Kafka 生产者、消费者与分区的关系
背景
最近和海康整数据对接, 需要将海康产生的结构化数据拿过来做二次识别.
基本的流程: 海康大数据 --> kafka server --> 平台
Kafka 的 topic
正常过车 topic: BAYONET_VEHICLEPASS
违法过车 topic: BAYONET_VEHICLEALARM
前言
首先我们需要对kafka中的一些名词有一定的了解, 有过一些使用经验, 一般来说, 生产者发送消息到主题, 而消费者从主题消费数据 ( 我初次接触的时候, 就是这样理解的, 后来在实践中慢慢发现分区这个角色的重要性 ), 主题下边是分区, 消息数据是存储在分区中的, 所以事实上是生产者发送消息到主题, 然后存储在分区上, 消费者从某个主题下的某个分区上消费数据, 那么生产者将消息发送到哪个分区, 消费者从哪个分区开始消费呢 ?
如何设置主题下的分区数量
在 config/server.properties 配置文件中, 可以设置一个全局的分区数量, 这个分区数量的含义是: 每个主题下的分区数量, 默认为 1
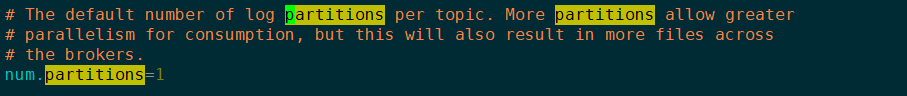
也可以在创建主题的时候, 使用 --partitions 参数指定分区数量
bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --create --topic my_topic --partitions 2 --replication-factor 1
查看已创建主题的分区数量:
bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --zookeeper localhost:2181 --topic my_topic

生产者与分区
在默认 1 个分区的情况下, 我们推测消息是发送到唯一的分区上, 那么在存在多个分区的情况下, 发送消息有没有什么规律呢, 怎么决定一条消息该往哪个分区上发送呢 ?
默认的分区策略:
The default partitioning strategy:
- If a partition is specified in the record, use it
- If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
- If no partition or key is present choose a partition in a round-robin fashion
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.DefaultPartitioner
默认的分区策略是:
- 如果在发消息的时候指定了分区,则消息投递到指定的分区
- 如果没有指定分区,但是消息的key不为空,则基于key的哈希值来选择一个分区
- 如果既没有指定分区,且消息的key也是空,则用轮询的方式选择一个分区
通过源代码可以佐证这一点:
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.size();
if (keyBytes == null) {
int nextValue = nextValue(topic);
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() > 0) {
int part = Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % availablePartitions.size();
return availablePartitions.get(part).partition();
} else {
// no partitions are available, give a non-available partition
return Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % numPartitions;
}
} else {
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
}
消费者与分区
还是刚才的问题, 在默认 1 个分区的情况下, 是从唯一的分区上去消费数据, 那么在存在多个分区的情况下, 消费消息有没有什么规律, 怎么决定从哪个分区上进行消费呢 ?
首先需要了解的是:
- 消费者是以组的名义订阅主题消息, 消费者组里边包含多个消费者实例.
- 主题下边包含多个分区
消费者实例与主题下分区的分配关系
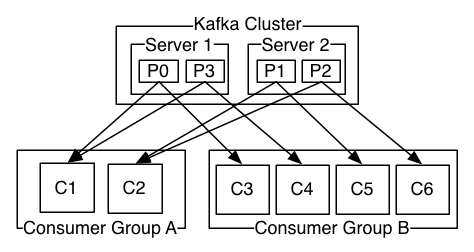
kafka 集群上有两个节点, 4 个分区
A组有 2 个消费者实例 (两个消费线程)
B组有 4 个消费者实例
由图可以看出, A组的消费者C1, C2 平均要消费两个分区的数据, 而 B 组的消费者平均消费 一 个分区的数据 ( 最理想的状态 ), 得到的结论是 : 一条消息只能被一个消费组中的一个消费者实例消费到, (换句话说, 不可能出现组中的两个消费者负责同一个分区, 同组内消费者不会重复消费 )
等等, 考虑的场景还不够, 下边再提些问题 :
如果分区数大于或等于组中的消费者实例数, 那就没有问题, 但是如果消费者实例的数量 > 主题下分区数量, 那么按照默认的策略 ( 之所以强调默认策略是因为可以自定义策略 ), 有一些消费者是多余的, 一直接不到消息而处于空闲状态.
