万字剖析Ribbon核心组件以及运行原理
大家好,本文我将继续来剖析SpringCloud中负载均衡组件Ribbon的源码。本来我是打算接着OpenFeign动态代理生成文章直接讲Feign是如何整合Ribbon的,但是文章写了一半发现,如果不把Ribbon好好讲清楚,那么有些Ribbon的细节理解起来就很困难,所以我还是打算单独写一篇文章来剖析Ribbon的源码,这样在讲Feign整合Ribbon的时候,我就不再赘述这些细节了。好了,话不多说,直接进入主题。
一、Ribbon的核心组件
1、Server
这是个很简单的东西,就是服务实例数据的封装,里面封装了服务实例的ip和端口之类的,一个服务有很多台机器,那就有很多个Server对象。
2、ServerList
public interface ServerList<T extends Server> {
public List<T> getInitialListOfServers();
/**
* Return updated list of servers. This is called say every 30 secs
* (configurable) by the Loadbalancer's Ping cycle
*
*/
public List<T> getUpdatedListOfServers();
}
ServerList是个接口,泛型是Server,提供了两个方法,都是获取服务实例列表的,这两个方法其实在很多实现类中实现是一样的,没什么区别。这个接口很重要,因为这个接口就是Ribbon获取服务数据的来源接口,Ribbon进行负载均衡的服务列表就是通过这个接口来的,那么可以想一想是不是只要实现这个接口就可以给Ribbon提供服务数据了?事实的确如此,在SpringCloud中,eureka、nacos等注册中心都实现了这个接口,都将注册中心的服务实例数据提供给Ribbon,供Ribbon来进行负载均衡。
3、ServerListUpdater
通过名字也可以知道,是用来更新服务注册表的数据,他有唯一的实现,就是PollingServerListUpdater,这个类有一个核心的方法,就是start,我们来看一下start的实现。
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
updateAction.doUpdate();
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
}; scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
wrapperRunnable,
initialDelayMs,
refreshIntervalMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}
通过这段方法我们可以看出,首先通过isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)来保证这个方法只会被调用一下,然后封装了一个Runnable,这个Runnable干了一件核心的事,就是调用传入的updateAction的doUpdate方法,然后将Runnable扔到了带定时调度功能的线程池,经过initialDelayMs(默认1s)时间后,会调用一次,之后都是每隔refreshIntervalMs(默认30s)调用一次Runnable的run方法,也就是调用updateAction的doUpdate方法。
所以这个类的核心作用就是每隔30s会调用一次传入的updateAction的doUpdate方法的实现,记住这个结论。
4、IRule
public interface IRule{
/*
* choose one alive server from lb.allServers or
* lb.upServers according to key
*
* @return choosen Server object. NULL is returned if none
* server is available
*/
public Server choose(Object key);
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}
IRule是负责负载均衡的算法的,也就是真正实现负载均衡获取一个服务实例就是这个接口的实现。比如说实现类RandomRule,就是从一堆服务实例中随机选取一个服务实例。
5、IClientConfig
就是一个配置接口,有个默认的实现DefaultClientConfigImpl,通过这个可以获取到一些配置Ribbon的一些配置。
6、ILoadBalancer
public interface ILoadBalancer {
public void addServers(List<Server> newServers);
public Server chooseServer(Object key);
public void markServerDown(Server server);
@Deprecated
public List<Server> getServerList(boolean availableOnly);
public List<Server> getReachableServers();
public List<Server> getAllServers();
}
这个接口的作用,对外主要提供了获取服务实例列表和选择服务实例的功能。虽然对外主要提供获取服务的功能,但是在实现的时候,主要是用来协调上面提到的各个核心组件的,使得他们能够协调工作,从而实现对外提供获取服务实例的功能。
这个接口的实现有好几个实现类,但是我讲两个比较重要的。
BaseLoadBalancer
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware { private final static IRule DEFAULT_RULE = new RoundRobinRule();
protected IRule rule = DEFAULT_RULE;
private IClientConfig config; protected volatile List<Server> allServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
protected volatile List<Server> upServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>()); public BaseLoadBalancer(String name, IRule rule, LoadBalancerStats stats,
IPing ping, IPingStrategy pingStrategy) { logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: initialized", name); this.name = name;
this.ping = ping;
this.pingStrategy = pingStrategy;
setRule(rule);
setupPingTask();
lbStats = stats;
init();
} public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config) {
initWithNiwsConfig(config);
}
public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, IRule rule, IPing ping) {
initWithConfig(config, rule, ping, createLoadBalancerStatsFromConfig(config));
} void initWithConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping, LoadBalancerStats stats) {
this.config = clientConfig;
String clientName = clientConfig.getClientName();
this.name = clientName;
int pingIntervalTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingInterval,
Integer.parseInt("30")));
int maxTotalPingTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerMaxTotalPingTime,
Integer.parseInt("2"))); setPingInterval(pingIntervalTime);
setMaxTotalPingTime(maxTotalPingTime); // cross associate with each other
// i.e. Rule,Ping meet your container LB
// LB, these are your Ping and Rule guys ...
