Java 对不同类型的数据文件的读写操作整合器[JSON,XML,CSV]-[经过设计模式改造](2020年寒假小目标03)
日期:2020.01.16
博客期:125
星期四
我想说想要构造这样一个通用文件读写器确实不容易,嗯~以后会添加更多的文件类型,先来熟悉一下文件内容样式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beangroup>
<javabean>
<data name='code'>A001</data>
<data name='name'>张三</data>
</javabean>
</beangroup>
XML文件类型
{
list:[
{
code:"A001",
name:"张三"
}
]
}
JSON文件类型
code,name
A001,张三
CSV文件类型
【此处预留给未来添加的文件类型】
我所需要的基本功能是对表型数据的读写,这一点对于CSV这一种标准表形式的文件来说,构造它轻而易举,也没什么难度!而对于JSON和XML来说很难,其实JSON和XML是可以相互转换的,或者说这二者可以等价,毕竟JSON对应属性和XML对应标签属性如出一辙!而XML的标签内部内容刚好对应JSON里的具体内容!
好了话不多说,赶紧加代码:
com.filedeal包:
package com.filedeal;
import java.io.File;
import com.dblink.bean.BeanGroup;
public interface FileControler {
//---[set、get方法]
//设置文件信息
void setFile(File file);
//获取处理的文件信息
File getFile();
//---[类与对象方法]
//释放
void free();
//重新设置
void reset();
//表型数据植入
public void setUnderprinted(BeanGroup bg);
//表型数据获取
public BeanGroup getUnderprinted();
}
FileControler.java
package com.filedeal; import com.dblink.bean.BeanGroup;
import com.dblink.bean.JavaBean;
import com.dblink.bean.ReadableTable;
import com.filedeal.csv.CSVFileDealer;
import com.filedeal.json.JSONFileDealer;
import com.filedeal.xml.XMLFileDealer; @SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class FileControlerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanGroup bg = new BeanGroup();
JavaBean jb1 = new JavaBean();
jb1.add("序号");
jb1.add("名称");
jb1.add("性别");
JavaBean jb2 = new JavaBean();
jb2.add(1);
jb2.add("张三");
jb2.add("男");
JavaBean jb3 = new JavaBean();
jb3.add(2);
jb3.add("李四");
jb3.add("女");
bg.add(jb1);
bg.add(jb2);
bg.add(jb3);
ReadableTable rt = ReadableTable.parseReadableTable(bg);
//CSV测试
/*
CSVFileDealer csv = new CSVFileDealer("src/testFiles/art.csv");
csv.setUnderprinted(bg);
csv.free();
*/
//XML测试
/*
XMLFileDealer xml = new XMLFileDealer("src/testFiles/aleion.xml");
xml.setUnderprinted(bg);
System.out.println(xml.getUnderprinted().toJSONArray());
*/
//JSON测试
JSONFileDealer json = new JSONFileDealer("src/testFiles/alert.json");
//json.setUnderprinted(bg);
//System.out.println(json.getUnderprinted());
//json.setUnderprinted(rt,false);
System.out.println(json.getUnderprinted(false).cloName);
System.out.println(json.getUnderprinted(false).beans);
}
}
FileControlerTest.java
com.filedeal.csv包:
package com.filedeal.csv; import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Scanner; import com.dblink.bean.BeanGroup;
import com.dblink.bean.JavaBean;
import com.filedeal.FileControler; public class CSVFileDealer implements FileControler {
protected File file;
@Override
public void setFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
@Override
public void free() {
// Do Nothing ...
}
@Override
public void reset() {
String name = this.file.getName();
this.free();
this.file = new File(name);
}
//---[数据处理]
//设置数据集合
@Override
public void setUnderprinted(BeanGroup bg) {
try {
if(!file.exists())
return;
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file),"GB2312")));
int leng = bg.size(); for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
JavaBean jb = bg.get(i);
String str = ""; int leng_s = jb.size(); for(int j=0;j<leng_s;++j)
{
String tmp = jb.get(j).toString();
if(j==0)
str += tmp;
else
str += ","+tmp;
} pw.println(str);
} pw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取数据集合
@Override
public BeanGroup getUnderprinted(){
BeanGroup bg = new BeanGroup();
try {
if(!this.file.exists())
return bg;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(this.file);
while(sc.hasNextLine())
{
String str = sc.nextLine();
String [] sg = str.split(","); JavaBean jb = new JavaBean(); int leng = sg.length; for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
String tmp = sg[i];
jb.add(tmp);
} bg.add(jb);
}
sc.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bg;
}
//---[构造方法]
public CSVFileDealer(String filePath){
super();
this.file = new File(filePath);
if(!this.file.exists())
{
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public CSVFileDealer(File file){
super();
this.file = file;
if(!this.file.exists())
{
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
CSVFileDealer.java
com.filedeal.xml包:
package com.filedeal.xml; import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import com.dblink.bean.BeanGroup;
import com.dblink.bean.JavaBean;
import com.dblink.bean.ReadableTable;
import com.filedeal.*; import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter; @SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class XMLFileDealer implements FileControler{
protected File file;
@Override
public void setFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
@Override
public void free() {
// Do Nothing ...
