Seaborn分布数据可视化---统计分布图
统计分布图
barplot()
sns.barplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
data=None,
order=None,
hue_order=None,
estimator=<function mean at 0x000001DA64AD3DC8>,
ci=95,
n_boot=1000,
units=None,
orient=None,
color=None,
palette=None,
saturation=0.75,
errcolor='.26',
errwidth=None,
capsize=None,
dodge=True,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Show point estimates and confidence intervals as rectangular bars.
A bar plot represents an estimate of central tendency for a numeric
variable with the height of each rectangle and provides some indication of
the uncertainty around that estimate using error bars. Bar plots include 0
in the quantitative axis range, and they are a good choice when 0 is a
meaningful value for the quantitative variable, and you want to make
comparisons against it.
For datasets where 0 is not a meaningful value, a point plot will allow you
to focus on differences between levels of one or more categorical
variables.
It is also important to keep in mind that a bar plot shows only the mean
(or other estimator) value, but in many cases it may be more informative to
show the distribution of values at each level of the categorical variables.
In that case, other approaches such as a box or violin plot may be more
appropriate.
Input data can be passed in a variety of formats, including:
- Vectors of data represented as lists, numpy arrays, or pandas Series
objects passed directly to the ``x``, ``y``, and/or ``hue`` parameters.
- A "long-form" DataFrame, in which case the ``x``, ``y``, and ``hue``
variables will determine how the data are plotted.
- A "wide-form" DataFrame, such that each numeric column will be plotted.
- An array or list of vectors.
In most cases, it is possible to use numpy or Python objects, but pandas
objects are preferable because the associated names will be used to
annotate the axes. Additionally, you can use Categorical types for the
grouping variables to control the order of plot elements.
This function always treats one of the variables as categorical and
draws data at ordinal positions (0, 1, ... n) on the relevant axis, even
when the data has a numeric or date type.
See the :ref:`tutorial <categorical_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
x, y, hue : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Inputs for plotting long-form data. See examples for interpretation.
data : DataFrame, array, or list of arrays, optional
Dataset for plotting. If ``x`` and ``y`` are absent, this is
interpreted as wide-form. Otherwise it is expected to be long-form.
order, hue_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to plot the categorical levels in, otherwise the levels are
inferred from the data objects.
estimator : callable that maps vector -> scalar, optional
Statistical function to estimate within each categorical bin.
ci : float or "sd" or None, optional
Size of confidence intervals to draw around estimated values. If
"sd", skip bootstrapping and draw the standard deviation of the
observations. If ``None``, no bootstrapping will be performed, and
error bars will not be drawn.
n_boot : int, optional
Number of bootstrap iterations to use when computing confidence
intervals.
units : name of variable in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Identifier of sampling units, which will be used to perform a
multilevel bootstrap and account for repeated measures design.
orient : "v" | "h", optional
Orientation of the plot (vertical or horizontal). This is usually
inferred from the dtype of the input variables, but can be used to
specify when the "categorical" variable is a numeric or when plotting
wide-form data.
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color for all of the elements, or seed for a gradient palette.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
saturation : float, optional
Proportion of the original saturation to draw colors at. Large patches
often look better with slightly desaturated colors, but set this to
``1`` if you want the plot colors to perfectly match the input color
spec.
errcolor : matplotlib color
Color for the lines that represent the confidence interval.
errwidth : float, optional
Thickness of error bar lines (and caps).
capsize : float, optional
Width of the "caps" on error bars.
dodge : bool, optional
When hue nesting is used, whether elements should be shifted along the
categorical axis.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
kwargs : key, value mappings
Other keyword arguments are passed through to ``plt.bar`` at draw
time.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
countplot : Show the counts of observations in each categorical bin.
pointplot : Show point estimates and confidence intervals using scatterplot
glyphs.
catplot : Combine a categorical plot with a class:`FacetGrid`.
x、y、hue:< data中的变量名词或者向量 >
data中用于绘制图表的变量名
data:< DataFrame, 数组, 数组列表 >
是用于绘图的数据集
order、hue_order:< 字符串列表 >
绘制类别变量的顺序,若没有,则会从数据对象中推断绘图顺序
estimator:< 映射向量 -> 标量 >
统计函数用于估计每个分类纸条中的值
ci:< float or “sd” or None >
估计值周围的置信区间大小。若输入的是sd,会跳过bootstrapping的过程,只绘制数据的标准差;
若输入的是None,不会执行bootstrapping,而且错误条也不会绘制
n_boot:< int >
计算置信区间需要的 Boostrap 迭代次数。
units:< data中的变量名词或向量 >
采样单元的标识符,用于执行多级 bootstrap 并解释重复测量设计。
orient:< “v” 或 “h” >
绘图的方向(垂直或水平)。这通常是从输入变量的数据类型推断出来的,但是可以用来指定“分类”变量是数字还是宽格式数据。
color:< matplotlib color >
作用于所有元素的颜色,或者渐变色的种子。
palette:< palette name, list, or dict >
不同级别的 hue 变量的颜色。 颜色要能被 [color_palette()]解释(seaborn.color_palette.html#seaborn.color_palette “seaborn.color_palette”), 或者一个能映射到 matplotlib 颜色的字典。
saturation:< float >
原始饱和度与绘制颜色的比例。大的色块通常在稍微不饱和的颜色下看起来更好,但是如果希望打印颜色与输入颜色规格完全匹配,请将其设置为1。
errcolor:< matplotlib color >
表示置信区间的线的颜色。
errwidth:< float >
误差条的线的厚度。
capsize:< float >
误差条端部的宽度。
dodge : < 布尔型 >
当使用色调嵌套时,元素是否应该沿分类轴移动。
ax:< matplotlib Axes >
指定一个 Axes 用于绘图,如果不指定,则使用当前的 Axes。
kwargs:< key, value mappings >
其他的关键词参数在绘图时通过 plt.bar 传入。
误差线表示数据误差(或不确定性)范围,以更准确的方式呈现数据。误差线可以用标准差(standard deviation,SD)、标准误(standard error,SE)和置信区间表示,使用时可选用任意一种表示方法并作相应说明即可。当误差线比较“长”时,一般要么是数据离散程度大,要么是数据样本少。
#垂直柱状图 + 误差线
ax = sns.barplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas)

