推荐 的FPGA设计经验(4) 时钟和寄存器控制架构特性使用
Use Clock and Register-Control Architectural Features
FPGAs provide device-wide clocks and register control signals that can improve performance.
Use Global Clock Network Resources
Altera FPGAs provide device-wide global clock routing resources and dedicated inputs. Use the FPGA’s low-skew, high fan-out dedicated routing where available.
FPGAs offer a number of low-skew global routing resources to distribute high fan-out signals to help withthe implementation of large designs with many clock domains.
Use Global Reset Resources
ASIC designs may use local resets to avoid long routing delays. Take advantage of the device-wide asynchronous reset pin available on most FPGAs to eliminate these problems. This reset signal provides low-skew routing across the device.
The following are three types of resets used in synchronous circuits:
• Synchronous Reset
• Asynchronous Reset
• Synchronized Asynchronous Reset—preferred when designing an FPGA circuit
Use Synchronous Resets
The synchronous reset ensures that the circuit is fully synchronous. You can easily time the circuit with the Quartus Prime TimeQuest analyzer.
Because clocks that are synchronous to each other launch and latch the reset signal, the data arrival and data required times are easily determined for proper slack analysis. The synchronous reset is easier to use with cycle-based simulators.
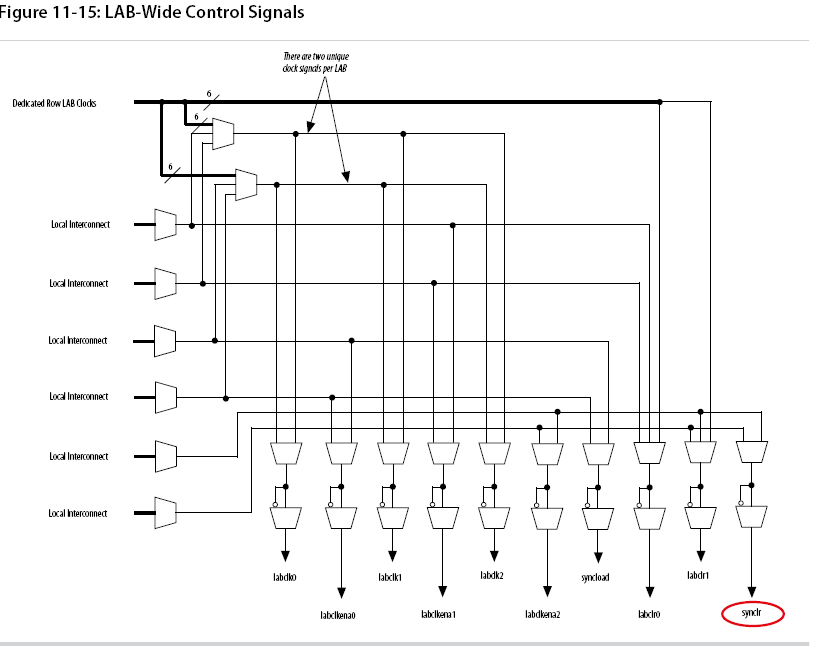
There are two methods by which a reset signal can reach a register; either by being gated in with the data input, or by using an LAB-wide control signal (synclr).
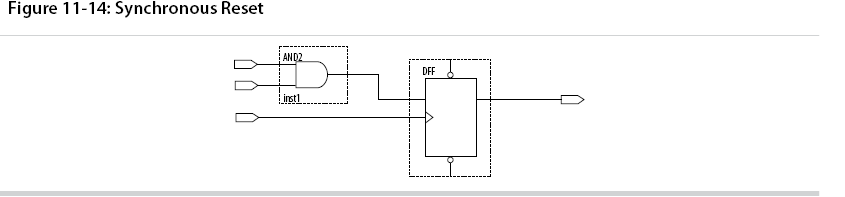
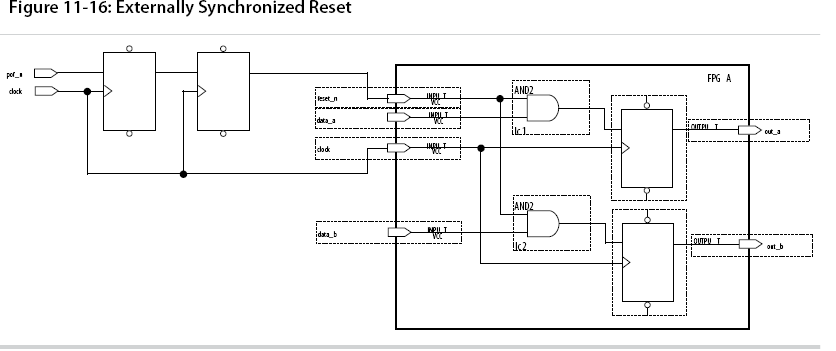
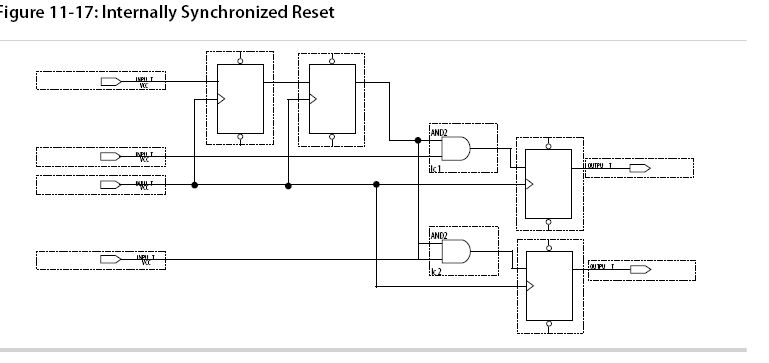
Consider two types of synchronous resets when you examine the timing analysis of synchronous resets—externally synchronized resets and internally synchronized resets.
