Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6689748
前文简要介绍了Android应用程序的Activity的启动过程。在Android系统中,应用程序是由Activity组成的,因此,应用程 序的启动过程实际上就是应用程序中的默认Activity的启动过程,本文将详细分析应用程序框架层的源代码,了解Android应用程序的启动过程。
在上一篇文章Android应用程序的Activity启动过程简要介绍和学习计划中, 我们举例子说明了启动Android应用程序中的Activity的两种情景,其中,在手机屏幕中点击应用程序图标的情景就会引发Android应用程序 中的默认Activity的启动,从而把应用程序启动起来。这种启动方式的特点是会启动一个新的进程来加载相应的Activity。这里,我们继续以这个 例子为例来说明Android应用程序的启动过程,即MainActivity的启动过程。
MainActivity的启动过程如下图所示:
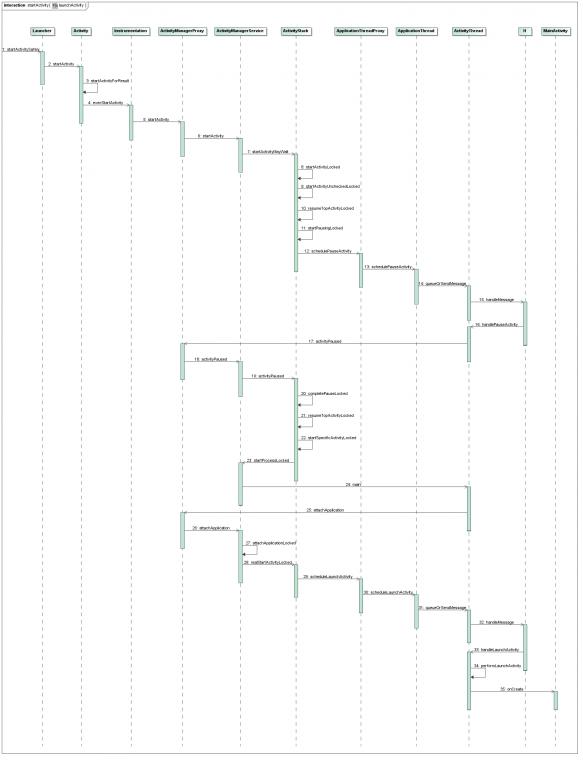
下面详细分析每一步是如何实现的。
Step 1. Launcher.startActivitySafely
在Android系统中,应用程序是由Launcher启动起来的,其实,Launcher本身也是一个应用程序,其它的应用程序安装后,就会Launcher的界面上出现一个相应的图标,点击这个图标时,Launcher就会对应的应用程序启动起来。
Launcher的源代码工程在packages/apps/Launcher2目录下,负责启动其它应用程序的源代码实现在src/com/android/launcher2/Launcher.java文件中:
- /**
- * Default launcher application.
- */
- public final class Launcher extends Activity
- implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks, AllAppsView.Watcher {
- ......
- /**
- * Launches the intent referred by the clicked shortcut.
- *
- * @param v The view representing the clicked shortcut.
- */
- public void onClick(View v) {
- Object tag = v.getTag();
- if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
- // Open shortcut
- final Intent intent = ((ShortcutInfo) tag).intent;
- int[] pos = new int[2];
- v.getLocationOnScreen(pos);
- intent.setSourceBounds(new Rect(pos[0], pos[1],
- pos[0] + v.getWidth(), pos[1] + v.getHeight()));
- startActivitySafely(intent, tag);
- } else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
- ......
- } else if (v == mHandleView) {
- ......
- }
- }
- void startActivitySafely(Intent intent, Object tag) {
- intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- try {
- startActivity(intent);
- } catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
- ......
- } catch (SecurityException e) {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- }
回忆一下前面一篇文章Android应用程序的Activity启动过程简要介绍和学习计划说到的应用程序Activity,它的默认Activity是MainActivity,这里是AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置的:
- <activity android:name=".MainActivity"
- android:label="@string/app_name">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
因此,这里的intent包含的信息为:action = "android.intent.action.Main",category="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER", cmp="shy.luo.activity/.MainActivity",表示它要启动的Activity为 shy.luo.activity.MainActivity。Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK表示要在一个新的Task中 启动这个Activity,注意,Task是Android系统中的概念,它不同于进程Process的概念。简单地说,一个Task是一系列 Activity的集合,这个集合是以堆栈的形式来组织的,遵循后进先出的原则。事实上,Task是一个非常复杂的概念,有兴趣的读者可以到官网http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/activity-element.html查看相关的资料。这里,我们只要知道,这个MainActivity要在一个新的Task中启动就可以了。
Step 2. Activity.startActivity
在Step 1中,我们看到,Launcher继承于Activity类,而Activity类实现了startActivity函数,因此,这里就调用了 Activity.startActivity函数,它实现在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app /Activity.java文件中:
- public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
- implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
- Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
- OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
- ......
- @Override
- public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
- startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
- }
- ......
- }
这个函数实现很简单,它调用startActivityForResult来进一步处理,第二个参数传入-1表示不需要这个Actvity结束后的返回结果。
Step 3. Activity.startActivityForResult
这个函数也是实现在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java文件中:
- public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper
- implements LayoutInflater.Factory,
- Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
- OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks {
- ......
- public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) {
- if (mParent == null) {
- Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
- mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
- this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
- intent, requestCode);
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这里的mInstrumentation是Activity类的成员变量,它的类型是Intrumentation,定义在 frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java文件中,它用来监控应用程序和 系统的交互。
这里的mMainThread也是Activity类的成员变量,它的类型是ActivityThread,它代表的是应用程序的主线程,我们在Android系统在新进程中启动自定义服务过程(startService)的原理分析一 文中已经介绍过了。这里通过mMainThread.getApplicationThread获得它里面的ApplicationThread成员变 量,它是一个Binder对象,后面我们会看到,ActivityManagerService会使用它来和ActivityThread来进行进程间通 信。这里我们需注意的是,这里的mMainThread代表的是Launcher应用程序运行的进程。
这里的mToken也是Activity类的成员变量,它是一个Binder对象的远程接口。
Step 4. Instrumentation.execStartActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java文件中:
- public class Instrumentation {
- ......