#横向分布,通过x和y轴数据调换设置
ax = sns.barplot(x='total_bill', y='day', data=tip_datas)

#hue设置分类
ax = sns.barplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas, hue='sex')

#hue设置分组分类
tip_datas['weekend'] = tip_datas['day'].isin(['Sat','Sun'])
ax = sns.barplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas, hue='weekend')

#ci设置估计值的置信区间大小,'sd'表示标准差,默认ci=95%
ax = sns.barplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas, ci='sd')

#capsize设置误差线端盖横线
ax = sns.barplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas, capsize=.2)

#分栏显示catplot() = barplot() + FacetGrid()
g = sns.catplot(x='sex', y='total_bill',
hue='smoker', col='time',
data=tip_datas, kind='bar',
height=4, aspect=.7
)

countplot()
绘制计数数据的柱状图。
sns.countplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
data=None,
order=None,
hue_order=None,
orient=None,
color=None,
palette=None,
saturation=0.75,
dodge=True,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Show the counts of observations in each categorical bin using bars.
A count plot can be thought of as a histogram across a categorical, instead
of quantitative, variable. The basic API and options are identical to those
for :func:`barplot`, so you can compare counts across nested variables.
Input data can be passed in a variety of formats, including:
- Vectors of data represented as lists, numpy arrays, or pandas Series
objects passed directly to the ``x``, ``y``, and/or ``hue`` parameters.
- A "long-form" DataFrame, in which case the ``x``, ``y``, and ``hue``
variables will determine how the data are plotted.
- A "wide-form" DataFrame, such that each numeric column will be plotted.
- An array or list of vectors.
In most cases, it is possible to use numpy or Python objects, but pandas
objects are preferable because the associated names will be used to
annotate the axes. Additionally, you can use Categorical types for the
grouping variables to control the order of plot elements.
This function always treats one of the variables as categorical and
draws data at ordinal positions (0, 1, ... n) on the relevant axis, even
when the data has a numeric or date type.
See the :ref:`tutorial <categorical_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
x, y, hue : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Inputs for plotting long-form data. See examples for interpretation.
data : DataFrame, array, or list of arrays, optional
Dataset for plotting. If ``x`` and ``y`` are absent, this is
interpreted as wide-form. Otherwise it is expected to be long-form.
order, hue_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to plot the categorical levels in, otherwise the levels are
inferred from the data objects.
orient : "v" | "h", optional
Orientation of the plot (vertical or horizontal). This is usually
inferred from the dtype of the input variables, but can be used to
specify when the "categorical" variable is a numeric or when plotting
wide-form data.
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color for all of the elements, or seed for a gradient palette.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
saturation : float, optional
Proportion of the original saturation to draw colors at. Large patches
often look better with slightly desaturated colors, but set this to
``1`` if you want the plot colors to perfectly match the input color
spec.
dodge : bool, optional
When hue nesting is used, whether elements should be shifted along the
categorical axis.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
kwargs : key, value mappings
Other keyword arguments are passed to ``plt.bar``.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
barplot : Show point estimates and confidence intervals using bars.
catplot : Combine a categorical plot with a class:`FacetGrid`.
#分类计数柱状图:countplot
titanic = sns.load_dataset('titanic', data_home='seaborn-data')
titanic

