JDK1.8源码阅读系列之四:HashMap (原创)
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 HashMap 源码期间的对于 HashMap 的一些实现上的个人理解,用于个人备忘,有不对的地方,请指出~
接下来会从以下几个方面介绍 HashMap 源码相关知识:
1、HashMap 存储结构
2、HashMap 各常量、成员变量作用
3、HashMap 几种构造方法
4、HashMap put 及其相关方法
5、HashMap get 及其相关方法
6、HashMap remove 及其相关方法(暂未理解透彻)
7、HashMap 扩容方法 resize()
介绍方法时会包含方法实现相关细节。
先来看一下 HashMap 的继承图:
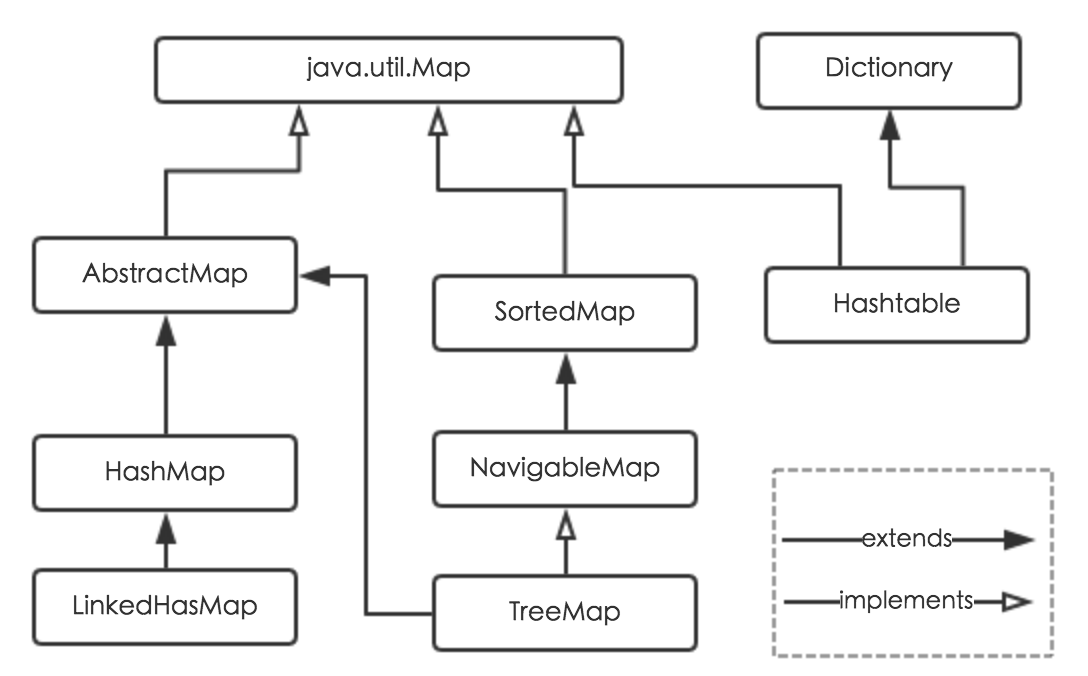
HashMap 根据键的 hashCode 值存储数据,大多数情况下可以直接定位到它的值,因而具有很快的访问速度,但遍历顺序却是不确定的。 HashMap 最多只允许一条记录的键为 null ,允许多条记录的值为 null 。HashMap 非线程安全,即任一时刻可以有多个线程同时写 HashMap,可能会导致数据的不一致。如果需要满足线程安全,可以用 Collections的synchronizedMap 方法使 HashMap 具有线程安全的能力,或者使用ConcurrentHashMap 。
一、HashMap 存储结构
HashMap是数组+链表+红黑树(JDK1.8增加了红黑树部分)实现的,如下图所示:
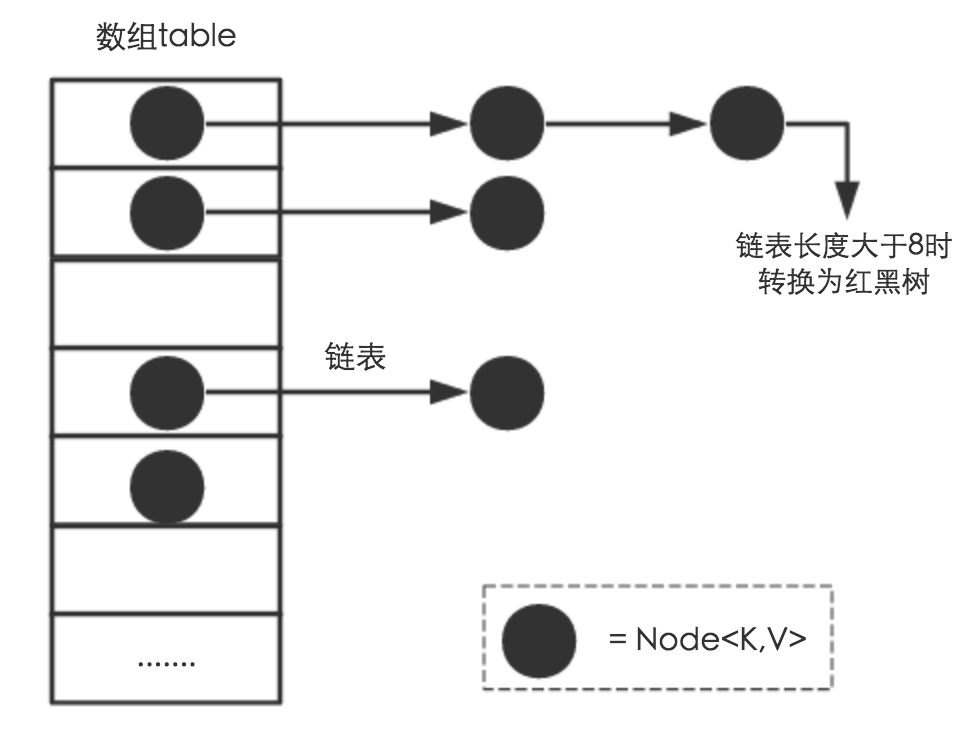
源码中具体实现如下:
// Node<K,V> 类用来实现数组及链表的数据结构
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; //保存节点的 hash 值
final K key; //保存节点的 key 值
V value; //保存节点的 value 值
Node<K,V> next; //指向链表结构下的当前节点的 next 节点,红黑树 TreeNode 节点中也有用到 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} public final K getKey() { }
public final V getValue() { }
public final String toString() { } public final int hashCode() {
} public final V setValue(V newValue) {
} public final boolean equals(Object o) {
}
} public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> {
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
} // TreeNode<K,V> 继承 LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>,用来实现红黑树相关的存储结构
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // 存储当前节点的父节点
TreeNode<K,V> left; //存储当前节点的左孩子
TreeNode<K,V> right; //存储当前节点的右孩子
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // 存储当前节点的前一个节点
boolean red; // 存储当前节点的颜色(红、黑)
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
} final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
} static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) {
} final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
} final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
} final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {
} final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