- public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
- Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
- Intent intent, int requestCode) {
- IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
- if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
- ......
- }
- try {
- int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
- .startActivity(whoThread, intent,
- intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
- null, 0, token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
- requestCode, false, false);
- ......
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
- return null;
- }
- ......
- }
这里的ActivityManagerNative.getDefault返回ActivityManagerService的远程接口,即ActivityManagerProxy接口,具体可以参考Android系统在新进程中启动自定义服务过程(startService)的原理分析一文。
这里的intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded返回这个intent的MIME类型,在这个例子中,没有AndroidManifest.xml设置MainActivity的MIME类型,因此,这里返回null。
这里的target不为null,但是target.mEmbddedID为null,我们不用关注。
Step 5. ActivityManagerProxy.startActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java文件中:
- class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
- {
- ......
- public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent,
- String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode,
- IBinder resultTo, String resultWho,
- int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
- boolean debug) throws RemoteException {
- Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
- data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
- intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
- data.writeString(resolvedType);
- data.writeTypedArray(grantedUriPermissions, 0);
- data.writeInt(grantedMode);
- data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
- data.writeString(resultWho);
- data.writeInt(requestCode);
- data.writeInt(onlyIfNeeded ? 1 : 0);
- data.writeInt(debug ? 1 : 0);
- mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
- reply.readException();
- int result = reply.readInt();
- reply.recycle();
- data.recycle();
- return result;
- }
- ......
- }
这里的参数比较多,我们先整理一下。从上面的调用可以知道,这里的参数resolvedType、grantedUriPermissions和
resultWho均为null;参数caller为ApplicationThread类型的Binder实体;参数resultTo为一个
Binder实体的远程接口,我们先不关注它;参数grantedMode为0,我们也先不关注它;参数requestCode为-1;参数
onlyIfNeeded和debug均空false。
Step 6. ActivityManagerService.startActivity
上一步Step
5通过Binder驱动程序就进入到ActivityManagerService的startActivity函数来了,它定义在
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am
/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller,
- Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
- int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo,
- String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
- boolean debug) {
- return mMainStack.startActivityMayWait(caller, intent, resolvedType,
- grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, resultTo, resultWho,
- requestCode, onlyIfNeeded, debug, null, null);
- }
- ......
- }
这里只是简单地将操作转发给成员变量mMainStack的startActivityMayWait函数,这里的mMainStack的类型为ActivityStack。
Step 7. ActivityStack.startActivityMayWait
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller,
- Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
- int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo,
- String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
- boolean debug, WaitResult outResult, Configuration config) {
- ......
- boolean componentSpecified = intent.getComponent() != null;
- // Don't modify the client's object!
- intent = new Intent(intent);
- // Collect information about the target of the Intent.
- ActivityInfo aInfo;
- try {
- ResolveInfo rInfo =
- AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
- intent, resolvedType,
- PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY
- | ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- ......
- }
- if (aInfo != null) {
- // Store the found target back into the intent, because now that
- // we have it we never want to do this again. For example, if the
- // user navigates back to this point in the history, we should
- // always restart the exact same activity.
- intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
- aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
- ......
- }
- synchronized (mService) {
- int callingPid;
- int callingUid;
- if (caller == null) {
- ......
- } else {
- callingPid = callingUid = -1;
- }
- mConfigWillChange = config != null
- && mService.mConfiguration.diff(config) != 0;
- ......
- if (mMainStack && aInfo != null &&
- (aInfo.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE) != 0) {
- ......
- }
- int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType,
- grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, aInfo,
- resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid, callingUid,
- onlyIfNeeded, componentSpecified);
- if (mConfigWillChange && mMainStack) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- if (outResult != null) {
- ......
- }
- return res;
- }
- }
- ......
- }
注意,从Step
6传下来的参数outResult和config均为null,此外,表达式
(aInfo.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE)
!= 0为false,因此,这里忽略了无关代码。
下面语句对参数intent的内容进行解析,得到MainActivity的相关信息,保存在aInfo变量中:
- ActivityInfo aInfo;
- try {
- ResolveInfo rInfo =
- AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
- intent, resolvedType,
- PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY
- | ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- ......
- }
解析之后,得到的aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName的值
为"shy.luo.activity",aInfo.name的值为"shy.luo.activity.MainActivity",这是在这个实例
的配置文件AndroidManifest.xml里面配置的。
此外,函数开始的地方调用intent.getComponent()函数的返回值不为null,因此,这里的componentSpecified变量为true。
接下去就调用startActivityLocked进一步处理了。
Step 8. ActivityStack.startActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
- Intent intent, String resolvedType,
- Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
- int grantedMode, ActivityInfo aInfo, IBinder resultTo,
- String resultWho, int requestCode,
- int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean onlyIfNeeded,
- boolean componentSpecified) {
- int err = START_SUCCESS;
- ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
- if (caller != null) {
- callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
- if (callerApp != null) {
- callingPid = callerApp.pid;
- callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
- ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
- if (resultTo != null) {
- int index = indexOfTokenLocked(resultTo);
- ......
- if (index >= 0) {
- sourceRecord = (ActivityRecord)mHistory.get(index);
- if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {
- ......
- }
- }
- }
- int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
- if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0
- && sourceRecord != null) {
- ......
- }
- if (err == START_SUCCESS && intent.getComponent() == null) {
- ......
- }
- if (err == START_SUCCESS && aInfo == null) {
- ......
- }
- if (err != START_SUCCESS) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid,
- intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration,
- resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);
- ......
- return startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord,
- grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, onlyIfNeeded, true);
- }
- ......
