尚硅谷springboot学习5-主入口类说明
package com.atguigu; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { // Spring应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication: Spring Boot应用标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor; /**
* Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more
* {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience
* annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration},
* {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication { /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "exclude")
Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "excludeName")
String[] excludeName() default {}; /**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; /**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; }
@SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot的配置类;标注在某个类上,表示这是一个Spring Boot的配置类;
* Copyright 2012-2016 the original author or authors. package org.springframework.boot; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /**
* Indicates that a class provides Spring Boot application
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}. Can be used as an alternative to the Spring's
* standard {@code @Configuration} annotation so that configuration can be found
* automatically (for example in tests).
* <p>
* Application should only ever include <em>one</em> {@code @SpringBootConfiguration} and
* most idiomatic Spring Boot applications will inherit it from
* {@code @SpringBootApplication}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.4.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { }
@Configuration:配置类上来标注这个注解;配置类 ----- 配置文件;配置类也是容器中的一个组件;@Component
/*
* Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.context.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* Indicates that a class declares one or more {@link Bean @Bean} methods and
* may be processed by the Spring container to generate bean definitions and
* service requests for those beans at runtime, for example:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* // instantiate, configure and return bean ...
* }
* }</pre>
*
* <h2>Bootstrapping {@code @Configuration} classes</h2>
*
* <h3>Via {@code AnnotationConfigApplicationContext}</h3>
*
* {@code @Configuration} classes are typically bootstrapped using either
* {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext} or its web-capable variant,
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
* AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext}. A simple example with the former follows:
*
* <pre class="code">
* AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
* ctx.register(AppConfig.class);
* ctx.refresh();
* MyBean myBean = ctx.getBean(MyBean.class);
* // use myBean ...
* </pre>
*
* See {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext} Javadoc for further details and see
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
* AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext} for {@code web.xml} configuration instructions.
*
* <h3>Via Spring {@code <beans>} XML</h3>
*
* <p>As an alternative to registering {@code @Configuration} classes directly against an
* {@code AnnotationConfigApplicationContext}, {@code @Configuration} classes may be
* declared as normal {@code <bean>} definitions within Spring XML files:
* <pre class="code">
* {@code
* <beans>
* <context:annotation-config/>
* <bean class="com.acme.AppConfig"/>
* </beans>}</pre>
*
* In the example above, {@code <context:annotation-config/>} is required in order to
* enable {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor} and other annotation-related
* post processors that facilitate handling {@code @Configuration} classes.
*
* <h3>Via component scanning</h3>
*
* <p>{@code @Configuration} is meta-annotated with {@link Component @Component}, therefore
* {@code @Configuration} classes are candidates for component scanning (typically using
* Spring XML's {@code <context:component-scan/>} element) and therefore may also take
* advantage of {@link Autowired @Autowired}/{@link javax.inject.Inject @Inject}
* like any regular {@code @Component}. In particular, if a single constructor is present
* autowiring semantics will be applied transparently:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class AppConfig {
* private final SomeBean someBean;
*
* public AppConfig(SomeBean someBean) {
* this.someBean = someBean;
* }
*
* // @Bean definition using "SomeBean"
*
* }</pre>
*
* <p>{@code @Configuration} classes may not only be bootstrapped using
* component scanning, but may also themselves <em>configure</em> component scanning using
* the {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} annotation:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @ComponentScan("com.acme.app.services")
* public class AppConfig {
* // various @Bean definitions ...
* }</pre>
*
* See the {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} javadoc for details.
*
* <h2>Working with externalized values</h2>
*
* <h3>Using the {@code Environment} API</h3>
*
* Externalized values may be looked up by injecting the Spring
* {@link org.springframework.core.env.Environment} into a {@code @Configuration}
* class the usual (e.g. using the {@code @Autowired} annotation):
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Autowired Environment env;
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* MyBean myBean = new MyBean();
* myBean.setName(env.getProperty("bean.name"));
* return myBean;
* }
* }</pre>
*
* Properties resolved through the {@code Environment} reside in one or more "property
* source" objects, and {@code @Configuration} classes may contribute property sources to
* the {@code Environment} object using
* the {@link org.springframework.core.env.PropertySources @PropertySources} annotation:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/acme/app.properties")
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Inject Environment env;
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* return new MyBean(env.getProperty("bean.name"));
* }
* }</pre>
*
* See {@link org.springframework.core.env.Environment Environment}
* and {@link PropertySource @PropertySource} Javadoc for further details.
