How to Repair GRUB2 When Ubuntu Won’t Boot
Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions use the GRUB2 boot loader. If GRUB2 breaks—for example, if you install Windows after installing Ubuntu, or overwrite your MBR—you won’t be able to boot into Ubuntu.
You can easily restore GRUB2 from a Ubuntu live CD or USB drive. This process is different from restoring the legacy GRUB boot loader on older Linux distributions.
This process should work on all versions of Ubuntu. It’s been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 and Ubuntu 14.04.
The Graphical Method: Boot Repair
Boot Repair is a graphical tool that can repair GRUB2 with a single click. This is the ideal solution to boot problems for most users.
If you have the media you installed Ubuntu from, insert it into your computer, restart, and boot from the removable drive. If you don’t, download a Ubuntu live CD and burn it to a disc or create a bootable USB flash drive.
When Ubuntu boots, click “Try Ubuntu” to get a usable desktop environment.
Ensure you have an Internet connection before continuing. You may need to choose a Wi-Fi network and enter its passphrase.
Open a Terminal window from the Dash and run the following commands to install and launch Boot Repair:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair boot-repair
The Boot Repair window will automatically scan your system after you run the boot-repair command. After it scans your system, click the “Recommended repair” button to repair GRUB2 with a single click.
You can choose to use the advanced options here, but Ubuntu’s wiki recommends you not use the advanced options unless you know what you’re doing. The recommended repair option can fix most problems automatically, and you could mess up your system even more by selecting the wrong advanced options.

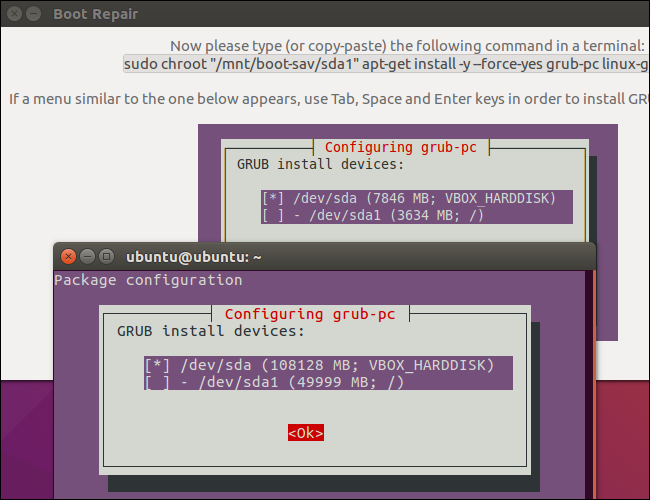
Boot Repair will begin working. It may ask you to open a Terminal and copy/paste a few commands into it.
Just follow the instructions that appear on your screen. Perform the instructions Boot Repair wants you to and click “Forward” to continue through the wizard. The tool will walk you through everything you need to do.
Restart your computer after the Boot Repair tool finishes applying its changes. Ubuntu should boot up normally.
The Terminal Method
If you’d rather get your hands dirty, you can do this yourself from a terminal. You’ll need to boot from a live CD or USB drive, as in the graphical method above. Ensure the version of Ubuntu on the CD is the same as the version of Ubuntu installed on your computer. For example, if you have Ubuntu 14.04 installed, ensure you use a Ubuntu 14.04 live CD.
Open a terminal after booting into the live environment. Identify the partition Ubuntu is installed on using one of the following commands:
sudo fdisk -l sudo blkid
Here’s the output of both commands. In the fdisk -l command, the Ubuntu partition is identified by the word Linux in the System column. In the blkid command, the partition is identified by its ext4 file system.
If you have multiple Linux ext4 partitions, you can get an idea of which is which by viewing the size of the partitions and their order on the disk here.

Run the following commands to mount the Ubuntu partition at /mnt/ubuntu, replacing/dev/sdX# with the device name of your Ubuntu partition from the above commands:
sudo mkdir /mnt/ubuntu sudo mount /dev/sdX# /mnt/ubuntu
In the screenshot above, our Ubuntu partition is /dev/sda1. This means the first partition on the first hard disk device.
Important: If you have a separate boot partition, skip the above command and mount the boot partition at /mnt/ubuntu/boot instead. If you don’t know whether you have a separate boot partition, you probably don’t.