module sync_reset_ext (
input clock,
input reset_n,
input data_a,
input data_b,
output out_a,
output out_b
);
reg reg1, reg2;
assign out_a = reg1;
assign out_b = reg2;
always @ (posedge clock)
begin
if (!reset_n)
begin
reg1 <= ’b0;
reg2 <= ’b0;
end
else
begin
reg1 <= data_a;
reg2 <= data_b;
end
end
endmodule // sync_reset_ext
verilog code for externally synchronized reset
module sync_reset (
input clock,
input reset_n,
input data_a,
input data_b,
output out_a,
output out_b
);
reg reg1, reg2;
reg reg3, reg4;
assign out_a = reg1;
assign out_b = reg2;
assign rst_n = reg4;
always @ (posedge clock)
begin
if (!rst_n)
begin
reg1 <= ’bo;
reg2 <= ’b0;
end
else
begin
reg1 <= data_a;
reg2 <= data_b;
end
end
always @ (posedge clock)
begin
reg3 <= reset_n;
reg4 <= reg3;
end
endmodule // sync_reset
verilog code for internally synchronized reset
In some cases, you might want to increase the noise immunity further and reject any asynchronous input reset that is less than n periods wide to debounce an asynchronous input reset.
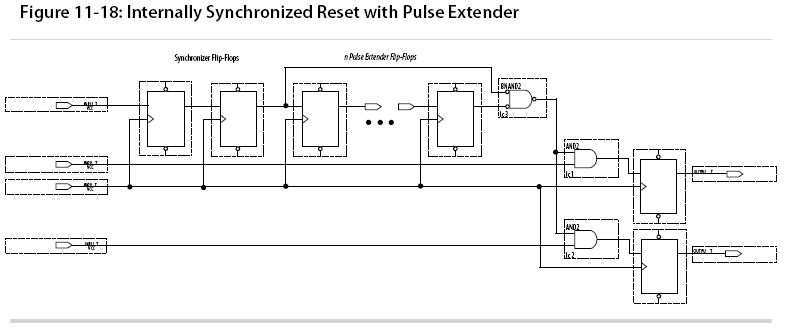
Using Asynchronous Resets
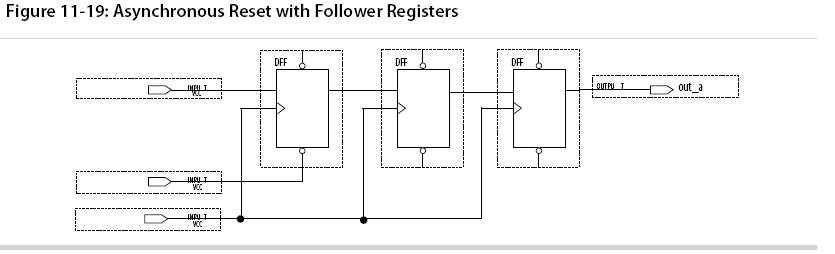
Asynchronous resets are the most common form of reset in circuit designs, as well as the easiest to implement.
However, when the reset is deasserted and does not pass the recovery (μtSU) or removal (μtH) time check (the TimeQuest analyzer recovery and removal analysis checks both times), the edge is said to have fallen into the metastability zone.