}
@Override
public void reset() {
String name = this.file.getName();
this.free();
this.file = new File(name);
}
@Override
public void setUnderprinted(BeanGroup bg) {
this.createFile();
ReadableTable rt = ReadableTable.parseReadableTable(bg);
try {
//基本属性构造
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(this.file);
Element root = doc.getRootElement(); //表头构造
Element e_header = root.addElement("cloumn"); int num_header = rt.cloName.size(); for(int i=0;i<num_header;++i)
{
Element e = e_header.addElement("info");
e.setText(rt.cloName.get(i).toString());
} //由BeanGroup构造数据
int leng = rt.beans.size(); for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
JavaBean jb = rt.beans.get(i);
Element e_body = root.addElement("javabean");
int leng_s = jb.size();
for(int j=0;j<leng_s;++j)
{
Element e = e_body.addElement("data");
e.setText(jb.get(j).toString());
}
} // 创建输出流
Writer out = new PrintWriter(this.file, "utf-8"); // 格式化
OutputFormat format = new OutputFormat("\t", true); //去掉原来的空白(\t和换行和空格)!
format.setTrimText(true); XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(out, format);
// 把document对象写到out流中。
writer.write(doc); out.close();
writer.close(); } catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public BeanGroup getUnderprinted() {
if(!file.exists())
return null;
BeanGroup bg = new BeanGroup();
try {
//基本属性构造
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(this.file);
Element root = doc.getRootElement(); //表头构造部分
Element es = root.element("cloumn");
List<Element> plist = es.elements("info");
int num_l = plist.size();
JavaBean jb_header = new JavaBean();
for(int i=0;i<num_l;++i)
{
jb_header.add(plist.get(i).getText());
}
bg.add(jb_header); //表内数据构造部分
List <Element> rd = root.elements("javabean");
int leng = rd.size();
for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
JavaBean jb = new JavaBean();
Element e = rd.get(i);
List<Element> list = e.elements("data");
int leng_s = list.size(); for(int j=0;j<leng_s;++j)
{
jb.add(list.get(j).getText());
}
bg.add(jb);
}
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return bg;
}
public void createFile() {
this.createFile("beangroup");
}
public void createFile(String rootName) {
if(this.file.exists())
this.file.delete();
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file),"GB2312")));
pw.println("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>");
pw.println("<"+rootName+">");
pw.println("</"+rootName+">");
pw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//---[构造方法]
public XMLFileDealer(File file) {
super();
this.file = file;
if(!this.file.exists())
this.createFile();
}
public XMLFileDealer(String filePath) {
super();
this.file = new File(filePath);
if(!this.file.exists())
this.createFile();
}
}
XMLFileDealer.java
com.filedeal.json包:
package com.filedeal.json; import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.Scanner; import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONObject; import com.dblink.bean.BeanGroup;
import com.dblink.bean.ReadableTable;
import com.filedeal.FileControler; public class JSONFileDealer implements FileControler {
protected File file;
@Override
public void setFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
@Override
public void free() {
// Do Nothing ...