- }
从传进来的参数caller得到调用者的进程信息,并保存在callerApp变量中,这里就是Launcher应用程序的进程信息了。
前面说过,参数resultTo是Launcher这个Activity里面的一个Binder对象,通过它可以获得Launcher这个Activity的相关信息,保存在sourceRecord变量中。
再接下来,创建即将要启动的Activity的相关信息,并保存在r变量中:
- ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid,
- intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration,
- resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);
接着调用startActivityUncheckedLocked函数进行下一步操作。
Step 9. ActivityStack.startActivityUncheckedLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final int startActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord r,
- ActivityRecord sourceRecord, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
- int grantedMode, boolean onlyIfNeeded, boolean doResume) {
- final Intent intent = r.intent;
- final int callingUid = r.launchedFromUid;
- int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
- // We'll invoke onUserLeaving before onPause only if the launching
- // activity did not explicitly state that this is an automated launch.
- mUserLeaving = (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION) == 0;
- ......
- ActivityRecord notTop = (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_PREVIOUS_IS_TOP)
- != 0 ? r : null;
- // If the onlyIfNeeded flag is set, then we can do this if the activity
- // being launched is the same as the one making the call... or, as
- // a special case, if we do not know the caller then we count the
- // current top activity as the caller.
- if (onlyIfNeeded) {
- ......
- }
- if (sourceRecord == null) {
- ......
- } else if (sourceRecord.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
- ......
- } else if (r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE
- || r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK) {
- ......
- }
- if (r.resultTo != null && (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
- ......
- }
- boolean addingToTask = false;
- if (((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0 &&
- (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK) == 0)
- || r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK
- || r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
- // If bring to front is requested, and no result is requested, and
- // we can find a task that was started with this same
- // component, then instead of launching bring that one to the front.
- if (r.resultTo == null) {
- // See if there is a task to bring to the front. If this is
- // a SINGLE_INSTANCE activity, there can be one and only one
- // instance of it in the history, and it is always in its own
- // unique task, so we do a special search.
- ActivityRecord taskTop = r.launchMode != ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE
- ? findTaskLocked(intent, r.info)
- : findActivityLocked(intent, r.info);
- if (taskTop != null) {
- ......
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- if (r.packageName != null) {
- // If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently
- // at the top, then we need to check if it should only be launched
- // once.
- ActivityRecord top = topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(notTop);
- if (top != null && r.resultTo == null) {
- if (top.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity)) {
- ......
- }
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- boolean newTask = false;
- // Should this be considered a new task?
- if (r.resultTo == null && !addingToTask
- && (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
- // todo: should do better management of integers.
- mService.mCurTask++;
- if (mService.mCurTask <= 0) {
- mService.mCurTask = 1;
- }
- r.task = new TaskRecord(mService.mCurTask, r.info, intent,
- (r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_CLEAR_TASK_ON_LAUNCH) != 0);
- ......
- newTask = true;
- if (mMainStack) {
- mService.addRecentTaskLocked(r.task);
- }
- } else if (sourceRecord != null) {
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- }
- ......
- startActivityLocked(r, newTask, doResume);
- return START_SUCCESS;
- }
- ......
- }
函数首先获得intent的标志值,保存在launchFlags变量中。
这个intent的标志值的位Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION没有置位,因此 ,成员变量mUserLeaving的值为true。
这个intent的标志值的位Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_PREVIOUS_IS_TOP也没有置位,因此,变量notTop的值为null。
由于在这个例子的AndroidManifest.xml文件中,MainActivity没有配置launchMode属值,因此,这里的
r.launchMode为默认值0,表示以标准(Standard,或者称为ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE)的方式来启动
这个Activity。Activity的启动方式有四种,其余三种分别是ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE、
ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK和ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP,具体可以参考官方网
站http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/pm/ActivityInfo.html。
传进来的参数r.resultTo为null,表示Launcher不需要等这个即将要启动的MainActivity的执行结果。
由于这个intent的标志值的位Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK被置位,而且Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK没有置位,因此,下面的if语句会被执行:
- if (((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0 &&
- (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK) == 0)
- || r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK
- || r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
- // If bring to front is requested, and no result is requested, and
- // we can find a task that was started with this same
- // component, then instead of launching bring that one to the front.
- if (r.resultTo == null) {
- // See if there is a task to bring to the front. If this is
- // a SINGLE_INSTANCE activity, there can be one and only one
- // instance of it in the history, and it is always in its own
- // unique task, so we do a special search.
- ActivityRecord taskTop = r.launchMode != ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE
- ? findTaskLocked(intent, r.info)
- : findActivityLocked(intent, r.info);
- if (taskTop != null) {
- ......
- }
- }
- }
这段代码的逻辑是查看一下,当前有没有Task可以用来执行这个Activity。由于r.launchMode的值不为
ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE,因此,它通过findTaskLocked函数来查找存不存这样的Task,
这里返回的结果是null,即taskTop为null,因此,需要创建一个新的Task来启动这个Activity。
接着往下看:
- if (r.packageName != null) {
- // If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently
- // at the top, then we need to check if it should only be launched
- // once.
- ActivityRecord top = topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(notTop);
- if (top != null && r.resultTo == null) {
- if (top.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity)) {
- ......
- }
- }
- }
这段代码的逻辑是看一下,当前在堆栈顶端的Activity是否就是即将要启动的Activity,有些情况下,如果即将要启动的Activity就在堆栈的顶端,那么,就不会重新启动这个Activity的别一个实例了,具体可以参考官方网站http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/pm/ActivityInfo.html。现在处理堆栈顶端的Activity是Launcher,与我们即将要启动的MainActivity不是同一个Activity,因此,这里不用进一步处理上述介绍的情况。
执行到这里,我们知道,要在一个新的Task里面来启动这个Activity了,于是新创建一个Task:
- if (r.resultTo == null && !addingToTask
- && (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
- // todo: should do better management of integers.
- mService.mCurTask++;
- if (mService.mCurTask <= 0) {
- mService.mCurTask = 1;
- }
- r.task = new TaskRecord(mService.mCurTask, r.info, intent,
- (r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_CLEAR_TASK_ON_LAUNCH) != 0);
- ......