} final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
boolean movable) {
} final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {
} /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
// Red-black tree methods, all adapted from CLR
// 红黑树相关操作
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> x) {
} static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceDeletion(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> x) {
} static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t) {
} }
二、HashMap 各常量、成员变量作用
//创建 HashMap 时未指定初始容量情况下的默认容量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; //HashMap 的最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //HashMap 默认的装载因子,当 HashMap 中元素数量超过 容量*装载因子 时,进行 resize() 操作
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //用来确定何时将解决 hash 冲突的链表转变为红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 用来确定何时将解决 hash 冲突的红黑树转变为链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /* 当需要将解决 hash 冲突的链表转变为红黑树时,需要判断下此时数组容量,若是由于数组容量太小(小于 MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY )导致的 hash 冲突太多,则不进行链表转变为红黑树操作,转为利用 resize() 函数对 hashMap 扩容 */
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
//保存Node<K,V>节点的数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table; //由 hashMap 中 Node<K,V> 节点构成的 set
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; //记录 hashMap 当前存储的元素的数量
transient int size; //记录 hashMap 发生结构性变化的次数(注意 value 的覆盖不属于结构性变化)
transient int modCount; //threshold的值应等于 table.length * loadFactor, size 超过这个值时进行 resize()扩容
int threshold; //记录 hashMap 装载因子
final float loadFactor;
三、HashMap 几种构造方法
//构造方法1,指定初始容量及装载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
/* tableSizeFor(initialCapacity) 方法返回的值是最接近 initialCapacity 的2的幂,若指定初始容量为9,则实际 hashMap 容量为16*/
//注意此种方法创建的 hashMap 初始容量的值存在 threshold 中
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
//tableSizeFor(initialCapacity) 方法返回的值是最接近 initialCapacity 的2的幂
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;// >>> 代表无符号右移
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
//构造方法2,仅指定初始容量,装载因子的值采用默认的 0.75
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//构造方法3,所有参数均采用默认值