*
* <h3>Using the {@code @Value} annotation</h3>
*
* Externalized values may be 'wired into' {@code @Configuration} classes using
* the {@link Value @Value} annotation:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/acme/app.properties")
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Value("${bean.name}") String beanName;
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* return new MyBean(beanName);
* }
* }</pre>
*
* This approach is most useful when using Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
* PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer}, usually enabled via XML with
* {@code <context:property-placeholder/>}. See the section below on composing
* {@code @Configuration} classes with Spring XML using {@code @ImportResource},
* see {@link Value @Value} Javadoc, and see {@link Bean @Bean} Javadoc for details on working with
* {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} types such as
* {@code PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer}.
*
* <h2>Composing {@code @Configuration} classes</h2>
*
* <h3>With the {@code @Import} annotation</h3>
*
* <p>{@code @Configuration} classes may be composed using the {@link Import @Import} annotation,
* not unlike the way that {@code <import>} works in Spring XML. Because
* {@code @Configuration} objects are managed as Spring beans within the container,
* imported configurations may be injected the usual way (e.g. via constructor injection):
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class DatabaseConfig {
*
* @Bean
* public DataSource dataSource() {
* // instantiate, configure and return DataSource
* }
* }
*
* @Configuration
* @Import(DatabaseConfig.class)
* public class AppConfig {
*
* private final DatabaseConfig dataConfig;
*
* public AppConfig(DatabaseConfig dataConfig) {
* this.dataConfig = dataConfig;
* }
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* // reference the dataSource() bean method
* return new MyBean(dataConfig.dataSource());
* }
* }</pre>
*
* Now both {@code AppConfig} and the imported {@code DatabaseConfig} can be bootstrapped
* by registering only {@code AppConfig} against the Spring context:
*
* <pre class="code">
* new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);</pre>
*
* <h3>With the {@code @Profile} annotation</h3>
*
* {@code @Configuration} classes may be marked with the {@link Profile @Profile} annotation to
* indicate they should be processed only if a given profile or profiles are <em>active</em>:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Profile("development")
* @Configuration
* public class EmbeddedDatabaseConfig {
*
* @Bean
* public DataSource dataSource() {
* // instantiate, configure and return embedded DataSource
* }
* }
*
* @Profile("production")
* @Configuration
* public class ProductionDatabaseConfig {
*
* @Bean
* public DataSource dataSource() {
* // instantiate, configure and return production DataSource
* }
* }</pre>
*
* Alternatively, you may also declare profile conditions at the {@code @Bean} method level,
* e.g. for alternative bean variants within the same configuration class:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class ProfileDatabaseConfig {
*
* @Bean("dataSource")
* @Profile("development")
* public DataSource embeddedDatabase() { ... }
*
* @Bean("dataSource")
* @Profile("production")
* public DataSource productionDatabase() { ... }
* }</pre>
*
* See the {@link Profile @Profile} and {@link org.springframework.core.env.Environment}
* javadocs for further details.
*
* <h3>With Spring XML using the {@code @ImportResource} annotation</h3>
*
* As mentioned above, {@code @Configuration} classes may be declared as regular Spring
* {@code <bean>} definitions within Spring XML files. It is also possible to
* import Spring XML configuration files into {@code @Configuration} classes using
* the {@link ImportResource @ImportResource} annotation. Bean definitions imported from
* XML can be injected the usual way (e.g. using the {@code Inject} annotation):
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* @ImportResource("classpath:/com/acme/database-config.xml")
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Inject DataSource dataSource; // from XML
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* // inject the XML-defined dataSource bean
* return new MyBean(this.dataSource);
* }
* }</pre>
*
* <h3>With nested {@code @Configuration} classes</h3>
*
* {@code @Configuration} classes may be nested within one another as follows:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @Configuration
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Inject DataSource dataSource;
*
* @Bean
* public MyBean myBean() {
* return new MyBean(dataSource);
* }
*
* @Configuration
* static class DatabaseConfig {
* @Bean
* DataSource dataSource() {
* return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder().build();
* }
* }
* }</pre>
*
* When bootstrapping such an arrangement, only {@code AppConfig} need be registered
* against the application context. By virtue of being a nested {@code @Configuration}
* class, {@code DatabaseConfig} <em>will be registered automatically</em>. This avoids
* the need to use an {@code @Import} annotation when the relationship between
* {@code AppConfig} {@code DatabaseConfig} is already implicitly clear.
