Java IO系列之四:NIO通信模型
分布式rpc框架有很多,比如dubbo,netty,还有很多其他的产品。但他们大部分都是基于nio的,
nio是非阻塞的io,那么它的内部机制是怎么实现的呢。
1.由一个专门的线程处理所有IO事件,并负责分发。
2.事件驱动机制,事件到来的时候触发操作,不需要阻塞的监视事件。
3.线程之前通过wait,notify通信,减少线程切换。
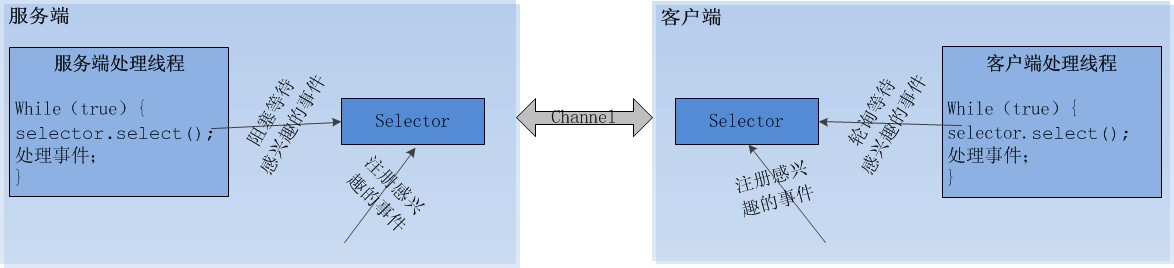

NIO使用步骤

服务端步骤:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new Thread(new ReactorTask()).start();
} public static class ReactorTask implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
public ReactorTask() {
try {
// 第一步:打开ServerSocketChannel,用于监听客户端的连接,它是所有客户端连接的父管道
ServerSocketChannel acceptorSvr = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 第二步:绑定监听端口,设置连接为非阻塞模式
acceptorSvr.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 1234));
acceptorSvr.configureBlocking(false); // 第三步:创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程
selector = Selector.open(); // 第四步:将ServerSocketChannel注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器Selector上,监听Accept事件
SelectionKey key = acceptorSvr.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); } catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} @Override
public void run() {
// 第五步:在run方法中无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key
while (true) {
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isValid()) {
// 处理新接入的请求消息
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 第六步:多路复用器监听到有新的客户端接入,处理新的接入请求,完成TCP三次握手,建立物理链路
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
// 第七步:设置客户端链路为非阻塞模式
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.socket().setReuseAddress(true);
// 第八步:将新接入的客户端连接注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器上,监听读操作,读取客户端发送的网络消息
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
// 第九步:异步读取客户端请求消息到缓存区
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer); // 第十步:对ByteBuffer进行编解码,如果有半包消息指针reset,继续读取后续的报文
if (readBytes > 0) {
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("The time server receive order : " + body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body)
? new java.util.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString()
: "BAD ORDER";
//写应答
byte[] bytes2 = currentTime.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes2.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes2);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
} else if (readBytes < 0) {
// 对端链路关闭
key.cancel();
sc.close();
} else
; // 读到0字节,忽略
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (key != null) {
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null)
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
注意:如果发送区TCP缓冲区满,会导致写半包,此时,需要注册监听写操作位,循环写,直到整包消息写入TCP缓冲区
客户端步骤:
客户端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; public class TimeClientHandle implements Runnable { private String host;
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel; private volatile boolean stop; public TimeClientHandle(String host, int port) {
this.host = host == null ? "127.0.0.1" : host;
this.port = port;
try {
//第一步:打开SocketChannel,用于创建客户端连接
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//第二步:设置SocketChannel为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//第三步:创建多路复用器(在Reactor线程中)
selector = Selector.open(); } catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
} @Override
public void run() {
try {
// 第四步:socketChannel发起连接
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))) {
//第五步:如果直接连接成功,则注册到多路复用器上
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//第六步:发送请求消息,读应答
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
if (!writeBuffer.hasRemaining())
System.out.println("Send order 2 server succeed.");
} else
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
while (!stop) {
try {
//第七步:多路复用器在run的无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
if (key.isValid()) {
//第八步:将连接成功的Channel注册到多路复用器上
// 判断是否连接成功
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
if (sc.finishConnect()) {
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//发送请求消息,读应答
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
if (!writeBuffer.hasRemaining())
System.out.println("Send order 2 server succeed.");
} else
System.exit(1);// 连接失败,进程退出
}
//监听读操作,读取服务端写回的网络信息
if (key.isReadable()) {
//第九步:读取信息到缓冲区
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Now is : " + body);
this.stop = true;
} else if (readBytes < 0) {
// 对端链路关闭
key.cancel();
sc.close();
} else
; // 读到0字节,忽略
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (key != null) {
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null)
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
} // 多路复用器关闭后,所有注册在上面的Channel和Pipe等资源都会被自动去注册并关闭,所以不需要重复释放资源
if (selector != null)
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.dxz.springsession.nio.demo6;
public class TimeClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) { int port = 1234;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 采用默认值
}
}
new Thread(new TimeClientHandle("127.0.0.1", port), "TimeClient-001")
.start();
}
}
抄录地址:
Java IO系列之四:NIO通信模型的更多相关文章
- java io系列16之 PrintStream(打印输出流)详解
本章介绍PrintStream以及 它与DataOutputStream的区别.我们先对PrintStream有个大致认识,然后再深入学习它的源码,最后通过示例加深对它的了解. 转载请注明出处:htt ...
