c++中有些重载运算符为什么要返回引用
事实上,我们的重载运算符返回void、返回对象本身、返回对象引用都是可以的,并不是说一定要返回一个引用,只不过在不同的情况下需要不同的返回值。
那么什么情况下要返回对象的引用呢?
原因有两个:
- 允许进行连续赋值
- 防止返回对象(返回对象也可以进行连续赋值(常规的情况,如a = b = c,而不是(a = b) = c))的时候调用拷贝构造函数和析构函数导致不必要的开销,降低赋值运算符的效率。
对于第二点原因:如果用”值传递“的方式,虽然功能仍然正确,但由于return语句要把*this拷贝到保存返回值的外部存储单元之中,增加了不必要的开销,会降低赋值函数的效率。
场景:
需要返回对象引用或者返回对象(效率没有返回引用高),需要实现连续赋值,使重载的运算符更符合C++本身的运算符语意,如连续赋值 = += -= *= 、=,<<输出流
关于赋值 =,我们知道赋值=有连续等于的特性
int x,y,z;
x=y=z=;
同样有趣的是,赋值采用的是右结合律,所以上述连锁赋值被解析为:
x=(y=(z=));//赋值连锁形式
这里15先被赋值给z,然后其结果(更新后的z)再被赋值给y,然后其结果(更新后的y)再被赋值给x。
为了实现”连锁赋值“,赋值操作符号返回一个reference(引用)指向操作符号的左侧实参(而事实上重载运算符的左侧实参就是调用对象本身,比如= += -=等),这是你为classes实现赋值操作符时应该遵循的协议:这个协议不仅仅适用于以上的标准赋值形式,也适用于所有赋值运算。
class Widght{
public:
.....
Widget& operator=(cosnt Widget& rhs)
{
...
return* this;
}
Widget& operator+=(cosnt Widget& rhs)
{
...
return* this;
}
Widget& operator-=(cosnt Widget& rhs)
{
...
return* this;
}
Widget& operator*=(cosnt Widget& rhs)
{
...
return* this;
}
Widget& operator/=(cosnt Widget& rhs)
{
...
return* this;
}
...
};
注意,这只是个协议,并无强制性,如果不遵循它,代码一样可以通过编译,然而这份协议被所有内置类型和标准程序库提供的类型入string,vector,complex,std::trl::shared_ptr或者即将提供的类型共同遵守。因此除非你有一个标新立异的好理由,不然还是随众吧。
下面看一个赋值运算符重载的例子:(连续赋值,常规的情况(a = b = c))
1、首先是返回对象的情况:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char *str;
int len;
public:
String(const char* s);//构造函数声明
String operator=(const String& another);//运算符重载,此时返回的是对象
void show()
{
cout << "value = " << str << endl;
} /*copy construct*/
String(const String& other)
{
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
cout << "copy construct" << endl;
} ~String()
{
delete[] str;
cout << "deconstruct" << endl;
}
}; String::String(const char* s)//构造函数定义
{
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, s);
} String String::operator=(const String &other)//运算符重载
{
if (this == &other)
return *this;
// return;
delete[] str;
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
return *this;
// return;
} int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
str3 = str1 = str2;//str3.operator=(str1.operator=(str2))
str3.show();
str1.show();
return ;
}
运行结果:

2、下面是返回引用的情况(String& operator = (const String& str)),直接贴运行结果:

当运算符重载返回的是对象时,会在连续赋值运算过程的返回途中,调用两次拷贝构造函数和析构函数(因为return的是个新的对象)
如果采用String& operator = (const String& str)这样就不会有多余的调用(因为这里直接return一个已经存在的对象的引用)
上面的栗子也说明一点:析构函数的调用是在变量作用域结束的时候(以及程序运行结束的时候)
如果采用return对象,那么第二次赋值运算调用的情况就是:
将一个新的String对象(returnStringObj)传递到operator = (const String& str)的参数中去 相当于
const String&str = returnStringObj;
如果采用return对象引用,那么第二次赋值运算的情况就是:
将一个已经存在的String对象的引用((其实就是str1))传递给operator = (const String& str)的参数中去
const String&str = returnReference; //(String& returnReference = str1;)
+=等运算符也是同样的考虑,比如
int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
str3 = str1 = str2;//str3.operator=(str1.operator=(str2))
str3.show();
str1.show(); int num = ;
num += (num += );
cout << num << endl;
return ;
}