}
@Override
public void reset() {
String name = this.file.getName();
this.free();
this.file = new File(name);
}
@Override
public void setUnderprinted(BeanGroup bg) {
this.createFile();
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(this.file);
out.write(bg.toJSONArray().toString().getBytes());
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public BeanGroup getUnderprinted() {
BeanGroup bg = null;
try {
String jarStr = "";
Scanner sc = new Scanner(this.file);
while(sc.hasNextLine())
{
jarStr += sc.nextLine();
}
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(jarStr);
bg = BeanGroup.parseJSONArray(jsonArray);
sc.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bg;
}
//---[面向ReadableTable的方法]
public void setUnderprinted(ReadableTable rt) {
setUnderprinted(rt,false);
}
public void setUnderprinted(ReadableTable rt,boolean isArray) {
this.createFile();
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(this.file);
if(isArray)
out.write(rt.toJSONArray().toString().getBytes());
else
out.write(rt.toJSONObject().toString().getBytes());
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public ReadableTable getUnderprinted(boolean isArray) {
ReadableTable rt = null; try {
String jarStr = "";
Scanner sc = new Scanner(this.file);
while(sc.hasNextLine())
{
jarStr += sc.nextLine();
}
if(isArray)
{
rt = ReadableTable.parseJSONArray(new JSONArray(jarStr));
}
else
{
rt = ReadableTable.parseJSONObject(new JSONObject(jarStr));
}
sc.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} return rt;
}
//---[其余方法]
public void createFile() {
if(this.file.exists())
this.file.delete();
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//---[构造方法]
public JSONFileDealer(File file) {
super();
this.file = file;
if(!this.file.exists())
{
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public JSONFileDealer(String filePath) {
super();
this.file = new File(filePath);
if(!this.file.exists())
{
try {
this.file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
JSONFileDealer.java
扩充的基本类型:(JavaBean,BeanGroup,ReadableTable)
com.dblink.bean包:
package com.dblink.bean; import org.json.JSONArray; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection; public class JavaBean extends ArrayList<Object> {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1272079633276217217L;
//---[方法区]
//构造方法
public JavaBean() {
super();
}
public JavaBean(Collection<Object> c) {
super(c);
}
public JavaBean(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
}
//转化方法
public String toString(){
return super.toString();
}
public JSONArray toJSONArray(){
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
int leng = super.size();
for(int i=0;i<leng;++i){
Object q = super.get(i);
jsonArray.put(q);
}
return jsonArray;
}
public static JavaBean parseJSONArray(JSONArray jsonArray) {
JavaBean jb = new JavaBean();
int leng = jsonArray.length();
for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
jb.add(jsonArray.get(i));
}
return jb;
}
}
JavaBean.java
package com.dblink.bean; import org.json.JSONArray; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection; public class BeanGroup extends ArrayList <JavaBean> {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3232871941539102307L;
//---[方法区]
//构造方法
public BeanGroup(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
