『数据结构与算法』二叉查找树(BST)
微信搜索:码农StayUp
主页地址:https://gozhuyinglong.github.io
源码分享:https://github.com/gozhuyinglong/blog-demos
1. 二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
二叉查找树又叫二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),或叫二叉搜索树,简称BST。BST是一种节点值之间有次序的二叉树。其特性是:
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于或等于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
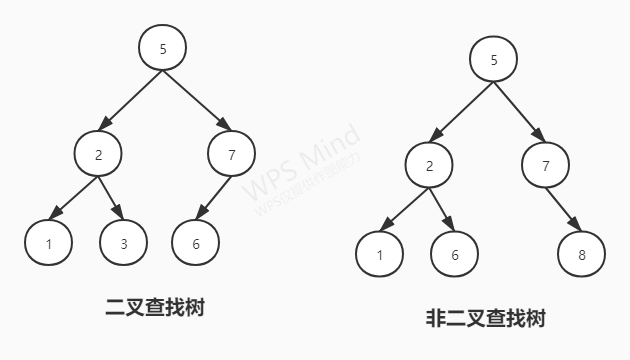
二叉查找树相比于其他数据结构的优势在于查找、插入的时间复杂度较低,为$O(logN)$。用大$O$符号表示的时间复杂度:
| 算法 | 平均 | 最差 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间 | $O(N)$ | $O(N)$ |
| 搜索 | $O(logN)$ | $O(N)$ |
| 插入 | $O(logN)$ | $O(N)$ |
| 删除 | $O(logN)$ | $O(N)$ |
2. BST的实现
二叉查找树要求所有的节点元素都能够排序,所以我们的Node节点类需要实现Comparable接口,树中的两个元素可以使用compareTo方法进行比较。
我们节点中元素的类型为int型,所以该接口泛型为Comparable<Integer>,下面是具体实现:
2.1 节点类
- element 为数据元素
- left 为左子节点
- right 为右子节点
class Node implements Comparable<Integer> {
private final int element; // 数据元素
private Node left; // 左子树
private Node right; // 右子树
private Node(Integer element) {
this.element = element;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Integer o) {
return o.compareTo(element);
}
}
2.2 二叉查找树类
- root 为树根,所有的操作均始于此
后面会在该类中增加其他方法,如添加、查找、删除等
class BinarySearchTree {
private Node root; // 树根
}
3. 插入节点
向二叉查找树中插入的节点总是叶子节点,插入过程如下:
- 若
root为空,则将插入节点设为root - 当前元素与插入元素通过
compareTo进行比较,若插入元素值小,并且左子节点left为空,则插入至当前节点左子节点;否则继续递归 - 若插入元素值大,且右子节点
right为空,则插入至当前节点右子节点;否则继续递归。 - 若插入元素等于当前节点元素,则插入失败。注:也可以将其插入到右子节点,我这里为了方便直接放弃插入。
具体实现:
在BinarySearchTree类中添加两个方法:
public boolean add(int element)为公开方法private boolean add(Node node, int element)为私有方法,内部递归使用
// 添加元素
public boolean add(int element) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(element);
return true;
}
return add(root, element);
}
// 添加元素(递归)
private boolean add(Node node, int element) {
if (node.compareTo(element) < 0) {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(element);
return true;
} else {
return add(node.left, element);
}
} else if (node.compareTo(element) > 0) {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(element);
return true;
} else {
return add(node.right, element);
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
4. 查找节点
通过二叉查找树查找元素,其过程如下:
- 若
root为空,则查找失败 - 将当前元素与目标元素对比,若相等则查找成功。
- 若不相等,则继续递归查找:若目标值小于当前节点值,则查找左子树;否则,查找右子树。
具体实现:
在BinarySearchTree类中添加两个方法:
public Node find(int element)为公开方法private Node find(Node node, int element)为私有方法,内部递归使用
// 查找元素
public Node find(int element) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return find(root, element);
}
// 查询元素(递归)
private Node find(Node node, int element) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int compareResult = node.compareTo(element);
if (compareResult < 0) {
return find(node.left, element);
} else if (compareResult > 0) {
return find(node.right, element);
} else {
return node;
}
}
5. 遍历节点
BST是一个有序二叉树,通过中序遍历可顺序输出树中节点。
中序遍历过程如下:
- 递归遍历左子节点
- 输出当前节点
- 递归遍历右子节点
具体实现:
在BinarySearchTree类中添加两个方法:
public void orderPrint()为公开方法private void orderPrint(Node node)为私有方法,内部递归使用
// 遍历节点
public void orderPrint() {
orderPrint(root);
}
// 遍历节点(递归)
private void orderPrint(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 递归左子节点
if (node.left != null) {