但是假设有消费者实例就是不安分, 就造成了多个消费者负责同一个分区, 这样会造成什么 ? (重复消费就太可怕了)
我们知道,Kafka它在设计的时候就是要保证分区下消息的顺序,也就是说消息在一个分区中的顺序是怎样的,那么消费者在消费的时候看到的就是什么样的顺序,那么要做到这一点就首先要保证消息是由消费者主动拉取的(pull),其次还要保证一个分区只能由一个消费者负责。倘若,两个消费者负责同一个分区,那么就意味着两个消费者同时读取分区的消息,由于消费者自己可以控制读取消息的offset (偏移量),就有可能C1才读到2,而C2读到1,C1还没提交 offset,这时C2读到2了,相当于多线程读取同一个消息,会造成消息处理的重复,且不能保证消息的顺序,这就跟主动推送(push)无异。
消费者分区分配策略 (两种)
range (默认的分配策略)
range策略是基于每个主题的,对于每个主题,我们以数字顺序排列可用分区,以字典顺序排列消费者。然后,将分区数量除以消费者总数,以确定分配给每个消费者的分区数量。如果没有平均划分(PS:除不尽),那么最初的几个消费者将有一个额外的分区。
简而言之:
- range分配策略针对的是主题(也就是说,这里所说的分区指的某个主题的分区,消费者值的是订阅这个主题的消费者组中的消费者实例)
- 首先,将分区按数字顺序排行序,消费者按消费者名称的字典顺序排好序.
- 然后,用分区总数除以消费者总数。如果能够除尽,则皆大欢喜,平均分配;若除不尽,则位于排序前面的消费者将多负责一个分区.
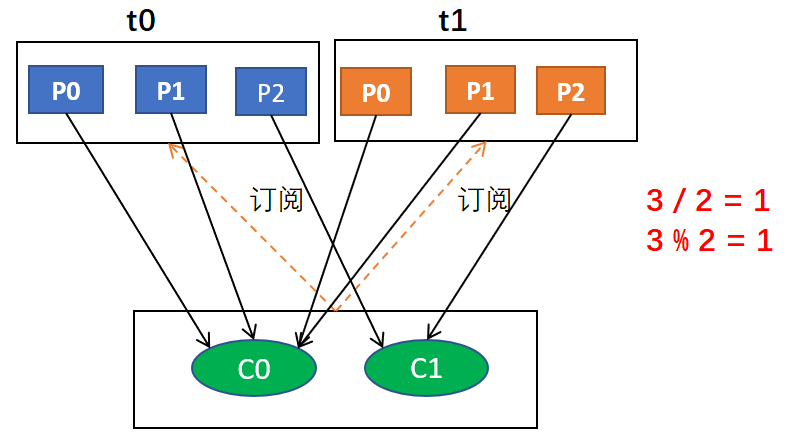
例如,假设有两个消费者C0和C1,两个主题t0和t1,并且每个主题有3个分区,分区的情况是这样的:t0p0,t0p1,t0p2,t1p0,t1p1,t1p2
那么,基于以上信息,最终消费者分配分区的情况是这样的:
C0: [t0p0, t0p1, t1p0, t1p1]
C1: [t0p2, t1p2]
因为,对于主题t0,分配的结果是C0负责P0和P1,C1负责P2;对于主题t2,也是如此,综合起来就是这个结果
上面的过程用图形表示的话大概是这样的 :
阅读源码, 更有助于理解 :
public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,
Map<String, Subscription> subscriptions) {
// 主题与消费者的映射
Map<String, List<String>> consumersPerTopic = consumersPerTopic(subscriptions);
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>();
for (String memberId : subscriptions.keySet())
assignment.put(memberId, new ArrayList<TopicPartition>());
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> topicEntry : consumersPerTopic.entrySet()) {
String topic = topicEntry.getKey(); // 主题
List<String> consumersForTopic = topicEntry.getValue(); // 消费者列表
// partitionsPerTopic表示主题和分区数的映射
// 获取主题下有多少个分区
Integer numPartitionsForTopic = partitionsPerTopic.get(topic);
if (numPartitionsForTopic == null)
continue;
// 消费者按字典序排序
Collections.sort(consumersForTopic);
// 分区数量除以消费者数量
int numPartitionsPerConsumer = numPartitionsForTopic / consumersForTopic.size();
// 取模,余数就是额外的分区
int consumersWithExtraPartition = numPartitionsForTopic % consumersForTopic.size();
List<TopicPartition> partitions = AbstractPartitionAssignor.partitions(topic, numPartitionsForTopic);
for (int i = 0, n = consumersForTopic.size(); i < n; i++) {
int start = numPartitionsPerConsumer * i + Math.min(i, consumersWithExtraPartition);
int length = numPartitionsPerConsumer + (i + 1 > consumersWithExtraPartition ? 0 : 1);
// 分配分区
assignment.get(consumersForTopic.get(i)).addAll(partitions.subList(start, start + length));
}
}
return assignment;
}
python版本
"""
The range assignor works on a per-topic basis. For each topic, we lay out
the available partitions in numeric order and the consumers in
lexicographic order. We then divide the number of partitions by the total
number of consumers to determine the number of partitions to assign to each
