四元数与欧拉角(RPY角)的相互转换
- RPY角与Z-Y-X欧拉角
描述坐标系{B}相对于参考坐标系{A}的姿态有两种方式。第一种是绕固定(参考)坐标轴旋转:假设开始两个坐标系重合,先将{B}绕{A}的X轴旋转$\gamma$,然后绕{A}的Y轴旋转$\beta$,最后绕{A}的Z轴旋转$\alpha$,就能旋转到当前姿态。可以称其为X-Y-Z fixed angles或RPY角(Roll, Pitch, Yaw)。
Roll:横滚

Pitch: 俯仰

Yaw: 偏航(航向)
由于是绕固定坐标系旋转,则旋转矩阵为($c\alpha$ is shorthand for $\cos\alpha$, $s\alpha$ is shorthand for $\sin\alpha$,and so on.)
$$R_{XYZ}(\gamma,\beta,\alpha)=R_Z(\alpha)R_Y(\beta)R_X(\gamma)=\begin{bmatrix}
c\alpha c\beta & c\alpha s\beta s\gamma-s\alpha c\gamma & c\alpha s\beta c\gamma+s\alpha s\gamma\\
s\alpha c\beta & s\alpha s\beta s\gamma+c\alpha c\gamma & s\alpha s\beta c\gamma-c\alpha s\gamma\\
-s\beta& c\beta s\gamma & c\beta c\gamma
\end{bmatrix}$$
另一种姿态描述方式是绕自身坐标轴旋转:假设开始两个坐标系重合,先将{B}绕自身的Z轴旋转$\alpha$,然后绕Y轴旋转$\beta$,最后绕X轴旋转$\gamma$,就能旋转到当前姿态。称其为Z-Y-X欧拉角,由于是绕自身坐标轴进行旋转,则旋转矩阵为:
$$R_{Z'Y'X'}(\alpha,\beta,\gamma)=R_Z(\alpha)R_Y(\beta)R_X(\gamma)=\begin{bmatrix}
c\alpha c\beta & c\alpha s\beta s\gamma-s\alpha c\gamma & c\alpha s\beta c\gamma+s\alpha s\gamma\\
s\alpha c\beta & s\alpha s\beta s\gamma+c\alpha c\gamma & s\alpha s\beta c\gamma-c\alpha s\gamma\\
-s\beta& c\beta s\gamma & c\beta c\gamma
\end{bmatrix}$$
可以发现这两种描述方式得到的旋转矩阵是一样的,即绕固定坐标轴X-Y-Z旋转$(\gamma,\beta,\alpha)$和绕自身坐标轴Z-Y-X旋转$(\alpha,\beta,\gamma)$的最终结果一样,只是描述的方法有差别而已。In gerenal: three rotations taken about fixed axes yield the same final orientation as the same three rotations taken in opposite order about the axes of the moving frame.
- Axis-Angle与四元数
绕坐标轴的多次旋转可以等效为绕某一转轴旋转一定的角度。假设等效旋转轴方向向量为$\vec{K}=[k_x,k_y,k_z]^T$,等效旋转角为$\theta$,则四元数$q=(x,y,z,w)$,其中:
$$\begin{align*}
x &= k_x \cdot sin \frac{\theta}{2}\\
y &= k_y \cdot sin \frac{\theta}{2}\\
z &= k_z \cdot sin \frac{\theta}{2}\\
w &= cos \frac{\theta}{2}
\end{align*}$$
且有$x^2+y^2+z^2+w^2=1$
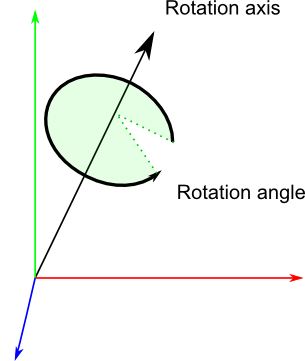
即四元数存储了旋转轴和旋转角的信息,它能方便的描述刚体绕任意轴的旋转。
四元数转换为旋转矩阵:
$$R=\begin{bmatrix}
1-2y^2-2z^2 & 2(xy-zw) & 2(xz+yw)\\
2(xy+zw) & 1-2x^2-2z^2 & 2(yz-xw)\\
2(xz-yw)& 2(yz+xw) & 1-2x^2-2y^2
\end{bmatrix}$$
已知旋转矩阵为:

则对应的四元数为:

- 四元数与欧拉角的相互转换
定义两个四元数:


 表示矢量
表示矢量

;而

表示矢量

四元数加法:

四元数乘法:
四元数的乘法的意义类似于矩阵的乘法,可以表示旋转的合成。当有多次旋转操作时,使用四元数可以获得更高的计算效率。



<<Quaternions` (* This loads the package *)
Quaternion[2, 1, 1, 3] ** Quaternion[2, 1, 1, 0] ** Quaternion[1, 1, 1, 1] (* Be sure to use ** rather than * when multiplying quaternions *)
计算结果为:Quaternion[-12, 4, 14, 2]
$$q=\begin{bmatrix}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}\\ 0\\ 0\\ \sin\frac{\gamma}{2}\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}\cos\frac{\beta}{2}\\ 0\\ \sin\frac{\beta}{2}\\ 0\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\\ \sin \frac{\alpha}{2}\\ 0\\ 0\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}
\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\beta}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}+\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\beta}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2}\\
\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\beta}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}-\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\beta}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2}\\ \cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\beta}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}+\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\beta}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2}
\\ \cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\beta}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2}-\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\beta}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}
\end{bmatrix}$$
$$\begin{bmatrix}\alpha\\ \beta\\ \gamma\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
\arctan\frac{2(q_0q_1+q_2q_3)}{1-2(q_1^2+q_2^2)}\\
\arcsin(2(q_0q_2-q_1q_3))\\
\arctan\frac{2(q_0q_3+q_1q_2)}{1-2(q_2^2+q_3^2)}
\end{bmatrix}$$
$$\begin{bmatrix}\alpha\\ \beta\\ \gamma\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
atan2(2(q_0q_1+q_2q_3),1-2(q_1^2+q_2^2))\\
\arcsin(2(q_0q_2-q_1q_3))\\
atan2(2(q_0 q_3+q_1 q_2),1-2(q_2^2+q_3^2))
\end{bmatrix}$$
θ = ATan(y / x)求出的θ取值范围是[-PI/2, PI/2];
θ = ATan2(y, x)求出的θ取值范围是[-PI, PI]。
当 (x, y) 在第一象限, 0 < θ < PI/2
当 (x, y) 在第二象限 PI/2 < θ≤PI
当 (x, y) 在第三象限, -PI < θ < -PI/2
当 (x, y) 在第四象限, -PI/2 < θ < 0
enum RotSeq{zyx, zyz, zxy, zxz, yxz, yxy, yzx, yzy, xyz, xyx, xzy,xzx};
// COMPILE: g++ -o quat2EulerTest quat2EulerTest.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath> using namespace std; ///////////////////////////////
// Quaternion struct
// Simple incomplete quaternion struct for demo purpose
///////////////////////////////
struct Quaternion{
Quaternion():x(), y(), z(), w(){};
Quaternion(double x, double y, double z, double w):x(x), y(y), z(z), w(w){}; void normalize(){
double norm = std::sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z + w*w);
x /= norm;
y /= norm;
z /= norm;
w /= norm;
} double norm(){
return std::sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z + w*w);
} double x;
double y;
double z;
double w; }; ///////////////////////////////
// Quaternion to Euler
///////////////////////////////
enum RotSeq{zyx, zyz, zxy, zxz, yxz, yxy, yzx, yzy, xyz, xyx, xzy,xzx}; void twoaxisrot(double r11, double r12, double r21, double r31, double r32, double res[]){
res[] = atan2( r11, r12 );
res[] = acos ( r21 );
res[] = atan2( r31, r32 );
} void threeaxisrot(double r11, double r12, double r21, double r31, double r32, double res[]){
res[] = atan2( r31, r32 );
res[] = asin ( r21 );
res[] = atan2( r11, r12 );
} void quaternion2Euler(const Quaternion& q, double res[], RotSeq rotSeq)
{
switch(rotSeq){
case zyx:
threeaxisrot( *(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
-*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
*(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case zyz:
twoaxisrot( *(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
*(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
*(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
-*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
res);
break; case zxy:
threeaxisrot( -*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
