spring-第九篇之高级依赖关系配置
1、关于配置文件一些使用
组件与组件之间的耦合,采用依赖注入管理;基本类型的成员变量值,应该直接在代码中设置。
2、获取其他bean的属性值
PorpertyPathFactoryBean用来获取目标bean的属性值(实际上就是它的getter方法的返回值),获得的值可以注入给其他bean,也可以直接定义成新的bean。使用PorpertyPathFactoryBean来调用其他bean的getter方法需要指定如下信息:
调用哪个对象:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)的方法指定。
调用哪个getter方法:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setPropertyPath(String propertyPath)方法指定。
举个例子:

Person.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public class Person {
private int age;
private Son son;
public Son getSon() {
return son;
}
public void setSon(Son son) {
this.son = son;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Son.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public class Son {
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Son[age="+age+"]";
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!--下面配置定义一个将要被引用的目标bean-->
<bean id="person" class="com.lfy.bean.Person">
<property name="age" value="30"/>
<property name="son">
<!-- 使用嵌套Bean定义setSon()方法的参数值 -->
<bean class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age" value="11" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 将指定Bean实例的getter方法返回值定义成son1 Bean -->
<bean id="son1" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,指定son1 Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法 -->
<property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/>
<!-- 指定son1 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,son代表getSon() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="son"/>
</bean> <!-- 下面定义son2 Bean -->
<bean id="son2" class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age">
<!-- 使用嵌套Bean为调用setAge()方法指定参数值 -->
<!-- 以下是访问指定Bean的getter方法的简单方式,
person.son.age代表获取person.getSon().getAge()-->
<bean id="person.son.age" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"/>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 -->
<bean id="theAge" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法的返回值 -->
<property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/>
<!-- 使用复合属性来指定getter方法。son.age代表getSon().getAge() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="son.age"/>
</bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 -->
<bean id="theAge2" class=
"org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean">
<!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge2 Bean来自哪个Bean的属性。
此处采用嵌套Bean定义目标Bean -->
<property name="targetObject">
<!-- 目标Bean不是容器中已经存在的Bean, 而是如下的嵌套Bean-->
<bean class="com.lfy.bean.Person">
<property name="age" value="30"/>
</bean>
</property>
<!-- 指定theAge2 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,age代表getAge() -->
<property name="propertyPath" value="age"/>
</bean> <!-- son1的简化配置 -->
<util:property-path id="son3" path="person.son"/> <!-- son2的简化配置 -->
<bean id="son4" class="com.lfy.bean.Son">
<property name="age">
<util:property-path path="person.son.age"/>
</property>
</bean> <!-- theAge的简化配置 -->
<util:property-path id="theAge3" path="person.son.age"/>
</beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Person; /**
*
* @author lfy
*
*/
public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建spring容器
ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
System.out.println("系统获取son1:"+ctx.getBean("son1"));
System.out.println("系统获取son2:"+ctx.getBean("son2"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge2"));
//简化配置
System.out.println("系统获取son3:"+ctx.getBean("son3"));
System.out.println("系统获取son4:"+ctx.getBean("son4"));
System.out.println("系统获取theAge3:"+ctx.getBean("theAge3"));
} }
运行结果:
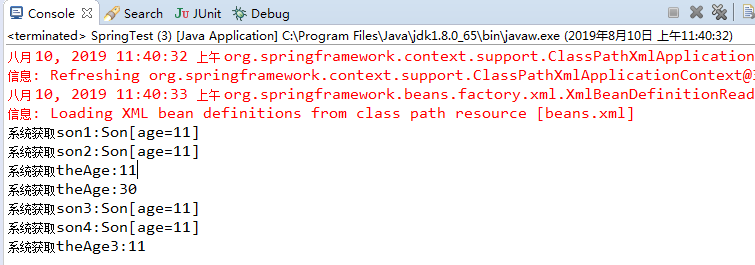
总结:<util:property-path.../>元素可以作为PropertyPathFactoryBean的简化配置,需要使用该元素,必须在配置文件中声明util:命名空间。其配置时指定的两个属性
id:该属性指定将getter方法的返回值定义成名为id的bean实例,如本例的son3。
path:该属性指定将哪个bean实例、哪个属性(可以是复合属性)暴露出来。
3、获取Field字段值
FieldRetrievingFactoryBean,可以访问类的静态Field或对象的实例Field值。使用FieldRetrievingFactoryBean访问Field分两种情形:
1》要访问的Field是静态Field,需要指定
调用哪个类:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
2》要访问的Filed是实例Field(要求实例的Field使用public控制访问权限,没太大用处),需要指定
调用哪个对象:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(String targetObject)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
4、获取方法返回值
MethodInvokingFactoryBean工厂bean,使用MethodInvokingFactoryBean两种情形:
1》要访问的是静态方法,需要指定
调用哪个类:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。
2》要访问的是实例方法,需要指定
调用哪个对象:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。
spring-第九篇之高级依赖关系配置的更多相关文章
- Spring框架学习之高级依赖关系配置(一)
上篇文章我们对Spring做了初步的学习,了解了基本的依赖注入思想.学会简单的配置bean.能够使用Spring容器管理我们的bean实例等.但这还只是相对较浅显的内容,本篇将介绍bean的相关更高级 ...