consumer. If it does not evenly divide, then the first few consumers will
have one extra partition.
For example, suppose there are two consumers C0 and C1, two topics t0 and
t1, and each topic has 3 partitions, resulting in partitions t0p0, t0p1,
t0p2, t1p0, t1p1, and t1p2.
The assignment will be:
C0: [t0p0, t0p1, t1p0, t1p1]
C1: [t0p2, t1p2]
"""
name = 'range'
version = 0
@classmethod
def assign(cls, cluster, member_metadata):
consumers_per_topic = collections.defaultdict(list)
for member, metadata in six.iteritems(member_metadata):
for topic in metadata.subscription:
consumers_per_topic[topic].append(member)
# construct {member_id: {topic: [partition, ...]}}
assignment = collections.defaultdict(dict)
for topic, consumers_for_topic in six.iteritems(consumers_per_topic):
partitions = cluster.partitions_for_topic(topic)
if partitions is None:
log.warning('No partition metadata for topic %s', topic)
continue
partitions = sorted(list(partitions))
partitions_for_topic = len(partitions)
consumers_for_topic.sort()
partitions_per_consumer = len(partitions) // len(consumers_for_topic)
consumers_with_extra = len(partitions) % len(consumers_for_topic)
for i in range(len(consumers_for_topic)):
start = partitions_per_consumer * i
start += min(i, consumers_with_extra)
length = partitions_per_consumer
if not i + 1 > consumers_with_extra:
length += 1
member = consumers_for_topic[i]
assignment[member][topic] = partitions[start:start + length]
protocol_assignment = {}
for member_id in member_metadata:
protocol_assignment[member_id] = ConsumerProtocolMemberAssignment(
cls.version,
sorted(assignment[member_id].items()),
b'')
return protocol_assi
roundrobin (轮询)
roundronbin分配策略的具体实现是org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RoundRobinAssignor
"""
The roundrobin assignor lays out all the available partitions and all the
available consumers. It then proceeds to do a roundrobin assignment from
partition to consumer. If the subscriptions of all consumer instances are
identical, then the partitions will be uniformly distributed. (i.e., the
partition ownership counts will be within a delta of exactly one across all
consumers.)
For example, suppose there are two consumers C0 and C1, two topics t0 and
t1, and each topic has 3 partitions, resulting in partitions t0p0, t0p1,
t0p2, t1p0, t1p1, and t1p2.
The assignment will be:
C0: [t0p0, t0p2, t1p1]
C1: [t0p1, t1p0, t1p2]
When subscriptions differ across consumer instances, the assignment process
still considers each consumer instance in round robin fashion but skips
over an instance if it is not subscribed to the topic. Unlike the case when
subscriptions are identical, this can result in imbalanced assignments.
