MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, Documents
MongoDB stores data records as BSON documents. BSON is a binary representation of JSON documents, though it contains more data types than JSON. For the BSON spec, see bsonspec.org. See also BSON Types.
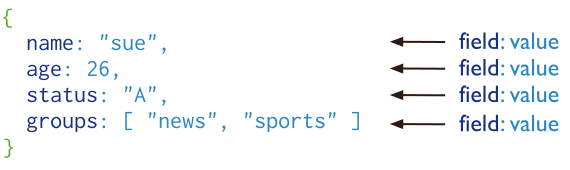
Document Structure
MongoDB documents are composed of field-and-value pairs and have the following structure:
- {
- field1: value1,
- field2: value2,
- field3: value3,
- ...
- fieldN: valueN
- }
The value of a field can be any of the BSON data types, including other documents, arrays, and arrays of documents. For example, the following document contains values of varying types:
- var mydoc = {
- _id: ObjectId("5099803df3f4948bd2f98391"),
- name: { first: "Alan", last: "Turing" },
- birth: new Date('Jun 23, 1912'),
- death: new Date('Jun 07, 1954'),
- contribs: [ "Turing machine", "Turing test", "Turingery" ],
- views : NumberLong(1250000)
- }
The above fields have the following data types:
- _id holds an ObjectId.
- name holds an embedded document that contains the fields first and last.
- birth and death hold values of the Date type.
- contribs holds an array of strings.
- views holds a value of the NumberLong type.
Field Names
Field names are strings.
Documents have the following restrictions on field names:
- The field name _id is reserved for use as a primary key; its value must be unique in the collection, is immutable, and may be of any type other than an array.
- The field names cannot start with the dollar sign ($) character.
- The field names cannot contain the dot (.) character.
- The field names cannot contain the null character.
BSON documents may have more than one field with the same name. Most MongoDB interfaces, however, represent MongoDB with a structure (e.g. a hash table) that does not support duplicate field names. If you need to manipulate documents that have more than one field with the same name, see the driver documentation for your driver.
Some documents created by internal MongoDB processes may have duplicate fields, but no MongoDB process will ever add duplicate fields to an existing user document.
Field Value Limit
For indexed collections, the values for the indexed fields have a Maximum Index Key Length limit. See Maximum Index Key Length for details.
Dot Notation
MongoDB uses the dot notation to access the elements of an array and to access the fields of an embedded document.
Arrays
To specify or access an element of an array by the zero-based index position, concatenate the array name with the dot (.) and zero-based index position, and enclose in quotes:
- "<array>.<index>"
For example, given the following field in a document:
- {
- ...
- contribs: [ "Turing machine", "Turing test", "Turingery" ],
- ...
- }
To specify the third element in the contribs array, use the dot notation "contribs.2".
SEE ALSO:
- $ positional operator for update operations,
- $ projection operator when array index position is unknown
- Query on Arrays for dot notation examples with arrays.
Embedded Documents
To specify or access a field of an embedded document with dot notation, concatenate the embedded document name with the dot (.) and the field name, and enclose in quotes:
- "<embedded document>.<field>"
For example, given the following field in a document:
- {
- ...
- name: { first: "Alan", last: "Turing" },
- contact: { phone: { type: "cell", number: "111-222-3333" } },
- ...
- }
- To specify the field named last in the name field, use the dot notation "name.last".
- To specify the number in the phone document in the contact field, use the dot notation "contact.phone.number".
SEE ALSO: Query on Embedded Documents for dot notation examples with embedded documents.
Document Limitations
Documents have the following attributes:
Document Size Limit
The maximum BSON document size is 16 megabytes.
The maximum document size helps ensure that a single document cannot use excessive amount of RAM or, during transmission, excessive amount of bandwidth. To store documents larger than the maximum size, MongoDB provides the GridFS API. See mongofiles and the documentation for your driver for more information about GridFS.
Document Field Order
MongoDB preserves the order of the document fields following write operations except for the following cases:
- The _id field is always the first field in the document.
- Updates that include renaming of field names may result in the reordering of fields in the document.
Changed in version 2.6: Starting in version 2.6, MongoDB actively attempts to preserve the field order in a document. Before version 2.6, MongoDB did not actively preserve the order of the fields in a document.
The _id Field
In MongoDB, each document stored in a collection requires a unique _id field that acts as a primary key. If an inserted document omits the _id field, the MongoDB driver automatically generates an ObjectId for the _id field.
This also applies to documents inserted through update operations with upsert: true.
The _id field has the following behavior and constraints:
By default, MongoDB creates a unique index on the _id field during the creation of a collection.
The _id field is always the first field in the documents. If the server receives a document that does not have the _id field first, then the server will move the field to the beginning.
The _id field may contain values of any BSON data type, other than an array.
WARNING: To ensure functioning replication, do not store values that are of the BSON regular expression type in the _id field.
The following are common options for storing values for _id:
Use an ObjectId.
Use a natural unique identifier, if available. This saves space and avoids an additional index.
Generate an auto-incrementing number.
Generate a UUID in your application code. For a more efficient storage of the UUID values in the collection and in the _id index, store the UUID as a value of the BSON BinData type.
