一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之一:getSingleton方法
要想讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期,真的是不容易,以AnnotationConfigApplicationContext上下文为基础来讲解bean的生命周期,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是基于注解的上下文,使用XML的方式现在很少见,所以以此上下文为基础,使用XML的上下文ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的步骤和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类似。
了解过spring源码的都知道,在AnnotationConfigApplicationContext中调用了父类AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法,
refresh方法中调用了10个左右的方法,具体方法不一一细看,看今天分析的重点方法finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法,
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
在该方法中又调用了preInstantiateSingletons()方法,这个方法才是今天的主角,在该方法中会生成所有非懒加载的单例bean。方法定义如下,
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
} // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
} // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
该方法完成的主要逻辑是遍历所有的beanName,调用getBean(beanName)方法生成单例bean,在遍历过程中对FactoryBean做了特殊的判断,大家都知道FactoryBean是一种特殊的bean,在《spring中FactoryBean是什么bean》重点分析该bean。重点看getBean(beanName)方法,getBean(beanName)方法调用了doGetBean(beanName)方法,
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
doGetBean方法定义如下,
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
} // Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
} if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
} try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
} // Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
} // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
doGetBean方法中有getSingleton、getObjectForBeanInstance、createBean等方法是很重要的。在doGetBean方法中首先调用getSingleton方法检查单例缓存中是否有该bean,如果没有则判断当前bean的作用域是单例(singleton)还是原型(prototype),如果是单例的,再次调用getSingleton方法,不过这次的该方法是重载的一个;如果是原型的则调用createBean方法生成bean,上面几个步骤生成的beanInstance均要调用getObjectForBeanInstance方法获得bean对象。先看getSingleton方法
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
在该方法中涉及到三个对象singletonObjects、earlySingletonObjects、singletonFactories,使用这三个对象可以很好的解决循环依赖的问题,这里暂时不讲这个,先看其中的逻辑,
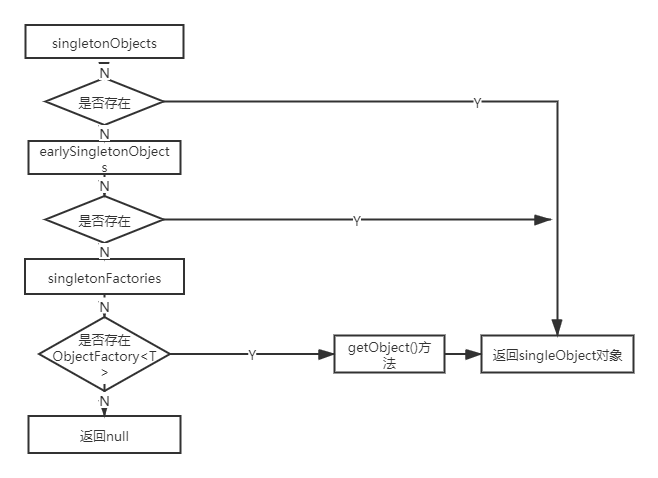
执行的逻辑大概是上面的过程。对singletonObject、earlySingletonObjects、singletonFactories逐级判断,其中singletonFactories中存储的是提前暴露的实例工厂,用来生成一个实例或者实例的代理类。
本文重点对spring生成bean的入门进行了分析,重点分析了代码的调用过程及getSingleton方法,该方法还有一个重载的方法,放到后面分析。

一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之一:getSingleton方法的更多相关文章
- 一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之二:FactoryBean的前世今生
前言 在<spring中FactoryBean是什么bean>一文中,带着小伙伴学习了spring中的FactoryBean,了解了到了FactoryBean其实是一种生产Bean的bea ...
- 一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之三:bean是如何实例化的
在前面的两篇博文<一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之一:getSingleton方法>和<一次性讲清楚spring中bean的生命周期之二:FactoryBean的前世今 ...
- JAVA面试题:Spring中bean的生命周期
Spring 中bean 的生命周期短暂吗? 在spring中,从BeanFactory或ApplicationContext取得的实例为Singleton,也就是预设为每一个Bean的别名只能维持一 ...
- 深入理解Spring中bean的生命周期
[Spring中bean的生命周期] bean的生命周期 1.以ApplocationContext上下文单例模式装配bean为例,深入探讨bean的生命周期: (1).生命周期图: (2).具体事例 ...
- Spring中Bean的生命周期及其扩展点
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址http://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/6106456.html Spring中Bean的管理是其最基本的功能,根据下面的图来了解Spr ...
- 简:Spring中Bean的生命周期及代码示例
(重要:spring bean的生命周期. spring的bean周期,装配.看过spring 源码吗?(把容器启动过程说了一遍,xml解析,bean装载,bean缓存等)) 完整的生命周期概述(牢记 ...
- 通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期
通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期及AOP原理 Spring源码解析(十一)Spring扩展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProces ...
- 一分钟掌握Spring中bean的生命周期!
Spring 中bean 的生命周期短暂吗? 在spring中,从BeanFactory或ApplicationContext取得的实例为Singleton,也就是预设为每一个Bean 的别名只能维持 ...
- Spring中bean的生命周期!
Spring 中bean 的生命周期短暂吗? 在spring中,从BeanFactory或ApplicationContext取得的实例为Singleton,也就是预设为每一个Bean的别名只能维持一 ...
随机推荐
- 游戏视野系统算法 (FOV using recursive shadowcasting)
原理 http://www.roguebasin.com/index.php?title=FOV_using_recursive_shadowcasting python代码实现 http://www ...
- 进程间IPC通信-stop waiting for thing to happen,go out and make them happen!!!
进程间通信: System V IPC对象: ipcs -q:查看消息队列 ipcs -m:查看共享内存 ipcs -s:查看信号灯集 ipcrm -q:删除消息队列 ipcrm -m:删除共 ...
- Linux信号与golang中的捕获处理
什么是信号 在计算机科学中,信号是Unix.类Unix以及其他POSIX兼容的操作系统中进程间通讯的一种有限制的方式.它是一种异步的通知机制,用来提醒进程一个事件已经发生. 当一个信号发送给一个进程, ...
- createrepo 建立本地yum源
linux使用createrepo制作本地yum源 目录 linux使用createrepo制作本地yum源 安装createrepo软件包 进入本地rpm包目录 执行完后可以看到生成的repod ...
- 查看当前目录下文件个数: $find ./ | wc -l
2.1. 创建和删除 创建:mkdir 删除:rm 删除非空目录:rm -rf file目录 删除日志 rm *log (等价: $find ./ -name "*log" -ex ...
- tail -n 10 /etc/passwd
# tail -n 10 /etc/passwdrpc:x:32:32:Rpcbind Daemon:/var/lib/rpcbind:/sbin/nologinchrony:x:992:987::/ ...
- S7 Linux用户管理及用户信息查询命令
7.1 useradd:创建用户 7.2-5 usermod 7.6 passwd:修改用户密码 7.7-9 chage.chpasswd.su 7.10-11 visudo.sudo 7.12-7. ...
- python3 访问windows共享目录
python3 访问windows共享目录 1.安装pysmb包 pip install pysmb 2.连接共享目录 #!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf- ...
- 5分钟安装docker教程
Centos安装docker需要操作系统是 CentOS 7 or 8,必须启用centos extras存储库.默认情况下,此存储库处于启用状态,但如果已禁用它,则需要重新启用它. 卸载旧版本 老版 ...
- Docker环境下运行python+selenium+chrome
Docker环境下运行python+selenium+chrome docker运行时占用的资源非常少,而且能将环境进行有效的隔离,可以快速的进行部署,因此可以将docker与selenium结合实现 ...