#单分类变量计数,x轴,纵向
ax = sns.countplot(x='class', data=titanic)

#单分类变量计数,y轴,横向
ax = sns.countplot(y='class', data=titanic)

#多变量分类计数
ax = sns.countplot(x='class', hue='who', data=titanic)

#facecolor设置填充颜色,edgecolor设置边框
ax = sns.countplot(x='who', data=titanic,
facecolor=(0, 0, 0, 0),
linewidth=5,
edgecolor=sns.color_palette('dark', 3)
)

#分栏绘制 : catplot() = countplot() + FaceGrid()
g = sns.catplot(x='class', hue='who', col='survived',
data=titanic, kind='count',
height=4, aspect=.7)

pointplot()
绘制带误差线的散点图。
sns.pointplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
data=None,
order=None,
hue_order=None,
estimator=<function mean at 0x000001DA64AD3DC8>,
ci=95,
n_boot=1000,
units=None,
markers='o',
linestyles='-',
dodge=False,
join=True,
scale=1,
orient=None,
color=None,
palette=None,
errwidth=None,
capsize=None,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Show point estimates and confidence intervals using scatter plot glyphs.
A point plot represents an estimate of central tendency for a numeric
variable by the position of scatter plot points and provides some
indication of the uncertainty around that estimate using error bars.
Point plots can be more useful than bar plots for focusing comparisons
between different levels of one or more categorical variables. They are
particularly adept at showing interactions: how the relationship between
levels of one categorical variable changes across levels of a second
categorical variable. The lines that join each point from the same ``hue``
level allow interactions to be judged by differences in slope, which is
easier for the eyes than comparing the heights of several groups of points
or bars.
It is important to keep in mind that a point plot shows only the mean (or
other estimator) value, but in many cases it may be more informative to
show the distribution of values at each level of the categorical variables.
In that case, other approaches such as a box or violin plot may be more
appropriate.
Input data can be passed in a variety of formats, including:
- Vectors of data represented as lists, numpy arrays, or pandas Series
objects passed directly to the ``x``, ``y``, and/or ``hue`` parameters.
- A "long-form" DataFrame, in which case the ``x``, ``y``, and ``hue``
variables will determine how the data are plotted.
- A "wide-form" DataFrame, such that each numeric column will be plotted.
- An array or list of vectors.
In most cases, it is possible to use numpy or Python objects, but pandas
objects are preferable because the associated names will be used to
annotate the axes. Additionally, you can use Categorical types for the
grouping variables to control the order of plot elements.
This function always treats one of the variables as categorical and
draws data at ordinal positions (0, 1, ... n) on the relevant axis, even
when the data has a numeric or date type.
See the :ref:`tutorial <categorical_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
x, y, hue : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Inputs for plotting long-form data. See examples for interpretation.
data : DataFrame, array, or list of arrays, optional
Dataset for plotting. If ``x`` and ``y`` are absent, this is
interpreted as wide-form. Otherwise it is expected to be long-form.
order, hue_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to plot the categorical levels in, otherwise the levels are
inferred from the data objects.
estimator : callable that maps vector -> scalar, optional
Statistical function to estimate within each categorical bin.
ci : float or "sd" or None, optional
Size of confidence intervals to draw around estimated values. If
"sd", skip bootstrapping and draw the standard deviation of the
observations. If ``None``, no bootstrapping will be performed, and
error bars will not be drawn.
n_boot : int, optional
Number of bootstrap iterations to use when computing confidence
intervals.
units : name of variable in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Identifier of sampling units, which will be used to perform a
multilevel bootstrap and account for repeated measures design.
markers : string or list of strings, optional
Markers to use for each of the ``hue`` levels.
linestyles : string or list of strings, optional
Line styles to use for each of the ``hue`` levels.
dodge : bool or float, optional
Amount to separate the points for each level of the ``hue`` variable
along the categorical axis.
join : bool, optional
If ``True``, lines will be drawn between point estimates at the same
``hue`` level.
scale : float, optional
Scale factor for the plot elements.
orient : "v" | "h", optional
Orientation of the plot (vertical or horizontal). This is usually
inferred from the dtype of the input variables, but can be used to
specify when the "categorical" variable is a numeric or when plotting
wide-form data.
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color for all of the elements, or seed for a gradient palette.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
errwidth : float, optional
Thickness of error bar lines (and caps).
capsize : float, optional
Width of the "caps" on error bars.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
barplot : Show point estimates and confidence intervals using bars.
catplot : Combine a categorical plot with a class:`FacetGrid`.
#数据
tip_datas

