MyBatis源码浅析
什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手工设置参数以及抽取结果集。MyBatis 使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射基本体,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
MyBatis简单示例
虽然在使用MyBatis时一般都会使用XML文件,但是本文为了分析程序的简单性,简单的测试程序将不包含XML配置,该测试程序包含一个接口、一个启动类:
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}")
User selectUser(int id);
}
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = initSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
User user = (User) session.selectOne(
"org.mybatis.example.UserMapper.selectUser", 1);
System.out.println(user.getUserAddress());
System.out.println(user.getUserName());
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
private static SqlSessionFactory initSqlSessionFactory() {
DataSource dataSource = new PooledDataSource("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver",
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc", "root", "");
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development",
transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.addMapper(UserMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(configuration);
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}
UserMapper是一个接口,我们在构建sqlSessionFactory时通过configuration.addMapper(UserMapper.class)把该接口注册进了sqlSessionFactory中。从上面的代码中我们可以看出,要使用MyBatis,我们应该经过以下步骤:1、创建sqlSessionFactory(一次性操作);2、用sqlSessionFactory对象构造sqlSession对象;3、调用sqlSession的相应方法;4、关闭sqlSession对象。
在main方法中,我们没有配置sql,也没有根据查询结果拼接对象,只需在调用sqlSession方法时传入一个命名空间以及方法参数参数即可,所有的操作都是面向对象的。在UserMapper接口中,我们定制了自己的sql,MyBatis把书写sql的权利给予了我们,方便我们进行sql优化及sql排错。
JDBC基础回顾
直接使用JDBC是很痛苦的,JDBC连接数据库包含以下几个基本步骤:1、注册驱动 ;2、建立连接(Connection);3、创建SQL语句(Statement);4、执行语句;5、处理执行结果(ResultSet);6、释放资源,示例代码如下:
public static void test() throws SQLException{
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.建立连接 url格式 - JDBC:子协议:子名称//主机名:端口/数据库名?属性名=属性值&…
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc", "root", "");
// 3.创建语句
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
// 4.执行语句
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user");
// 5.处理结果
while (rs.next()) {
User user = new User(rs.getObject(1), rs.getObject(2));
}
// 6.释放资源
rs.close();
st.close();
conn.close();
}
可以看到与直接使用JDBC相比,MyBatis为我们简化了很多工作:
1、把创建连接相关工作抽象成一个sqlSessionFactory对象,一次创建多次使用;
2、把sql语句从业务层剥离,代码逻辑更加清晰,增加可维护性;
3、自动完成结果集处理,不需要我们编写重复代码。
但是,我们应该知道的是,框架虽然能够帮助我们简化工作,但是框架底层的代码肯定还是最基础的JDBC代码,因为这是Java平台连接数据库的通用方法,今天我将分析一下MyBatis源码,看看MyBatis是如何把这些基础代码封装成一个框架的。
MyBatis调用流程
我们最终调用的是sqlSession对象上的方法,所以我们先跟踪sqlSession的创建方法:sqlSessionFactory.openSession(),最终这个方法会调用到DefaultSqlSessionFactory的以下方法:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
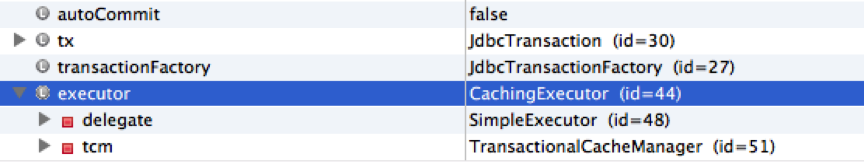
最终返回的对象是一个DefaultSqlSession对象,在调试模式下,我们看到autoCommit为false,executor为CachingExecutor类型,在CachingExecutor里面有属性delegate,其类型为simpleExecutor:
现在,我们跟进DefaultSqlSession的selectOne()方法,查看该方法的调用流程,selectOne()方法又会调用selectList()方法:
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
可以看到要得到查询结果,最终还是要调用executor上的query方法,这里的executor是CachingExecutor实例,跟进程序得到如下代码:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578. Query must be not synchronized to prevent deadlocks
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
MyBatis框架首先生成了一个boundSql和CacheKey,在boundSql中包含有我们传入的sql语句:

生成boundSql和CacheKey后会调用一个重载函数,在重载函数中,我们会检测是否有缓存,这个缓存是MyBatis的二级缓存,我们没有配置,那么直接调用最后一句delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql),前面说过这个delagate其实就是simpleExecutor,跟进去查看一下:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear(); // issue #601
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache(); // issue #482
}
}
return list;
}
关键代码是以下三行:
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
首先尝试从localCache中根据key得到List,这里的localCache是MyBatis的一级缓存,如果得不到则调用queryFromDatabase()从数据库中查询:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
其中关键代码是调用doQuery()代码,SimpleExecutor的doQuery()方法如下:
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
调用了prepareStatement方法,该方法如下:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
终于,我们看到熟悉的代码了,首先得到Connection,然后从Connection中得到Statement,同时在调试模式下我们看到,我们的sql语句已经被设置到stmt中了:

现在Statement对象有了,sql也设置进去了,就只差执行以及对象映射了,继续跟进代码,我们会跟踪到org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.