setRule(rule);
setPing(ping); setLoadBalancerStats(stats);
rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
if (ping instanceof AbstractLoadBalancerPing) {
((AbstractLoadBalancerPing) ping).setLoadBalancer(this);
}
logger.info("Client: {} instantiated a LoadBalancer: {}", name, this);
boolean enablePrimeConnections = clientConfig.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.EnablePrimeConnections, DefaultClientConfigImpl.DEFAULT_ENABLE_PRIME_CONNECTIONS); if (enablePrimeConnections) {
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(true);
PrimeConnections primeConnections = new PrimeConnections(
this.getName(), clientConfig);
this.setPrimeConnections(primeConnections);
}
init(); } public void setRule(IRule rule) {
if (rule != null) {
this.rule = rule;
} else {
/* default rule */
this.rule = new RoundRobinRule();
}
if (this.rule.getLoadBalancer() != this) {
this.rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
}
} public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
} }
核心属性
allServerList:缓存了所有的服务实例数据
upServerList:缓存了能够使用的服务实例数据。
rule:负载均衡算法组件,默认是RoundRobinRule
核心方法
setRule:这个方法是设置负载均衡算法的,并将当前这个ILoadBalancer对象设置给IRule,从这可以得出一个结论,IRule进行负载均衡的服务实例列表是通过ILoadBalancer获取的,也就是 IRule 和 ILoadBalancer相互引用。setRule(rule)一般是在构造对象的时候会调用。
chooseServer:就是选择一个服务实例,是委派给IRule的choose方法来实现服务实例的选择。
BaseLoadBalancer这个实现类总体来说,已经实现了ILoadBalancer的功能的,所以这个已经基本满足使用了。
说完BaseLoadBalancer这个实现类,接下来说一下DynamicServerListLoadBalancer实现类。DynamicServerListLoadBalancer继承自BaseLoadBalancer,DynamicServerListLoadBalancer主要是对BaseLoadBalancer功能进行扩展。
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.class);
volatile ServerList<T> serverListImpl;
volatile ServerListFilter<T> filter;
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers();
}
};
protected volatile ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater;
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping,
ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping);
this.serverListImpl = serverList;
this.filter = filter;
this.serverListUpdater = serverListUpdater;
if (filter instanceof AbstractServerListFilter) {
((AbstractServerListFilter) filter).setLoadBalancerStats(getLoadBalancerStats());
}
restOfInit(clientConfig);
}
@Override
public void setServersList(List lsrv) {
super.setServersList(lsrv);
List<T> serverList = (List<T>) lsrv;
Map<String, List<Server>> serversInZones = new HashMap<String, List<Server>>();
for (Server server : serverList) {
// make sure ServerStats is created to avoid creating them on hot
// path
getLoadBalancerStats().getSingleServerStat(server);
String zone = server.getZone();
if (zone != null) {
zone = zone.toLowerCase();
List<Server> servers = serversInZones.get(zone);
if (servers == null) {
servers = new ArrayList<Server>();
serversInZones.put(zone, servers);
}
servers.add(server);
}
}
setServerListForZones(serversInZones);
}
protected void setServerListForZones(
Map<String, List<Server>> zoneServersMap) {
LOGGER.debug("Setting server list for zones: {}", zoneServersMap);
