tensorflow 从入门到摔掉肋骨 教程二
构造你自己的第一个神经网络
通过手势的图片识别图片比划的数字:
1) 现在用1080张64*64的图片作为训练集
2) 用120张图片作为测试集

定义初始化值
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_signs.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_signs.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0])) return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
小测:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
index = 0
plt.imshow(X_train_orig[index])
print(Y_train_orig)
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(Y_train_orig[:, index])))
小测2:把矩阵降维为一维,并做分类映射
# Flatten the training and test images
X_train_flatten = X_train_orig.reshape(X_train_orig.shape[0], -1).T
X_test_flatten = X_test_orig.reshape(X_test_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# Normalize image vectors
X_train = X_train_flatten/255.
X_test = X_test_flatten/255.
# Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6)
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6) print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[1]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[1]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape)) 结果:number of training examples = 1080
number of test examples = 120
X_train shape: (12288, 1080)
Y_train shape: (6, 1080)
X_test shape: (12288, 120)
Y_test shape: (6, 120)
线性回归模型:LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX.
Softmax 是判断哪个分类的概率最大
3.1 创建容器 存放变量
def create_placeholders(n_x,n_y):
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[n_x, None])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[n_y, None])
return X,Y
小测:
X, Y = create_placeholders(12288, 6)
print ("X = " + str(X))
print ("Y = " + str(Y))
3.2 初始化参数
在tensorflow里有get_variable初始化参数,通过Xavier进行设置变量的权重
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", [25,12288], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b1 = tf.get_variable("b1", [25,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
def initialize_parameters():
tf.set_random_seed(1) # so that your "random" numbers match ours ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 6 lines of code)
W1 = tf.get_variable("W1", [25,12288], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b1 = tf.get_variable("b1", [25,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W2 = tf.get_variable("W2", [12,25], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b2 = tf.get_variable("b2", [12,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
W3 = tf.get_variable("W3", [6,12], initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed = 1))
b3 = tf.get_variable("b3", [6,1], initializer = tf.zeros_initializer())
### END CODE HERE ### parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
"W3": W3,
"b3": b3} return parameters
3.3 向前传播 训练集训练
常用到的tensorflow函数:
tf.add(…,..)
tf.matmul(..,..) 矩阵阶乘
tf.nn.relu(..) Relu激活函数
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
print(X.shape)
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
W3 = parameters['W3']
b3 = parameters['b3'] ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 5 lines) # Numpy Equivalents:
Z1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W1, X), b1) # Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1) # A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W2, A1), b2) # Z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2) # A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W3, A2), b3) # Z3 = np.dot(W3,Z2) + b3
### END CODE HERE ### return Z3
小测:
tf.reset_default_graph()
With tf.Session() as sess:
X,Y = create_placeholders(12888,6)
Parameters = initialize_parameters()
Z3 = forward_propagation(X,parameters)
Print(“Z3=”+str(Z3))
3.4 计算损失函数(成本函数 Cost function)
在tensorflow 函数里 有tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=…,labels=…)) 其中
softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits是计算softmax函数
def conpute_cost(Z3,Y)
logits = tf.transpose(Z3) ##向量的转置
labels = tf.transpose(Y) ##向量的转置 cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels))
return cost
3.5 向后传播 求导 参数更新
向后传播 主要是通过求导来进行梯度下降 然后优化参数模型
其根本就是对损失函数求最小值
优化函数:
Optimizer = tf.train.GrandientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost)
执行函数:
_,c=sess.run([optimizer,cost],feed_dict={X:minibatch_X,Y:minibatch_Y})
3.6 一个完整的例子 (把上面的代码块汇总成功能)
def model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, learning_rate = 0.0001,
num_epochs = 1500, minibatch_size = 32, print_cost = True):
"""
Implements a three-layer tensorflow neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SOFTMAX. Arguments:
X_train -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 1080)
Y_train -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of training examples = 1080)
X_test -- training set, of shape (input size = 12288, number of training examples = 120)
Y_test -- test set, of shape (output size = 6, number of test examples = 120)
learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization
num_epochs -- number of epochs of the optimization loop
minibatch_size -- size of a minibatch
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 100 epochs Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
""" ops.reset_default_graph() # to be able to rerun the model without overwriting tf variables
tf.set_random_seed(1) # to keep consistent results
seed = 3 # to keep consistent results
(n_x, m) = X_train.shape # (n_x: input size, m : number of examples in the train set)
n_y = Y_train.shape[0] # n_y : output size
costs = [] # To keep track of the cost # Create Placeholders of shape (n_x, n_y)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
X, Y = create_placeholders(n_x, n_y)
### END CODE HERE ### # Initialize parameters
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
parameters = initialize_parameters()
### END CODE HERE ### # Forward propagation: Build the forward propagation in the tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
Z3 = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
### END CODE HERE ### # Cost function: Add cost function to tensorflow graph
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
cost = compute_cost(Z3, Y)