- Java IO系列之一:IO
1. 概述 Java IO一般包含两个部分: 1.java.io包中堵塞型IO: 2.java.nio包中的非堵塞型IO,通常称为New IO. java.io包下,分为四大块近80个类: 1.基于字 ...
- java io系列21之 InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter 是字节流通向字符流的桥梁:它使用指定的 charset 读写字节并将其解码为字符.InputStreamReader 的作用是 ...
- java io系列25之 PrintWriter (字符打印输出流)
更多内容请参考:java io系列01之 "目录" PrintWriter 介绍 PrintWriter 是字符类型的打印输出流,它继承于Writer.PrintStream 用于 ...
- java io系列01之 "目录"
java io 系列目录如下: 01. java io系列01之 "目录" 02. java io系列02之 ByteArrayInputStream的简介,源码分析和示例(包括 ...
- java io系列06之 序列化总结(Serializable 和 Externalizable)
本章,我们对序列化进行深入的学习和探讨.学习内容,包括序列化的作用.用途.用法,以及对实现序列化的2种方式Serializable和Externalizable的深入研究. 转载请注明出处:http: ...
- java io系列15之 DataOutputStream(数据输出流)的认知、源码和示例
本章介绍DataOutputStream.我们先对DataOutputStream有个大致认识,然后再深入学习它的源码,最后通过示例加深对它的了解. 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblog ...
- java io系列17之 System.out.println("hello world")原理
我们初学java的第一个程序是"hello world" public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] ar ...
- java io系列02之 ByteArrayInputStream的简介,源码分析和示例(包括InputStream)
我们以ByteArrayInputStream,拉开对字节类型的“输入流”的学习序幕.本章,我们会先对ByteArrayInputStream进行介绍,然后深入了解一下它的源码,最后通过示例来掌握它的 ...
随机推荐
- 安卓9.0系统机器(亲测有效)激活Xposed框架的步骤
对于喜欢玩手机的哥们来说,经常会用到xposed框架及其种类繁多功能无敌的模块,对于5.0以下的系统版本,只要手机能获得root权限,安装和激活xposed框架是非常简便的,但随着系统版本的持续更新, ...
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016 RC3 安装
首先下载SQL Server 2016 RC3 安装iso 下载链接 ed2k://|file|cn_sql_server_2016_rc_3_x64_dvd_8566578.iso|24648232 ...
- 转:Git Submodule管理项目子模块
使用场景 当项目越来越庞大之后,不可避免的要拆分成多个子模块,我们希望各个子模块有独立的版本管理,并且由专门的人去维护,这时候我们就要用到git的submodule功能. 常用命令 git clone ...
- c/c++ 模板 类型推断
模板类型的推断 下面的函数f是个模板函数,typename T.下表是,根据调用测的实参,推断出来的T的类型. 请注意下表的红字部分, f(T&& t)看起来是右值引用,但其实它会根据 ...
- Centos7 安装mysql-8.0.13(rpm)
yum or rpm? yum安装方式很方便,但是下载mysql的时候从官网下载,速度较慢. rpm安装方式可以从国内镜像下载mysql的rpm包,比较快.rpm也适合离线安装. 环境说明 操作系统: ...
- PowerDesigner 提示 Existence of index、key、reference错误
一.建立一个表后,为何检测出现Existence of index的警告 A table should contain at least one column, one index, one key, ...
- 阿狸V任务页面爬取数据解析
需求: 爬取:https://v.taobao.com/v/content/video 所有主播详情页信息 首页分析 分析可以得知数据是通过ajax请求获取的. 分析请求头 详情页分析 详情页和详情页 ...
- 记录学习antd design pro dva的过程,主要记错, 多图预警,如有理解偏差,忘指出,多谢!
首要问题: 如何增加菜单项 答案: 在router.config中添加路由,在locales语言国际化增加选项 问题1: 答案1: 问题2: 这个要修改state,正确写法 存在的疑惑:为什么不能直接 ...
- 【alpha阶段】第十次Scrum Meeting
每日任务内容 队员 昨日完成任务 明日要完成的任务 牛宇航 #26 评价总览接口编写https://github.com/rRetr0Git/rateMyCourse/issues/26 alpha阶 ...
- 如何改善SSH连接过慢(效率)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++问题:通过SSH链接远程Linux主机过慢.重点:学习如何通过调整ssh_config配置文件,提高SSH连接效率.时 ...