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
四、HashMap put 及其相关方法
这部分我觉得是 hashMap 中比较重要的代码,介绍如下:
//指定节点 key,value,向 hashMap 中插入节点
public V put(K key, V value) {
//注意待插入节点 hash 值的计算,调用了 hash(key) 函数
//实际调用 putVal()进行节点的插入
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
/*key 的 hash 值的计算是通过hashCode()的高16位异或低16位实现的:(h = k.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16),主要是从速度、功效、质量来考虑的,这么做可以在数组table的length比较小的时候,也能保证考虑到高低Bit都参与到Hash的计算中,同时不会有太大的开销*/
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
} public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
/*把Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m 中的元素插入到 hashMap 中,若 evict 为 false,代表是在创建 hashMap 时调用了这个函数,例如利用上述构造函数3创建 hashMap;若 evict 为true,代表是在创建 hashMap 后才调用这个函数,例如上述的 putAll 函数。*/ final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
/*如果是在创建 hashMap 时调用的这个函数则 table 一定为空*/
if (table == null) {
//根据待插入的map 的 size 计算要创建的 hashMap 的容量。
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
//把要创建的 hashMap 的容量存在 threshold 中
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
//判断待插入的 map 的 size,若 size 大于 threshold,则先进行 resize()
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
//实际也是调用 putVal 函数进行元素的插入
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
/*根据 hash 值确定节点在数组中的插入位置,若此位置没有元素则进行插入,注意确定插入位置所用的计算方法为 (n - 1) & hash,由于 n 一定是2的幂次,这个操作相当于
hash % n */
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//说明待插入位置存在元素
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//比较原来元素与待插入元素的 hash 值和 key 值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//若原来元素是红黑树节点,调用红黑树的插入方法:putTreeVal
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {//证明原来的元素是链表的头结点,从此节点开始向后寻找合适插入位置
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//找到插入位置后,新建节点插入
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//若链表上节点超过TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1,将链表变为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}//end else
if (e != null) { // 待插入元素在 hashMap 中已存在
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}//end else
