《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.31

代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 8.31 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Fp = 3.2; % analog passband freq in kHz 6.4 kpi
Fs = 3.8; % analog stopband freq in kHz 7.6 kpi
fs = 8; % sampling rate in kHz 16.0 kpi % -------------------------------
% Ω=(2/T)tan(ω/2)
% ω=2*[atan(ΩT/2)]
% Digital Filter Specifications:
% -------------------------------
wp = 2*pi*Fp/fs % digital passband freq in rad 0.8pi
%wp = Fp;
ws = 2*pi*Fs/fs % digital stopband freq in rad 0.95pi
%ws = Fs;
Rp = 0.5; % passband ripple in dB
As = 45; % stopband attenuation in dB Ripple = 10 ^ (-Rp/20) % passband ripple in absolute
Attn = 10 ^ (-As/20) % stopband attenuation in absolute % Analog prototype specifications: Inverse Mapping for frequencies
T = 1/8000; % set T = 1
%fs = 1/T;
OmegaP = (2/T)*tan(wp/2) % prototype passband freq 1.9593pi 15675pi
OmegaS = (2/T)*tan(ws/2) % prototype stopband freq 8.089pi 64712pi % Analog Chebyshev-1 Prototype Filter Calculation:
[cs, ds] = afd_chb1(OmegaP, OmegaS, Rp, As); % Calculation of second-order sections:
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: START *****\n');
[CS, BS, AS] = sdir2cas(cs, ds)
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: END *****\n'); % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db_s, mag_s, pha_s, ww_s] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 8*pi/T); % --------------------------------------------------------------------
% find exact band-edge frequencies for the given dB specifications
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
[diff_to_45dB, ind] = min(abs(db_s+45))
db_s(ind-3 : ind+3) % magnitude response, dB ww_s(ind)/(pi) % analog frequency in kpi units
%ww_s(ind)/(2*pi) % analog frequency in Hz units [sA,index] = sort(abs(db_s+45));
AA_dB = db_s(index(1:8))
AB_rad = ww_s(index(1:8))/(pi)
AC_Hz = ww_s(index(1:8))/(2*pi)
% ------------------------------------------------------------------- % Calculation of Impulse Response:
[ha, x, t] = impulse(cs, ds); % Impulse Invariance Transformation:
%[b, a] = imp_invr(cs, ds, T); % Bilinear Transformation
[b, a] = bilinear(cs, ds, 1/T)
[C, B, A] = dir2cas(b, a) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db, mag, pha, grd, ww] = freqz_m(b, a); % --------------------------------------------------------------------
% find exact band-edge frequencies for the given dB specifications
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
[diff_to_45dB, ind] = min(abs(db+45))
