HDU 1711 Number Sequence(KMP)附带KMP的详解
题目代号:HDU 1711
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1711
Number Sequence
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 28288 Accepted Submission(s): 11891
13 5
1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 2
1 2 3 1 3
13 5
1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 2
1 2 3 2 1
-1
题目大意:给你两个数组的所有元素,让你对它们进行匹配,当位置为多少时候它们能完全匹配。
解题思路:
现在我们对第一个例子的数组进行分析,我们一开始想到的肯定是通过循环一个一个去进行匹配,碰见不匹配了就退出一层循环,然后重新搜索进行匹配,如下所示:



至此,匹配已经全部完成,代码也非常简单
# include <iostream>
# include <cstring>
# include <cstdlib>
# include <cstdio>
# include <cmath>
# include <ctime>
# include <set>
# include <map>
# include <queue>
# include <stack>
# include <vector>
# include <fstream>
# include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
# define eps 1e-
# define pb push_back
# define pi acos(-1.0)
# define bug puts("H")
# define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
# define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
# define FO(i,n,a) for(int i=n; i>=a; --i)
# define FOR(i,a,n) for(int i=a; i<=n; ++i)
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
# define MOD
/// 123456789
# pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef long long LL;
inline int Scan() {
int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-''; ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
///coding................................... int a[],b[]; int main()
{
IOS;
#ifdef FLAG
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif /// FLAG
int t;
cin>>t;
int n,m;
while(t--) {
cin>>n>>m;
int flag=;
FOR(i,,n)cin>>a[i];
FOR(i,,m)cin>>b[i];
FOR(i,,n-m+) {
FOR(j,,m) {
if(b[j]!=a[i+j-])break;
if(j==m&&b[j]==a[i+j-])flag=i;
}
if(flag)break;
}
if(flag)cout<<flag<<endl;
else cout<<-<<endl;
}
return ;
}
可是还有一个问题呢!提交之后显示TEL,超时!!!为什么呢,这是显然的,这是两重循环一个一个的匹配完成的在最坏的情况下时间复杂度接近O(nm)那么很显然,m最大的值可达10^6而n可达10^4,那么综合时间复杂度接近10^10,而oj上一秒钟只能跑10^7~10^8,那么我们应该怎么去解决这一个问题呢?通过上面的一步一步的观察,我们可以发现其中是有着很多重复的步骤,那我们要怎样才能将这个重复的步骤次数减少到可以接受的情况呢?这就是我下面要介绍的一个算法——KMP,KMP是扩展KMP以及AC自动机的基础所以作为一个ACMER我们一定要学会这个贼强的算法,而不是通过套KMP的模板来完成题目。好了下面切入正题,KMP中最重要的东西就是一个预处理的过程,通过定义一个next数组来储存之后应该所移动的位置量。
下面是next数组的预处理核心代码:
void find_next_() {
int j=,i=;
next_[]=;
while(i<m) {
if(j==||b[j]==b[i]) {
++i,++j;
if(b[i]!=b[j])next_[i]=j;
else next_[i]=next_[j];
}
else j = next_[j];
}
}
这回是以下图为例来进行示范:(因为上面的例子不太好用)
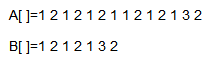
我们使用KMP预处理对B数组进行一个搜索,然后得到一个next数组,实际上就是统计出B中相同的连续元素,然后进行一个标记的操作
然后我们经过处理后得到的next数组为: 我们先不要管这个数组为什么要通过计算,以及这个数组的作用是什么,我们再来模拟一遍KMP的操作,因为时间原因,我就简单操作一遍,我们直接跳到不同的那个步骤:
我们先不要管这个数组为什么要通过计算,以及这个数组的作用是什么,我们再来模拟一遍KMP的操作,因为时间原因,我就简单操作一遍,我们直接跳到不同的那个步骤:

经过我们观察,是不是能够发现B[6]之前有着相同的元素1,2,1,那么我们是不是能够让相同的部分重叠,来减少这个匹配所移动的次数呢?
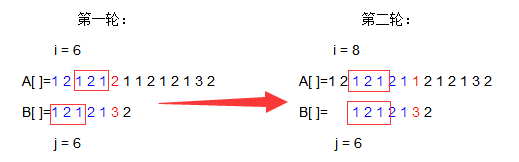

你看这样是不是能一步达到我们所需要的条件,然后我们继续操作,


你看,我们我们又节省了一部分时间,但是没有1 2 1可以匹配了怎么办?没关系,接着往下看,


这样我们又将两个1匹配在了一起,但是A[i]!=B[j],并且之前只有一个元素可以匹配,完全不能移动了,那么我们应该怎么继续操作呢?什么,B[ ]整体向右移动?没错!这样我们又能得到,