- newTask = true;
- if (mMainStack) {
- mService.addRecentTaskLocked(r.task);
- }
- }
新建的Task保存在r.task域中,同时,添加到mService中去,这里的mService就是ActivityManagerService了。
最后就进入startActivityLocked(r, newTask,
doResume)进一步处理了。这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server
/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- private final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask,
- boolean doResume) {
- final int NH = mHistory.size();
- int addPos = -1;
- if (!newTask) {
- ......
- }
- // Place a new activity at top of stack, so it is next to interact
- // with the user.
- if (addPos < 0) {
- addPos = NH;
- }
- // If we are not placing the new activity frontmost, we do not want
- // to deliver the onUserLeaving callback to the actual frontmost
- // activity
- if (addPos < NH) {
- ......
- }
- // Slot the activity into the history stack and proceed
- mHistory.add(addPos, r);
- r.inHistory = true;
- r.frontOfTask = newTask;
- r.task.numActivities++;
- if (NH > 0) {
- // We want to show the starting preview window if we are
- // switching to a new task, or the next activity's process is
- // not currently running.
- ......
- } else {
- // If this is the first activity, don't do any fancy animations,
- // because there is nothing for it to animate on top of.
- ......
- }
- ......
- if (doResume) {
- resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里的NH表示当前系统中历史任务的个数,这里肯定是大于0,因为Launcher已经跑起来了。当NH>0时,并且现在要切换新任务时,要做一
些任务切的界面操作,这段代码我们就不看了,这里不会影响到下面启Activity的过程,有兴趣的读取可以自己研究一下。
这里传进来的参数doResume为true,于是调用resumeTopActivityLocked进一步操作。
Step 10. Activity.resumeTopActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- /**
- * Ensure that the top activity in the stack is resumed.
- *
- * @param prev The previously resumed activity, for when in the process
- * of pausing; can be null to call from elsewhere.
- *
- * @return Returns true if something is being resumed, or false if
- * nothing happened.
- */
- final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
- // Find the first activity that is not finishing.
- ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- // Remember how we'll process this pause/resume situation, and ensure
- // that the state is reset however we wind up proceeding.
- final boolean userLeaving = mUserLeaving;
- mUserLeaving = false;
- if (next == null) {
- ......
- }
- next.delayedResume = false;
- // If the top activity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
- if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED) {
- ......
- }
- // If we are sleeping, and there is no resumed activity, and the top
- // activity is paused, well that is the state we want.
- if ((mService.mSleeping || mService.mShuttingDown)
- && mLastPausedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.PAUSED) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- // If we are currently pausing an activity, then don't do anything
- // until that is done.
- if (mPausingActivity != null) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- // We need to start pausing the current activity so the top one
- // can be resumed...
- if (mResumedActivity != null) {
- ......
- startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false);
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
函数先通过调用topRunningActivityLocked函数获得堆栈顶端的Activity,这里就是MainActivity了,这是在上面的Step 9设置好的,保存在next变量中。
接下来把mUserLeaving的保存在本地变量userLeaving中,然后重新设置为false,在上面的Step 9中,mUserLeaving的值为true,因此,这里的userLeaving为true。
这里的mResumedActivity为Launcher,因为Launcher是当前正被执行的Activity。
当我们处理休眠状态时,mLastPausedActivity保存堆栈顶端的Activity,因为当前不是休眠状态,所以mLastPausedActivity为null。
有了这些信息之后,下面的语句就容易理解了:
- // If the top activity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
- if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED) {
- ......
- }
- // If we are sleeping, and there is no resumed activity, and the top
- // activity is paused, well that is the state we want.
- if ((mService.mSleeping || mService.mShuttingDown)
- && mLastPausedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.PAUSED) {
- ......
- }
它首先看要启动的Activity是否就是当前处理Resumed状态的Activity,如果是的话,那就什么都不用做,直接返回就可以了;否则再看
一下系统当前是否休眠状态,如果是的话,再看看要启动的Activity是否就是当前处于堆栈顶端的Activity,如果是的话,也是什么都不用做。
上面两个条件都不满足,因此,在继续往下执行之前,首先要把当处于Resumed状态的Activity推入Paused状态,然后才可以启动新的
Activity。但是在将当前这个Resumed状态的Activity推入Paused状态之前,首先要看一下当前是否有Activity正在进入
Pausing状态,如果有的话,当前这个Resumed状态的Activity就要稍后才能进入Paused状态了,这样就保证了所有需要进入
Paused状态的Activity串行处理。
这里没有处于Pausing状态的Activity,即mPausingActivity为null,而且mResumedActivity也不为
null,于是就调用startPausingLocked函数把Launcher推入Paused状态去了。
Step 11. ActivityStack.startPausingLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- private final void startPausingLocked(boolean userLeaving, boolean uiSleeping) {
- if (mPausingActivity != null) {
- ......
- }
- ActivityRecord prev = mResumedActivity;
- if (prev == null) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- mResumedActivity = null;
- mPausingActivity = prev;
- mLastPausedActivity = prev;
- prev.state = ActivityState.PAUSING;
- ......
- if (prev.app != null && prev.app.thread != null) {
- ......
- try {
- ......
- prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev, prev.finishing, userLeaving,
- prev.configChangeFlags);
- ......
- } catch (Exception e) {
- ......
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
函数首先把mResumedActivity保存在本地变量prev中。在上一步Step
10中,说到mResumedActivity就是Launcher,因此,这里把Launcher进程中的ApplicationThread对象取出
来,通过它来通知Launcher这个Activity它要进入Paused状态了。当然,这里的prev.app.thread是一个
ApplicationThread对象的远程接口,通过调用这个远程接口的schedulePauseActivity来通知Launcher进入
Paused状态。
参数prev.finishing表示prev所代表的Activity是否正在等待结束的Activity列表中,由于Laucher这个
Activity还没结束,所以这里为false;参数prev.configChangeFlags表示哪些config发生了变化,这里我们不关心它
的值。
Step 12. ApplicationThreadProxy.schedulePauseActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ApplicationThreadNative.java文件中:
- class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread {
- ......