db(ind-3 : ind+3) % magnitude response, dB ww(ind)/(pi) (2/T)*tan(ww(ind)/2)/pi [sA,index] = sort(abs(db+45));
AA_dB = db(index(1:8))'
AB_rad = ww(index(1:8))'/pi
AC_Hz = (2/T)*tan(ww(index(1:8))'/2)/pi
% ------------------------------------------------------------------- %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Analog Chebyshev-I lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 1.0; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww_s/pi, mag_s); grid on; %axis([-10, 10, 0, 1.2]);
xlabel(' Analog frequency in \piHz units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude in Absolute');
% set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8.089, -1.9593, 0, 1.9593, 8.089]); % T = 1
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-80000, -64712, -15675, 0, 15675, 64712, 80000]); % T = 1/8000
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.006, 0.94, 1.0, 1.5]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww_s/pi, db_s); grid on; %axis([0, M, -50, 10]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in \piHz units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
% set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8.089, -1.9593, 0, 1.9593, 5.7, 8.089]); % T = 1
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-80000, -64712, -15675, 0, 15675, 45696, 64712, 80000]); % T = 1/8000
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-45, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['45';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww_s/pi, pha_s/pi); grid on; %axis([-10, 10, -1.2, 1.2]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in \piHz nuits'); ylabel('radians'); title('Phase Response');
% set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8.089, -1.9593, 0, 1.9593, 8.089]); % T = 1
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-80000, -64712, -15675, 0, 15675, 45696, 64712, 80000]); % T = 1/8000
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:0.5:1]); subplot(2,2,4); plot(t, ha); grid on; %axis([0, 30, -0.05, 0.25]);
xlabel('time in seconds'); ylabel('ha(t)'); title('Impulse Response'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Digital Chebyshev-I lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 2; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww/pi, mag); axis([0, M, 0, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel(' Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0056, 0.9441, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww/pi, pha/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:1:1]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww/pi, db); axis([0, M, -80, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.93, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-70, -45, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['70';'45';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, grd); grid on; %axis([0, M, 0, 35]);