getLoadBalancerStats().updateZoneServerMapping(zoneServersMap);
}
@VisibleForTesting
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
/**
* Update the AllServer list in the LoadBalancer if necessary and enabled
*
* @param ls
*/
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
}
成员变量
serverListImpl:上面说过,通过这个接口获取服务列表
filter:起到过滤的作用,一般不care
updateAction:是个匿名内部类,实现了doUpdate方法,会调用updateListOfServers方法
serverListUpdater:上面说到过,默认就是唯一的实现类PollingServerListUpdater,也就是每个30s就会调用传入的updateAction的doUpdate方法。
这不是巧了么,serverListUpdater的start方法需要一个updateAction,刚刚好成员变量有个updateAction的匿名内部类的实现,所以serverListUpdater的start方法传入的updateAction的实现其实就是这个匿名内部类。
那么哪里调用了serverListUpdater的start方法传入了updateAction呢?是在构造的时候调用的,具体的调用链路是调用 restOfInit -> enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature(),这里就不贴源码了
所以,其实DynamicServerListLoadBalancer在构造完成之后,默认每隔30s中,就会调用updateAction的匿名内部类的doUpdate方法,从而会调用updateListOfServers。所以我们来看一看 updateListOfServers 方法干了什么。
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
这个方法实现很简单,就是通过调用 ServerList 的getUpdatedListOfServers获取到一批服务实例数据,然后过滤一下,最后调用updateAllServerList方法,进入updateAllServerList方法。
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
其实很简单,就是调用每个服务实例的setAlive方法,将isAliveFlag设置成true,然后调用setServersList。setServersList这个方法的主要作用是将服务实例更新到内部的缓存中,也就是上面提到的allServerList和upServerList,这里就不贴源码了。
其实分析完updateListOfServers方法之后,再结合上面源码的分析,我们可以清楚的得出一个结论,那就是默认每隔30s都会重新通过ServerList组件获取到服务实例数据,然后更新到BaseLoadBalancer缓存中,IRule的负载均衡所需的服务实例数据,就是这个内部缓存。
从DynamicServerListLoadBalancer的命名也可以看出,他相对于父类BaseLoadBalancer而言,提供了动态更新内部服务实例列表的功能。
为了便于大家记忆,我画一张图来描述这些组件的关系以及是如何运作的。
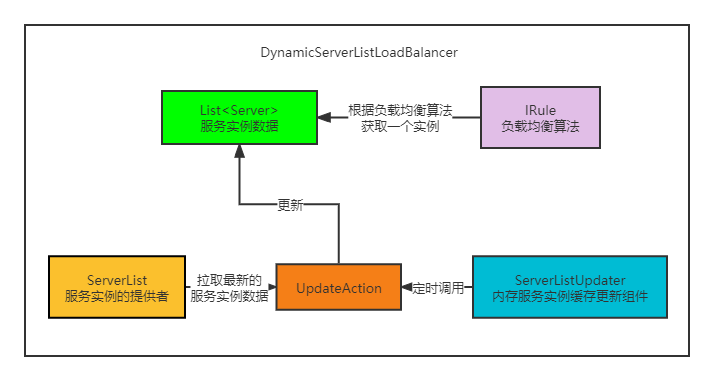
说完一些核心的组件,以及他们跟ILoadBalancer的关系之后,接下来就来分析一下,ILoadBalancer是在ribbon中是如何使用的。
8、AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient
ILoadBalancer是一个可以获取到服务实例数据的组件,那么服务实例跟什么有关,那么肯定是跟请求有关,所以在Ribbon中有这么一个抽象类,AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient,这个是用来执行请求的,我们来看一下这个类的构造。
public AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient(ILoadBalancer lb) {
super(lb);
}
/**
* Delegate to {@link #initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig)}
* @param clientConfig
*/
public AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient(ILoadBalancer lb, IClientConfig clientConfig) {
super(lb, clientConfig);
}
通过上面可以看出,在构造的时候需要传入一个ILoadBalancer。
AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient中有一个方法executeWithLoadBalancer,这个是用来执行传入的请求,以负载均衡的方式。
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = buildLoadBalancerCommand(request, requestConfig);
try {
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof ClientException) {
throw (ClientException) t;
} else {
throw new ClientException(e);
}
}
}
这个方法构建了一个LoadBalancerCommand,随后调用了submit方法,传入了一个匿名内部类,这个匿名内部类中有这么一行代码很重要。
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
这行代码是根据给定的一个Server重构了URI,这是什么意思呢?举个例子,在OpenFeign那一篇文章我说过,会根据服务名拼接出类似http://ServerA的地址,那时是没有服务器的ip地址的,只有服务名,假设请求的地址是http://ServerA/api/sayHello,那么reconstructURIWithServer干的一件事就是将ServerA服务名替换成真正的服务所在的机器的ip和端口,假设ServerA所在的一台机器(Server里面封装了某台机器的ip和端口)是192.168.1.101:8088,那么重构后的地址就变成http://192.168.1.101:8088/api/sayHello,这样就能发送http请求到ServerA服务所对应的一台服务器了。