}
public BeanGroup() {
super();
}
public BeanGroup(Collection<JavaBean> c) {
super(c);
}
//转化方法
public String toString(){
return super.toString();
}
public JSONArray toJSONArray(){
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
int leng = super.size();
for(int i=0;i<leng;++i){
JavaBean jb = super.get(i);
jsonArray.put(jb.toJSONArray());
}
return jsonArray;
}
public static BeanGroup parseJSONArray(JSONArray jsonArray) {
BeanGroup bg = new BeanGroup();
int leng = jsonArray.length();
for(int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
bg.add(JavaBean.parseJSONArray(jsonArray.getJSONArray(i)));
}
return bg;
}
}
BeanGroup.java
package com.dblink.bean; import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONObject; public class ReadableTable {
//---[属性成员]
//列名称集合
public JavaBean cloName;
//表格详细信息
public BeanGroup beans;
//---[方法成员]
/*转移方法*/
public static ReadableTable parseReadableTable(BeanGroup bg) {
JavaBean jb = new JavaBean();
jb.addAll(bg.get(0));
BeanGroup bgs = new BeanGroup();
for(int i=1;i<bg.size();++i)
{
bgs.add(bg.get(i));
}
return new ReadableTable(jb,bgs);
}
/*构造方法*/
public ReadableTable(){
this.cloName = null;
this.beans = null;
}
public ReadableTable(JavaBean cloName,BeanGroup beans){
this.cloName = cloName;
this.beans = beans;
}
/*格式转化*/
public JSONObject toJSONObject(){
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("Length",this.beans.size());
jsonObject.put("Column",this.cloName.size());
jsonObject.put("ColNames",this.cloName.toJSONArray());
jsonObject.put("Beans",this.beans.toJSONArray());
return jsonObject;
}
public JSONArray toJSONArray(){
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
int leng = this.beans.size();
int cloNum = this.cloName.size();
jsonObject.put("Length",leng);
jsonObject.put("Column",cloNum);
jsonObject.put("ColNames",this.cloName.toJSONArray());
jsonArray.put(jsonObject);
for (int i=0;i<leng;++i)
{
JSONObject jso = new JSONObject();
JavaBean jb = this.beans.get(i);
for(int j=0;j<cloNum;++j)
{
Object obj = jb.get(j);
String name = this.cloName.get(j).toString();
jso.put(name,obj);
}
jsonArray.put(jso);
}
return jsonArray;
}
public static ReadableTable parseJSONArray(JSONArray json) {
ReadableTable rt = new ReadableTable();
JSONObject jsonObj = json.getJSONObject(0);
int length = Integer.parseInt(jsonObj.get("Length").toString());
int column = Integer.parseInt(jsonObj.get("Column").toString());
rt.cloName = JavaBean.parseJSONArray(jsonObj.getJSONArray("ColNames"));
rt.beans = new BeanGroup();
for(int i = 0;i<length;++i)
{
JavaBean jb = new JavaBean(); for(int j=0;j<column;++j)
{
jb.add(json.getJSONObject(i).get(rt.cloName.get(j).toString()));
} rt.beans.add(jb);
}
return rt;
}
public static ReadableTable parseJSONObject(JSONObject json) {
ReadableTable rt = new ReadableTable();
rt.cloName = JavaBean.parseJSONArray(json.getJSONArray("ColNames"));
rt.beans = BeanGroup.parseJSONArray(json.getJSONArray("Beans"));
return rt;
}
}
ReadableTable.java
添加了JSONArray、JSONObject与上述类型之间的类型转换(实现双向)
【此处预留给未来添加的文件类型】
实现类图:
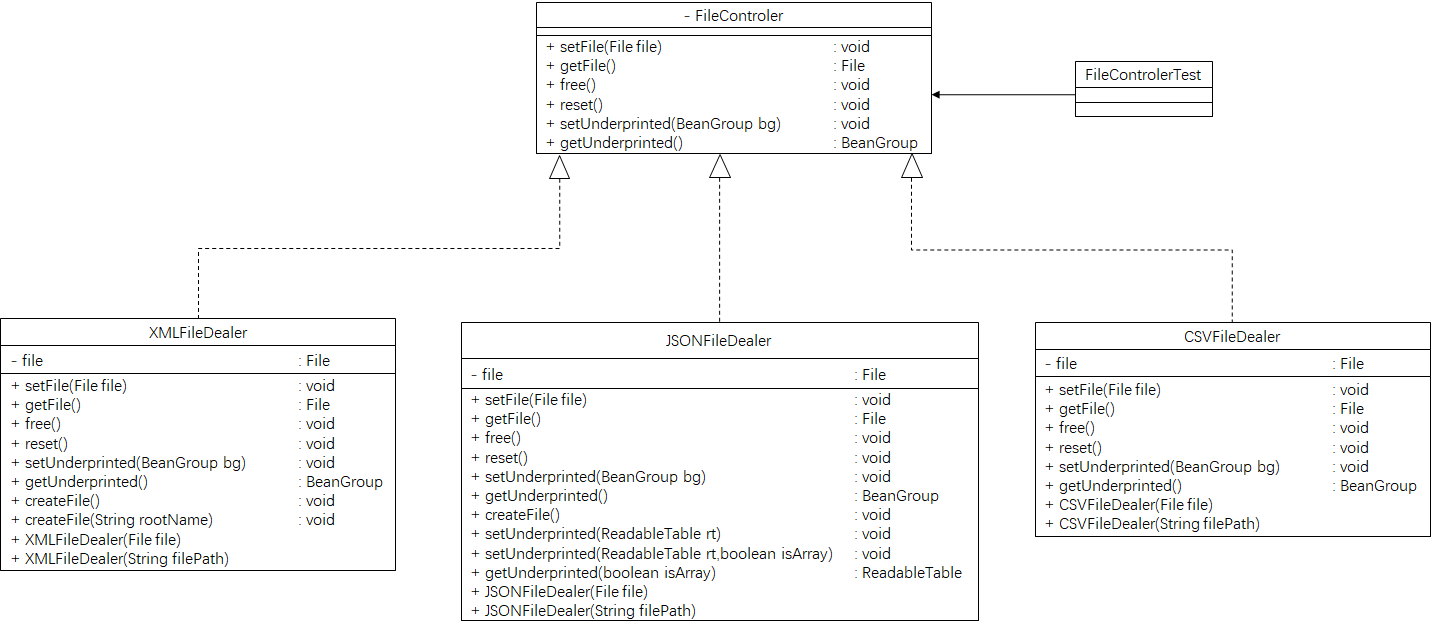
所用设计模式:
1、策略模式:我发现这个模式真好用,而且简单,而且好用,嗯!针对文件处理不同的文件类型采取不一样的策略
2、模板方法模式:文件的读写操作算是基本的模板方法!
3、代理模式:嗯~要想json和xml的数据源完成读写事先需要调用ReadableTable类的方法进行数据整理,这一部分方法被封装在代理类里面,也可以不做数据处理,这正是代理模式的初衷!