Run the following command to reinstall grub from the live CD, replacing /dev/sdX with the device name of the hard disk above. Omit the number. For example, if you used/dev/sda1 above, use /dev/sda here.
sudo grub-install --boot-directory=/mnt/ubuntu/boot /dev/sdX

Restart your computer and Ubuntu should boot properly.
How to Repair GRUB2 When Ubuntu Won’t Boot的更多相关文章
- ubuntu下提示/boot空间不足,解决办法
在安装 ubuntu的时候 , 给/boot文件目录分配空间的时候,是100M,/boot可以单独分成一个区,也可以不单独分,在/(根目录)下也会自动为其创建一个boot目录.顺便提一下,linux分 ...
- Ubuntu提示卷boot仅剩0字节的硬盘空间,解决办法
查看当前安装的linux内核版本号 dpkg --get-selections |grep linux-image 查看当前使用的内核版本号 uname -a 卸载不需要的内核 sudo apt-ge ...
- 安装ubuntu时将boot目录单独挂载的意义
只有一个意义那就是当你的情况是:单个硬盘里面安装多个系统. 如果不是这样,就别动它.
- Ubuntu升级出现/boot空间不足解决
经常升级Linux内核,导致更新时警告/boot分区空间不足.这是以为多次升级内核后,导致内核版本太多,清理一下没用的内核文件就行了.命令如下: zht@zht-Ubuntu:~$ dpkg -l ' ...
- ubuntu更新提示/boot空间不足
1. 查看当前使用的内核版本 uname -a 2.在终端下察看已经安装的旧的内核: ctrl+alt+t——>进入终端——>输入命令: dpkg --get-selections|gre ...
- Ubuntu升级出现/boot空间不足解决(转)
经常升级Linux内核,导致更新时警告/boot分区空间不足.这是以为多次升级内核后,导致内核版本太多,清理一下没用的内核文件就行了.命令如下: zht@zht-Ubuntu:~$ dpkg -l ' ...
- ubuntu修改grub2
转自修改系统启动项 grub2配置的方法 ubuntu 在早期的Ubuntu中,使用Grub作为系统的启动引导程序,想修改系统启动项非常简单,只要用gedit打开系统菜单设定文件( sudo gedi ...
- 修改系统启动项 grub2配置的方法 ubuntu[转]
在 早期的Ubuntu中,使用Grub作为系统的启动引导程序,想修改系统启动项非常简单,只要用gedit打开系统菜单设定文件( sudo gedit /boot/grub/menu.lst ),修改该 ...
- 使用 boot-repair 对 Windows + Ubuntu 双系统引导修复
问题描述: 由于在windows上进行更新/重装/修改了引导设置以后,windows会“自私”地重写引导,导致Ubuntu系统引导消失而无法选择Ubuntu启动.
随机推荐
- 架构师成长之路6.5 DNS服务器搭建(添加记录、负载均衡、DNS视图)
点击返回架构师成长之路 架构师成长之路6.5 DNS服务器搭建(添加记录.负载均衡.DNS视图) 部署主DNS : 点击 部署从DNS : 点击 1.添加A记录.CNAME记录.MX记录.PTR记录 ...
- [hgoi#2019/2/16t1]math
题目描述 解法 我们稍微枚举一下前面几位,可以得到这样的规律. \[X_i=\frac{1}{2^{i+1}-1}\] \[Y_i=\frac{1}{2^{2^i}-1}\] 那么要使\(xm=yn\ ...
- Spark 集成开发
WordCount.py # coding:utf-8 from pyspark import SparkContext from pyspark import SparkConf def SetLo ...
- Android下载管理DownloadManager功能扩展和bug修改
http://www.trinea.cn/android/android-downloadmanager-pro/ 本文主要介绍如何修改Android系统下载管理,以支持更多的功能及部分bug修改和如 ...
- centos6.5安装jdk(解压tar.gz)
0.说明 下载jdk文件包jdk-7u79-linux-x64.tar.gz. 1.环境清理(系统自带的OpenJDK) 1.1 查看OpenJDK的安装包 $ rpm -qa |grep java ...
- shoi2017小结
某省选 胡雨菲让我做的,她自己已经AK了... 在loj(自由oj?)上面搜索shoi2017即可. 洛谷上也有,搜六省联考就行 第一题:大水题枚举 P3745 看题目就很水:(其实是因为胡雨菲给我讲 ...
- (转)JVM——自定义类加载器
背景:为什么要自定义,如何自定义,实现过程 转载:http://blog.csdn.net/SEU_Calvin/article/details/52315125 0. 为什么需要自定义类加载器 网上 ...
- 描述符__get__(),__set__(),__delete__()(三十七)
http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/articles/6204014.html#_label12 描述符是什么:描述符本质就是一个新式类,在这个新式类中,至少实现了__ ...
- Sublime Text3—常用插件Emmet
摘要 安装请看上一篇Sublime Text-安装,和sublime自带快捷键一起用,写html简直快的飞起. 下面整理的是常用的,完整的可看emmet官方文档. 一.生成标签 1.快速生成文档结构 ...
- word产品密钥激活
1.找到对应版本 2.在网上找对应的破解软件和激活密钥 注意有些软件是不能在你的电脑上运行达到所要结果的,多试几个 有点软件在打开时需要把杀毒软件关了.下载后先杀毒确定没有病毒后,把把杀毒软件关了,并 ...