#单个分类变量统计点图
ax = sns.pointplot(x='time', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas)

#多个分类变量统计点图
ax = sns.pointplot(x='time', y='total_bill', hue='smoker', data=tip_datas)

#多个分类变量统计点图,dodge设置点的位置错开
ax = sns.pointplot(x='time', y='total_bill',
hue='smoker', data=tip_datas, dodge=True)

#多个分类变量统计点图,markers设置点的类型,linestyle设置线类型
ax = sns.pointplot(x='time', y='total_bill',
hue='smoker',
markers=['o','x'],
linestyles=['-','--'],
data=tip_datas)

#纵向分布
ax = sns.pointplot(x='tip', y='day', data=tip_datas)

#纵向分布,join设置是否连线
ax = sns.pointplot(x='tip', y='day', data=tip_datas, join=False)

#以中位值median作为估计值
from numpy import median
ax = sns.pointplot(x='tip', y='day', data=tip_datas, join=False, estimator=median)

#ci设置置信区间
ax = sns.pointplot(x='day', y='tip', data=tip_datas, ci='sd')

#capsize设置误差线端帽
ax = sns.pointplot(x='day', y='tip', data=tip_datas, ci='sd', capsize=.2)
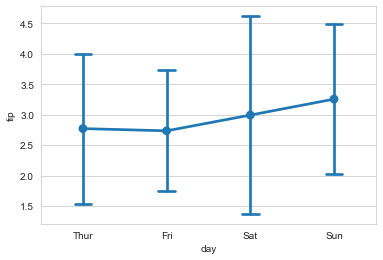
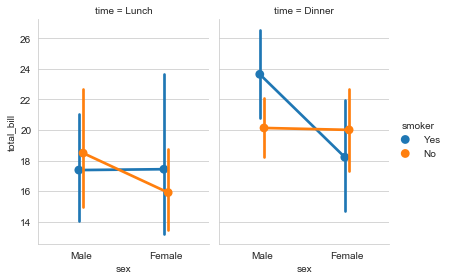
#catplot() = pointplot() + FaceGrid()
g = sns.catplot(x='sex', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
hue='smoker', col='time', kind='point',
dodge=True, height=4, aspect=.7
)
Seaborn分布数据可视化---统计分布图的更多相关文章
- seaborn分布数据可视化:直方图|密度图|散点图
系统自带的数据表格(存放在github上https://github.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data),使用时通过sns.load_dataset('表名称')即可,结果为一个Dat ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:1. 风格| 分布数据可视化-直方图| 密度图| 散点图
conda install seaborn 是安装到jupyter那个环境的 1. 整体风格设置 对图表整体颜色.比例等进行风格设置,包括颜色色板等调用系统风格进行数据可视化 set() / se ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化
转载:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1178368 seaborn针对分类型的数据有专门的可视化函数,这些函数可大致分为三种: 分类数据散点图 ...
- seaborn线性关系数据可视化:时间线图|热图|结构化图表可视化
一.线性关系数据可视化lmplot( ) 表示对所统计的数据做散点图,并拟合一个一元线性回归关系. lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, p ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化:散点图|箱型图|小提琴图|lv图|柱状图|折线图
一.散点图stripplot( ) 与swarmplot() 1.分类散点图stripplot( ) 用法stripplot(x=None, y=None, hue=None, data=None, ...
- 用seaborn对数据可视化