参考文献:
1、XML的写文件方法
https://blog.csdn.net/Alias_fa/article/details/82049872
Java 对不同类型的数据文件的读写操作整合器[JSON,XML,CSV]-[经过设计模式改造](2020年寒假小目标03)的更多相关文章
- Java 使用 JDBC 连接数据库的代码整合[MySql、SqlServer、Oracle]-[经过设计模式改造](2020年寒假小目标01)
日期:2020.01.08 博客期:121 星期三 今天对过去整个大二和大三上半学期用到的数据库的方法进行汇总,可以有效的使用.套用,每一个部分都有<软件设计模式>知识,上述代码满足了开闭 ...
- Python基础 | 数据文件的读写
目录 txt txt的读入 txt的写出 csv xls\xlsx 在线网页数据 常用的工具 爬虫的步骤 pdf pdfrw PyPDF2 提取文档信息 word文档 其他统计软件生成文件 本文总结使 ...
- Java中double类型的数据精确到小数点后两位
Java中double类型的数据精确到小数点后两位 多余位四舍五入,四种方法 一: double f = 111231.5585;BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(f); d ...
- java文件的读写操作
java文件的读写操作主要是对输入流和输出流的操作,由于流的分类很多,所以概念很容易模糊,基于此,对于流的读写操作做一个小结. 1.根据数据的流向来分: 输出流:是用来写数据的,是由程序(内存)--- ...
- Java程序员的日常—— Properties文件的读写
在日常的Java程序开发中,Properties文件的读写是很常用的.经常有开发系统通过properties文件来当做配置文件,方便用户对系统参数进行调整. 那么本片就来简单的介绍下,如何使用Prop ...
- java 文件的读写操作
java 文件的读写操作 一.读: public String getSetting() { HttpServletRequest request=org.apache.struts2.Servle ...
- 在java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流”(stream)方式进行
在java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流”(stream)方式进行
- 营销MM让我讲MySQL日志顺序读写及数据文件随机读写原理
摘要:你知道吗,MySQL在实际工作时候的两种数据读写机制? 本文分享自华为云社区<MySQL日志顺序读写及数据文件随机读写原理>,作者:JavaEdge . MySQL在实际工作时候的两 ...
- C++学习48 对ASCII文件的读写操作
如果文件的每一个字节中均以ASCII代码形式存放数据,即一个字节存放一个字符,这个文件就是ASCII文件(或称字符文件).程序可以从ASCII文件中读入若干个字符,也可以向它输出一些字符. 对ASCI ...
随机推荐
- 吴裕雄--天生自然神经网络与深度学习实战Python+Keras+TensorFlow:TensorFlow与神经网络的实现
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np ''' 初始化运算图,它包含了上节提到的各个运算单元,它将为W,x,b,h构造运算部件,并将它们连接 起来 ''' ...
- Robot Framework高级
一.Web自动化测试 二.C/S自动化测试 三.数据库自动化测试 四.接口自动化测试 五.RF内置测试库 六.持续集成内置测试库 七.移动自动化测试 八.自定义RF
- 实验四《Android程序设计》
实验四<Android程序设计> 一.实验内容 1.Android Stuidio的安装测试 2.Activity测试 3.UI测试 4.布局测试 5.事件处理测试 二.实验步骤 第一部分 ...
- left join 、right join 和inner join之间的区别
SQL的left join .right join 和inner join之间的区别 left join(左联接) 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录 right join(右联接) ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow训练神经网络:不使用滑动平均
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data INPUT_NODE = 784 ...
- 牛客跨年AK场-小sum的假期安排
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/3800/G来源:牛客网 题目描述 小 sun 非常喜欢放假,尤其是那种连在一起的长假,在放假的时候小 sun 会感到快乐 ...
- Atcoder Grand Contest 039B(思维,BFS)
#define HAVE_STRUCT_TIMESPEC#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int col[207],s[207],n;c ...
- vue+element ui table组件封装,使用render渲染
后台管理经常会用到表格,一开始封装了一个常用的功能性表格,点击这里: 后来由于需求增加,在表格中还会用到switch,select,input等多种组件,每次都要在html中增加<el-tabl ...
- 「CF383C Propagating tree」
这应该属于一个比较麻烦的数据结构处理树上问题. 题目大意 给出一颗根节点编号为 \(1\) 的树,对于一个节点修改时在它的子树中对于深度奇偶性相同的节点加上这个权值,不同则减去这个值,单点查询. 分析 ...
- FTP-Publisher Plugin
使用 FTP-Publisher Plugin 在 http://wiki.hudson-ci.org/display/HUDSON/FTP-Publisher+Plugin 有详细说明, 需要注意的 ...