哇,所有匹配都全部完成了诶!你看,这样是不是很能节省我们之前那种操作循环所需要的时间?其实KMP当中的预处理就是扮演了一个这样的角色,他告诉我们当A[i]!=B[j]时我们应该怎样整体移动B[ ]的数组,next预处理函数所做的只是查找当A[i]与B[j]不匹配时,A[i]之前的后m个元素与B[ ]数组开头的前m个元素顺序相同时的提取下标的操作,你看看之前的操作是不是这样进行操作的呢?
好了,KMP的核心预处理的讲解就告一段落了,相信如果认真的去看之前的操作,都能够清晰了解KMP的具体操作了,下面放上完整的AC代码:
# include <iostream>
# include <cstring>
# include <cstdlib>
# include <cstdio>
# include <cmath>
# include <ctime>
# include <set>
# include <map>
# include <queue>
# include <stack>
# include <vector>
# include <fstream>
# include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
# define eps 1e-
# define pb push_back
# define pi acos(-1.0)
# define bug puts("H")
# define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
# define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
# define FO(i,n,a) for(int i=n; i>=a; --i)
# define FOR(i,a,n) for(int i=a; i<=n; ++i)
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
# define MOD
/// 123456789
# pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef long long LL;
inline int Scan(){
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-') f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
///coding................................... int a[];
int b[];
int next_[];
int m,n; void find_next_() {
int j=,i=;
next_[]=;
while(i<m) {
if(j==||b[j]==b[i]) {
++i,++j;
if(b[i]!=b[j])next_[i]=j;
else next_[i]=next_[j];
}
else j = next_[j];
}
}
int kmp() {
int i=,j=;
while(i<=n&&j<=m) {
if(j==||a[i]==b[j])++i,++j;
else j=next_[j];
}
if(j==m+)return i-m;
else return -;
}
int main()
{
IOS;
#ifdef FLAG
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif /// FLAG
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n>>m;
FOR(i,,n)cin>>a[i];
FOR(i,,m)cin>>b[i];
find_next_();
cout<<kmp()<<endl;
}
return ;
}
HDU 1711 Number Sequence(KMP)附带KMP的详解的更多相关文章
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence (字符串匹配,KMP算法)
HDU 1711 Number Sequence (字符串匹配,KMP算法) Description Given two sequences of numbers : a1, a2, ...... , ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence(数列)
HDU 1711 Number Sequence(数列) Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Ja ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence 【KMP应用 求成功匹配子串的最小下标】
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1711 Number Sequence Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/O ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence(KMP裸题,板子题,有坑点)
Number Sequence Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence (KMP简单题)
Number Sequence Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 1711 Number Sequence KMP 基础题
Number Sequence Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- KMP - HDU 1711 Number Sequence
Number Sequence Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence(kmp)
Problem Description Given two sequences of numbers : a[1], a[2], ...... , a[N], and b[1], b[2], .... ...
- HDU 1711 Number Sequence(KMP模板)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1711 这道题就是一个KMP模板. #include<iostream> #include<cs ...
随机推荐
- python 并发编程 多线程 线程queue
线程queue 线程之间已经是共享数据的,为什么还使用线程queue? 线程需要自己加锁,线程queue帮我们处理好加锁的问题 有三种不同的用法 第一种方法: class queue.Queue(ma ...
- 第j九周学习总结暨第七周实验报告
完成火车站售票程序的模拟. 要求: (1)总票数1000张: (2)10个窗口同时开始卖票: (3)卖票过程延时1秒钟: (4)不能出现一票多卖或卖出负数号票的情况. 一:实验代码 package d ...
- 4、android studio打包的时候遇到的问题
那就去掉该签名 但是如果使用generated apk的话,则是不会去调用build.gradle文件的,需要使用gradle命令来打包 https://blog.csdn.net/cencibuqi ...
- 使用Tomcat、JNDI与ActiveMQ实现JMS消息通信服务
前言 之所以使用JNDI 是出于通用性考虑,该例子使用JMS规范提供的通用接口,没有使用具体JMS提供者的接口,这样可以保证我们编写的程序适用于任何一种JMS实现(ActiveMQ.HornetQ等) ...
- vue-router的query和params的区别
vue-router的query和params的区别 首先简单来说明一下$router和$route的区别 $router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同url,则使用$router.push ...
- TCP的三次握手与四次挥手理解及面试题
TCP的三次握手与四次挥手理解及面试题(很全面) 转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38950316/article/details/81087809 本文经过借鉴书籍资料.他 ...
- chrome插件2
转自:http://www.codeceo.com/article/15-chrome-extension.html 1. Web Developer 支持Chrome的Web Developer扩展 ...
- linux centos中安装flash player
本机为centos 7.0 64 1.用火狐浏览器随便打开一个视频网站,找到一个视频点进去,网站会提示未安装flash player.点击进去到adobe官网.2.下载flash player插件,可 ...
- ARM工作模式寻址
用户模式(User) usr 快速中断模式(FIQ) fiq 普通终端模式(IRQ) irq 保护模式(Supervisor) svc 数据访问终止模式(Abo ...
- nginx反向代理+负载均衡+url重写+ssl认证
Nginx (engine x) 是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,也是一个IMAP/POP3/SMTP服务器.Nginx是由伊戈尔·赛索耶夫为俄罗斯访问量第二的Rambler.ru站点(俄 ...