To avoid this, add a few follower registers after the register with the asynchronous reset and use the output of these registers in the
design.
module async_reset (
input clock,
input reset_n,
input data_a,
output out_a,
);
reg reg1, reg2, reg3;
assign out_a = reg3;
always @ (posedge clock, negedge reset_n)
begin
if (!reset_n)
reg1 <= ’b0;
else
reg1 <= data_a;
end
always @ (posedge clock)
begin
reg2 <= reg1;
reg3 <= reg2;
end
endmodule // async_reset
verilog code of asychronous reset with follower register
The asynchronous reset is susceptible to noise, and a noisy asynchronous reset can cause a spurious reset. You must ensure that the asynchronous reset is debounced and filtered. You can easily enter into a reset asynchronously, but releasing a reset asynchronously can lead to potential problems (also referred to as “reset removal”) with metastability, including the hazards of
unwanted situations with synchronous circuits involving feedback.
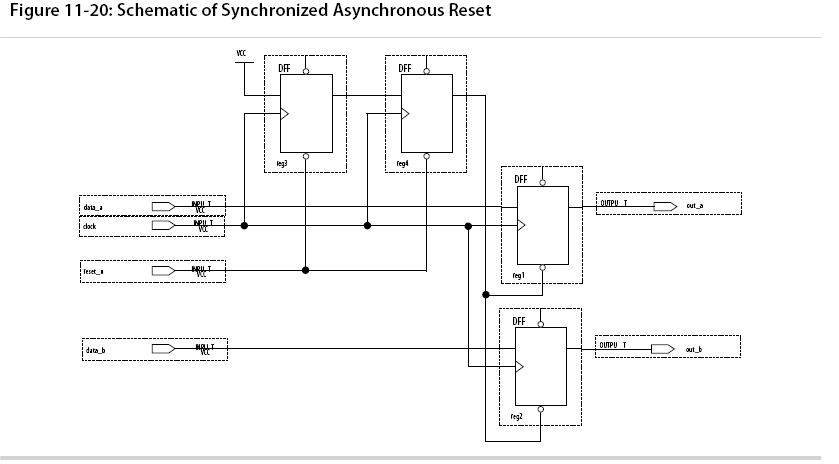
Use Synchronized Asynchronous Reset
To avoid potential problems associated with purely synchronous resets and purely asynchronous resets, you can use synchronized asynchronous resets. Synchronized asynchronous resets combine the advantages of synchronous and asynchronous resets.
This takes effect almost instantaneously, and ensures that no data path for speed is involved, and that the circuit is synchronous for timing analysis and is resistant to noise.
module sync_async_reset (
input clock,
input reset_n,
input data_a,
input data_b,
output out_a,
output out_b
);
reg reg1, reg2;
reg reg3, reg4;
assign out_a = reg1;
assign out_b = reg2;
assign rst_n = reg4;
always @ (posedge clock, negedge reset_n)
begin
if (!reset_n)
begin
reg3 <= ’b0;
reg4 <= ’b0;
end
else
begin
reg3 <= ’b1;
reg4 <= reg3;
end
end
always @ (posedge clock, negedge rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
begin
reg1 <= ’b0;
reg2 <= ;b0;
end
else
begin
reg1 <= data_a;
reg2 <= data_b;
end
end
endmodule // sync_async_reset
verilog code for synchronized asynchronous reset
To minimize the metastability effect between the two synchronization registers, and to increase
the MTBF, the registers should be located as close as possible in the device to minimize routing delay. If possible, locate the registers in the same logic array block (LAB).
Avoid Asynchronous Register Control Signals
Avoid using an asynchronous load signal if the design target device architecture does not include registers with dedicated circuitry for asynchronous loads. Also, avoid using both asynchronous clear and preset if the architecture provides only one of these control signals.
When the target device does not directly support the signals, the synthesis or placement and routing software must use combinational logic to implement the same functionality. In addition, if you use signals in a priority other than the inherent priority in the device architecture, combinational logic may be required to implement the necessary control signals. Combinational logic is less efficient and can cause glitches and other problems; it is best to avoid these implementations.
Implementing Embedded RAM
Altera’s dedicated memory architecture offers many advanced features that you can enable with Altera provided IP cores. Use synchronous memory blocks for your design, so that the blocks can be mapped directly into the device dedicated memory blocks.
In many synthesis tools, you can specify that the read-during-write behavior is not important to your design; if, for example, you never read and write from the same address in the same clock cycle. For
Quartus Prime integrated synthesis, add the synthesis attribute ramstyle=”no_rw_check” to allow the software to choose the read-during-write behavior of a RAM, rather than using the read-during-write
behavior specified in your HDL code. Using this type of attribute prevents the synthesis tool from using extra logic to implement the memory block and, in some cases, can allow memory inference when it
would otherwise be impossible.