For example, suppose we have three consumers C0, C1, C2, and three topics
t0, t1, t2, with unbalanced partitions t0p0, t1p0, t1p1, t2p0, t2p1, t2p2,
where C0 is subscribed to t0; C1 is subscribed to t0, t1; and C2 is
subscribed to t0, t1, t2.
The assignment will be:
C0: [t0p0]
C1: [t1p0]
C2: [t1p1, t2p0, t2p1, t2p2]
"""
轮询分配策略是基于所有可用的消费者和所有可用的分区的
与前面的range策略最大的不同就是它不再局限于某个主题
如果所有的消费者实例的订阅都是相同的,那么这样最好了,可用统一分配,均衡分配
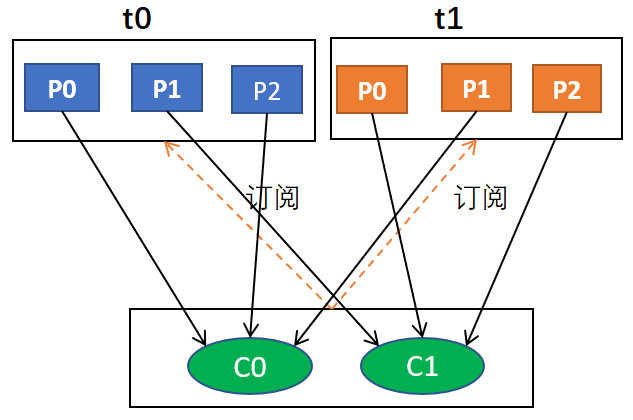
例如,假设有两个消费者C0和C1,两个主题t0和t1,每个主题有3个分区,分别是t0p0,t0p1,t0p2,t1p0,t1p1,t1p2
那么,最终分配的结果是这样的:
C0: [t0p0, t0p2, t1p1]
C1: [t0p1, t1p0, t1p2]
用图形表示大概是这样的:
一个较为复杂的场景:
假设,组中每个消费者订阅的主题不一样,分配过程仍然以轮询的方式考虑每个消费者实例,但是如果没有订阅主题,则跳过实例。当然,这样的话分配肯定不均衡。
什么意思呢?也就是说,消费者组是一个逻辑概念,同组意味着同一时刻分区只能被一个消费者实例消费,换句话说,同组意味着一个分区只能分配给组中的一个消费者。事实上,同组也可以不同订阅,这就是说虽然属于同一个组,但是它们订阅的主题可以是不一样的。
例如,假设有3个主题t0,t1,t2;其中,t0有1个分区p0,t1有2个分区p0和p1,t2有3个分区p0,p1和p2;有3个消费者C0,C1和C2;C0订阅t0,C1订阅t0和t1,C2订阅t0,t1和t2。那么,按照轮询分配的话,C0应该负责
首先,肯定是轮询的方式,其次,比如说有主题t0,t1,t2,它们分别有1,2,3个分区,也就是t0有1个分区,t1有2个分区,t2有3个分区;有3个消费者分别从属于3个组,C0订阅t0,C1订阅t0和t1,C2订阅t0,t1,t2;那么,按照轮询分配的话,C0应该负责t0p0,C1应该负责t1p0,其余均由C2负责。
上述过程用图形表示大概是这样的:
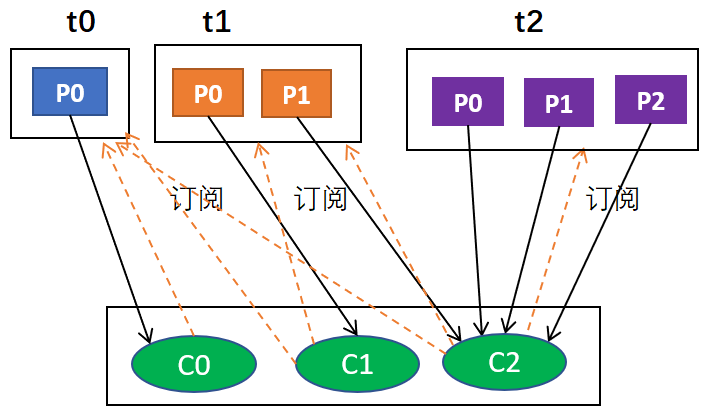
为什么最后的结果是:
C0: [t0p0]
C1: [t1p0]
C2: [t1p1, t2p0, t2p1, t2p2]
这是因为,按照轮询t0p1由C0负责,t1p0由C1负责,由于同组,C2只能负责t1p1,由于只有C2订阅了t2,所以t2所有分区由C2负责,综合起来就是这个结果
细想一下可以发现,这种情况下跟range分配的结果是一样的
测试代码 (python):
producer.py
# coding: utf-8
import time
import json
from kafka import KafkaProducer
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
from kafka.errors import KafkaError
class Producer(object):
"""
使用kafka的生产模块
"""
def __init__(self, kafkahost, kafkaport, kafkatopic):
self.kafkaHost = kafkahost
self.kafkaPort = kafkaport
self.kafkatopic = kafkatopic
self.producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers='{kafka_host}:{kafka_port}'.format(
kafka_host=self.kafkaHost,
kafka_port=self.kafkaPort
))
def sendjsondata(self, params):
try:
parmas_message = json.dumps(params)
producer = self.producer
producer.send(self.kafkatopic, parmas_message.encode('utf-8'))
producer.flush()
except KafkaError as e:
print(e)
def main():
"""
测试consumer和producer
:return:
"""
# 测试生产模块
producer = Producer("10.10.4.70", 9092, "push")
for i in range(10000):
params = 'test---' + str(i)
print(params)
producer.sendjsondata(params)
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
consumer.py
# coding: utf-8
from kafka import KafkaConsumer
class Kafka_consumer(object):
'''
使用Kafka—python的消费模块
'''
def __init__(self, kafkahost, kafkaport, kafkatopic, groupid):
self.kafkaHost = kafkahost
self.kafkaPort = kafkaport
self.kafkatopic = kafkatopic
self.groupid = groupid
self.consumer = KafkaConsumer(self.kafkatopic, group_id=self.groupid,
bootstrap_servers='{kafka_host}:{kafka_port}'.format(
kafka_host=self.kafkaHost,