- Spring框架学习之高级依赖关系配置(二)
紧接着上篇内容,本篇文章将主要介绍XML Schema的简化配置和使用SpEL表达式语言来优化我们的配置文件. 一.基于XML Schema的简化配置方式 从Spring2.0以来,Spring支持使 ...
- Spring第九篇【Spring与Hibernate整合】
前言 前面已经学习了如何使用Spring与Struts2进行整合,本博文主要讲解如何使用Spring对Hibernate进行整合 Spring和Hibernate整合的关键点: SessionFact ...
- Spring boot starter pom的依赖关系说明
Spring Boot 通过starter依赖为项目的依赖管理提供帮助.starter依赖起始就是特殊的maven依赖,利用了传递依赖解析,把常用库聚合在一起,组成了几个为特定功能而定制的依赖. sp ...
- Spring应用教程-3 依赖关系配置
注:组件与组件之间的耦合,采用依赖注入管理,但普通的JavaBean属性值,应直接在代码中设置. 1. 注入其他Bean的属性值 我们分析一下,Bean_A的一个属性要依赖Bean_B的一个属性值.这 ...
- spring各个包之间的依赖关系
从图中可以看到: 1.spring core,spring beans被其他较多包依赖,spring aop,spring context,spring expression分别被两个包依赖,而spr ...
- Jenkins job之间依赖关系配置(联动构建)
使用场景: 想要在某APP打新包之后,立即执行自动化测试的job来验证该新包.比如Job A 执行完执行Job B ,如下图所示,如何建立依赖呢? 主要有两种方法: 1.配置上游依赖: 2.配置下游依 ...
- Jenkins-job之间依赖关系配置
使用场景: 想要在某APP打新包之后,立即执行自动化测试的job来验证该新包. 比如Job A 执行完执行Job B ,如下图所示,如何建立依赖呢? 1.配置上游依赖 构建触发器-配置如下信息: 选择 ...
- SpringMvc+Spring+Mybatis的jar包依赖关系图
随机推荐
- 云中沙箱学习笔记2-ECS之初体验
1.1 背景知识 云服务器(Elastic Compute Service, 简称ECS),是一种简单高效,处理能力可以弹性伸缩的计算服务.ECS的相关术语说明如下: --实例(Instance):是 ...
- linux ssh 服务优化
linux 默认管理员 root,port 端口号是 22,为了安全,我们要改掉默认的管理员和端口 配置文件/etc/ssh/sshd_config [root@oldboy ~]# vi /etc/ ...
- pg_dump - 将一个PostgreSQL数据库抽出到一个脚本文件或者其它归档文件中
SYNOPSIS pg_dump [ option...] [ dbname] DESCRIPTION 描述 pg_dump 是一个用于备份 PostgreSQL 数据库的工具.它甚至可以在数据库正在 ...
- 消灭 Java 代码的“坏味道”
消灭 Java 代码的“坏味道” 原创: 王超 阿里巴巴中间件 昨天 导读 明代王阳明先生在<传习录>谈为学之道时说: 私欲日生,如地上尘,一日不扫,便又有一层.着实用功,便见道无终穷,愈 ...
- V7双雄-基于Virtex7XC7VX690T的高性能计算板卡解决方案
北京太速V7双雄-基于Virtex7XC7VX690T的高性能计算板卡
- 锁、volatile、CAS的比较
一.锁 锁是一种悲观的机制.为多线程提供了互斥的访问机制.多个线程同时竞争锁时,没获得锁的线程将会被挂起(智能的JVM会根据之前获取锁操作中对锁的持有时间长短来判断是使线程挂起还是自旋) 锁的劣势:1 ...
- thinkphp 视图view
一. 继承Controller类 <?php namespace app\index\controller; use http\Params; use think\Config; use thi ...
- Map和Set的联系
Java中的集合 Java中的集合包括三大类,它们是Set.List和Map,它们都处于java.util包中,Set.List和Map都是接口,它们有各自的实现类.Set的实现类主要有HashSet ...
- python tkinter坐标转换
tkinter中坐标原点在左上角,横坐标向右,纵坐标向下,画图需要将坐标转换成右下角的某个点来符合我们的常用坐标 坐标原点设为(x0,y0),横坐标向右,纵坐标向上,: 转换:想实现坐标点(x,y)的 ...
- 【leetcode】449. Serialize and Deserialize BST
题目如下: Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits ...