之后根据新的地址,调用这个类中的execute方法来执行请求,execute方法是个抽象方法,也就是交给子类实现,子类就可以通过实现这个方法,来发送http请求,实现rpc调用。
那么这台Server是从获取的呢?其实猜猜也知道,肯定是通过ILoadBalancer获取的,因为submit方法比较长,这里我直接贴出submit方法中核心的一部分代码
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
就是通过selectServer来选择一个Server的,selectServer我就不翻源码了,其实最终还是调用ILoadBalancer的方法chooseServer方法来获取一个服务,之后就会调用上面的说的匿名内部类的方法,重构URI,然后再交由子类的execut方法来实现发送http请求。
所以,通过对AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient的executeWithLoadBalancer方法,我们可以知道,这个抽象类的主要作用就是通过负载均衡算法,找到一个合适的Server,然后将你传入的请求路径http://ServerA/api/sayHello重新构建成类似http://192.168.1.101:8088/api/sayHello这样,之后调用子类实现的execut方法,来发送http请求,就是这么简单。到这里其实Ribbon核心组件和执行原理我就已经说的差不多了,再来画一张图总结一下
二、SpringCloud中使用的核心组件的实现都有哪些
说完了Ribbon的一些核心组件和执行原理之后,我们再来看一下在SpringCloud环境下,这些组件到底是用的哪些实现,毕竟有写时接口,有的是抽象类。
Ribbon的自动装配类:RibbonAutoConfiguration,我拎出了核心的源码
@Configuration
@RibbonClients
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration { @Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
}
RibbonAutoConfiguration配置类上有个@RibbonClients注解,接下来讲解一下这个注解的作用
@Import(RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar.class)
public @interface RibbonClients { RibbonClient[] value() default {}; Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {}; }
看过我写的OpenFeign的文章小伙伴肯定知道,要使用Feign,得需要使用@EnableFeignClients,@EnableFeignClients的作用可以扫描指定包路径下的@FeignClient注解,也可以声明配置类;同样RibbonClients的作用也是可以声明配置类,同样也使用了@Import注解注解来实现的,RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar这个配置类的作用就是往spring容器中注入每个服务的Ribbon组件(@RibbonClient里面可以声明每个服务对应的配置)的配置类和默认配置类,将配置类封装为RibbonClientSpecification注入到spring容器中,其实就跟@FeignClient注解声明配置的作用是一样的。
RibbonAutoConfiguration的主要作用就是注入了一堆RibbonClientSpecification,就是每个服务对应的配置类,然后声明了SpringClientFactory这个bean,将配置类放入到里面。
SpringClientFactory是不是感觉跟OpenFeign中的FeignContext很像,其实两个的作用是一样的,SpringClientFactory也继承了NamedContextFactory,实现了配置隔离,同时也在构造方法中传入了每个容器默认的配置类RibbonClientConfiguration。至于什么是配置隔离,我在OpenFeign那篇文章说过,不清楚的小伙伴可以后台回复feign01即可获得文章链接。
配置优先级问题
这里我说一下在OpenFeign里没仔细说的配置优先级的事情,因为有这么多配置类,都可以在配置类中声明对象,那么到底使用哪个配置类声明的对象呢。
优先级最高的是springboot启动的时候的容器,因为这个容器是每个服务的容器的父容器,而在配置类声明bean的时候,都有@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解,一旦父容器有这个bean,那么子容器就不会初始化。
优先级第二高的是每个客户端声明的配置类,也就是通过@FeignClient和@RibbonClient的configuration属性声明的配置类
优先级第三高的是@EnableFeignClients和@RibbonClients注解中configuration属性声明的配置类
优先级最低的就是FeignContext和SpringClientFactory构造时传入的配置类
至于优先级怎么来的,其实是在NamedContextFactory中createContext方法中构建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时按照配置的优先级一个一个传进去的。
RibbonClientConfiguration提供的默认的bean
接下来我们看一下RibbonClientConfiguration都提供了哪些默认的bean
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {
DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();
config.loadProperties(this.name);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.GZipPayload, DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD);
return config;