*
* <p>Note also that nested {@code @Configuration} classes can be used to good effect
* with the {@code @Profile} annotation to provide two options of the same bean to the
* enclosing {@code @Configuration} class.
*
* <h2>Configuring lazy initialization</h2>
*
* <p>By default, {@code @Bean} methods will be <em>eagerly instantiated</em> at container
* bootstrap time. To avoid this, {@code @Configuration} may be used in conjunction with
* the {@link Lazy @Lazy} annotation to indicate that all {@code @Bean} methods declared within
* the class are by default lazily initialized. Note that {@code @Lazy} may be used on
* individual {@code @Bean} methods as well.
*
* <h2>Testing support for {@code @Configuration} classes</h2>
*
* The Spring <em>TestContext framework</em> available in the {@code spring-test} module
* provides the {@code @ContextConfiguration} annotation, which as of Spring 3.1 can
* accept an array of {@code @Configuration} {@code Class} objects:
*
* <pre class="code">
* @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
* @ContextConfiguration(classes={AppConfig.class, DatabaseConfig.class})
* public class MyTests {
*
* @Autowired MyBean myBean;
*
* @Autowired DataSource dataSource;
*
* @Test
* public void test() {
* // assertions against myBean ...
* }
* }</pre>
*
* See TestContext framework reference documentation for details.
*
* <h2>Enabling built-in Spring features using {@code @Enable} annotations</h2>
*
* Spring features such as asynchronous method execution, scheduled task execution,
* annotation driven transaction management, and even Spring MVC can be enabled and
* configured from {@code @Configuration}
* classes using their respective "{@code @Enable}" annotations. See
* {@link org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync @EnableAsync},
* {@link org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling @EnableScheduling},
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement @EnableTransactionManagement},
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy @EnableAspectJAutoProxy},
* and {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc @EnableWebMvc}
* for details.
*
* <h2>Constraints when authoring {@code @Configuration} classes</h2>
*
* <ul>
* <li>Configuration classes must be provided as classes (i.e. not as instances returned
* from factory methods), allowing for runtime enhancements through a generated subclass.
* <li>Configuration classes must be non-final.
* <li>Configuration classes must be non-local (i.e. may not be declared within a method).
* <li>Any nested configuration classes must be declared as {@code static}.
* <li>{@code @Bean} methods may not in turn create further configuration classes
* (any such instances will be treated as regular beans, with their configuration
* annotations remaining undetected).
* </ul>
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.0
* @see Bean
* @see Profile
* @see Import
* @see ImportResource
* @see ComponentScan
* @see Lazy
* @see PropertySource
* @see AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment
* @see org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration { /**
* Explicitly specify the name of the Spring bean definition associated
* with this Configuration class. If left unspecified (the common case),
* a bean name will be automatically generated.
* <p>The custom name applies only if the Configuration class is picked up via
* component scanning or supplied directly to a {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext}.
* If the Configuration class is registered as a traditional XML bean definition,
* the name/id of the bean element will take precedence.
* @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultBeanNameGenerator
*/
String value() default ""; }
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;以前我们需要配置的东西,Spring Boot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效;
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.tomcat.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader; /**
* Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and
* configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually
* applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined. For example, If you
* have {@code tomcat-embedded.jar} on your classpath you are likely to want a
* {@link TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory} (unless you have defined your own
* {@link EmbeddedServletContainerFactory} bean).
* <p>
* When using {@link SpringBootApplication}, the auto-configuration of the context is
* automatically enabled and adding this annotation has therefore no additional effect.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration tries to be as intelligent as possible and will back-away as you
* define more of your own configuration. You can always manually {@link #exclude()} any
* configuration that you never want to apply (use {@link #excludeName()} if you don't
* have access to them). You can also exclude them via the
* {@code spring.autoconfigure.exclude} property. Auto-configuration is always applied
* after user-defined beans have been registered.
* <p>
* The package of the class that is annotated with {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration},
* usually via {@code @SpringBootApplication}, has specific significance and is often used
* as a 'default'. For example, it will be used when scanning for {@code @Entity} classes.