kafka_port=self.kafkaPort))
def consume_data(self):
try:
for message in self.consumer:
print(message.value)
self.consumer.commit()
continue
except KeyboardInterrupt as e:
print(e)
def main():
'''
测试consumer和producer
:return:
'''
# 测试消费模块
# 消费模块的返回格式为ConsumerRecord(topic=u'ranktest', partition=0, offset=202, timestamp=None,
# \timestamp_type=None, key=None, value='"{abetst}:{null}---0"', checksum=-1868164195,
# \serialized_key_size=-1, serialized_value_size=21)
consumer = Kafka_consumer('10.10.4.70', 9092, "push", 'police_seemmo1')
consumer.consume_data()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
测试代码 (java):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cjs.example</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>kafka-demo</name>
<description></description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
producer.java
package com.cjs.kafka.producer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class HelloProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.1.133:9092");
props.put("acks", "all");
props.put("retries", 0);
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(props);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("abc", Integer.toString(i), Integer.toString(i)), new Callback() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) {
if (null != e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}else {
System.out.println("callback: " + recordMetadata.topic() + " " + recordMetadata.partition() + " " + recordMetadata.offset());
}
}
});
}
producer.close();
}
}
consumer.java
package com.cjs.kafka.consumer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Properties;
public class HelloConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.1.133:9092");
props.put("group.id", "test");
props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true");
props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");
// props.put("partition.assignment.strategy", "org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RoundRobinAssignor");
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("foo", "bar", "abc"));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100);
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
System.out.printf("partition = %s, offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.partition(), record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
}
}
}
}
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/cjsblog/p/9664536.html
http://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#consumerconfigs
https://blog.csdn.net/feelwing1314/article/details/81097167
ending ~
Kafka 生产者、消费者与分区的关系的更多相关文章
- Python 使用python-kafka类库开发kafka生产者&消费者&客户端
使用python-kafka类库开发kafka生产者&消费者&客户端 By: 授客 QQ:1033553122 1.测试环境 python 3.4 zookeeper- ...