orderPrint(node.left);
}
// 输出当前节点
System.out.println(node.element);
// 递归右子节点
if (node.right != null) {
orderPrint(node.right);
}
}
6. 删除节点
删除节点最为复查,共有三种情况:
6.1 目标元素为叶子节点
叶子节点最容易删除,过程如下:
- 找到目标节点的父节点
- 判断目标节点是父节点的左子树还是右子树
- 若是左子树,将父节点的
left设为空;否则将父节点的right设为空
6.2 目标元素即有左子树,也有右子树
该情况删除操作最为复杂,过程如下:
- 找到目标节点的父节点
- 判断目标节点是父节点的左子树还是右子树
- 找到右子树中最小元素(叶子节点),将其赋给临时变量
minNode,再将该元素从树中删除 - 将目标元素的属性赋予
minNode。 - 若目标元素是父节点的左子树,将父节点的
left设为minNode;否则将父节点的right设为minNode
6.3 目标元素只有左子树,或只有右子树
删除过程如下
- 找到目标节点的父节点
- 判断目标节点是父节点的左子树还是右子树
- 若是左子树,将父节点的
left设为目标节点不为空的子树;否则将父节点的right设为目标节点不为空的子树
具体实现
在BinarySearchTree类中添加两个方法:
public boolean remove(int element)为公开方法private boolean remove(Node parentNode, Node node, int element)为私有方法,内部递归使用
// 删除节点
public boolean remove(int element) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
// 如果删除的元素是root
if (root.compareTo(element) == 0) {
if (root.right == null) {
root = root.left;
} else {
root.right.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
return remove(null, root, element);
}
// 删除节点(递归)
private boolean remove(Node parentNode, Node node, int element) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 先找到目标元素
int compareResult = node.compareTo(element);
if (compareResult < 0) {
return remove(node, node.left, element);
}
if (compareResult > 0) {
return remove(node, node.right, element);
}
// 找到目标元素,判断该节点是父节点的左子树还是右子树
boolean isLeftOfParent = false;
if (parentNode.left != null && parentNode.left.compareTo(element) == 0) {
isLeftOfParent = true;
}
// 删除目标元素
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { // (1)目标元素为叶子节点,直接删除
if (isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = null;
} else {
parentNode.right = null;
}
} else if (node.left != null && node.right != null) { // (2)目标元素即有左子树,也有右子树
// 找到右子树最小值(叶子节点),并将其删除
Node minNode = findMin(node.right);
remove(minNode.element);
// 将该最小值替换要删除的目标节点
minNode.left = node.left;
minNode.right = node.right;
if(isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = minNode;
} else {
parentNode.right = minNode;
}
} else { // (3)目标元素只有左子树,或只有右子树
if (isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
} else {
parentNode.right = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
}
}
return true;
}
}
7. 完整代码
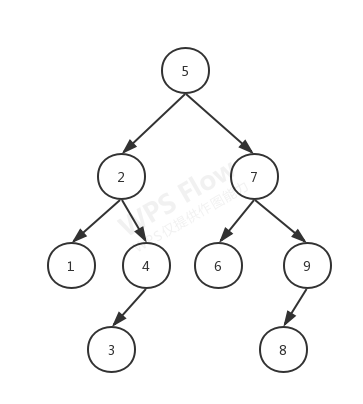
该代码根据下图二叉查找树实现,其操作包括:添加、查找、遍历、删除、查询最小值、查询最大值。
public class BinarySearchTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
System.out.println("----------------------添加元素");
Integer[] array = {5, 2, 7, 1, 4, 3, 7, 6, 9, 8};
for (Integer element : array) {
System.out.printf("添加元素[%s] --> %s\n", element, tree.add(element));
}
System.out.println("----------------------顺序输出(中序遍历)");
tree.orderPrint();
System.out.println("----------------------查找元素");
System.out.println(tree.find(7));
System.out.println("----------------------查找最小元素");
System.out.println(tree.findMin());
System.out.println("----------------------查找最大元素");
System.out.println(tree.findMax());
System.out.println("----------------------是否包含元素");
System.out.println("是否包含[0] --> \t" + tree.contains(0));
System.out.println("是否包含[2] --> \t" + tree.contains(2));
System.out.println("----------------------删除目标元素");