* It is generally recommended that you place {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} (if you're
* not using {@code @SpringBootApplication}) in a root package so that all sub-packages
* and classes can be searched.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration classes are regular Spring {@link Configuration} beans. They are
* located using the {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} mechanism (keyed against this class).
* Generally auto-configuration beans are {@link Conditional @Conditional} beans (most
* often using {@link ConditionalOnClass @ConditionalOnClass} and
* {@link ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnMissingBean} annotations).
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @see ConditionalOnBean
* @see ConditionalOnMissingBean
* @see ConditionalOnClass
* @see AutoConfigureAfter
* @see SpringBootApplication
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; /**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {}; }
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):
Spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class;
将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器;
/*
* Copyright 2012-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; /**
* Indicates that the package containing the annotated class should be registered with
* {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.3.0
* @see AutoConfigurationPackages
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { }
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);给容器中导入组件
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;
将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中;
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import org.springframework.context.annotation.DeferredImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata; /**
* {@link DeferredImportSelector} to handle {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration}. This class can also be subclassed if a custom variant of
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration}. is needed.
*
* @deprecated as of 1.5 in favor of {@link AutoConfigurationImportSelector}
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Madhura Bhave
* @since 1.3.0
* @see EnableAutoConfiguration
*/
@Deprecated
public class EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector
extends AutoConfigurationImportSelector { @Override
protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (getClass().equals(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)) {
return getEnvironment().getProperty(
EnableAutoConfiguration.ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class,
true);
}
return true;
} }
/*
* Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.RelaxedPropertyResolver;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.DeferredImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAttributes;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /**
* {@link DeferredImportSelector} to handle {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration}. This class can also be subclassed if a custom variant of
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration}. is needed.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Madhura Bhave
* @since 1.3.0
* @see EnableAutoConfiguration
*/
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware,
BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = {}; private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class); private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory; private Environment environment; private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; @Override
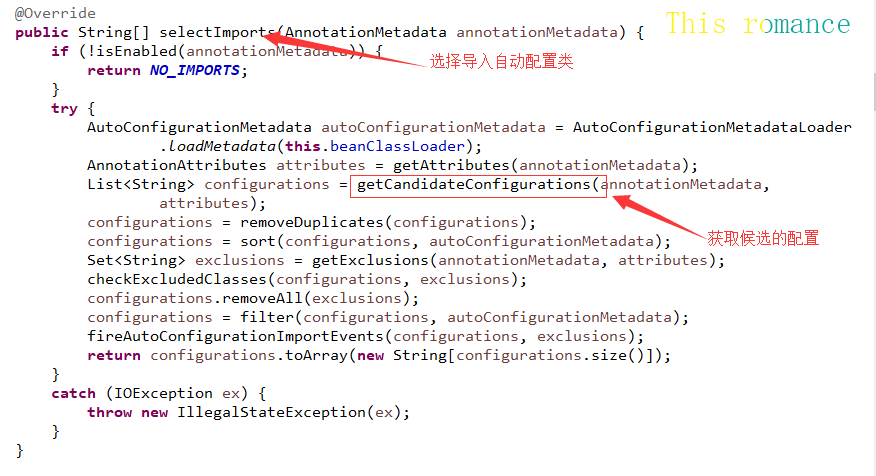
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
try {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
configurations = sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
} protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return true;
} /**
* Return the appropriate {@link AnnotationAttributes} from the
* {@link AnnotationMetadata}. By default this method will return attributes for
* {@link #getAnnotationClass()}.
* @param metadata the annotation metadata
* @return annotation attributes
*/
protected AnnotationAttributes getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
String name = getAnnotationClass().getName();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(name, true));
Assert.notNull(attributes,
"No auto-configuration attributes found. Is " + metadata.getClassName()
+ " annotated with " + ClassUtils.getShortName(name) + "?");
return attributes;
} /**
* Return the source annotation class used by the selector.