- public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
- boolean userLeaving, int configChanges) throws RemoteException {
- Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
- data.writeStrongBinder(token);
- data.writeInt(finished ? 1 : 0);
- data.writeInt(userLeaving ? 1 :0);
- data.writeInt(configChanges);
- mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_PAUSE_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null,
- IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
- data.recycle();
- }
- ......
- }
这个函数通过Binder进程间通信机制进入到ApplicationThread.schedulePauseActivity函数中。
Step 13. ApplicationThread.schedulePauseActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中,它是ActivityThread的内部类:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
- ......
- public final void schedulePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
- boolean userLeaving, int configChanges) {
- queueOrSendMessage(
- finished ? H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING : H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
- token,
- (userLeaving ? 1 : 0),
- configChanges);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这里调用的函数queueOrSendMessage是ActivityThread类的成员函数。
上面说到,这里的finished值为false,因此,queueOrSendMessage的第一个参数值为H.PAUSE_ACTIVITY,表示要暂停token所代表的Activity,即Launcher。
Step 14. ActivityThread.queueOrSendMessage
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1) {
- queueOrSendMessage(what, obj, arg1, 0);
- }
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2) {
- synchronized (this) {
- ......
- Message msg = Message.obtain();
- msg.what = what;
- msg.obj = obj;
- msg.arg1 = arg1;
- msg.arg2 = arg2;
- mH.sendMessage(msg);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里首先将相关信息组装成一个msg,然后通过mH成员变量发送出去,mH的类型是H,继承于Handler类,是ActivityThread的内部类,因此,这个消息最后由H.handleMessage来处理。
Step 15. H.handleMessage
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class H extends Handler {
- ......
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- ......
- switch (msg.what) {
- ......
- case PAUSE_ACTIVITY:
- handlePauseActivity((IBinder)msg.obj, false, msg.arg1 != 0, msg.arg2);
- maybeSnapshot();
- break;
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这里调用ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity进一步操作,msg.obj是一个ActivityRecord对象的引用,它代表的是Launcher这个Activity。
Step 16. ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
- boolean userLeaving, int configChanges) {
- ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
- if (r != null) {
- //Slog.v(TAG, "userLeaving=" + userLeaving + " handling pause of " + r);
- if (userLeaving) {
- performUserLeavingActivity(r);
- }
- r.activity.mConfigChangeFlags |= configChanges;
- Bundle state = performPauseActivity(token, finished, true);
- // Make sure any pending writes are now committed.
- QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
- // Tell the activity manager we have paused.
- try {
- ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token, state);
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
函数首先将Binder引用token转换成ActivityRecord的远程接口ActivityClientRecord,然后做了三个事情:1.
如果userLeaving为true,则通过调用performUserLeavingActivity函数来调用
Activity.onUserLeaveHint通知Activity,用户要离开它了;2.
调用performPauseActivity函数来调用Activity.onPause函数,我们知道,在Activity的生命周期中,当它要让位
于其它的Activity时,系统就会调用它的onPause函数;3.
它通知ActivityManagerService,这个Activity已经进入Paused状态了,ActivityManagerService
现在可以完成未竟的事情,即启动MainActivity了。
Step 17. ActivityManagerProxy.activityPaused
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java文件中:
- class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
- {
- ......
- public void activityPaused(IBinder token, Bundle state) throws RemoteException
- {
- Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
- data.writeStrongBinder(token);
- data.writeBundle(state);
- mRemote.transact(ACTIVITY_PAUSED_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
- reply.readException();
- data.recycle();
- reply.recycle();
- }
- ......
- }
这里通过Binder进程间通信机制就进入到ActivityManagerService.activityPaused函数中去了。
Step 18. ActivityManagerService.activityPaused
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public final void activityPaused(IBinder token, Bundle icicle) {
- ......
- final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
- mMainStack.activityPaused(token, icicle, false);
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这里,又再次进入到ActivityStack类中,执行activityPaused函数。
Step 19. ActivityStack.activityPaused
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final void activityPaused(IBinder token, Bundle icicle, boolean timeout) {
- ......
- ActivityRecord r = null;
- synchronized (mService) {
- int index = indexOfTokenLocked(token);
- if (index >= 0) {
- r = (ActivityRecord)mHistory.get(index);
- if (!timeout) {
- r.icicle = icicle;
- r.haveState = true;
- }
- mHandler.removeMessages(PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
- if (mPausingActivity == r) {
- r.state = ActivityState.PAUSED;
- completePauseLocked();
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里通过参数token在mHistory列表中得到ActivityRecord,从上面我们知道,这个ActivityRecord代表的是
Launcher这个Activity,而我们在Step
11中,把Launcher这个Activity的信息保存在mPausingActivity中,因此,这里mPausingActivity等于r,
于是,执行completePauseLocked操作。
Step 20. ActivityStack.completePauseLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- private final void completePauseLocked() {
- ActivityRecord prev = mPausingActivity;
- ......
- if (prev != null) {
- ......
- mPausingActivity = null;
- }
- if (!mService.mSleeping && !mService.mShuttingDown) {
- resumeTopActivityLocked(prev);
- } else {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
函数首先把mPausingActivity变量清空,因为现在不需要它了,然后调用resumeTopActivityLokced进一步操作,它传入的参数即为代表Launcher这个Activity的ActivityRecord。
Step 21. ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLokced
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
- ......
- // Find the first activity that is not finishing.
- ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- // Remember how we'll process this pause/resume situation, and ensure
- // that the state is reset however we wind up proceeding.
- final boolean userLeaving = mUserLeaving;
- mUserLeaving = false;
- ......
- next.delayedResume = false;
- // If the top activity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
- if (mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED) {
- ......
- return false;
- }
- // If we are sleeping, and there is no resumed activity, and the top
- // activity is paused, well that is the state we want.