### END CODE HERE ### # Backpropagation: Define the tensorflow optimizer. Use an AdamOptimizer.
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost)
### END CODE HERE ### # Initialize all the variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # Start the session to compute the tensorflow graph
with tf.Session() as sess: # Run the initialization
sess.run(init) # Do the training loop
for epoch in range(num_epochs): epoch_cost = 0. # Defines a cost related to an epoch
num_minibatches = int(m / minibatch_size) # number of minibatches of size minibatch_size in the train set
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X_train, Y_train, minibatch_size, seed) for minibatch in minibatches: # Select a minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch # IMPORTANT: The line that runs the graph on a minibatch.
# Run the session to execute the "optimizer" and the "cost", the feedict should contain a minibatch for (X,Y).
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
_ , minibatch_cost = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: minibatch_X, Y: minibatch_Y})
### END CODE HERE ### epoch_cost += minibatch_cost / num_minibatches # Print the cost every epoch
if print_cost == True and epoch % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" % (epoch, epoch_cost))
if print_cost == True and epoch % 5 == 0:
costs.append(epoch_cost) # plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show() # lets save the parameters in a variable
parameters = sess.run(parameters)
print ("Parameters have been trained!") # Calculate the correct predictions
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(Z3), tf.argmax(Y)) # Calculate accuracy on the test set
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) print ("Train Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_train, Y: Y_train}))
print ("Test Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({X: X_test, Y: Y_test})) return parameters
我们执行:
parameters = model(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)
得到结果:

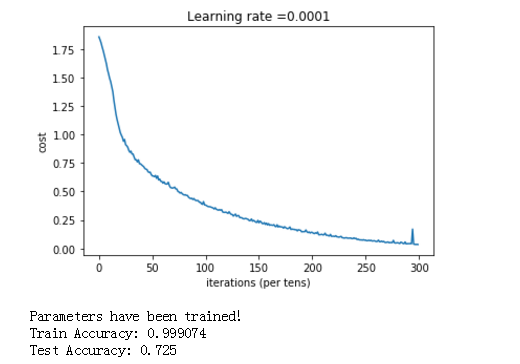
tensorflow的 函数库很多,这里是冰山一角,还有很多需要我们去学习。后面有时间,就把图像识别的卷积的tensorflow例子给搬出研究一下。
我的大都内容来自吴恩达的公益视频和教案,特此鸣谢。
参考:吴恩达网易课程
tensorflow 从入门到摔掉肋骨 教程二的更多相关文章
- 给深度学习入门者的Python快速教程 - numpy和Matplotlib篇
始终无法有效把word排版好的粘贴过来,排版更佳版本请见知乎文章: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24309547 实在搞不定博客园的排版,排版更佳的版本在: 给深度学习入 ...