System.out.println("删除[0] --> \t" + tree.remove(0));
tree.orderPrint();
System.out.println("删除[1] --> \t" + tree.remove(1));
tree.orderPrint();
System.out.println("删除[4] --> \t" + tree.remove(4));
tree.orderPrint();
System.out.println("删除[7] --> \t" + tree.remove(7));
tree.orderPrint();
}
private static class BinarySearchTree {
private Node root; // 树根
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param element
* @return
*/
public boolean add(int element) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(element);
return true;
}
return add(root, element);
}
/**
* 添加元素(递归)
*
* @param node
* @param element
* @return
*/
private boolean add(Node node, int element) {
if (node.compareTo(element) < 0) {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(element);
return true;
} else {
return add(node.left, element);
}
} else if (node.compareTo(element) > 0) {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(element);
return true;
} else {
return add(node.right, element);
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 查询元素
*
* @param element
* @return
*/
public Node find(int element) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return find(root, element);
}
/**
* 查询元素(递归)
*
* @param node
* @param element
* @return
*/
private Node find(Node node, int element) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int compareResult = node.compareTo(element);
if (compareResult < 0) {
return find(node.left, element);
} else if (compareResult > 0) {
return find(node.right, element);
} else {
return node;
}
}
/**
* 查找最大值
*
* @return
*/
public Node findMax() {
return findMax(root);
}
/**
* 查找最大值(递归)
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
private Node findMax(Node node) {
if (node.right == null) {
return node;
}
return findMax(node.right);
}
/**
* 查找最小值
*
* @return
*/
private Node findMin() {
return findMin(root);
}
/**
* 查找最小值(递归)
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
private Node findMin(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
return findMin(node.left);
}
/**
* 顺序输出
*/
public void orderPrint() {
orderPrint(root);
}
/**
* 顺序输出(递归)
*
* @param node
*/
private void orderPrint(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 递归左子节点
if (node.left != null) {
orderPrint(node.left);
}
// 输出当前节点
System.out.println(node.element);
// 递归右子节点
if (node.right != null) {
orderPrint(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 是否包含某值
*
* @param element
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(int element) {
if (find(element) == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除目标元素
*
* @param element
* @return
*/
public boolean remove(int element) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
// 如果删除的元素是root
if (root.compareTo(element) == 0) {
if (root.right == null) {
root = root.left;
} else {
root.right.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
return remove(null, root, element);
}
/**
* 删除目标元素(递归),有三种情况:
* (1)目标元素为叶子节点
* (2)目标元素即有左子树,也有右子树
* (3)目标元素只有左子树,或只有右子树
*
* @param parentNode 当前节点的父节点
* @param node 当前节点(若当前节点上的元素与要删除的元素匹配,则删除当前节点)
* @param element 要删除的元素
* @return
*/
private boolean remove(Node parentNode, Node node, int element) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 先找到目标元素