- if ((mService.mSleeping || mService.mShuttingDown)
- && mLastPausedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.PAUSED) {
- ......
- return false;
- }
- .......
- // We need to start pausing the current activity so the top one
- // can be resumed...
- if (mResumedActivity != null) {
- ......
- return true;
- }
- ......
- if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
- }
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
通过上面的Step
9,我们知道,当前在堆栈顶端的Activity为我们即将要启动的MainActivity,这里通过调用
topRunningActivityLocked将它取回来,保存在next变量中。之前最后一个Resumed状态的Activity,即
Launcher,到了这里已经处于Paused状态了,因此,mResumedActivity为null。最后一个处于Paused状态的
Activity为Launcher,因此,这里的mLastPausedActivity就为Launcher。前面我们为MainActivity创
建了ActivityRecord后,它的app域一直保持为null。有了这些信息后,上面这段代码就容易理解了,它最终调用
startSpecificActivityLocked进行下一步操作。
Step 22. ActivityStack.startSpecificActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- private final void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
- boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
- // Is this activity's application already running?
- ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
- r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
- ......
- if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
- try {
- realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
- return;
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- ......
- }
- }
- mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
- "activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false);
- }
- ......
- }
注意,这里由于是第一次启动应用程序的Activity,所以下面语句:
- ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
- r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
取回来的app为null。在Activity应用程序中的AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中,我们没有指定Application标
签的process属性,系统就会默认使用package的名称,这里就是"shy.luo.activity"了。每一个应用程序都有自己的uid,因
此,这里uid +
process的组合就可以为每一个应用程序创建一个ProcessRecord。当然,我们可以配置两个应用程序具有相同的uid和package,或
者在AndroidManifest.xml配置文件的application标签或者activity标签中显式指定相同的process属性值,这
样,不同的应用程序也可以在同一个进程中启动。
函数最终执行ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked函数进行下一步操作。
Step 23. ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
- ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
- String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting) {
- ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid);
- ......
- String hostingNameStr = hostingName != null
- ? hostingName.flattenToShortString() : null;
- ......
- if (app == null) {
- app = new ProcessRecordLocked(null, info, processName);
- mProcessNames.put(processName, info.uid, app);
- } else {
- // If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
- app.addPackage(info.packageName);
- }
- ......
- startProcessLocked(app, hostingType, hostingNameStr);
- return (app.pid != 0) ? app : null;
- }
- ......
- }
这里再次检查是否已经有以process +
uid命名的进程存在,在我们这个情景中,返回值app为null,因此,后面会创建一个ProcessRecord,并存保存在成员变量
mProcessNames中,最后,调用另一个startProcessLocked函数进一步操作:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app,
- String hostingType, String hostingNameStr) {
- ......
- try {
- int uid = app.info.uid;
- int[] gids = null;
- try {
- gids = mContext.getPackageManager().getPackageGids(
- app.info.packageName);
- } catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- int debugFlags = 0;
- ......
- int pid = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
- mSimpleProcessManagement ? app.processName : null, uid, uid,
- gids, debugFlags, null);
- ......
- } catch (RuntimeException e) {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里主要是调用Process.start接口来创建一个新的进程,新的进程会导入android.app.ActivityThread类,并且执行
它的main函数,这就是为什么我们前面说每一个应用程序都有一个ActivityThread实例来对应的原因。
Step 24. ActivityThread.main
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final void attach(boolean system) {
- ......
- mSystemThread = system;
- if (!system) {
- ......
- IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
- try {
- mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- public static final void main(String[] args) {
- .......
- ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
- thread.attach(false);
- ......
- Looper.loop();
- .......
- thread.detach();
- ......
- }
- }
这个函数在进程中创建一个ActivityThread实例,然后调用它的attach函数,接着就进入消息循环了,直到最后进程退出。
函数attach最终调用了ActivityManagerService的远程接口ActivityManagerProxy的
attachApplication函数,传入的参数是mAppThread,这是一个ApplicationThread类型的Binder对象,它的
作用是用来进行进程间通信的。
Step 25. ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java文件中:
- class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
- {
- ......
- public void attachApplication(IApplicationThread app) throws RemoteException
- {
- Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
- data.writeStrongBinder(app.asBinder());
- mRemote.transact(ATTACH_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
- reply.readException();
- data.recycle();
- reply.recycle();
- }
- ......
- }
这里通过Binder驱动程序,最后进入ActivityManagerService的attachApplication函数中。
Step 26. ActivityManagerService.attachApplication
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
- synchronized (this) {
- int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
- final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
- attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
- Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里将操作转发给attachApplicationLocked函数。
Step 27. ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
- implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
- ......
- private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
- int pid) {
- // Find the application record that is being attached... either via
- // the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the
- // next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads.
- ProcessRecord app;
- if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
- synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
- app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
- }
- } else if (mStartingProcesses.size() > 0) {
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- }
- if (app == null) {
- ......
- return false;
- }
- ......
- String processName = app.processName;
- try {
- thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(new AppDeathRecipient(
- app, pid, thread), 0);
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- ......
- return false;
- }
- ......
- app.thread = thread;
- app.curAdj = app.setAdj = -100;
- app.curSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT;
- app.setSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE;
- app.forcingToForeground = null;
- app.foregroundServices = false;
- app.debugging = false;
- ......
- boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);
- ......
- boolean badApp = false;
- boolean didSomething = false;
- // See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
- ActivityRecord hr = mMainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
- if (hr != null && normalMode) {
- if (hr.app == null && app.info.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
- && processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
- try {
- if (mMainStack.realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {
- didSomething = true;
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- ......
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
在前面的Step
23中,已经创建了一个ProcessRecord,这里首先通过pid将它取回来,放在app变量中,然后对app的其它成员进行初始化,最后调用
mMainStack.realStartActivityLocked执行真正的Activity启动操作。这里要启动的Activity通过调用
mMainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null)从堆栈顶端取回来,这时候在堆栈顶端的Activity就是
MainActivity了。
Step 28. ActivityStack.realStartActivityLocked
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java文件中:
- public class ActivityStack {
- ......