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
%set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:5:35]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Pole-Zero Plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title(sprintf('Pole-Zero Plot'));
%pzplotz(b,a); % ----------------------------------------------
% Calculation of Impulse Response
% ----------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Imp & Freq Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
t = [0: 0.000005 : 8*0.0001]; subplot(2,1,1); impulse(cs,ds,t); grid on; % Impulse response of the analog filter
axis([0, 8*0.0001, -1.5*10000, 2.0*10000]);hold on n = [0:1:7*0.0001/T]; hn = filter(b,a,impseq(0,0,7*0.0001/T)); % Impulse response of the digital filter
stem(n*T,hn); xlabel('time in sec'); title (sprintf('Impulse Responses T=%2d',T));
hold off % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbs, mags, phas, wws] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 8*pi/T); % Analog frequency s-domain [dbz, magz, phaz, grdz, wwz] = freqz_m(b, a); % Digital z-domain %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- subplot(2,1,2); plot(wws/(2*pi), mags/T, 'b+', wwz/(2*pi*T), magz, 'r'); grid on; xlabel('frequency in Hz'); title('Magnitude Responses'); ylabel('Magnitude'); text(-0.8,0.15,'Analog filter', 'Color', 'b'); text(0.6,1.05,'Digital filter', 'Color', 'r'); %% -----------------------------------------------------------------------
%% MATLAB cheby1 function
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- % Analog Prototype Order Calculations:
ep = sqrt(10^(Rp/10)-1); % Passband Ripple Factor
A = 10^(As/20); % Stopband Attenuation Factor
OmegaC = OmegaP; % Analog Chebyshev-1 prototype cutoff freq
OmegaR = OmegaS/OmegaP; % Analog prototype Transition ratio
g = sqrt(A*A-1)/ep; % Analog prototype Intermediate cal N = ceil(log10(g+sqrt(g*g-1))/log10(OmegaR+sqrt(OmegaR*OmegaR-1)));
fprintf('\n\n ********** Chebyshev-I Filter Order = %3.0f \n', N) % Digital Chebyshev-1 Filter Design:
wn = wp/pi; % Digital Chebyshev-1 cutoff freq in pi units [b, a] = cheby1(N, Rp, wn)