}
配置类对应的bean,这里设置了ConnectTimeout和ReadTimeout都是1s中。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name);
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();
rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return rule;
}
IRule,默认是ZoneAvoidanceRule,这个Rule带有过滤的功能,过滤哪些不可用的分区的服务(这个过滤可以不用care),过滤成功之后,继续采用线性轮询的方式从过滤结果中选择一个出来。至于这个propertiesFactory,可以不用管,这个是默认读配置文件的中的配置,一般不设置,后面看到都不用care。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name);
}
ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
默认是ConfigurationBasedServerList,也就是基于配置来提供服务实例列表。但是在SpringCloud环境中,这是不可能的,因为服务信息是在注册中心,所以应该是服务注册中心对应实现的,比如Nacos的实现NacosServerList,这里我贴出NacosServerList的bean的声明,在配置类NacosRibbonClientConfiguration中
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerList<?> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config,
NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosDiscoveryProperties) {
NacosServerList serverList = new NacosServerList(nacosDiscoveryProperties);
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
至于为什么容器选择NacosServerList而不是ConfigurationBasedServerList,主要是因为NacosRibbonClientConfiguration这个配置类是通过@RibbonClients导入的,也就是比SpringClientFactory导入的RibbonClientConfiguration配置类优先级高。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {
return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);
}
ServerListUpdater,就是我们剖析的PollingServerListUpdater,默认30s更新一次BaseLoadBalancer内部服务的缓存。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
ILoadBalancer,默认是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer,构造的时候也传入了上面声明的的bean,ZoneAwareLoadBalancer这个类继承了DynamicServerListLoadBalancer,所以这个类功能也符合我们剖析的源码,至于ZoneAwareLoadBalancer多余的特性,也不用care。
到这里,Ribbon在SpringCloud的配置我们就讲完了,主要就是声明了很多核心组件的bean,最后都设置到ZoneAwareLoadBalancer中。但是,AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient这个对象的声明我们并没有在配置类中找到,主要是因为这个对象是OpenFeign整合Ribbon的一个入口,至于是如何整合的,这个坑就留给下篇文章吧。
那么在springcloud中,上图就可以加上注册中心。

三、总结
本文剖析了Ribbon这个负载均衡组件中的一些核心组件的源码,并且将这些组件之间的关系一一描述清楚,同时也剖析了在发送请求的时候是如何通过ILoadBalancer获取到一个服务实例,重构URI的过程。希望本篇文章能够让你知道Ribbon是如何工作的。至于OpenFeign整合Ribbon,详见文章 【SpringCloud原理】OpenFeign原来是这么基于Ribbon来实现负载均衡的。
往期热门文章推荐
扫码或者搜索关注公众号 三友的java日记 ,及时干货不错过,公众号致力于通过画图加上通俗易懂的语言讲解技术,让技术更加容易学习。
万字剖析Ribbon核心组件以及运行原理的更多相关文章
- 【SpringCloud原理】Ribbon核心组件以及运行原理万字源码剖析
大家好,本文我将继续来剖析SpringCloud中负载均衡组件Ribbon的源码.本来我是打算接着OpenFeign动态代理生成文章直接讲Feign是如何整合Ribbon的,但是文章写了一半发现,如果 ...
- 【SpringCloud原理】万字剖析OpenFeign之FeignClient动态代理生成源码
年前的时候我发布两篇关于nacos源码的文章,一篇是聊一聊nacos是如何进行服务注册的,另一篇是一文带你看懂nacos是如何整合springcloud -- 注册中心篇.今天就继续接着剖析Sprin ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件)
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件) Startup Class 1.Startup Constructor(构造函数) 2.Configure ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行 核心框架 ASP.NET Core APP 创建与运行 总结 之前两篇文章简析.NET Core 以及与 .NET Framew ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析
1. ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析 1.1. 概述 1.2. 文件配置 1.2.1. Starup文件配置 Configure ConfigureServices 1.2.2. appset ...