PreparedStatementHandler类的executor方法:
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
在这里,调用了ps.execute()方法执行sql,接下来调用的resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps)方法明显是对结果集进行封装,我就不继续跟进了。
MyBatis的数据库连接池
上面一部分介绍了MyBatis执行的整体流程,这一部分打算讨论一个具体话题:MyBatis的数据库连接池。
我们知道,每次连接数据库时都创建Connection是十分耗费性能的,所以我们在写JDBC代码时,一般都会使用数据库连接池,把用过的Connection不是直接关闭,而是放入数据库连接池中,方便下次复用,开源的数据库连接池有DBCP、C3P0等,MyBatis也实现了自己的数据库连接池,在这一节我将探索一下MyBatis实现的数据库连接池源码。
跟进上一节的getConnection()方法,我们最终会进入JdbcTransaction的getConnection()方法,getConnection()方法又会调用openConnection()方法,而openConnection()又将调用dataSource的getConnection()方法:
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
这里的dataSource是PooledDataSource类型,跟进查看源码如下:
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
//暂不分析
}
可以看到,在这里我们返回的对象其实已经不是原生的Connection对象了,而是一个动态代理对象,是PooledConnection的一个属性,所有对对Connection对象的操作都将被PooledConnection拦截,我们可以查看PooledConnection的定义如下:
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
private static final String CLOSE = "close";
private static final Class<?>[] IFACES = new Class<?>[] { Connection.class };
private int hashCode = 0;
private PooledDataSource dataSource;
private Connection realConnection;
private Connection proxyConnection;
private long checkoutTimestamp;
private long createdTimestamp;
private long lastUsedTimestamp;
private int connectionTypeCode;
private boolean valid;
public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.hashCode = connection.hashCode();
this.realConnection = connection;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.valid = true;
this.proxyConnection = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this);
}
public void invalidate() {
valid = false;
}
public boolean isValid() {
return valid && realConnection != null
&& dataSource.pingConnection(this);
}
public Connection getRealConnection() {
return realConnection;
}
public Connection getProxyConnection() {
return proxyConnection;
}
public int getRealHashCode() {
if (realConnection == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return realConnection.hashCode();
}
}
public int getConnectionTypeCode() {
return connectionTypeCode;
}
public void setConnectionTypeCode(int connectionTypeCode) {
this.connectionTypeCode = connectionTypeCode;
}
public long getCreatedTimestamp() {
return createdTimestamp;
}
public void setCreatedTimestamp(long createdTimestamp) {
this.createdTimestamp = createdTimestamp;
}
public long getLastUsedTimestamp() {
return lastUsedTimestamp;
}
public void setLastUsedTimestamp(long lastUsedTimestamp) {
this.lastUsedTimestamp = lastUsedTimestamp;
}
public long getTimeElapsedSinceLastUse() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - lastUsedTimestamp;
}
public long getAge() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - createdTimestamp;
}
public long getCheckoutTimestamp() {
return checkoutTimestamp;
}
public void setCheckoutTimestamp(long timestamp) {
this.checkoutTimestamp = timestamp;
}
public long getCheckoutTime() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - checkoutTimestamp;
}
public int hashCode() {
return hashCode;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof PooledConnection) {
return realConnection.hashCode() == (((PooledConnection) obj).realConnection
.hashCode());
} else if (obj instanceof Connection) {
return hashCode == obj.hashCode();
} else {
return false;
}
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode()
&& CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
private void checkConnection() throws SQLException {
if (!valid) {
throw new SQLException(
"Error accessing PooledConnection. Connection is invalid.");
}
}
}
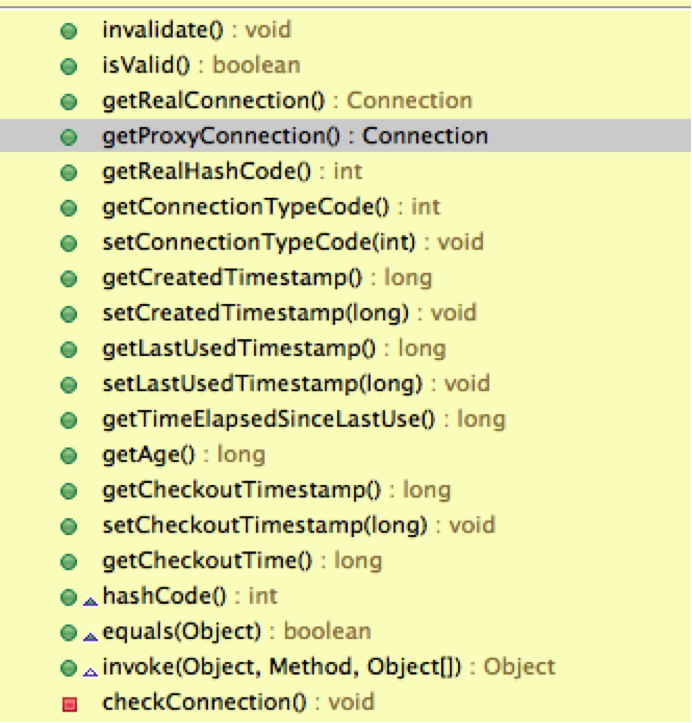
可以看到这个类暴露了很多接口检测Connection状态,例如连接是否有效,连接创建时间最近使用连接等:
这个类实现了InvocationHandler接口,最主要的一个方法如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