* @return the annotation class
*/
protected Class<?> getAnnotationClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
} /**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
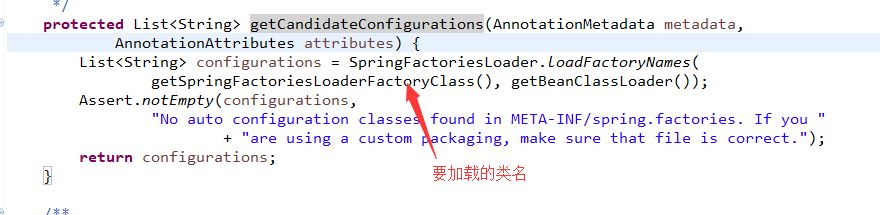
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
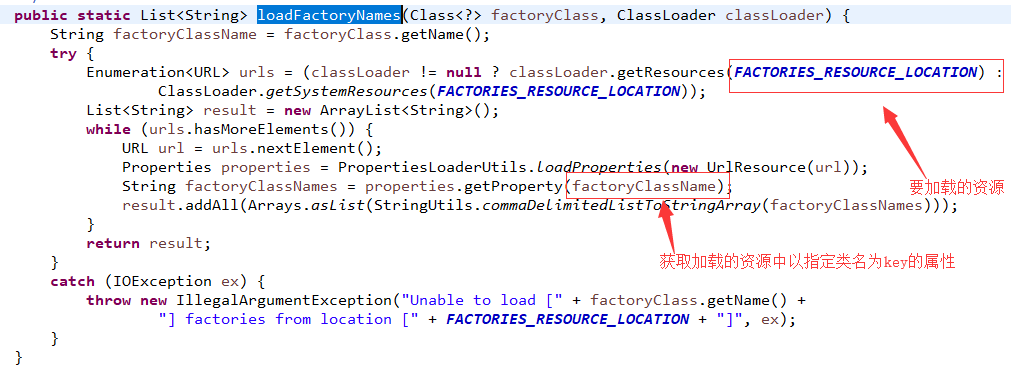
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
} /**
* Return the class used by {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} to load configuration
* candidates.
* @return the factory class
*/
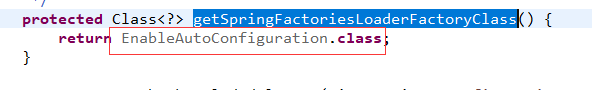
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
} private void checkExcludedClasses(List<String> configurations,
Set<String> exclusions) {
List<String> invalidExcludes = new ArrayList<String>(exclusions.size());
for (String exclusion : exclusions) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(exclusion, getClass().getClassLoader())
&& !configurations.contains(exclusion)) {
invalidExcludes.add(exclusion);
}
}
if (!invalidExcludes.isEmpty()) {
handleInvalidExcludes(invalidExcludes);
}
} /**
* Handle any invalid excludes that have been specified.
* @param invalidExcludes the list of invalid excludes (will always have at least one
* element)
*/
protected void handleInvalidExcludes(List<String> invalidExcludes) {
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
for (String exclude : invalidExcludes) {
message.append("\t- ").append(exclude).append(String.format("%n"));
}
throw new IllegalStateException(String
.format("The following classes could not be excluded because they are"
+ " not auto-configuration classes:%n%s", message));
} /**
* Return any exclusions that limit the candidate configurations.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return exclusions or an empty set
*/
protected Set<String> getExclusions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
Set<String> excluded = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
excluded.addAll(asList(attributes, "exclude"));
excluded.addAll(Arrays.asList(attributes.getStringArray("excludeName")));
excluded.addAll(getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty());
return excluded;
} private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(
this.environment, "spring.autoconfigure.");
Map<String, Object> properties = resolver.getSubProperties("exclude");
if (properties.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<String> excludes = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
if (name.isEmpty() || name.startsWith("[") && value != null) {
excludes.addAll(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(StringUtils
.tokenizeToStringArray(String.valueOf(value), ","))));
}
}
return excludes;
}
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(getEnvironment(),
"spring.autoconfigure.");
String[] exclude = resolver.getProperty("exclude", String[].class);
return (Arrays.asList(exclude == null ? new String[0] : exclude));
} private List<String> sort(List<String> configurations,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) throws IOException {
configurations = new AutoConfigurationSorter(getMetadataReaderFactory(),
autoConfigurationMetadata).getInPriorityOrder(configurations);