-*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case zxz:
twoaxisrot( *(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
-*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
*(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
res);
break; case yxz:
threeaxisrot( *(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
-*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
*(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case yxy:
twoaxisrot( *(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
*(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
-*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
res);
break; case yzx:
threeaxisrot( -*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
-*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case yzy:
twoaxisrot( *(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
-*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
*(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
res);
break; case xyz:
threeaxisrot( -*(q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
-*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case xyx:
twoaxisrot( *(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
-*(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
*(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
res);
break; case xzy:
threeaxisrot( *(q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x),
q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x + q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
-*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
*(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
res);
break; case xzx:
twoaxisrot( *(q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y),
*(q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z),
q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z,
*(q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y),
-*(q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z),
res);
break;
default:
std::cout << "Unknown rotation sequence" << std::endl;
break;
}
} ///////////////////////////////
// Helper functions
///////////////////////////////
Quaternion operator*(Quaternion& q1, Quaternion& q2){
Quaternion q;
q.w = q1.w*q2.w - q1.x*q2.x - q1.y*q2.y - q1.z*q2.z;
q.x = q1.w*q2.x + q1.x*q2.w + q1.y*q2.z - q1.z*q2.y;
q.y = q1.w*q2.y - q1.x*q2.z + q1.y*q2.w + q1.z*q2.x;
q.z = q1.w*q2.z + q1.x*q2.y - q1.y*q2.x + q1.z*q2.w;
return q;
} ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& stream, const Quaternion& q) {
cout << q.w << " "<< showpos << q.x << "i " << q.y << "j " << q.z << "k";
cout << noshowpos;
} double rad2deg(double rad){
return rad*180.0/M_PI;
} ///////////////////////////////
// Main
///////////////////////////////
int main(){ Quaternion q; // x,y,z,w
Quaternion qx45(sin(M_PI/), ,, cos(M_PI/) );
Quaternion qy45(, sin(M_PI/), , cos(M_PI/));
Quaternion qz45(, , sin(M_PI/), cos(M_PI/));
Quaternion qx90(sin(M_PI/), ,, cos(M_PI/) );
Quaternion qy90(, sin(M_PI/), , cos(M_PI/));
Quaternion qz90(, , sin(M_PI/), cos(M_PI/)); double res[]; q = qz45*qx45;
q.normalize();
quaternion2Euler(q, res, zyx);
cout << "Rotation sequence: X->Y->Z" << endl;
cout << "x45 -> z45" << endl;
cout << "q: " << q << endl;
cout << "x: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " y: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " z: " << rad2deg(res[]) << endl << endl; q = qz90*qx90;
q.normalize();
quaternion2Euler(q, res, zyx);
cout << "Rotation sequence: X->Y->Z" << endl;
cout << "x90 -> z90" << endl;
cout << "q: " << q << endl;
cout << "x: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " y: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " z: " << rad2deg(res[]) << endl << endl; q = qx90*qz90;
q.normalize();
quaternion2Euler(q, res, xyz);
cout << "Rotation sequence: Z->Y->X" << endl;
cout << "z90 -> x90" << endl;
cout << "q: " << q << endl;
cout << "x: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " y: " << rad2deg(res[]) << " z: " << rad2deg(res[]) << endl;
}
上面的代码存在一个问题,即奇异性没有考虑。下面看一种特殊的情况(参考Maths - Conversion Quaternion to Euler):假设一架飞机绕Y轴旋转了90°(俯仰角pitch=90),机头垂直向上,此时如何计算航向角和横滚角?