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}//end putval
/*读懂这个函数要注意理解 hash 冲突发生的几种情况
1、两节点 key 值相同(hash值一定相同),导致冲突
2、两节点 key 值不同,由于 hash 函数的局限性导致hash 值相同,冲突
3、两节点 key 值不同,hash 值不同,但 hash 值对数组长度取模后相同,冲突
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
//从根节点开始查找合适的插入位置(与二叉搜索树查找过程相同)
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1; // dir小于0,接下来查找当前节点左孩子
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1; // dir大于0,接下来查找当前节点右孩子
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk)))
//进入这个else if 代表 hash 值相同,key 相同
return p;
/*要进入下面这个else if,代表有以下几个含义:
1、当前节点与待插入节点 key 不同, hash 值相同
2、k是不可比较的,即k并未实现 comparable<K> 接口
(若 k 实现了comparable<K> 接口,comparableClassFor(k)返回的是k的 class,而不是 null)
或者 compareComparables(kc, k, pk) 返回值为 0
(pk 为空 或者 按照 k.compareTo(pk) 返回值为0,
返回值为0可能是由于 k的compareTo 方法实现不当引起的,compareTo 判定相等,而上个 else if 中 equals 判定不等)*/
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
//在以当前节点为根的整个树上搜索是否存在待插入节点(只会搜索一次)
if (!searched) {
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
//若树中存在待插入节点,直接返回
return q;
}
// 既然k是不可比较的,那我自己指定一个比较方式
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}//end else if TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
//找到了待插入的位置,xp 为待插入节点的父节点
//注意TreeNode节点中既存在树状关系,也存在链式关系,并且是双端链表
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
//插入节点后进行二叉树的平衡操作
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}//end for
}//end putTreeVal
static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {
int d;
//System.identityHashCode()实际是利用对象 a,b 的内存地址进行比较
if (a == null || b == null ||
(d = a.getClass().getName().
compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)
d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ?
-1 : 1);
return d;
}
五、HashMap get 及其相关方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
//实际上是根据输入节点的 hash 值和 key 值利用getNode 方法进行查找
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
//若定位到的节点是 TreeNode 节点,则在树中进行查找
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {//否则在链表中进行查找
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
//从根节点开始,调用 find 方法进行查找
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);
}
