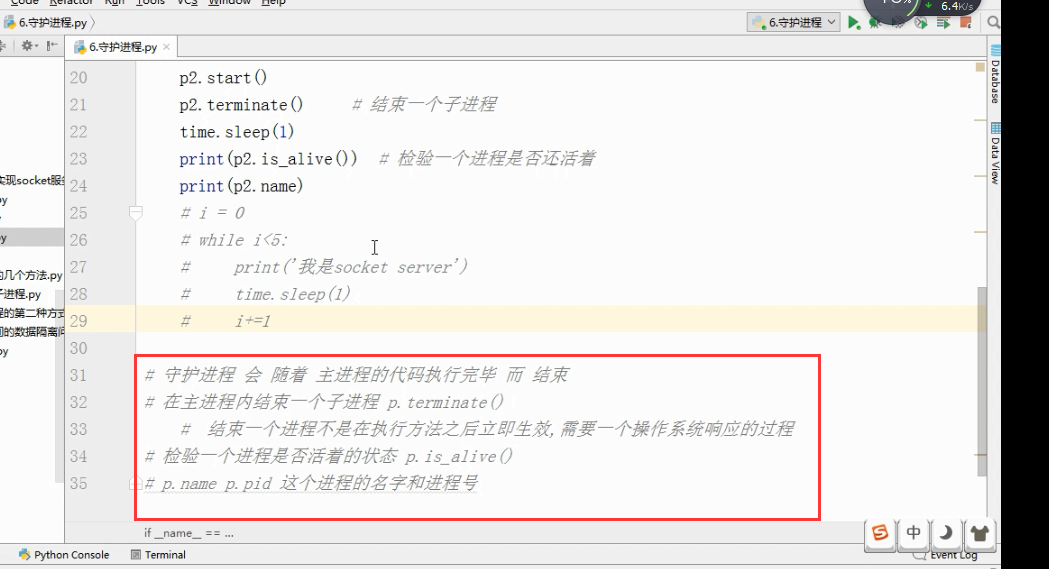
标签(空格分隔): 守护进程 主进程创建子进程,然后将该进程设置成守护自己的进程,守护进程就好比崇祯皇帝身边的老太监,崇祯皇帝已死老太监就跟着殉葬了: 关于守护进程需要强调两点: 其一:守护进程会在主 ...
- 【Linux 进程】孤儿进程、僵尸进程和守护进程
1.孤儿进程: 孤儿进程:一个父进程退出,而它的一个或多个子进程还在运行,那么那些子进程将成为孤儿进程.孤儿进程将被init进程(进程号为1)所收养,并由init进程对它们完成状态收集工作.孤儿进程是 ...
- Linux进程学习 - 孤儿进程和守护进程
孤儿进程和守护进程 通过前面的学习我们了解了如何通过fork()函数和vfork()函数来创建一个进程.现在 我们继续深入来学习两个特殊的进程:孤儿进程和守护进程 一.孤儿进程 1.什么是 孤儿进程如 ...
- Linux 普通进程 后台进程 守护进程(转)
一.普通进程与后台进程 默认情况下,进程是在前台运行的,这时就把shell给占据了,我们无法进行其它操作.对于那些没有交互的进程,很多时候,我们希望将其在后台启动,可以在启动参数的时候加一个'& ...
- python并发编程之进程1(守护进程,进程锁,进程队列)
进程的其他方法 P = Process(target=f,) P.Pid 查看进程号 查看进程的名字p.name P.is_alive() 返回一个true或者False P.terminate( ...
- 8.9 day30 并发编程 进程理论 进程方法 守护进程 互斥锁
多道技术 1.空间上的复用 多个程序共用一套计算机硬件 多道技术原理 2.时间上的复用 切换+保存状态 1.当一个程序遇到IO操作 操作系统会剥夺该程序的CPU执行权限( 提高了CPU的利用率 ...
随机推荐
- Java动态代理机制详解(类加载,JDK 和CGLIB,Javassist,ASM)
class文件简介及加载 Java编译器编译好Java文件之后,产生.class 文件在磁盘中.这种class文件是二进制文件,内容是只有JVM虚拟机能够识别的机器码.JVM虚拟机读取字节码文件,取出 ...
- dump打印
- 配置tomcat server.xml 文件 ,虚拟路径
<Context path="/web" docBase="D:\workspace\web\src\main\webapp" reloadable=& ...
- linux下集成开发环境之ECLIPSE--在线调试、编译程序
裸机开发流程 1.编写裸机程序:2.调试裸机程序:3.生成2进制映象(编译.链接.格式转换):4.烧写/运行2进制映象. 注意:我们自己开发的程序等等需要下载到开发板的Nandflash(类似于硬盘功 ...
- 使用Jsoup获取网页内容超时设置
使用Jsoup获取网页内容超时设置 最近使用Jsoup来抓取网页,并对网页进行解析,发现很好用.在抓取过程中遇到一个问题,有些页面总是报Timeout异常,开始想是不是被抓取网站对IP进行了限制,后来 ...
- MUI框架开发HTML5手机APP(一)--搭建第一个手机APP(转)
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/jerehedu/p/7832808.html 前 言 JRedu 随着HTML5的不断发展,移动开发成为主流趋势!越来越多的公司开始选择使用H ...
- UVaLive 3487 Duopoly (最小割)
题意:有两个公司A和B在申请一些资源,现在给出两个公司所申请的内容,内容包括价钱和申请的资源 ,现在你做为官方,你只能拒绝一个申请或者接受一个申请,同一个资源不能两个公司都拥有,且申请的资源不能只给部 ...
- AngularJS标准Web业务流程开发框架—1.AngularJS模块以及启动分析
前言: AngularJS中提到模块是自定义的模块标准,提到这不得不说AngularJS是框架中的老大哥,思想相当的前卫..在这框架满天横行的时代,AngularJS有些思想至今未被超越,当然仁者见仁 ...
- C#中验证sql语句是否正确(不执行语句)
SET PARSEONLY检查每个 Transact-SQL 语句的语法并返回任何错误消息,但不编译和执行语句.SET PARSEONLY { ON | OFF }当 SET PARSEONLY 为 ...
- matlab练习程序(生成希尔伯特曲线)
能够使用这样一条线遍历图像中所有的像素,不过这里没有这样做,而只是生成了这样一条曲线. 程序中h,w是最终图像的高和宽,n为希尔伯特曲线阶数. 这里如果n等于log2(h)或log2(w),则图像就全 ...