- final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
- ProcessRecord app, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig)
- throws RemoteException {
- ......
- r.app = app;
- ......
- int idx = app.activities.indexOf(r);
- if (idx < 0) {
- app.activities.add(r);
- }
- ......
- try {
- ......
- List<ResultInfo> results = null;
- List<Intent> newIntents = null;
- if (andResume) {
- results = r.results;
- newIntents = r.newIntents;
- }
- ......
- app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r,
- System.identityHashCode(r),
- r.info, r.icicle, results, newIntents, !andResume,
- mService.isNextTransitionForward());
- ......
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
这里最终通过app.thread进入到ApplicationThreadProxy的scheduleLaunchActivity函数中,注意,
这里的第二个参数r,是一个ActivityRecord类型的Binder对象,用来作来这个Activity的token值。
Step 29. ApplicationThreadProxy.scheduleLaunchActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ApplicationThreadNative.java文件中:
- class ApplicationThreadProxy implements IApplicationThread {
- ......
- public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
- ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
- List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward)
- throws RemoteException {
- Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
- intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
- data.writeStrongBinder(token);
- data.writeInt(ident);
- info.writeToParcel(data, 0);
- data.writeBundle(state);
- data.writeTypedList(pendingResults);
- data.writeTypedList(pendingNewIntents);
- data.writeInt(notResumed ? 1 : 0);
- data.writeInt(isForward ? 1 : 0);
- mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_LAUNCH_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, null,
- IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
- data.recycle();
- }
- ......
- }
这个函数最终通过Binder驱动程序进入到ApplicationThread的scheduleLaunchActivity函数中。
Step 30. ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
- ......
- // we use token to identify this activity without having to send the
- // activity itself back to the activity manager. (matters more with ipc)
- public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
- ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
- List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) {
- ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
- r.token = token;
- r.ident = ident;
- r.intent = intent;
- r.activityInfo = info;
- r.state = state;
- r.pendingResults = pendingResults;
- r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents;
- r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
- r.isForward = isForward;
- queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
函数首先创建一个ActivityClientRecord实例,并且初始化它的成员变量,然后调用ActivityThread类的queueOrSendMessage函数进一步处理。
Step 31. ActivityThread.queueOrSendMessage
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
- ......
- // if the thread hasn't started yet, we don't have the handler, so just
- // save the messages until we're ready.
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj) {
- queueOrSendMessage(what, obj, 0, 0);
- }
- ......
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2) {
- synchronized (this) {
- ......
- Message msg = Message.obtain();
- msg.what = what;
- msg.obj = obj;
- msg.arg1 = arg1;
- msg.arg2 = arg2;
- mH.sendMessage(msg);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
函数把消息内容放在msg中,然后通过mH把消息分发出去,这里的成员变量mH我们在前面已经见过,消息分发出去后,最后会调用H类的handleMessage函数。
Step 32. H.handleMessage
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class H extends Handler {
- ......
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- ......
- switch (msg.what) {
- case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
- ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
- r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
- r.activityInfo.applicationInfo);
- handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
- } break;
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这里最后调用ActivityThread类的handleLaunchActivity函数进一步处理。
Step 33. ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
- ......
- Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
- if (a != null) {
- r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
- Bundle oldState = r.state;
- handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward);
- ......
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这里首先调用performLaunchActivity函数来加载这个Activity类,即
shy.luo.activity.MainActivity,然后调用它的onCreate函数,最后回到handleLaunchActivity函
数时,再调用handleResumeActivity函数来使这个Activity进入Resumed状态,即会调用这个Activity的
onResume函数,这是遵循Activity的生命周期的。
Step 34. ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity
这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
- ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
- if (r.packageInfo == null) {
- r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo,
- Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
- }
- ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
- if (component == null) {
- component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
- mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
- r.intent.setComponent(component);
- }
- if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
- component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
- r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
- }
- Activity activity = null;
- try {
- java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
- activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
- cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
- r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
- if (r.state != null) {
- r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- ......
- }
- try {
- Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
- ......
- if (activity != null) {
- ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();
- appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this);
- appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
- CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
- Configuration config = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
- ......
- activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
- r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
- r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstance,
- r.lastNonConfigurationChildInstances, config);
- if (customIntent != null) {
- activity.mIntent = customIntent;
- }
- r.lastNonConfigurationInstance = null;
- r.lastNonConfigurationChildInstances = null;
- activity.mStartedActivity = false;
- int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
- if (theme != 0) {
- activity.setTheme(theme);
- }
- activity.mCalled = false;
- mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
- ......
- r.activity = activity;
- r.stopped = true;
- if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
- activity.performStart();
- r.stopped = false;
- }
- if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
- if (r.state != null) {
- mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
- }
- }
- if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
- activity.mCalled = false;
- mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
- if (!activity.mCalled) {
- throw new SuperNotCalledException(
- "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
- " did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
- }
- }
- }
- r.paused = true;
- mActivities.put(r.token, r);
- } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
- ......
- } catch (Exception e) {
- ......
- }
- return activity;
- }
- ......
- }
函数前面是收集要启动的Activity的相关信息,主要package和component信息:
- ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
- if (r.packageInfo == null) {
- r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo,
- Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
- }
- ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
- if (component == null) {
- component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
- mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
- r.intent.setComponent(component);
- }
- if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
- component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
- r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
- }
然后通过ClassLoader将shy.luo.activity.MainActivity类加载进来:
- Activity activity = null;
- try {
- java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
- activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
- cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
- r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
- if (r.state != null) {
- r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- ......