可以看到,PooledConnection会拦截close方法,当客户端调用close()方法时,程序不会关闭Connection,而是会调用dataSource.pushConnection(this)方法,该方法的实现如下:
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
synchronized (state) {
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
state.notifyAll();
} else {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
可以看到,首先会把Connection从活跃列表中删除,然后检测空闲列表的长度有没有达到最大长度(默认为5),若没有达到,把Connection放入空闲链表,否则关闭连接。这里的state是一个PoolState对象,该对象定义如下:
public class PoolState {
protected PooledDataSource dataSource;
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
protected long requestCount = 0;
protected long accumulatedRequestTime = 0;
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTime = 0;
protected long claimedOverdueConnectionCount = 0;
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections = 0;
protected long accumulatedWaitTime = 0;
protected long hadToWaitCount = 0;
protected long badConnectionCount = 0;
public PoolState(PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public synchronized long getRequestCount() {
return requestCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageRequestTime() {
return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedRequestTime / requestCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageWaitTime() {
return hadToWaitCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedWaitTime / hadToWaitCount;
}
public synchronized long getHadToWaitCount() {
return hadToWaitCount;
}
public synchronized long getBadConnectionCount() {
return badConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getClaimedOverdueConnectionCount() {
return claimedOverdueConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageOverdueCheckoutTime() {
return claimedOverdueConnectionCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections / claimedOverdueConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageCheckoutTime() {
return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTime / requestCount;
}
public synchronized int getIdleConnectionCount() {
return idleConnections.size();
}
public synchronized int getActiveConnectionCount() {
return activeConnections.size();
}
}
可以看到最终我们的Connection对象是放在ArrayList中的,该类还提供一些接口返回连接池基本信息。
好了,现在我们可以回去看看PooledDataSource的popConnection方法了:
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {
if (state.idleConnections.size() > 0) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// Pool does not have available connection
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// Can create new connection
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
//used in logging, if enabled
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Cannot create new connection
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// Can claim overdue connection
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// Must wait
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + 3)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
可以看到获取Connection一共分以下几种情况:1、如果有空闲Connection,那么直接使用空闲Connection,否则2;2、如果活跃Connection没有达到活跃Connection的上限,那么创建一个新Connection并返回,否则3;3、如果达到活跃上限,且被检出的Connection检出时间过长,那么把该Connection置为失效,新创建一个Connection,否则4;4、等待空闲Connection。
至此,我们就把MyBatis的数据库连接池代码整理了一遍,其中有两个关键点:1、检出的Connection其实不是原生Connection,而是一个代理对象;2、存放Connection的容器是ArrayList,Connection的检出遵从先进先出原则。
MyBatis的缓存
这篇博客讲的很好,mark一下:http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/mybatis-cache.html
MyBatis的事务
首先回顾一下JDBC的事务知识。
JDBC可以操作Connection的setAutoCommit()方法,给它false参数,提示数据库启动事务,在下达一连串的SQL命令后,自行调用Connection的commit()方法,提示数据库确认(Commit)操作。如果中间发生错误,则调用rollback(),提示数据库撤销(ROLLBACK)所有执行。同时,如果仅想要撤回某个SQL执行点,则可以设置存储点(SAVEPOINT)。一个示范的事务流程如下:
Connection conn = ...;
Savepoint point = null;
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO ...");
...
point = conn.setSavepoint();
stmt.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO ...");
...
