使用TensorFlow给花朵🌺分类
第一步:准备好需要的库
- tensorflow-gpu 1.8.0
- opencv-python 3.3.1
- numpy
- skimage
- os
- pillow
第二步:准备数据集:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Kbz_UaRhAfhlweFY28R8Sw 密码:iym3
本次使用了花朵分类的数据集,总共有5类

每类里面有不同形态的同一类花朵

在下载完数据集之后,我们对数据集进行预处理:
from skimage import io, transform
import os
import numpy as np # 将所有的图片resize成100*100
w = 100
h = 100
c = 3 # 读取图片
def read_img(path):
imgs = []
labels = []
classs = os.listdir(path) for idx, folder in enumerate(classs):
cate = os.path.join(path, folder)
for im in os.listdir(cate):
img_path =os.path.join(cate, im)
# print('reading the images:%s' % (img_path))
img = io.imread(img_path)
img = transform.resize(img, (w, h))
# with open('tests.txt', 'a') as f:
# f.write(img_path+'_'+str(idx)+'\n')
imgs.append(img)
labels.append(idx)
return np.asarray(imgs, np.float32), np.asarray(labels, np.int32) def suffer(data, label):
# 打乱顺序
num_example = data.shape[0]
arr = np.arange(num_example)
np.random.shuffle(arr)
data = data[arr]
label = label[arr] # 将所有数据分为训练集和验证集
ratio = 0.8
s = np.int(num_example * ratio)
x_train = data[:s]
y_train = label[:s]
x_val = data[s:]
y_val = label[s:]
return x_train,y_train,x_val,y_val def minibatches(inputs=None, targets=None, batch_size=None, shuffle=False):
assert len(inputs) == len(targets)
if shuffle:
indices = np.arange(len(inputs))
np.random.shuffle(indices)
for start_idx in range(0, len(inputs) - batch_size + 1, batch_size):
if shuffle:
excerpt = indices[start_idx:start_idx + batch_size]
else:
excerpt = slice(start_idx, start_idx + batch_size)
yield inputs[excerpt], targets[excerpt]
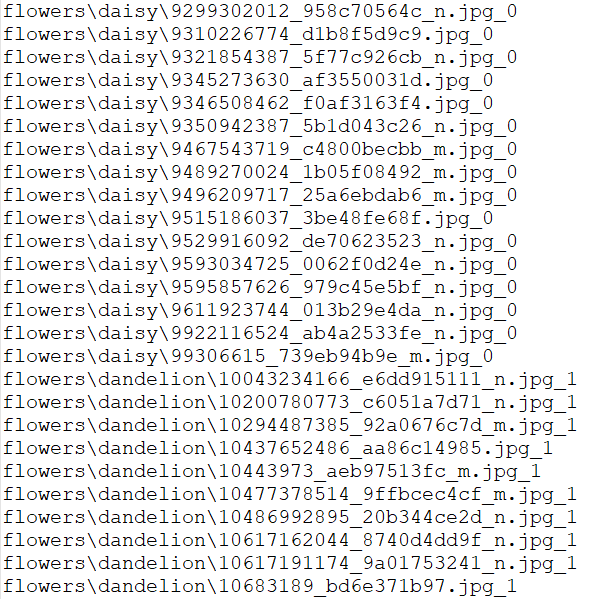
我们将图片统一设为100×100的大小,然后对每一个文件夹标号,作为标签。为了检验我们是否将标签与图片对齐,我预留了一个写文件路径+标签的一个文件。
写出来是这样的
在做处理好标签和图片之后我们将其设定为 np.asarray(imgs, np.float32)的格式。
然后将这些图片随机打乱顺序。以8:2的比例划分训练集和验证集。
接着我们来生成minibatch:将数据切分成batch_size的大小送入网络。
在预处理完数据之后,我们开始进行网络的构建
import tensorflow as tf def batch_norm(x, momentum=0.9, epsilon=1e-5, train=True, name='bn'):
return tf.layers.batch_normalization(x,
momentum=momentum,
epsilon=epsilon,
scale=True,
training=train,
name=name) def simple_cnn(x):
# 第一个卷积层(100——>50)
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=x,
filters=32,
kernel_size=[3, 3],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01))
conv1 = batch_norm(conv1, name='pw_bn1')
pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) # 第二个卷积层(50->25)
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool1,
filters=64,
kernel_size=[3, 3],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01))
conv2 = batch_norm(conv2, name='pw_bn2')
pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv2, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) # 第三个卷积层(25->12)
conv3 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool2,
filters=128,
kernel_size=[3, 3],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01))
conv3 = batch_norm(conv3, name='pw_bn3') pool3 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv3, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) # 第四个卷积层(12->6)
conv4 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool3,
filters=128,
kernel_size=[3, 3],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01))