- SpringBoot入门教程(二)CentOS部署SpringBoot项目从0到1
在之前的博文<详解intellij idea搭建SpringBoot>介绍了idea搭建SpringBoot的详细过程, 并在<CentOS安装Tomcat>中介绍了Tomca ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- Tensorflow高速入门2--实现手写数字识别
Tensorflow高速入门2–实现手写数字识别 环境: 虚拟机ubuntun16.0.4 Tensorflow 版本号:0.12.0(仅使用cpu下) Tensorflow安装见: http://b ...
- 给深度学习入门者的Python快速教程
给深度学习入门者的Python快速教程 基础篇 numpy和Matplotlib篇 本篇部分代码的下载地址: https://github.com/frombeijingwithlove/dlcv_f ...
- TensorFlow从入门到实战资料汇总 2017-02-02 06:08 | 数据派
TensorFlow从入门到实战资料汇总 2017-02-02 06:08 | 数据派 来源:DataCastle数据城堡 TensorFlow是谷歌基于DistBelief进行研发的第二代人工智能学 ...
- 【0】TensorFlow光速入门-序
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tujia/p/13863181.html 序言: 对于我这么一个技术渣渣来说,想学习TensorFlow机器学习,实在是太难了: 百度&qu ...
- 【2】TensorFlow光速入门-数据预处理(得到数据集)
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tujia/p/13862351.html 系列文章: [0]TensorFlow光速入门-序 [1]TensorFlow光速入门-tenso ...
- 无废话ExtJs 入门教程二十一[继承:Extend]
无废话ExtJs 入门教程二十一[继承:Extend] extjs技术交流,欢迎加群(201926085) 在开发中,我们在使用视图组件时,经常要设置宽度,高度,标题等属性.而这些属性可以通过“继承” ...
随机推荐
- EasyUI ComboTree无限层级异步加载示例
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="EasuUIDemoTree.a ...
- DataRow和DataRowView的区别
可以将DataView同数据库的视图类比,不过有点不同,数据库的视图可以跨表建立视图,DataView则只能对某一个DataTable建立视图. DataView一般通过DataTable.Defau ...
- zookeeper 笔记-机制的特点
zookeeper的getData(),getChildren()和exists()方法都可以注册watcher监听.而监听有以下几个特性: 一次性触发(one-time trigger) 当数据改变 ...
- idea 创建多模块依赖Maven项目
本来网上的教程还算多,但是本着自己有的才是自己的原则,还是自己写一份的好,虽然可能自己也不会真的用得着. 1. 创建一个新maven项目 2. 3. 输入groupid和artifactid,后面步骤 ...
- win8在安装office visio2003出现“请求的操作需要提升”,解决方法
单击右键,然后以管理员身份运行即可
- tomcat默认日志路径更改
在项目访问量不断增加时,tomcat下logs也迅速增大,有时甚至因为填满了所在分区而出现无空间写入日志而导致程序出问题. 这时要更改logs的默认目录,指向更大的磁盘.修改主要有两步: 1. 修改t ...
- Problem J
Problem Description 有一楼梯共M级,刚开始时你在第一级,若每次只能跨上一级或二级,要走上第M级,共有多少种走法? Input 输入数据首先包含一个整数N,表示测试实例的个数,然后是 ...
- 最最简单的CentOs6在线源搭建
非常实用的在线源搭建,只要4步骤 1.点击进入http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo ,这是阿里云的源 2.复制所有的代码 ctrl+a,ctrl+c ...
- hive的简单理解--笔记
Hive的理解 数据仓库的工具 Hive仅仅是在hadoop上面包装了SQL: Hive的数据存储在hadoop上 Hive的计算由MR进行 Hive批量处理数据 Hive的特点 1 可扩展性(h ...
- empty()和remove()的区别
这两个都是删除元素,但是两者还是有区别的. remove()这个方法呢是删除被选元素的所有文本和子元素,当然包括被选元素自己. 而empty()呢,被选元素自己是不会被删除的. 比如: <div ...