推荐 的FPGA设计经验(4) 时钟和寄存器控制架构特性使用的更多相关文章
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(2)-时钟策略优化
Optimizing Clocking Schemes Avoid using internally generated clocks (other than PLLs) wherever possi ...
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(3) 物理实现和时间闭环优化
Optimizing Physical Implementation and Timing Closure Planning Physical Implementation When planning ...
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(1)组合逻辑优化
主要内容摘自Quartus prime Recommended Design Practices For optimal performance, reliability, and faster ti ...
- 影响FPGA设计中时钟因素的探讨。。。转
http://www.fpga.com.cn/advance/skill/speed.htm http://www.fpga.com.cn/advance/skill/design_skill3.ht ...
- FPGA分频与倍频的简单总结(涉及自己设计,调用时钟IP核,调用MMCM原语模块)
原理介绍 1.分频 FPGA设计中时钟分频是重要的基础知识,对于分频通常是利用计数器来实现想要的时钟频率,由此可知分频后的频率周期更大.一般而言实现偶数系数的分频在程序设计上较为容易,而奇数分频则相对 ...
- FPGA设计思想与技巧(转载)
题记:这个笔记不是特权同学自己整理的,特权同学只是对这个笔记做了一下完善,也忘了是从那DOWNLOAD来的,首先对整理者表示感谢.这些知识点确实都很实用,这些设计思想或者也可以说是经验吧,是很值得每一 ...
- 【设计经验】2、ISE中ChipScope使用教程
一.软件与硬件平台 软件平台: 操作系统:Windows 8.1 开发套件:ISE14.7 硬件平台: FPGA型号:XC6SLX45-CSG324 二.ChipScope介绍 ChipScope是X ...
- 【转】 FPGA设计的四种常用思想与技巧
本文讨论的四种常用FPGA/CPLD设计思想与技巧:乒乓操作.串并转换.流水线操作.数据接口同步化,都是FPGA/CPLD逻辑设计的内在规律的体现,合理地采用这些设计思想能在FPGA/CPLD设计工作 ...
- FPGA 设计流程,延迟,时间
FPGA 设计流程,延迟,时间 流程:每个时钟周期可以传输的数据比特. 延迟:从输入到时钟周期的输出数据需要经验. 时间:两个元件之间的最大延迟,最高时钟速度. 1 採用流水线能够提高 流量: 比如计 ...
随机推荐
- 解决Unity3D操作界面字体模糊的问题
新装的电脑安装了UNITY后,操作界面的字体异常模糊,搜了半天看看有没有换字体的功能,也没找到 后来快放弃的时候,偶然看到这篇文章http://eyehere.net/2014/unity3d-int ...
- Go语言(二) 继承和重载
继承 package main import "fmt" type Skills []string type person struct { name string age int ...
- r.js压缩打包(require + backbone)项目开发文件
最近项目稳定了一点,之前一直没空关注的开发文件压缩打包问题也有时间来解决了 AMD模块化开发中的代码压缩打包工具——r.js 环境搭建基于nodejs:用于AMD模块化开发中的项目文件压缩打包,不是A ...
- python进阶介绍(进阶1)
转载请标明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/why168888/p/6411664.html 本文出自:[Edwin博客园] python进阶介绍(进阶1) 1. python基础 ...
- vim使用常看
原网址http://www.runoob.com/linux/linux-vim.html 补充参考https://blog.csdn.net/w178191520/article/details/8 ...
- SSH2整合需要jar包解释
hibernate3.jar, Hibernate的库,必须使用的jar包 antlr-2.7.6.jar, 语法分析生成器 语言转换工具,hibernate利用它实现HQL到SQL的转换 cglib ...
- ctrl + alt + o 快速删除掉没有使用的 import
ctrl + alt + o 优化导入,可以快速删除掉没有使用的 import
- CTSC2018 && APIO2018 && SDOI2018R2游记
Day -? 占个坑先.希望CTSC,APIO别打铁,R2别滚粗QAQ CTSC Day 0 早起坐车睡觉颓废报道颓废 反正游记就是咕懒得写了 Day 1 早上四点被xp的闹钟吵醒(???还两次) 幸 ...
- ThinkPHP3.2.3快速入门:基础篇
一.安装 thinkphp无需安装,只需将从官网上下载的压缩包解压后,把所有文件放到localhost根目录里就行了 二.压缩包中文件简述 :应用程序文件夹.自己所写的文件都放在这个文件夹里面 :公用 ...
- Selenium基础知识(8大元素定位概说)
1. By.name() 页面源码如下: [html] : <button id="gbqfba"aria-label="Google Search" n ...