conv4 = batch_norm(conv4, name='pw_bn4') pool4 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv4, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2) re1 = tf.reshape(pool4, [-1, 6 * 6 * 128]) # 全连接层
dense1 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=re1,
units=1024,
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
kernel_regularizer=tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.003))
dense2 = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dense1,
units=512,
activation=tf.nn.relu,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
kernel_regularizer=tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.003))
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dense2,
units=5,
activation=None,
kernel_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
kernel_regularizer=tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.003))
pred = tf.nn.softmax(logits, name='prob')
return logits, pred
我们的网络由4个卷积层,两个全连接层,一个softmax层组成。在每一层的卷积后面加入了batch_normalization,relu和池化。
batch_normalization层很好用,加上它之后,有效的预防了梯度消逝和爆炸,还加速了收敛。
在搭建好网络之后,我们开始编写训练模块
import tensorflow as tf
import cnn
import dataset
# 将所有的图片resize成100*100
w = 100
h = 100
c = 3
path = 'flowers' x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, w, h, c], name='x')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, ], name='y_') logits,pred = cnn.simple_cnn(x)
loss = tf.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(labels=y_, logits=logits)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(loss)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.cast(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.int32), y_)
acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) data, label = dataset.read_img(path)
x_train, y_train,x_val, y_val = dataset.suffer(data, label) # 训练和测试数据,可将n_epoch设置更大一些
n_epoch = 11
batch_size = 16
def train():
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
for epoch in range(n_epoch):
train_loss, train_acc, n_batch = 0, 0, 0
for x_train_a, y_train_a in dataset.minibatches(x_train, y_train, batch_size, shuffle=True):
_, err, ac = sess.run([train_op, loss, acc], feed_dict={x: x_train_a, y_: y_train_a})
train_loss += err
train_acc += ac
n_batch += 1 print('Epoch %d - train loss: %f'%(epoch, (train_loss / n_batch)))
print('Epoch %d - train acc: %f'%(epoch,train_acc / n_batch)) # validation
val_loss, val_acc, n_batch = 0, 0, 0
for x_val_a, y_val_a in dataset.minibatches(x_val, y_val, batch_size, shuffle=False):
err, ac = sess.run([loss, acc], feed_dict={x: x_val_a, y_: y_val_a})
val_loss += err
val_acc += ac
n_batch += 1
print('Epoch %d - Validation loss: %f' %(epoch, val_loss / n_batch))
print('Epoch %d - Validation Accuracy: %f'%( epoch,(val_acc / n_batch)))
if epoch % 5 == 0:
saver.save(sess, "./model/save_net.ckpt",epoch)
print('Trained Model Saved.') train()
训练时我们首先要定义X,Y作为索引
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, w, h, c], name='x')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, ], name='y_') 然后对于刚才构建的网络进行损失的计算,精确度计算以及优化器的选择。
接着我们将session初始化
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
然后将定义的X,Y索引与你的真实数据,标签对齐。
使用