Index keys that are of the BinData type are more efficiently stored in the index if:
- the binary subtype value is in the range of 0-7 or 128-135, and
- the length of the byte array is: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20, 24, or 32.
Use your driver’s BSON UUID facility to generate UUIDs. Be aware that driver implementations may implement UUID serialization and deserialization logic differently, which may not be fully compatible with other drivers. See your driver documentation for information concerning UUID interoperability.
NOTE: Most MongoDB driver clients will include the _id field and generate an ObjectId before sending the insert operation to MongoDB; however, if the client sends a document without an _id field, the mongod will add the _id field and generate the ObjectId.
Other Uses of the Document Structure
In addition to defining data records, MongoDB uses the document structure throughout, including but not limited to: query filters, update specifications documents, and index specification documents
Query Filter Documents
Query filter documents specify the conditions that determine which records to select for read, update, and delete operations.
You can use <field>:<value> expressions to specify the equality condition and query operator expressions.
- {
- <field1>: <value1>,
- <field2>: { <operator>: <value> },
- ...
- }
For examples, see Query filters or specifications.
Update Specification Documents
Update specification documents use update operators to specify the data modifications to perform on specific fields during an db.collection.update() operation.
- {
- <operator1>: { <field1>: <value1>, ... },
- <operator2>: { <field2>: <value2>, ... },
- ...
- }
For examples, see Update specifications.
Index Specification Documents
Index specifications document define the field to index and the index type:
- { <field1>: <type1>, <field2>: <type2>, ... }
MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, Documents的更多相关文章
- MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, Capped Collections
Overview Capped collections are fixed-size collections that support high-throughput operations that ...
- MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, MongoDB Extended JSON
JSON can only represent a subset of the types supported by BSON. To preserve type information, Mongo ...
- MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB
MongoDB is an open-source document database that provides high performance, high availability, and a ...
- MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, BSON Types
BSON is a binary serialization format used to store documents and make remote procedure calls in Mon ...
- MongoDB - Introduction to MongoDB, Databases and Collections
MongoDB stores BSON documents, i.e. data records, in collections; the collections in databases. Data ...
- mongoDB & Nodejs 访问mongoDB (一)
最近的毕设需要用到mongoDB数据库,又把它拿出来再学一学,下盘并不是很稳,所以做一些笔记,不然又忘啦. 安装 mongoDB & mongoVUE mongoDB: https://www ...
- java操作mongodb & springboot整合mongodb
简单的研究原生API操作MongoDB以及封装的工具类操作,最后也会研究整合spring之后作为dao层的完整的操作. 1.原生的API操作 pom.xml <!-- https://mvnre ...
- mongoDB操作命令及mongoDB的helper
此项目已开源,开源地址是: http://mongodbhelper-csharp.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ mongodb的helper using System; usi ...
- mongodb系列之--mongodb 主从配置与说明
一.为什么要配置mongodb的主从: 1.做主从,可以说是做数据的备份,有利于故障的恢复 2.做主从,可以做到读写分离,主节点负责写操作,从节点负责读操作,这样就把读写压力分开,保证系统的稳定性. ...
随机推荐
- 简单的圆形图标鼠标hover效果 | CSS3教程
演示 本教程将和大将分享一些简单的圆形图标在鼠标hover时的动画效果.这种效果在不少时尚的酷站上都有.本教程中的例子主要是利用在a元素的伪元素上使用CSS transitions和animation ...
- Codeforces Round #245 (Div. 1) B. Working out (简单DP)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/429/B 给你一个矩阵,一个人从(1, 1) ->(n, m),只能向下或者向右: 一个人从(n, ...
- TypeScript学习笔记(一):介绍及环境搭建
官网 TypeScript目前还在快速的发展中,当前的版本是1.6,有关TypeScript更多的信息可以在其官网中获取. http://www.typescriptlang.org/ 什么是Type ...
- SQL Server 数据类型映射 (ADO.NET)
SQL Server 数据类型映射 (ADO.NET) .NET Framework 3.5 更新:November 2007 SQL Server 和 .NET Framework 基于不同的类型系 ...
- Javascript继承实现
S1:js中一切皆对象,想想如果要实现对父对象属性和方法的继承,最初我们会怎样子来实现呢,考虑到原型的概念,最初我是这样来实现继承的 function Parent(){ this.name='123 ...
- [0.1]Plan of kidsearch
To be honest, it's not pretty easy to complete the project. So we have to sort out ideas first. In t ...
- URAL 1780 G - Gray Code 找规律
G - Gray CodeTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/view ...
- MyBatis之二:简单增删改查
这一篇在上一篇的基础上简单讲解如何进行增删改查操作. 一.在mybatis的配置文件conf.xml中注册xml与注解映射 <!-- 注册映射文件 --> <mappers> ...
- C语言默认參数值的实现
from http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/25437893 C语言中没有參数默认值的概念,能够利用宏来模拟參数默认值: (对于有多个參数的 ...
- u检验、t检验、F检验、X2检验 (转)
http://blog.renren.com/share/223170925/14708690013 常用显著性检验 1.t检验 适用于计量资料.正态分布.方差具有齐性的两组间小样本比较.包括配对资料 ...