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (conn != null) {
try {
if (point == null) {
conn.rollback();
} else {
conn.rollback(point);
conn.releaseSavepoint(point);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
} finally {
...
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在MyBatis调用流程一节就写过,在调试模式下,我们看到autoCommit为false,所以每个sqlSession其实都是一个事务,这也是为什么每次做删、改、查时都必须调用commit的原因。
MyBatis源码浅析的更多相关文章
- 【深入浅出jQuery】源码浅析--整体架构
最近一直在研读 jQuery 源码,初看源码一头雾水毫无头绪,真正静下心来细看写的真是精妙,让你感叹代码之美. 其结构明晰,高内聚.低耦合,兼具优秀的性能与便利的扩展性,在浏览器的兼容性(功能缺陷.渐 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(一)开篇
源码学习的好处不用多说,Mybatis源码量少.逻辑简单,将写个系列文章来学习. SqlSession Mybatis的使用入口位于org.apache.ibatis.session包中的SqlSes ...
- 【深入浅出jQuery】源码浅析2--奇技淫巧
最近一直在研读 jQuery 源码,初看源码一头雾水毫无头绪,真正静下心来细看写的真是精妙,让你感叹代码之美. 其结构明晰,高内聚.低耦合,兼具优秀的性能与便利的扩展性,在浏览器的兼容性(功能缺陷.渐 ...
- MyBatis源码分析-MyBatis初始化流程
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简 ...
- MyBatis源码分析-SQL语句执行的完整流程
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简 ...
- MyBatis源码分析-IDEA新建MyBatis源码工程
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(5)——内置DataSource实现
@(MyBatis)[DataSource] MyBatis源码分析(5)--内置DataSource实现 MyBatis内置了两个DataSource的实现:UnpooledDataSource,该 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(4)—— Cache构建以及应用
@(MyBatis)[Cache] MyBatis源码分析--Cache构建以及应用 SqlSession使用缓存流程 如果开启了二级缓存,而Executor会使用CachingExecutor来装饰 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(3)—— Cache接口以及实现
@(MyBatis)[Cache] MyBatis源码分析--Cache接口以及实现 Cache接口 MyBatis中的Cache以SPI实现,给需要集成其它Cache或者自定义Cache提供了接口. ...
随机推荐
- 使用GitHub(一):添加SSHkey
使用GitHub(一):添加SSHkey 本文简单介绍使用GitHub对代码进行版本控制,包括添加SSHkey.配置Git.使用Git创建版本库并在GitHub上进行管理,主要目的是对学习内容进行总结 ...
- DataList是外部传入的子项数据列表
//定义适配器类public class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.MyViewHolder>{ private C ...
- python正则之模式re.I re.M
re.I 忽略大小写 >>> re.match(r"A","abc",re.I) <_sre.SRE_Match object at 0 ...
- 20165218 《网络对抗技术》 Exp8 Web基础
Exp8 Web基础 基础问题回答 (1)什么是表单 表单可以收集用户的信息和反馈意见,是网站管理者与浏览者之间沟通的桥梁. 一个表单有三个基本组成部分: 表单标签 表单域:包含了文本框.密码框.隐藏 ...
- python常用笔记
A trick when you want to flatten a matrix X of shape (a,b,c,d) to a matrix X_flatten of shape (b*c*d ...
- 【转】UNITY中相机空间,投影空间的正向问题
原文链接1:https://www.cnblogs.com/wantnon/p/4570188.html 原文链接2:https://www.cnblogs.com/hefee/p/3820610.h ...
- input 输入框效验
input 输入框效验 1:只能输入正整数: <el-input v-model.number="formData.projectNum" type='number' min ...
- JavaScript中this的一些坑
我们经常在回调函数里面会遇到一些坑: var obj = { name: 'qiutc', foo: function() { console.log(this); }, foo2: function ...
- c++ 事件回调 java
#pragma once #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif typedef void(*sig_t)(int); int FirstEl ...
- Lesson 2 Thirteen equals one
vicar 牧师 grocer 杂货铺店主 with a start 由于受到惊吓 Whtaever are you dong up here?你究竟在这上面干什么?whatever用于疑问句中,用以 ...