这时会发生自由度丢失的情况,即Yaw和Roll会变为一个自由度。此时再使用上面的公式根据四元数计算欧拉角会出现问题:
$\arcsin(2(q_0q_2-q_1q_3))$的定义域为$[-1,1]$,因此$(q_0q_2-q_1q_3)\in[-0.5, 0.5]$,当$q_0q_2-q_1q_3=0.5$时(在程序中浮点数不能直接进行等于判断,要使用合理的阈值),俯仰角$\beta$为90°,将其带入正向公式计算出四元数$(q_0,q_1,q_2,q_3)$,然后可以发现逆向公式中atan2函数中的参数全部为0,即出现了$\frac{0}{0}$的情况!无法计算。
$\beta=\pi/2$时,$\sin\frac{\beta}{2}=\cos\frac{\beta}{2}=0.707$,将其带入公式中有
$$q=\begin{bmatrix}w\\ x\\ y\\ z\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
0.707(\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}+\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2})\\
0.707(\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}-\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2})\\
0.707(\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2}+\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2})\\
0.707(\cos\frac{\alpha}{2}\sin\frac{\gamma}{2}-\sin\frac{\alpha}{2}\cos\frac{\gamma}{2})
\end{bmatrix}=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.707\cos\frac{\alpha-\gamma}{2}\\
0.707\sin\frac{\alpha-\gamma}{2}\\
0.707\cos\frac{\alpha-\gamma}{2}\\
0.707\sin\frac{\alpha-\gamma}{2}
\end{bmatrix}$$
则$\frac{x}{w}=\frac{z}{y}=\tan\frac{\alpha-\gamma}{2}$,于是有
$$\alpha-\gamma = 2\cdot atan2(x,w)$$
通常令$\alpha=0$,这时$\gamma = -2\cdot atan2(x,w)$。可以进行验证:当四元数为(w,x,y,z)=(0.653,-0.271,0.653,0.271)时,根据这些规则计算出来的ZYX欧拉角为α=0°,β=90°,γ=45°