[C, B, A] = dir2cas(b, a) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db, mag, pha, grd, ww] = freqz_m(b, a); % --------------------------------------------------------------------
% find exact band-edge frequencies for the given dB specifications
% --------------------------------------------------------------------
[diff_to_45dB, ind] = min(abs(db+45))
db(ind-3 : ind+3) % magnitude response, dB ww(ind)/(pi) (2/T)*tan(ww(ind)/2)/pi [sA,index] = sort(abs(db+45));
AA_dB = db(index(1:8))'
AB_rad = ww(index(1:8))'/pi
AC_Hz = (2/T)*tan(ww(index(1:8))'/2)/pi
% ------------------------------------------------------------------- %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Digital Chebyshev-I lowpass by cheby1 function')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 2; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww/pi, mag); axis([0, M, 0, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0056, 0.9441, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww/pi, pha/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:1:1]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww/pi, db); axis([0, M, -100, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.93, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-60, -45, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['60';'45';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, grd); grid on; %axis([0, M, 0, 35]);
xlabel('Digital frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
%set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:5:35]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Pole-Zero Plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title(sprintf('Pole-Zero Plot'));
%pzplotz(b,a); % ----------------------------------------------
% Calculation of Impulse Response
% ----------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.31 Imp & Freq Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
t = [0: 0.000005 : 8*0.0001]; subplot(2,1,1); impulse(cs,ds,t); grid on; % Impulse response of the analog filter
axis([0, 8*0.0001, -1.5*10000, 2.0*10000]);hold on n = [0:1:7*0.0001/T]; hn = filter(b,a,impseq(0,0,7*0.0001/T)); % Impulse response of the digital filter
stem(n*T,hn); xlabel('time in sec'); title (sprintf('Impulse Responses T=%2d',T));
hold off % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbs, mags, phas, wws] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 8*pi/T); % Analog frequency s-domain [dbz, magz, phaz, grdz, wwz] = freqz_m(b, a); % Digital z-domain %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- subplot(2,1,2); plot(wws/(2*pi), mags/T, 'b+', wwz/(2*pi*T), magz, 'r'); grid on; xlabel('frequency in Hz'); title('Magnitude Responses'); ylabel('Magnitude'); text(-0.8,0.15,'Analog filter', 'Color', 'b'); text(0.6,1.05,'Digital filter', 'Color', 'r');