- kafka对消费者分配分区规则(Java源码)
在上一篇 kafka topic消息分配partition规则(Java源码) 我们对生产者产生的消息分配partition规则进行了分析,那么本章我们来看看消费者是怎么样分配partition的. ...
- kafka集群搭建和使用Java写kafka生产者消费者
1 kafka集群搭建 1.zookeeper集群 搭建在110, 111,112 2.kafka使用3个节点110, 111,112 修改配置文件config/server.properties ...
- java kafka 生产者消费者demo
一.修改kafka server.porperties的ip是你本机的ip listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.111.130:9092 二.生产者的例子 import o ...
- kafka 生产者消费者 api接口
生产者 import java.util.Properties; import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer; import kafka.producer.Keyed ...
- kafka生产者消费者
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord; import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.Co ...
- kafka生产者 消费者
publisher.php <?php $rk = new RdKafka\Producer(); $rk->addBrokers("192.168.33.50"); ...
- kafka-python开发kafka生产者和消费者
1.安装kafka-python 执行命令 pip install kafka-python kafka-python 1.4.6 2.编写python kafka 生产者消费者代码 # ...
- (转)生产者/消费者问题的多种Java实现方式 (待整理)
实质上,很多后台服务程序并发控制的基本原理都可以归纳为生产者/消费者模式,而这是恰恰是在本科操作系统课堂上老师反复讲解,而我们却视而不见不以为然的.在博文<一种面向作业流(工作流)的轻量级可复用 ...
随机推荐
- visual studio 2019 企业版下载
由于visual studio从2017开始就是网络下载安装,所以网速慢的朋友安装上就存在时间感,所以笔者在百度云上提供了visual studio 2019的下载包.需要的朋友自己下载安装.不过,2 ...
- linux中nohup 与 & 的区别
Linux/Unix下,通常只有守护进程可在脱离终端的情况下能继续执行,而普通进程在关闭终端时会因收到SIGHUP信号(挂起信号)而退出.当终端退出后,由该终端启动的后台程序自动退出. 若想命令在后台 ...
- wx.request 请求与django
wx.request 1.wx.request相当于ajax请求,和django后台进行交互 官方文档:https://developers.weixin.qq.com/miniprogram/dev ...
- Spark程序打包
背景: spark程序,使用scala语言开发.整个项目中包含多个子模块,依赖包文件使用maven来管理. 打包: 方法一:使用artifacts来 选择模块,选择对应的主函数: 点ok保存. 由于s ...
- 关于Oracle to_date函数的高级用法
由于种种原因,在我们的系统中,账套期间(PERIOD_NAME)由于格式设置的原因,数据库层存储的格式如下 Mar-19,而不是常规的2019-03. 我们无法更改数据库,涉及到的点太多. 但是期间数 ...
- idea 出现 bootstrap.properties 中的内容不能识别
错误截图如下 依赖库引用问题 第一种: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> < ...
- 为什么java里面经常作List判断的时候,既要判断list不为null,又要判断size>0呢?
没有考虑到具体的问题上面,我们单纯的来讲: 为什么java里面经常作List判断的时候,既要判断list不为null,又要判断size>0呢? list == null 说明list没有初始化( ...
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/1038c6170775
import os # 方法一: os.walk实现 def items_dir(rootname): l = [] for main_dir, dirs, file_name_list in os. ...
- SQL Server:时间范围查询重叠
常常碰到要校验数据范围是否存在重叠冲突的情况,典型的场景是房间预订. 假如房间A已经有9月1日-9月10日的预订记录,当其它客人再来预订时,系统必须判断,不能与这个日期范围产生重叠. 有四种情况会产生 ...
- 【转】解决深入学习PHP的瓶颈?
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/aksir/p/6774115.html PHP给学习者的感觉是:初学的时候很容易,但是学了2-3年,就深刻感觉遇到了瓶颈,很难深入,放弃又可惜. ...