- }
接下来是创建Application对象,这是根据AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中的Application标签的信息来创建的:
- Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
后面的代码主要创建Activity的上下文信息,并通过attach方法将这些上下文信息设置到MainActivity中去:
- activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
- r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
- r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstance,
- r.lastNonConfigurationChildInstances, config);
最后还要调用MainActivity的onCreate函数:
- mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
这里不是直接调用MainActivity的onCreate函数,而是通过mInstrumentation的
callActivityOnCreate函数来间接调用,前面我们说过,mInstrumentation在这里的作用是监控Activity与系统的
交互操作,相当于是系统运行日志。
Step 35. MainActivity.onCreate
这个函数定义在packages/experimental/Activity/src/shy/luo/activity/MainActivity.java文件中,这是我们自定义的app工程文件:
- public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
- ......
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- ......
- Log.i(LOG_TAG, "Main Activity Created.");
- }
- ......
- }
这样,MainActivity就启动起来了,整个应用程序也启动起来了。
整个应用程序的启动过程要执行很多步骤,但是整体来看,主要分为以下五个阶段:
一. Step1 - Step 11:Launcher通过Binder进程间通信机制通知ActivityManagerService,它要启动一个Activity;
二. Step 12 - Step 16:ActivityManagerService通过Binder进程间通信机制通知Launcher进入Paused状态;
三. Step 17 - Step
24:Launcher通过Binder进程间通信机制通知ActivityManagerService,它已经准备就绪进入Paused状态,于是
ActivityManagerService就创建一个新的进程,用来启动一个ActivityThread实例,即将要启动的Activity就是在
这个ActivityThread实例中运行;
四. Step 25 - Step
27:ActivityThread通过Binder进程间通信机制将一个ApplicationThread类型的Binder对象传递给
ActivityManagerService,以便以后ActivityManagerService能够通过这个Binder对象和它进行通信;
五. Step 28 - Step 35:ActivityManagerService通过Binder进程间通信机制通知ActivityThread,现在一切准备就绪,它可以真正执行Activity的启动操作了。
这里不少地方涉及到了Binder进程间通信机制,相关资料请参考Android进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder简要介绍和学习计划一文。
这样,应用程序的启动过程就介绍完了,它实质上是启动应用程序的默认Activity,在下一篇文章中,我们将介绍在应用程序内部启动另一个
Activity的过程,即新的Activity与启动它的Activity将会在同一个进程(Process)和任务(Task)运行,敬请关注。
老罗的新浪微博:http://weibo.com/shengyangluo,欢迎关注!
Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析的更多相关文章
- Android 应用程序启动过程源代码分析
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6689748 前文简要介绍了Android应用程序的Activity的启动过程.在And ...
- Android应用程序安装过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6766010 Android系统在启动的过程中, ...
- Android系统默认Home应用程序(Launcher)的启动过程源代码分析
在前面一篇文章中,我们分析了Android系统在启动时安装应用程序的过程,这些应用程序安装好之后,还需要有一个 Home应用程序来负责把它们在桌面上展示出来,在Android系统中,这个默认的Home ...
- Android应用程序组件Content Provider的启动过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6963418 通过前面的学习,我们知道在Andr ...
- Activity启动过程源代码分析
事实上写分析源代码文章总会显得非常复杂非常乏味,可是梳理自己看源代码时的一些总结也是一种提高. 这篇博客分析下Activity启动过程源代码,我会尽量说得简单点. 个人的观点是看源代码不能看得太细,否 ...
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server启动过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6629298 在前面一篇文章浅谈Android系 ...
- Android应用程序启动过程(二)分析
本文依据Android6.0源码,从点击Launcher图标,直至解析到MainActivity#OnCreate()被调用. Launcher简析 Launcher也是个应用程序,不过是个特殊的应用 ...
- Android应用程序启动过程(一)总结
一.App启动方式 1,冷启动 冷启动:当启动应用时,后台没有该应用的进程,这时系统会重新创建一个新的进程分配给该应用. 冷启动的特点:因为系统会重新创建一个新的进程分配给它,所以会创建和初始化App ...
- Android应用程序启动过程
有没有想过,当我们点击桌面应用程序图标是怎样打开APP启动应用程序的呢? 当我们点击应用图标会调用Launcher的startActivitySafely()方法,方法实现如下,其实是调用的start ...
随机推荐
- C#递归算法详解
递归呢就是自己调用自己,在搜索文件夹下的文件和目录时也能用到,我这里就写一个简单的递归,代码如下: /// <summary> /// 递归算法 /// </summary> ...
- playbin2 成员
1. playbin2 struct _GstPlayBin { GstPipeline parent; GMutex *lock; GstSourceGroup groups[2]; G ...
- 普通用户之间的ssh无密码访问设置方法
两台CentOS6.2服务器,客户端是node1,服务器是node2,先都用root用户配置,方法如下: 第一步:在客户端Node1:生成密匙对,我用的是rsa的密钥.使用命令 "ssh-k ...
- android default_workspace.xml
//default_workspace.xml中,支持的标签有: favorite:应用程序快捷方式. shortcut:链接,如网址,本地磁盘路径等. search:搜索框. clock:桌面上的钟 ...
- 严重: Exception starting filter struts2 --Unable to load configuration
严重: Exception starting filter struts2 Unable to load configuration. - [unknown location] at com.open ...
- Http Clinet使用
Http Client是个apache下的一个开源包,用于使用http协议访问服务的java代码编写. Http Client的主要功能: (1)实现了所有 HTTP 的方法(GET,POST,PUT ...
- poj2378 树形DP
C - 树形dp Crawling in process... Crawling failed Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit ...
- win8 Pro 64位在 UEFI模式下Ghost系统 备份 恢复
一:在win8 安装U 盘中 1. 新建 “Ghost” 文件夹 2. 将下载的Ghost64.exe 文件拷贝到文件夹 二: 启动的时候 按下F12 选择 HDDUSB 1.Windows 安装 ...
- jsp 、js和css
css的一些样式 1.自动换行 .AutoNewline { Word-break: break-all;/*必须*/ width :50px;/*这里是设置多宽就进行换行 */ }
- Linux下装VirtualBox
一:下载 进入VirtualBox的下载地址:https://www.virtualbox.org/ 点击左侧的download, 选择适合自己系统的版本,我的是红帽,故选择: 进行下载. 二:安装 ...