运行结果:
这里放上T=1/8000sec的结果。
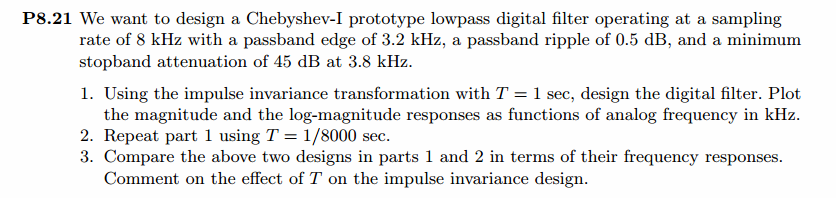
模拟chebyshev-1型低通,幅度谱、相位谱和脉冲响应
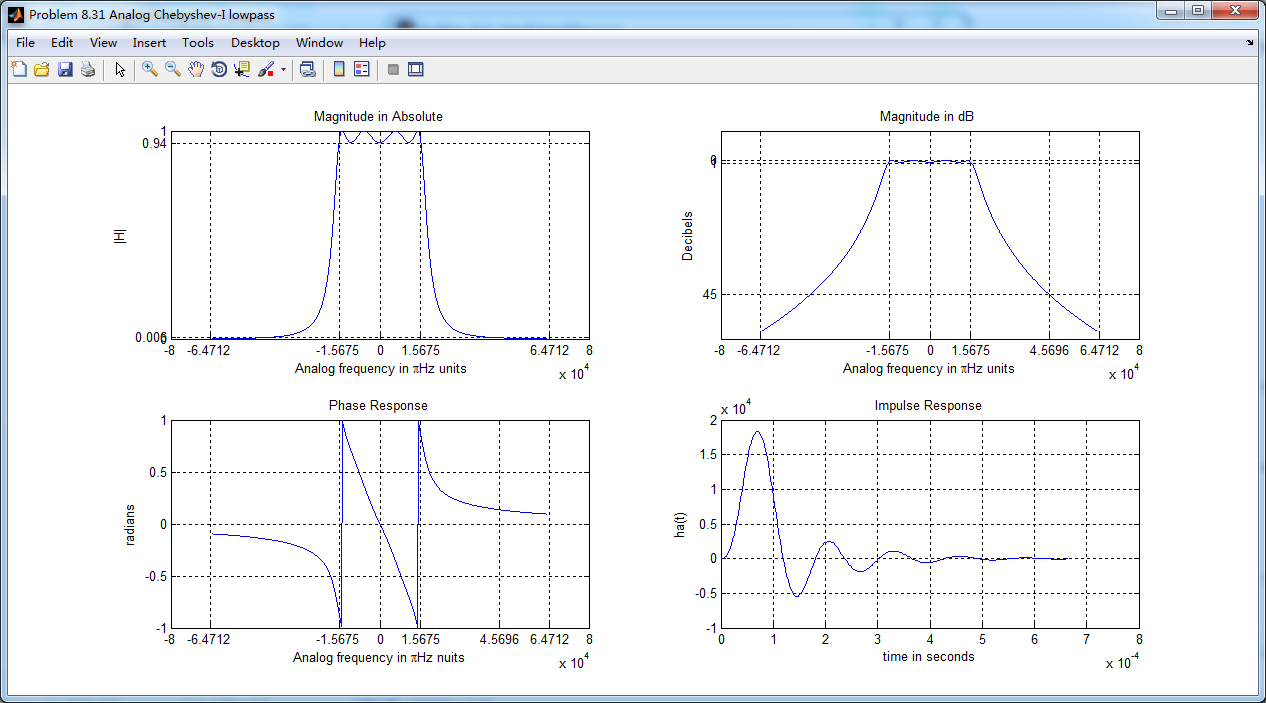
采用双线性变换法,得到数字chebyshev-1型低通滤波器,幅度谱、相位谱和群延迟响应
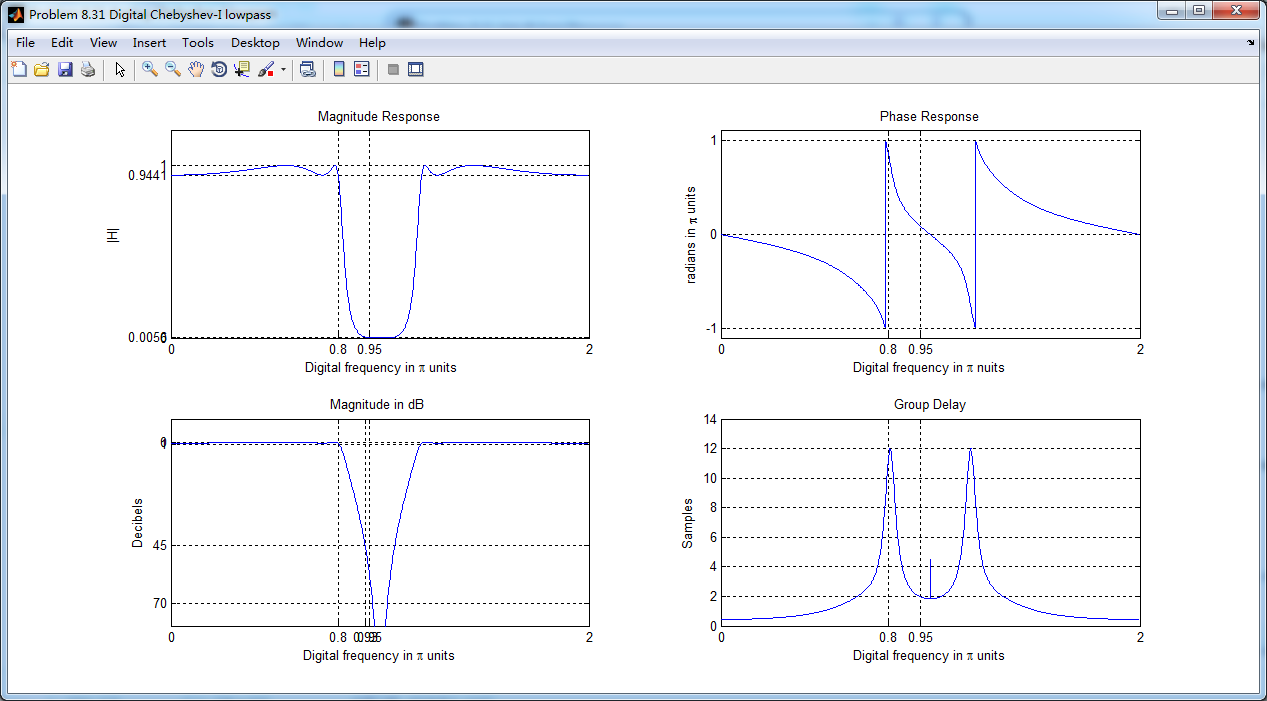
采用MATLAB自带cheby1函数得到的数字低通,其幅度谱、相位谱和群延迟

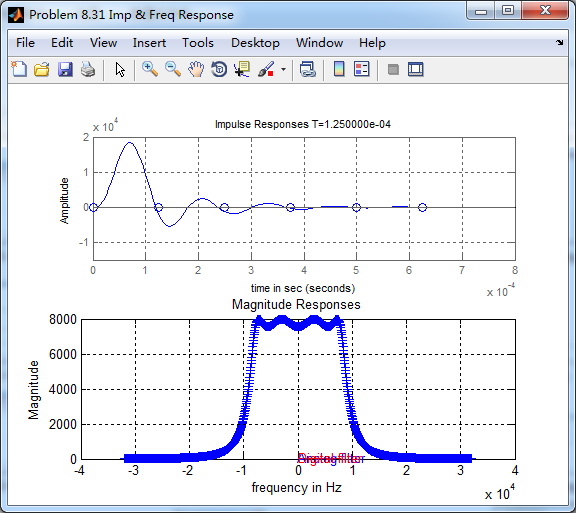
cheby1函数得到的数字低通,和相应的模拟原型的脉冲响应,二者形态不同。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.31的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.31
第3小题: 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Out ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.31
参照Example7.27,因为0.1π=2πf1 f1=0.05,0.9π=2πf2 f2=0.45 所以0.1π≤ω≤0.9π,0.05≤|H|≤0.45 代码: %% +++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.12
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.10
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.7
1.代码: function [xe,xo,m] = evenodd_cv(x,n) % % Complex signal decomposition into even and odd parts ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.6
1.代码 %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info abou ...
随机推荐
- 应用Dubbo框架打造仿猫眼项目 理解微服务核心思想
1:传统应用带来的问题 单一业务开发的迭代问题 扩容困难 部署回滚困难2:微服务概述 微服务是一种将业务系统进一步拆分的架构风格 ...
- java 对象转Map方法Demo
/** * 用于对Object进行解析并且转换成Map键值对的形式 * */ public class ObjectUtils { private static final String JAVAP ...
- vue使用CDN全局安装百度地图
参考: https://www.zhangshengrong.com/p/O3aA7x5X4E/ 一.在public/index.html中引入cdn <script src="htt ...
- PHP算法之IP 地址无效化
给你一个有效的 IPv4 地址 address,返回这个 IP 地址的无效化版本. 所谓无效化 IP 地址,其实就是用 "[.]" 代替了每个 ".". 示例 ...
- JS随机产生颜色
<script> function selectForm(lowerValue,upperValue){ var choices=upperValue-lowerValue+1; retu ...
- CSIC_716_20191114【生成器、匿名函数、内置函数、三元表达式、列表生成式、生成器表达式】
生成器: 函数与yield连用,凡是函数中有yield的,调用该函数的时候均不会立即执行,而是会返回一个生成器. 生成器本质上是一个迭代器,需要通过 [生成器.__next__()]或者[nex ...
- jmeter遇到的问题:java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect
1.使用jmeter执行脚本,在察看结果树的的响应数据中看到的错误提示如下: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect at jav ...
- 简单的 js手写轮播图
html: <div class="na1"> <div class="pp"> <div class="na ...
- 使用ProGuard混淆JAR包
1.在Input/OutPut选项下面,add input 导入需要混淆的jar包2.点击add output,设置混淆后输出jar包的名字和路径.如下图:3.在下面的编辑区右边点击add增加要混淆的 ...
- MVC到底是设计模式还是一种框架还是一种架构? https://www.zhihu.com/question/31079945
具体知乎讨论内容:https://www.zhihu.com/question/31079945 MVC到底是设计模式还是一种框架还是一种架构? 我认为它是3种设计模式的演变和组合:观察者模式(Obs ...