return configurations;
} private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
String[] candidates = configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length];
boolean skipped = false;
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {
invokeAwareMethods(filter);
boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (!match[i]) {
skip[i] = true;
skipped = true;
}
}
}
if (!skipped) {
return configurations;
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(candidates.length);
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (!skip[i]) {
result.add(candidates[i]);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int numberFiltered = configurations.size() - result.size();
logger.trace("Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
+ TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startTime)
+ " ms");
}
return new ArrayList<String>(result);
} protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
} private MetadataReaderFactory getMetadataReaderFactory() {
try {
return getBeanFactory().getBean(
SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer.BEAN_NAME,
MetadataReaderFactory.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
return new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(this.resourceLoader);
}
} protected final <T> List<T> removeDuplicates(List<T> list) {
return new ArrayList<T>(new LinkedHashSet<T>(list));
} protected final List<String> asList(AnnotationAttributes attributes, String name) {
String[] value = attributes.getStringArray(name);
return Arrays.asList(value == null ? new String[0] : value);
} private void fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(List<String> configurations,
Set<String> exclusions) {
List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> listeners = getAutoConfigurationImportListeners();
if (!listeners.isEmpty()) {
AutoConfigurationImportEvent event = new AutoConfigurationImportEvent(this,
configurations, exclusions);
for (AutoConfigurationImportListener listener : listeners) {
invokeAwareMethods(listener);
listener.onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(event);
}
}
} protected List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> getAutoConfigurationImportListeners() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportListener.class,
this.beanClassLoader);
} private void invokeAwareMethods(Object instance) {
if (instance instanceof Aware) {
if (instance instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) instance)
.setBeanClassLoader(this.beanClassLoader);
}
if (instance instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) instance).setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
if (instance instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) instance).setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
if (instance instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) instance).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
}
} @Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
} protected final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
} @Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = classLoader;