以下用sns作为seaborn的别名 1.seaborn整体布局设置 sns.set_syle()函数设置图的风格,传入的参数可以是"darkgrid", "whiteg ...
- Python Seaborn综合指南,成为数据可视化专家
概述 Seaborn是Python流行的数据可视化库 Seaborn结合了美学和技术,这是数据科学项目中的两个关键要素 了解其Seaborn作原理以及使用它生成的不同的图表 介绍 一个精心设计的可视化 ...
- Seaborn数据可视化入门
在本节学习中,我们使用Seaborn作为数据可视化的入门工具 Seaborn的官方网址如下:http://seaborn.pydata.org 一:definition Seaborn is a Py ...
- geotrellis使用(十五)使用Bokeh进行栅格数据可视化统计
Geotrellis系列文章链接地址http://www.cnblogs.com/shoufengwei/p/5619419.html 目录 前言 实现方案 总结 一.前言 之前有篇文章 ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化-分类散点图|分布图(箱型图|小提琴图|LV图表)|统计图(柱状图|折线图)
1. 分类数据可视化 - 分类散点图 stripplot( ) / swarmplot( ) sns.stripplot(x="day",y="total_bill&qu ...
随机推荐
- 在Winform界面中使用自定义控件,丰富界面的效果处理
我们在<SqlSugar开发框架>中,Winform界面开发部分往往也用到了自定义的用户控件,对应一些特殊的界面或者常用到的一些局部界面内容,我们可以使用自定义的用户控件来提高界面的统一性 ...
- Java面向对象之内部类的几类使用场景
介绍 Java内部类是一种特殊的类,它定义在另一个类的内部.内部类提供了许多有用的特性,包括访问外部类的私有成员.隐藏实现细节以及实现回调接口等.以下是Java内部类的一些常用场景及其举例说明: 回调 ...
- Android 大致可以分为四层架构
Android 系统架构 为了让你能够更好地理解 Android 系统是怎么工作的,我们先来看一下它的系统架构. Android 大致可以分为四层架构:Linux 内核层.系统运行库层.应用框架层和应 ...
- Java 线程通信的应用:经典例题:生产者/消费者问题
1 package bytezero.threadcommunication; 2 3 /** 4 * 线程通信的应用:经典例题:生产者/消费者问题 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * @author B ...
- Java 重写小练习
1 package com.bytezero.inherit3; 2 3 public class CylinderTest 4 { 5 public static void main(String[ ...
- Codeforces Round 928 (Div. 4)(A、B、C、D、E、G)
目录 A B C D E G A 统计A.B输出 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long #define rep(i,a,b) for ...
- [.Net]使用Soa库+Abp搭建微服务项目框架(一):Abp与DDD相关知识回顾
在企业中大型项目中,随着业务的不断拓展,项目发展到一定程度,需要寻求项目的各模块解耦,独立成为微服务.如何实现呢? 首先我们先来简单回顾一下Abp框架怎样实现(DDD)领域驱动设计的,Abp框架的 ...
- Zabbix6.0使用教程 (三)—zabbix6.0的安装要求
接上篇,我们继续为大家详细介绍zabbix6.0的使用教程之zabbix6.0的安装部署.接下来我们将从zabbix部署要求到四种不同的安装方式逐一详细的为大家介绍.本篇讲的是部署zabbix6.0的 ...
- 序列图 时序图 PlantUML vscode drawio 制作
序列图 时序图 PlantUML vscode drawio 制作 需求 最近发现 序列图 很多文档都用到,而且很好用.经过研究用vscode,idea都可以编写.这里用vscode编写比较简单. d ...
- 向TreeView添加自定义信息
可在 Windows 窗体 TreeView 控件中创建派生节点,或在 ListView 控件中创建派生项. 通过派生可添加任何所需字段,以及添加处理这些字段的自定义方法和构造函数. 此功能的用途之一 ...