当俯仰角为-90°,即机头竖直向下时的情况也与之类似,可以推导出奇异姿态时的计算公式。比较完整的四元数转欧拉角(Z-Y-X order)的代码如下:
CameraSpacePoint QuaternionToEuler(Vector4 q) // Z-Y-X Euler angles
{
CameraSpacePoint euler = { };
const double Epsilon = 0.0009765625f;
const double Threshold = 0.5f - Epsilon; double TEST = q.w*q.y - q.x*q.z; if (TEST < -Threshold || TEST > Threshold) // 奇异姿态,俯仰角为±90°
{
int sign = Sign(TEST); euler.Z = - * sign * (double)atan2(q.x, q.w); // yaw euler.Y = sign * (PI / 2.0); // pitch euler.X = ; // roll }
else
{
euler.X = atan2( * (q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x), q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z);
euler.Y = asin(- * (q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y));
euler.Z = atan2( * (q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z), q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z);
} return euler;
}
在DirectXMath Library中有许多与刚体姿态变换相关的函数可以直接调用:
- 四元数乘法:XMQuaternionMultiply method --Computes the product of two quaternions.
- 旋转矩阵转四元数:XMQuaternionRotationMatrix method --Computes a rotation quaternion from a rotation matrix.
- 四元数转旋转矩阵:XMMatrixRotationQuaternion method -- Builds a rotation matrix from a quaternion.
- 欧拉角转四元数:XMQuaternionRotationRollPitchYaw method --Computes a rotation quaternion based on the pitch, yaw, and roll (Euler angles).
- 四元数转Axis-Angle:XMQuaternionToAxisAngle method --Computes an axis and angle of rotation about that axis for a given quaternion.
- 欧拉角转旋转矩阵:XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw method --Builds a rotation matrix based on a given pitch, yaw, and roll (Euler angles).
- Axis-Angle转旋转矩阵:XMMatrixRotationAxis method --Builds a matrix that rotates around an arbitrary axis.
- 构造绕X/Y/Z轴的旋转矩阵:XMMatrixRotationX method --Builds a matrix that rotates around the x-axis.(Angles are measured clockwise when looking along the rotation axis toward the origin)
下面的代码中坐标系绕X轴旋转90°(注意这里不是按照右手定则的方向,而是沿着坐标轴向原点看过去以顺时针方式旋转,因此与传统的右手定则刚好方向相反),来进行变换:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream> #include <DirectXMath.h>
using namespace DirectX; #define PI 3.1415926 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//-------------------Computes the product of two quaternions.
XMVECTOR q1 = XMVectorSet(, , , );
XMVECTOR q2 = XMVectorSet(, , , );
XMVECTOR q3 = XMVectorSet(, , , ); XMVECTOR result = XMQuaternionMultiply(XMQuaternionMultiply(q3, q2), q1); // Returns the product of two quaternions as q1*q2*q3 std::cout << "Quaternion Multiply:" << std::endl;
std::cout << XMVectorGetX(result) << "," << XMVectorGetY(result) << "," << XMVectorGetZ(result) << "," << XMVectorGetW(result) << std::endl << std::endl; //------------------Computes a rotation quaternion based on the pitch, yaw, and roll (Euler angles).
float pitch = 90.0 * PI / 180.0; // Angle of rotation around the x-axis, in radians.
float yaw = ; // Angle of rotation around the y-axis, in radians.
float roll = ; // Angle of rotation around the z - axis, in radians. result = XMQuaternionRotationRollPitchYaw(pitch, yaw, roll); std::cout << "RPY/Euler angles to Quaternion:" << std::endl;
std::cout << XMVectorGetX(result) << "," << XMVectorGetY(result) << "," << XMVectorGetZ(result) << "," << XMVectorGetW(result) << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Computes a rotation quaternion from a rotation matrix.
float matrix[] = { , , , , , , , , , -, , , , , , };
XMMATRIX trans(matrix); // Initializes a new instance of the XMMATRIX structure from a sixteen element float array. result = XMQuaternionRotationMatrix(trans); // This function only uses the upper 3x3 portion of the XMMATRIX. std::cout << "Matrix to Quaternion:" << std::endl;
std::cout << XMVectorGetX(result) << "," << XMVectorGetY(result) << "," << XMVectorGetZ(result) << "," << XMVectorGetW(result) << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Builds a rotation matrix from a quaternion.
trans = XMMatrixRotationQuaternion(result); XMFLOAT3X3 fView;
XMStoreFloat3x3(&fView, trans); // Stores an XMMATRIX in an XMFLOAT3X3
std::cout << "Quaternion to Matrix:" << std::endl;
std::cout << fView._11 << "," << fView._12 << "," << fView._13 << std::endl
<< fView._21 << "," << fView._22 << "," << fView._23 << std::endl
<< fView._31 << "," << fView._32 << "," << fView._33 << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Computes an axis and angle of rotation about that axis for a given quaternion.
float Angle = ;
XMVECTOR Axis; XMQuaternionToAxisAngle(&Axis, &Angle, result); Axis = XMVector3Normalize(Axis); // Returns the normalized version of a 3D vector
std::cout << "Quaternion to Axis-Angle:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Axis: " << XMVectorGetX(Axis) << "," << XMVectorGetY(Axis) << "," << XMVectorGetZ(Axis) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Angle: " << Angle*180.0 / PI << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Builds a matrix that rotates around an arbitrary axis.
Angle = 90.0 * PI / 180.0; trans = XMMatrixRotationAxis(Axis, Angle); XMStoreFloat3x3(&fView, trans); // Stores an XMMATRIX in an XMFLOAT3X3
std::cout << "Axis-Angle to Matrix:" << std::endl;
std::cout << fView._11 << "," << fView._12 << "," << fView._13 << std::endl
<< fView._21 << "," << fView._22 << "," << fView._23 << std::endl
<< fView._31 << "," << fView._32 << "," << fView._33 << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Builds a rotation matrix based on a given pitch, yaw, and roll(Euler angles).
trans = XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw(pitch, yaw, roll); XMStoreFloat3x3(&fView, trans); // Stores an XMMATRIX in an XMFLOAT3X3
std::cout << "RPY/Euler angles to Matrix:" << std::endl;
std::cout << fView._11 << "," << fView._12 << "," << fView._13 << std::endl
<< fView._21 << "," << fView._22 << "," << fView._23 << std::endl
<< fView._31 << "," << fView._32 << "," << fView._33 << std::endl << std::endl; //-----------------Builds a matrix that rotates around the x - axis.
trans = XMMatrixRotationX(Angle); // Angles are measured clockwise when looking along the rotation axis toward the origin. XMStoreFloat3x3(&fView, trans); // Stores an XMMATRIX in an XMFLOAT3X3
std::cout << "Builds a matrix that rotates around the x-axis.:" << std::endl;
std::cout << fView._11 << "," << fView._12 << "," << fView._13 << std::endl
<< fView._21 << "," << fView._22 << "," << fView._23 << std::endl
<< fView._31 << "," << fView._32 << "," << fView._33 << std::endl << std::endl; return ;
}
结果如下图所示:

参考:
DirectXMath Library Quaternion Functions
Convert quaternion to euler rotations
Conversion between quaternions and Euler angles
Maths - Conversion Quaternion to Euler
Coordinate Transformations in Robotics—MATLAB
Introduction to Robotics - Mechanics and Control. Chapter 2 Spatial descriptions and transformations
四元数与欧拉角(RPY角)的相互转换的更多相关文章
- 3D数学基础:四元数与欧拉角之间的转换
在3D图形学中,最常用的旋转表示方法便是四元数和欧拉角,比起矩阵来具有节省存储空间和方便插值的优点.本文主要归纳了两种表达方式的转换,计算公式采用3D笛卡尔坐标系: 单位四元数可视化为三维矢量加上第四 ...
- eigen 中四元数、欧拉角、旋转矩阵、旋转向量
一.旋转向量 1.0 初始化旋转向量:旋转角为alpha,旋转轴为(x,y,z) Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector(alpha,Vector3d(x,y,z)) 1. ...
- 3D数学基础(四)四元数和欧拉角
一.四元数 四元数本质上是个高阶复数,可视为复数的扩展,表达式为y=a+bi+cj+dk.在说矩阵旋转的时候提到了它,当然四元数在Unity里面主要作用也在于此.在Unity编辑器中的Transfor ...
- OSG四元数与欧拉角之间的转换
osg::Quat HPRToQuat(double heading, double pitch, double roll) { osg::Quat q( roll, osg::Vec3d(0.0, ...
- python 使用PyKDL 四元数转欧拉角
安装: sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-kdl-parser-py 使用: import PyKDLimport math def quat_to_angle(quat ...
- python ros 四元数转欧拉角
#! /usr/bin/python import PyKDL import rospy from sensor_msgs.msg import Imu from nav_msgs.msg impor ...
- ros python 四元数 转 欧拉角
import sysimport math w = -0.99114048481x = -0.00530699081719y = 0.00178255140781z = -0.133612662554 ...
- Unity手游之路<四>3d旋转-四元数,欧拉角和变幻矩阵
http://blog.csdn.net/janeky/article/details/17272625 今天我们来谈谈关于Unity中的旋转.主要有三种方式.变换矩阵,四元数和欧拉角. 定义 变换矩 ...
- Unity的旋转-四元数,欧拉角用法简介
当初弄不明白旋转..居然找不到资料四元数应该用轴角相乘...后来自己摸明白了 通过两种旋转的配合,可以告别世界空间和本地空间矩阵转换了,大大提升效率. 每个轴相乘即可,可以任意轴,无限乘.无万向节锁问 ...
随机推荐
- Linux下解压.tar.xz格式文件的方法
前言 对于xz这个压缩相信很多人陌生,但xz是绝大数linux默认就带的一个压缩工具,xz格式比7z还要小. 今天在下载Node.js源码包的时候遇到的这种压缩格式.查了一下资料,这里进行一下记录,分 ...
- Java 11 快要来了,编译 & 运行一个命令搞定!
Java 11 马上要来了,原定于 9 月发布,还有不到 3 个月了,敬请期待更多新功能被加入到 11 当中,本文本讲的是 JEP 330 这个新特性. 化繁为简,一个命令编译运行源代码 看下面的代码 ...
- 【xsy2479】counting 生成函数+多项式快速幂
题目大意:在字符集大小为$m$的情况下,有多少种构造长度为$n$的字符串$s$的方案,使得$C(s)=k$.其中$C(s)$表示字符串$s$中出现次数最多的字符的出现次数. 对$998244353$取 ...
- url参数+,&,=,/等转义编码
url出现了有+,空格,/,?,%,#,&,= 等特殊符号的时候,可能在服务器端无法获得正确的参数值. 案例: <img src="BarCode39.aspx?barcode ...
- 课程三(Structuring Machine Learning Projects),第一周(ML strategy(1)) —— 0.Learning Goals
Learning Goals Understand why Machine Learning strategy is important Apply satisficing and optimizin ...
- vector源码3(参考STL源码--侯捷):pop_back、erase、clear、insert
vector源码1(参考STL源码--侯捷) vector源码2(参考STL源码--侯捷):空间分配.push_back vector源码(参考STL源码--侯捷)-----空间分配导致迭代器失效 v ...
- C++中的字符串可以这样换行写
运行结果:
- SpringBoot 三种方式配置 Druid(包括纯配置文件配置)
记录一下在项目中用纯 YML(application.yml 或者 application.properties)文件.Java 代码配置 Bean 和注解三种方式配置 Alibaba Druid 用 ...
- SpringMVC4集成ehcache
前言 使用SpringMVC4集成ehcache来缓存服务器数据. 开发环境 SpringMVC4.ehcache2.6. 项目结构 SpringMVC 集成ehcache 1.pom.xml //除 ...
- Linux进程间通信(System V) --- 信号量
信号量 IPC 原理 信号量通信机制主要用来实现进程间同步,避免并发访问共享资源.信号量可以标识系统可用资源的个数.最简单的信号量为二元信号量 下图为 Linux 信号量通信机制的概念图.在实际应用中 ...