} protected ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader;
} @Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
} protected final Environment getEnvironment() {
return this.environment;
} @Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
} protected final ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
} @Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1;
} }
说一下AutoConfigurationImportSelector
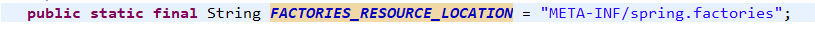
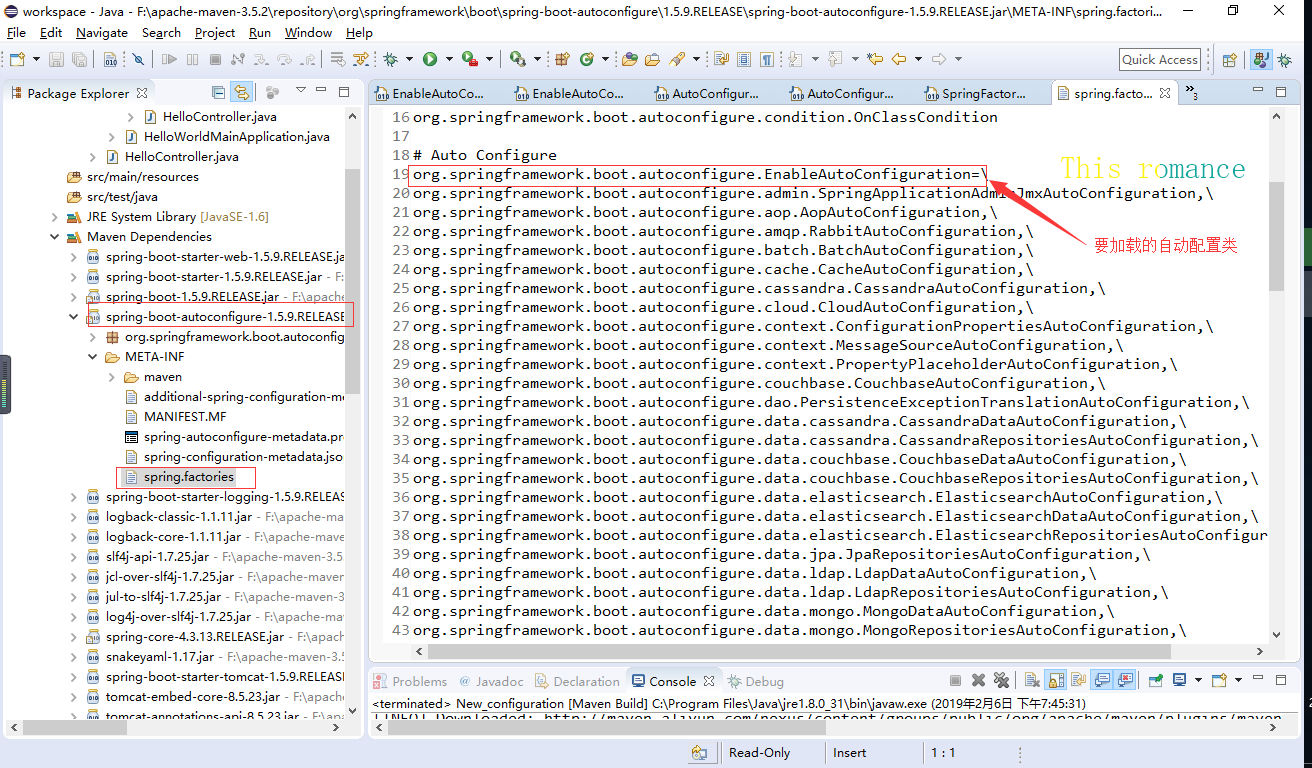
有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;以前我们需要自己配置的东西,自动配置类都帮我们;
J2EE的整体整合解决方案和自动配置都在spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.9.RELEASE.jar;
尚硅谷springboot学习5-主入口类说明的更多相关文章
- 尚硅谷springboot学习14-自动配置原理
配置文件能配置哪些属性 配置文件能配置的属性参照 自动配置的原理 1).SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration 2).@Ena ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习35-启动原理
先列出几个重要的事件回调机制 配置在META-INF/spring.factories ApplicationContextInitializer SpringApplicationRunListen ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习34-整合SpringData JPA
SpringData简介
- 尚硅谷springboot学习27-使用外置servlet容器
嵌入式Servlet容器:应用打成可执行的jar 优点:简单.便携: 缺点:默认不支持JSP.优化定制比较复杂(使用定制器[ServerProperties.自定义EmbeddedServle ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习33-整合mybatis
引入mybatis依赖(还要引入mysql和jdbc依赖) <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId& ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习24-错误处理
1.SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制 默认效果: 1).浏览器,返回一个默认的错误页面
- 尚硅谷springboot学习23-SpringMVC配置
1. Spring MVC auto-configuration 以下是SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置:(WebMvcAutoConfiguration) Inclusion of ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习22-Thymeleaf入门
Thymeleaf是一种模板引擎,类似于JSP.Velocity.Freemarker
- 尚硅谷springboot学习20-web开发简介
使用SpringBoot 1).创建SpringBoot应用,添加我们需要的模块: 2).SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来 3).自己编写业 ...
随机推荐
- vultr 上实现高可用冗余浮动公网IP出口(使用BIRD+BGP协议)High Availability on Vultr with Floating IP and BGP
官方文档: https://www.vultr.com/docs/high-availability-on-vultr-with-floating-ip-and-bgp https://www.vul ...
- win7 没有权限使用网络资源
局域网下同一工作组电脑无法访问 提示"....没有权限使用网络资源...." 一.组策略 win + R 输入gpedit.msc并回车,打开本地组策略编辑器 按如下展开 计算机配 ...
- Linux常用命令1-50(持续更新中)
1:echo $PATH (打印出PATH变量的值) 不同用户下面的PATH值有可能不一样 echo 有显示打印的意思 $ 表示后面的是一个变量的意思 PATH 变量 /usr ...
- CRM 2016 IFrame 函数修改 父页面字段
IFrame js 代码: parent.Xrm.Page.getAttribute("new_xxxx").setValue(123); 当然,可以设置 new_xxxx 字段的 ...
- U3d学习001-RollBox例子
1.世界坐标系和局部坐标系(参照物坐标系)——以参照物为父物体节点 2.刚体组件: 获得GetComponent<Rigidbody>(); 移动AddForce(n ...
- (转)C#实现注册码
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/netcorner/archive/2011/08/31/2911922.html 开发软件时,当用到商业用途时,注册码与激活码就显得很重要了. ...
- 搭建(WSTMart)php电商环境时缺少fileinfo函数
搭建WSTMart环境步骤: 第一步:安装phpstudy,一键安装即可 第二步:把下好的系统源码,放到一个文件夹中,并放到刚刚安装好的phpstudy下WWW文件夹下,如WWW>WSTMart ...
- Android手动控制软键盘的开启和关闭,判断软键盘是否显示;
工具类,拿走就能用: import android.annotation.TargetApi; import android.app.Activity; import android.content. ...
- 二、Html5元素、属性、格式化
- 字符串截取函数slice, substring, substr
在日常项目需求中,常常会遇到需要截取字符串操作的工作,而ECMAScript为我们提供了原生的截取字符串的函数,而且提供了三个:slice, substring, substr.我们怎么判断在什么时候 ...