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk;
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
//首先进行hash 值的比较,若不同令当前节点变为它的左孩子或者右孩子
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
//hash 值相同,进行 key 值的比较
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
//执行到这儿,意味着hash 值相同,key 值不同
//若k 是可比较的并且k.compareTo(pk) 返回结果不为0可进入下面elseif
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
/*若 k 是不可比较的 或者 k.compareTo(pk) 返回结果为0则在整棵树中进行查找,先找右子树,右子树没有再找左子树*/
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null;
}
七、HashMap 扩容方法 resize()
resize() 方法中比较重要的是链表和红黑树的 rehash 操作,先来说下 rehash 的实现原理:
我们在扩容的时候,一般是把长度扩为原来2倍,所以,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置。看下图可以明白这句话的意思,n为table的长度,图(a)表示扩容前的key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,图(b)表示扩容后key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,其中hash1是key1对应的哈希与高位运算结果。
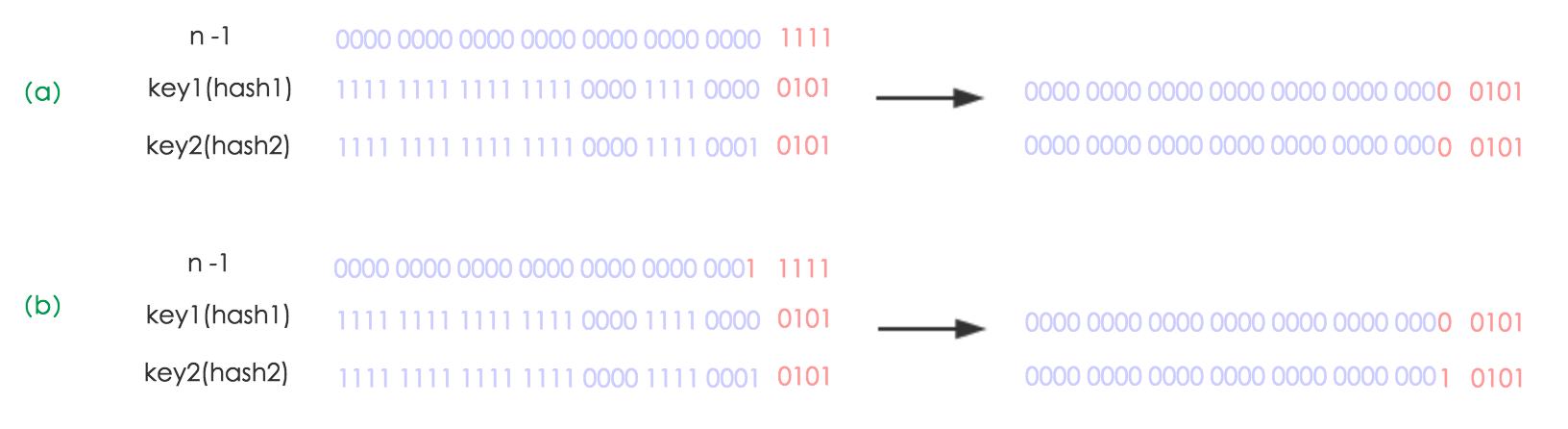
元素在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit(红色),因此新的index就会发生这样的变化:
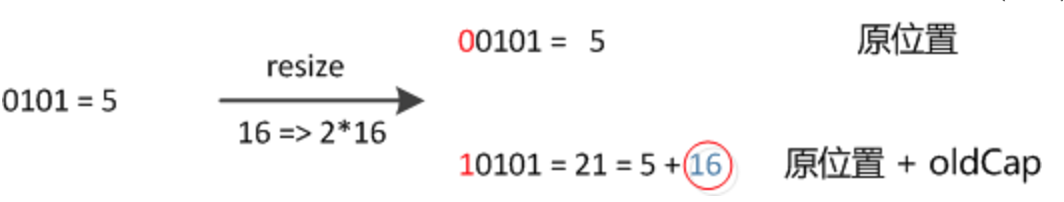
因此,我们在扩充HashMap的时候,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”,可以看看下图为16扩充为32的resize示意图:
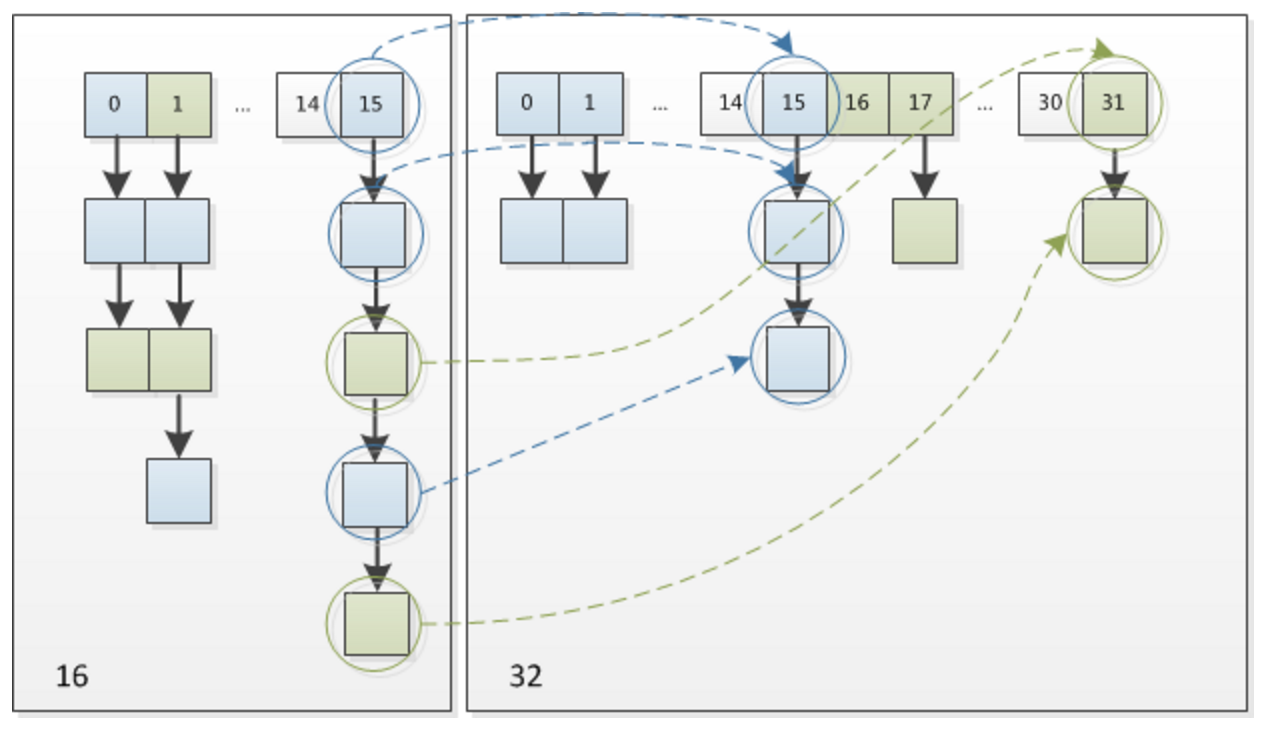
这个算法很巧妙,既省去了重新计算hash值的时间,而且同时,由于新增的1bit是0还是1可以认为是随机的,因此resize的过程,均匀的把之前的冲突的节点分散到新的槽中了。
具体源码介绍:
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
/*
1、resize()函数在size > threshold时被调用。
oldCap大于 0 代表原来的 table 表非空, oldCap 为原表的大小,
oldThr(threshold) 为 oldCap × load_factor
*/
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
/*
2、resize()函数在table为空被调用。
oldCap 小于等于 0 且 oldThr 大于0,代表用户创建了一个 HashMap,但是使用的构造函数为
HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) 或 HashMap(int initialCapacity)
或 HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m),导致 oldTab 为 null,oldCap 为0,
oldThr 为用户指定的 HashMap的初始容量。
*/
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
/*
3、resize()函数在table为空被调用。
oldCap 小于等于 0 且 oldThr 等于0,用户调用 HashMap()构造函数创建的 HashMap,所有值均采用默认值,
oldTab(Table)表为空,oldCap为0,oldThr等于0,
*/
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
//把 oldTab 中的节点 reHash 到 newTab 中去
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