- Flink 集群运行原理兼部署及Yarn运行模式深入剖析
1 Flink的前世今生(生态很重要) 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/shenshouniu/article/details/84439459 很多人可能都是在 2015 年才听到 ...
- SpringCloud | 通过电商业务场景让你彻底明白SpringCloud核心组件的底层原理
本文分为两个部分: Spring Cloud"全家桶"简单介绍. 通过实际电商业务场景,让你彻底明白Spring Cloud几个核心组件的底层原理. Spring Cloud介绍 ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[4]:进入HttpContext的世界
HttpContext是ASP.NET中的核心对象,每一个请求都会创建一个对应的HttpContext对象,我们的应用程序便是通过HttpContext对象来获取请求信息,最终生成响应,写回到Http ...
- Spark核心技术原理透视一(Spark运行原理)
在大数据领域,只有深挖数据科学领域,走在学术前沿,才能在底层算法和模型方面走在前面,从而占据领先地位. Spark的这种学术基因,使得它从一开始就在大数据领域建立了一定优势.无论是性能,还是方案的统一 ...
随机推荐
- Blazor技术开发了一个访客管理系统
简单介绍一下系统功能 该系统为了在疫情期间能很好管理访客登记做好风险管控,同时可以整合智能设备做到自动确认并跟踪访客的行动轨迹,该项目完全开源. 系统流程 访客可以同通过手机进行预注册,同时上传照片, ...
- hashlib加密模块、logging日志模块
hashlib模块 加密:将明文数据通过一系列算法变成密文数据 目的: 就是为了数据的安全 基本使用 基本使用 import hashlib # 1.先确定算法类型(md5普遍使用) md5 = ha ...
- DRF JWT认证(一)
为什么要使用JWT认证?构成和原理又是什么?怎么还有Base64的事?我都写了
- JVM虚拟机类加载机制(一)
类从被加载到虚拟机内存中开始,到卸载出内存截止,整个生命周期包括:加载.验证.准备.解析,初始化.使用.卸载七个阶段.其中验证.准备.解析三个部分统称为连接. 类初始化情况: 遇到new.getsta ...
- Vue使用PostCSS 插件和如何使用sass及常用语法
为什么要使用PostCss 转换 px 单位的插件有很多,知名的有 postcss-px-to-viewport 和 postcss-pxtorem,前者是将 px 转成 vw,后者是将 px 转成 ...
- AngularJS性能优化心得,自己踩过的抗,及一些别人的经验(转哦)
脏数据检查 != 轮询检查更新 谈起angular的脏检查机制(dirty-checking), 常见的误解就是认为: ng是定时轮询去检查model是否变更.其实,ng只有在指定事件触发后,才进入$ ...
- 【原创】记一次DouPHP站点的RCE实战之旅
声明 本次实践是在合法授权情况下进行,数据已经全部脱敏,主要是提供思路交流学习,请勿用于任何非法活动,否则后果自负. 实战记录 信息收集 1,踩点站点 通过fofa 查到目标DouPHP框架该站点(也 ...
- 《手写Mybatis》第5章:数据源的解析、创建和使用
作者:小傅哥 博客:https://bugstack.cn 沉淀.分享.成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获! 一.前言 管你吃几碗粉,有流量就行! 现在我们每天所接收的信息量越来越多,但很多的个人却没有多 ...
- 音视频基本概念和FFmpeg的简单入门
写在前面 最近正好有音视频编辑的需求,虽然之前粗略的了解过FFmpeg不过肯定是不够用的,借此重新学习下: 基本概念 容器/文件(Conainer/File): 即特定格式的多媒体文件,一般来说一个视 ...
- Halo 开源项目学习(一):项目启动
项目简介 Halo 是一个优秀的开源博客发布应用,在 GitHub 上广受好评,正好最近在练习写博客,借此记录一下学习 Halo 的过程. 项目下载 从 GitHub 上拉取项目源码,Halo 从 1 ...