int compareResult = node.compareTo(element);
if (compareResult < 0) {
return remove(node, node.left, element);
}
if (compareResult > 0) {
return remove(node, node.right, element);
}
// 找到目标元素,判断该节点是父节点的左子树还是右子树
boolean isLeftOfParent = false;
if (parentNode.left != null && parentNode.left.compareTo(element) == 0) {
isLeftOfParent = true;
}
// 删除目标元素
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { // (1)目标元素为叶子节点,直接删除
if (isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = null;
} else {
parentNode.right = null;
}
} else if (node.left != null && node.right != null) { // (2)目标元素即有左子树,也有右子树
// 找到右子树最小值(叶子节点),并将其删除
Node minNode = findMin(node.right);
remove(minNode.element);
// 将该最小值替换要删除的目标节点
minNode.left = node.left;
minNode.right = node.right;
if(isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = minNode;
} else {
parentNode.right = minNode;
}
} else { // (3)目标元素只有左子树,或只有右子树
if (isLeftOfParent) {
parentNode.left = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
} else {
parentNode.right = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
}
}
return true;
}
}
private static class Node implements Comparable<Integer> {
private final Integer element; // 数据元素
private Node left; // 左子树
private Node right; // 右子树
private Node(Integer element) {
this.element = element;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Integer o) {
return o.compareTo(element);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"element=" + element +
'}';
}
}
}
输出结果:
----------------------添加元素
添加元素[5] --> true
添加元素[2] --> true
添加元素[7] --> true
添加元素[1] --> true
添加元素[4] --> true
添加元素[3] --> true
添加元素[7] --> false
添加元素[6] --> true
添加元素[9] --> true
添加元素[8] --> true
----------------------顺序输出(中序遍历)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
----------------------查找元素
Node{element=7}
----------------------查找最小元素
Node{element=1}
----------------------查找最大元素
Node{element=9}
----------------------是否包含元素
是否包含[0] --> false
是否包含[2] --> true
----------------------删除目标元素
删除[0] --> false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
删除[1] --> true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
删除[4] --> true
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
删除[7] --> true
2
3
5
6
8
9
推荐阅读
- 《 数组 》
- 《 稀疏数组 》
- 《 链表(单链表、双链表、环形链表) 》
- 《 栈 》
- 《 队列 》
- 《 树 》
- 《 二叉树 》
- 《 二叉查找树(BST) 》
- 《 AVL树(平衡二叉树) 》
- 《 B树 》
- 《 散列表(哈希表) 》
『数据结构与算法』二叉查找树(BST)的更多相关文章
- Java数据结构与算法(4):二叉查找树
一.二叉查找树定义 二叉树每个节点都不能有多于两个的儿子.二叉查找树是特殊的二叉树,对于树中的每个节点X,它的左子树中的所有项的值小于X中的项,而它的右子树中所有项的值大于X中的项. 二叉查找树节点的 ...
- Java数据结构和算法(五)二叉排序树(BST)
Java数据结构和算法(五)二叉排序树(BST) 数据结构与算法目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10115867.html) 二叉排序树(Binary S ...
- 数据结构和算法(Golang实现)(27)查找算法-二叉查找树
二叉查找树 二叉查找树,又叫二叉排序树,二叉搜索树,是一种有特定规则的二叉树,定义如下: 它是一颗二叉树,或者是空树. 左子树所有节点的值都小于它的根节点,右子树所有节点的值都大于它的根节点. 左右子 ...
- HDU 3791 二叉搜索树 (数据结构与算法实验题 10.2 小明) BST
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3791 中文题不说题意. 建立完二叉搜索树后进行前序遍历或者后序遍历判断是否一样就可以了. 跟这次的作业第 ...
- 【数据结构与算法Python版学习笔记】树——二叉查找树 Binary Search Tree
二叉搜索树,它是映射的另一种实现 映射抽象数据类型前面两种实现,它们分别是列表二分搜索和散列表. 操作 Map()新建一个空的映射. put(key, val)往映射中加入一个新的键-值对.如果键已经 ...
- javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树
javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树 树是计算机科学中经常用到的一种数据结构.树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分成的方式存储数据,树被用来存储具有层级关系的数据,比如文件系统的文件,树还被用来存 ...
- 第一章:javascript: 数据结构与算法
在前端工程师中,常常有一种声音,我们为什么要学数据结构与算法,没有数据结构与算法,我们一样很好的完成工作.实际上,算法是一个宽泛的概念,我们写的任何程序都可以称为算法,甚至往冰箱里放大象,也要通过开门 ...
- 数据结构与算法JS实现
行解算法题,没错,就是这么方便. 当然也可以使用 Node.js 环境来执行,具体参考Node.js官方文档即可. 二 对象和面向对象编程 js中5种数据类型,并没有定义更多的数据类型,但是运用j ...
- 查找系列合集-二叉查找树BST
一. 二叉树 1. 什么是二叉树? 在计算机科学中,二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构. 通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree). 二叉树常 ...
随机推荐
- 每月一更的《HelloGitHub》第 58 期,来啦!
HelloGitHub 分享 GitHub 上有趣.入门级的开源项目.欢迎大家: 贡献代码 宣传你觉得优秀的项目 Star 项目️ 本月刊是每月 28 号更新,再见月刊就是年后了.在这里提前祝大家:新 ...
- 请不要继续将数据库称为 CP 或 AP - 掘金 https://juejin.im/post/6844903878102614030
请不要继续将数据库称为 CP 或 AP - 掘金 https://juejin.im/post/6844903878102614030
- URI与URL傻傻分不清楚?
前言 总所周知,缓存是解决Http1.1协议传输性能的问题中最主要的手段. 缓存既可以存在于浏览器上,也可以存在于服务器中. 而影响缓存的Http头部有很多,其中Cache-Control是比较重要的 ...
- 五万字长文带你学会Spring
Sping Spring概念介绍 spring是啥呢,你在斗地主的时候把别人打爆了那叫spring, 你成功的追到了你爱慕已久的女神,人生中的春天来了,那也叫sping 好了别看我老婆了,咱来讲讲啥是 ...
- MySQL的索引为什么用B+Tree?InnDB的数据存储文件和MyISAM的有何不同?
前言 这篇文章的题目,是我真实在面试过程中遇到的问题,某互联网众筹公司在考察面试者MySQL相关知识的第一个问题,我当时还是比较懵的,没想到这年轻人不讲武德,不按套路出牌,一般的问MySQL的相关知识 ...
- 同时执行多个$.getJSON() 出现数据混乱的问题的解决
$.getJSON() $.getJSON( url [, data ] [, success(data, textStatus, jqXHR) ] ) url是必选参数,表示json数据的地址: d ...
- lodash的debounce函数的使用
最新,在react新项目的开发中使用到了lodash类库的debounce方法,就随手梳理了一下此方法的方便之处 未使用debounce之前 如果不考虑使用debounce,那么在用户连续点击的情况之 ...
- 应急响应-PDCERF模型 (转)
目录 应急响应流程 防御模型 SDL 应急响应流程 很多人认为应急响应就是脸上被黑的机器去查查什么情况,是不是被中了botnet病毒.是不是被人中了rootkit等,是不是被挂了webshell等.应 ...
- SparkSql 数据类型转换
SparkSql 数据类型转换 1.SparkSql数据类型 1.1数字类型 1.2复杂类型 2.Spark Sql数据类型和Scala数据类型对比 3.Spark Sql数据类型转换案例 3.1获取 ...
- Mysql,Oracle与Java字段类型映射关系
Mysql,Oracle与Java字段类型映射关系 参考相关博文 MySQL/Oracle字段类型 Java字段类型 最大长度 BIT java.lang.Boolean 1 BLOB java.la ...