//若节点是单个节点,直接在 newTab 中进行重定位
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//若节点是 TreeNode 节点,要进行 红黑树的 rehash 操作
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
//若是链表,进行链表的 rehash 操作
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
//根据算法 e.hash & oldCap 判断节点位置 rehash 后是否发生改变
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
// rehash 后节点新的位置一定为原来基础上加上 oldCap
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
//这个函数的功能是对红黑树进行 rehash 操作
final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {
TreeNode<K,V> b = this;
// Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
//由于 TreeNode 节点之间存在双端链表的关系,可以利用链表关系进行 rehash
for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
e.next = null;
if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
++hc;
}
} //rehash 操作之后注意对根据链表长度进行 untreeify 或 treeify 操作
if (loHead != null) {
if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index] = loHead;
if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
loHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
if (hiHead != null) {
if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
if (loHead != null)
hiHead.treeify(tab);
}
}//end if
}//end split
关于 HashMap 源码阅读的相关知识就先介绍到这里,有一些地方我还没有理解透彻(例如红黑树的插入节点之后的平衡操作,删除节点操作),后期会继续补充。
如果你觉得本篇文章对你有用的话,请顺手点一下推荐,让更多的人看到,感谢!
参考文章:http://tech.meituan.com/java-hashmap.html
JDK1.8源码阅读系列之四:HashMap (原创)的更多相关文章
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之三:Vector
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 Vector 源码期间的对于 Vector 的一些实现上的个人理解,用于个人备忘,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 Vector 的继承图: 可以看出,Vector 的直 ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之一:ArrayList
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 ArrayList 源码期间的对于 ArrayList 的一些实现上的个人理解,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 ArrayList 的继承图: 由图可以看出,Array ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之二:LinkedList
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 LinkedList 源码期间的对于 LinkedList 的一些实现上的个人理解,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 LinkedList 的继承图: 由于 Abstra ...