如果使用+=或其它上面举出的运算符进行连续操作时,,则这些运算符的返回值一定要是一个对象或者引用才行,不然就会出现错误(参数类型不符合)。什么意思呢,下面举个栗子。
我现在让运算符重载返回的类型为空,单个赋值,不使用连续赋值:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char *str;
int len;
public:
String(const char* s);//构造函数声明
void operator=(const String& another);//运算符重载,此时返回为空
void show()
{
cout << "value = " << str << endl;
} /*copy construct*/
String(const String& other)
{
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
cout << "copy construct" << endl;
} ~String()
{
delete[] str;
cout << "deconstruct" << endl;
}
}; String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, s);
} void String::operator=(const String &other)
{
if (this == &other)
// return *this;
return;
delete[] str;
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
// return *this;
return;
} int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
str3 = str1;//这样OK
str3.show();
str1.show();
return ;
}
运行结果:
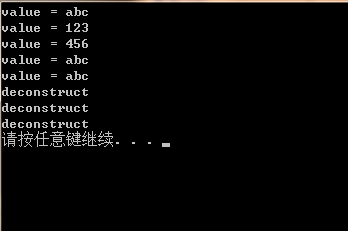
但当我把主函数中str1,str2,str3改为连续赋值时:
int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
str3 = str1=str2;//这样不OK
str3.show();
str1.show();
return ;
}
出错:

所以,当你确定不使用连续赋值时,直接返回void也是可以的。要明白一点:
运算符左侧的对象就是操作对象,比如
ObjectA = ObjectB 等同于ObjectA.operator=(ObjectB)
ObjectA+=ObjectB 等同于ObjectA.operator+(ObjectB)
最后要说明一点:并非必须返回引用,返回引用的好处既可以避免拷贝构造函数和析构函数的调用,又可以保证= +=等运算符的原始语义清晰。
啥叫原始语义清晰呢?
如
(str3 = str1) = str2;
我们的意识里,就是先执行括号内容,即str1赋值给str3,然后str2再赋值给str3,最后str3输出的内容是str2的。
即如果运算符重载返回的是对象引用时,
//返回的是对象引用的情况
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char *str;
int len;
public:
String(const char* s);//构造函数声明
String& operator=(const String& another);//运算符重载,此时返回为引用
void show()
{
cout << "value = " << str << endl;
} /*copy construct*/
String(const String& other)
{
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
cout << "copy construct" << endl;
} ~String()
{
delete[] str;
cout << "deconstruct" << endl;
}
}; String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, s);
} String& String::operator=(const String &other)
{
if (this == &other)
return *this;
// return;
delete[] str;
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
return *this;
// return;
} int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
(str3 = str1) = str2;
cout << "str3的内容为:" << endl;
str3.show();
return ;
}
运行结果:

str3得到了str2的内容,与我们认识的‘=’运算符逻辑相符。
而如果运算符重载返回的是对象时,
//这是返回类型为对象的情况
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
private:
char *str;
int len;
public:
String(const char* s);//构造函数声明
String operator=(const String& another);//运算符重载,此时返回为空
void show()
{
cout << "value = " << str << endl;
} /*copy construct*/
String(const String& other)
{
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
cout << "copy construct" << endl;
} ~String()
{
delete[] str;
cout << "deconstruct" << endl;
}
}; String::String(const char* s)
{
len = strlen(s);
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, s);
} String String::operator=(const String &other)
{
if (this == &other)
return *this;
// return;
delete[] str;
len = other.len;
str = new char[len + ];
strcpy(str, other.str);
return *this;
// return;
} int main()
{
String str1("abc");
String str2("");
String str3("");
str1.show();
str2.show();
str3.show();
(str3 = str1) = str2;
cout << "赋值后str3的内容为:" << endl;
str3.show();
return ;
}
运行结果:

str3只得到了str1的内容,并没有得到str2的内容,这是因为执行(str3=str1)后,因为返回的是对象(一个临时对象,str3的一个拷贝),不是引用,所以此时str3不在后面的‘=str2’的操作中,而是str2对一个临时对象赋值,所以str3的内容保持不变(等于str1)。
总结
所以,对此类运算符重载时,还是老老实实的返回引用,少搞事,做个好男孩:)
c++中有些重载运算符为什么要返回引用的更多相关文章
- C++ 重载运算符和重载函数
C++ 重载运算符和重载函数 C++ 允许在同一作用域中的某个函数和运算符指定多个定义,分别称为函数重载和运算符重载. 重载声明是指一个与之前已经在该作用域内声明过的函数或方法具有相同名称的声明,但是 ...
- C++解析七-重载运算符和重载函数
重载运算符和重载函数C++ 允许在同一作用域中的某个函数和运算符指定多个定义,分别称为函数重载和运算符重载.重载声明是指一个与之前已经在该作用域内声明过的函数或方法具有相同名称的声明,但是它们的参数列 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然C++语言学习笔记:C++ 重载运算符和重载函数
C++ 允许在同一作用域中的某个函数和运算符指定多个定义,分别称为函数重载和运算符重载. 重载声明是指一个与之前已经在该作用域内声明过的函数或方法具有相同名称的声明,但是它们的参数列表和定义(实现)不 ...
- c++的重载运算符
c++中允许重载运算符: 这是我辛苦的结果 #include"iostream"using namespace std;class aaa{ int x;public: aaa() ...
- JavaScript中的逗号运算符
JavaScript逗号运算符 阅读本文的前提,明确表达式.短语.运算符.运算数这几个概念. 所谓表达式,就是一个JavaScript的“短语”,JavaScript解释器可以计算它,从而生成一个值 ...
- C++ 重载运算符简单举例
我们可以重定义或重载大部分 C++ 内置的运算符.这样,就能使用自定义类型的运算符. 重载的运算符是带有特殊名称的函数,函数名是由关键字 operator 和其后要重载的运算符符号构成的.与其他函数一 ...
- C++中,用类和重载运算符写高精模板
先放代码: #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; s ...
- 高精度运算略解 在struct中重载运算符
高精度 高精度,即高精度算法,属于处理大数字的数学计算方法.在一般的科学计算中,会经常算到小数点后几百位或者更多,当然也可能是几千亿几百亿的大数字. 重载运算符 运算符重载,就是对已有的运算符重新进行 ...
- 【C++】C++中重载运算符和类型转换
输入输出运算符 输入输出运算符 输入输出运算符 算术和关系运算符 相等运算符 关系运算符 赋值运算符 复合赋值运算符 下标运算符 递增和递减运算符 成员访问运算符 函数调用运算符 lambda是函数对 ...
随机推荐
- NFS和mount常用参数详解
NFS权限参数配置 ro 只读访问 rw 读写访问 sync 所有数据在请求时写入共享 async NFS在写入数据前可以相应请求 secure NFS通过1024以下的安全TCP/IP端口发送 in ...
- bufferedimage 转换成 inputstream并保存文件
BufferedImage img = removeBackgroud(file);//去除重影 //bufferedimage 转换成 inputstream ByteArrayOutputStre ...
- Java微博搜索关键字采集
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import ja ...
- jquery验证手机号码和固定电话号码
<pre name="code" class="javascript"> //验证手机号码或者电话号码 function checkContactN ...
- [转]servlet的执行原理与生命周期
一.先从servlet容器说起:大家最为熟悉的servlet容器就是Tomcat ,Servlet 容器是如何管理 Servlet? 先看一下tomcat的容器模型: 从上图可以看出 Tomcat 的 ...
- IN和EXISTS的详解
从效率来看: 1) select * from T1 where exists(select 1 from T2 where T1.a=T2.a) ; T1数据量小而T2数据量非常大时,T1<& ...
- 五步搞定Android开发环境部署——非常详细的Android开发环境搭建教程
在windows安装Android的开发环境不简单也说不上算复杂,本文写给第一次想在自己Windows上建立Android开发环境投入Android浪潮的朋友们,为了确保大家能顺利完成开发环境的搭 ...
- 《转载》化繁为简 如何向老婆解释MapReduce?
本文转载自http://server.zol.com.cn/329/3295529.html 昨天,我在Xebia印度办公室发表了一个关于MapReduce的演说.演说进行得很顺利,听众们都能够理解M ...
- 【leetcode】Insert Interval
Insert Interval Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals ( ...
- python之打包相关
打包手册:https://python-packaging-user-guide.readthedocs.org/en/latest/installing.html#installing-from-a ...