- 【JDK1.8】 Java小白的源码学习系列:HashMap
目录 Java小白的源码学习系列:HashMap 官方文档解读 基本数据结构 基本源码解读 基本成员变量 构造器 巧妙的tableSizeFor put方法 巧妙的hash方法 JDK1.8的putV ...
- 源码阅读系列:EventBus
title: 源码阅读系列:EventBus date: 2016-12-22 16:16:47 tags: 源码阅读 --- EventBus 是人们在日常开发中经常会用到的开源库,即使是不直接用的 ...
- 【Dubbo源码阅读系列】之远程服务调用(上)
今天打算来讲一讲 Dubbo 服务远程调用.笔者在开始看 Dubbo 远程服务相关源码的时候,看的有点迷糊.后来慢慢明白 Dubbo 远程服务的调用的本质就是动态代理模式的一种实现.本地消费者无须知道 ...
- 【Dubbo源码阅读系列】服务暴露之本地暴露
在上一篇文章中我们介绍 Dubbo 自定义标签解析相关内容,其中我们自定义的 XML 标签 <dubbo:service /> 会被解析为 ServiceBean 对象(传送门:Dubbo ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读笔记(1)Object类
JDK1.8源码阅读笔记(1)Object类 Object 类属于 java.lang 包,此包下的所有类在使⽤时⽆需⼿动导⼊,系统会在程序编译期间⾃动 导⼊.Object 类是所有类的基类,当⼀ ...
- Spring源码阅读系列总结
最近一段时间,粗略的查看了一下Spring源码,对Spring的两大核心和Spring的组件有了更深入的了解.同时在学习Spring源码时,得了解一些设计模式,不然阅读源码还是有一定难度的,所以一些重 ...
随机推荐
- laravel项目安装debugbar
在github上有laravel项目的debugbar,可以查看项目的页面引用.变量.数据库使用.内存和反应时间等,貌似是一个还不错的小工具,效果如下: 安装地址:https://github.com ...
- 使用STM8SF103 ADC采样电压(转)
源:使用STM8SF103 ADC采样电压 硬件环境: STM8SF103 TSSOP20封装 因为项目需要用到AD采样电池电压,于是便开始了使用STM8S ADC进行采样,也就有了下文. 手册上对S ...
- 【转】人工智能(AI)资料大全
这里收集的是关于人工智能(AI)的教程.书籍.视频演讲和论文. 欢迎提供更多的信息. 在线教程 麻省理工学院人工智能视频教程 – 麻省理工人工智能课程 人工智能入门 – 人工智能基础学习.Peter ...
- Android自定义控件(状态提示图表) (转)
源:Android自定义控件(状态提示图表) 源:Android应用开发 [工匠若水 http://blog.csdn.net/yanbober 转载烦请注明出处,尊重分享成果] 1 背景 前面分析 ...
- iOS调试-LLDB学习总结
from:http://www.jianshu.com/p/d6a0a5e39b0e LLDB阐述 LLDB 是一个有着 REPL 的特性和 C++ ,Python 插件的开源调试器.LLDB 绑定在 ...
- module_param()函数
1.定义模块参数的方法: module_param(name, type, perm); 其中,name:表示参数的名字; type:表示参数的类型; perm:表示参数的访问权限; ...
- FlexGrid简单demo
1.首先加入以下代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <hea ...
- UVa 10057 - A mid-summer night's dream
题目大意:给n个数,找一个数A使得A与这n个数的差的绝对值最小.输出A最小的可能值,n个数中满足A的性质的数的个数以及满足A性质的不同的数的个数(不必从这n个数中挑选). 看见绝对值就想到了数轴上点之 ...
- MVC 视图-模型,动态更新
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Binding</title> <script src=&q ...
- iOS 之 #import与#include的区别及@class
#import 相比#include不会引起交叉编译. @class一般用于头文件中需要声明该类的变量时用到