_, err, ac = sess.run([train_op, loss, acc], feed_dict={x: x_train_a, y_: y_train_a})
开始运行就可以了。
测试同理,不过测试的时候不需要优化器,所以只需要加入参数loss,acc就可以了。
我们每隔5次保存一次模型。
在训练结束后,我们对使用之前训练好的模型进行预测:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
from cnn import simple_cnn
# 将所有的图片resize成100*100
w = 100
h = 100
c = 3
classes = ['daisy','dandelion','roses','sunflowers','tulips']
image_test = Image.open('44079668_34dfee3da1_n.jpg')
resized_image = image_test.resize((w, h), Image.BICUBIC)
image_data = np.array(resized_image, dtype='float32') imgs_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, w, h, c]) logits,pred = simple_cnn(imgs_holder) saver = tf.train.Saver()
ckpt_dir = './model/' with tf.Session() as sess:
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(ckpt_dir)
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
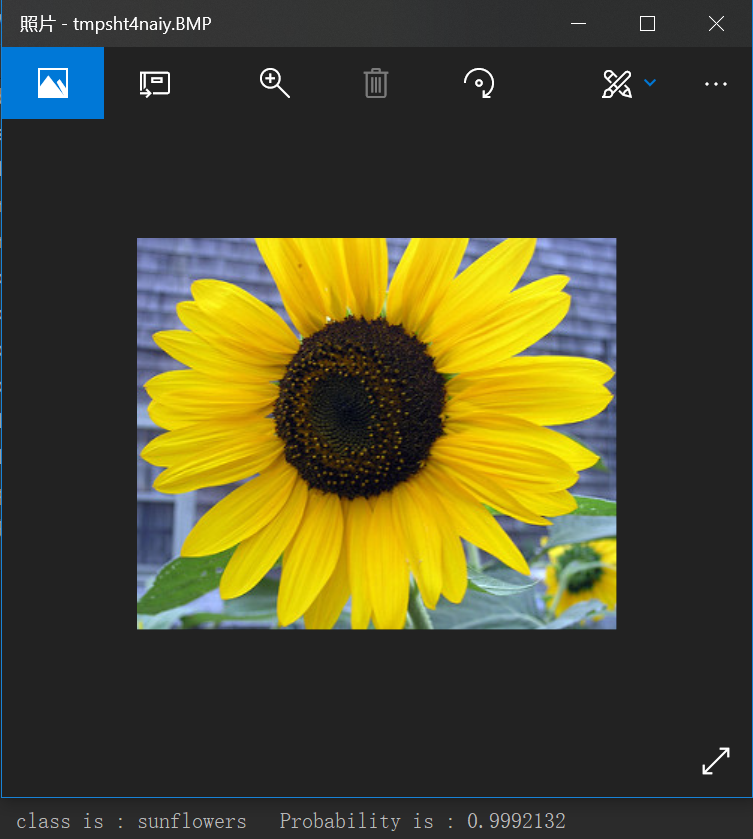
classes_ = sess.run(pred,feed_dict={ imgs_holder: np.reshape(image_data , [1, w, h, c])}) num = np.argmax(classes_)
print('class is :',classes[int(num)],' Probability is :',classes_[0][int(num)])
在预测时,因为子还需要输入一张图片就可以了,所以我们只制作图片的索引
imgs_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, w, h, c]) 然后读取刚才保存的参数,只需要输入目录,即可自动读取最后训练的模型。
然后运行:
classes_ = sess.run(pred,feed_dict={ imgs_holder: np.reshape(image_data , [1, w, h, c])})
输出每个类的概率值。
我们将这个概率最大的值的标号读取出来,对应之前文件夹的标号。
classes = ['daisy','dandelion','roses','sunflowers','tulips']
然后将这个标号对应的概率数标出来。
本次使用了tf.layer进行了简单CNN的构建,并且使用了tensorflow传统的sess.run
的方法来运行图,没有使用之前提到的高级API。
在这种方法上进行了简单的尝试,接下来会尝试使用slim框架构建网络。
使用TensorFlow给花朵🌺分类的更多相关文章
- SVM原理以及Tensorflow 实现SVM分类(附代码)
1.1. SVM介绍 1.2. 工作原理 1.2.1. 几何间隔和函数间隔 1.2.2. 最大化间隔 - 1.2.2.0.0.1. \(L( {x}^*)\)对$ {x}^*$求导为0 - 1.2.2 ...
- 芝麻HTTP:TensorFlow LSTM MNIST分类
本节来介绍一下使用 RNN 的 LSTM 来做 MNIST 分类的方法,RNN 相比 CNN 来说,速度可能会慢,但可以节省更多的内存空间. 初始化 首先我们可以先初始化一些变量,如学习率.节点单元数 ...
- tensorflow实现二分类
读万卷书,不如行万里路.之前看了不少机器学习方面的书籍,但是实战很少.这次因为项目接触到tensorflow,用一个最简单的深层神经网络实现分类和回归任务. 首先说分类任务,分类任务的两个思路: 如果 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记————分类MNIST数据集
在使用tensorflow分类MNIST数据集中,最容易遇到的问题是下载MNIST样本的问题. 一般是通过使用tensorflow内置的函数进行下载和加载, from tensorflow.examp ...
- Tensorflow实现手写体分类(含dropout)
一.手写体分类 1. 数据集 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data im ...
- 用 TensorFlow 实现 SVM 分类问题
这篇文章解释了底部链接的代码. 问题描述  如上图所示,有一些点位于单位正方形内,并做好了标记.要求找到一条线,作为分类的标准.这些点的数据在 inearly_separable_data.csv ...
- TF Boys (TensorFlow Boys ) 养成记(四):TensorFlow 简易 CIFAR10 分类网络
前面基本上把 TensorFlow 的在图像处理上的基础知识介绍完了,下面我们就用 TensorFlow 来搭建一个分类 cifar10 的神经网络. 首先准备数据: cifar10 的数据集共有 6 ...
- tensorflow 教程 文本分类 IMDB电影评论
昨天配置了tensorflow的gpu版本,今天开始简单的使用一下 主要是看了一下tensorflow的tutorial 里面的 IMDB 电影评论二分类这个教程 教程里面主要包括了一下几个内容:下载 ...
- 基于tensorflow的文本分类总结(数据集是复旦中文语料)
代码已上传到github:https://github.com/taishan1994/tensorflow-text-classification 往期精彩: 利用TfidfVectorizer进行 ...
随机推荐
- 前端学习 -- Css -- 选择器的优先级
当使用不同的选择器,选中同一个元素时并且设置相同的样式时,这时样式之间产生了冲突,最终到底采用哪个选择器定义的样式,由选择器的优先级(权重)决定优先级高的优先显示. 优先级的规则 内联样式 , 优先级 ...
- IntelliJ IDEA(2018)安装详解
转: IntelliJ IDEA(2018)安装详解 置顶 2018年06月06日 22:58:45 Lazymanx 阅读数:95701 版权声明: https://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- Mac OS利用ssh访问ubuntu虚拟机及云端操作
1.桥接模式 将该虚拟机的网口设置成桥接模式(Bridged Adapter),以确保主机可以ping通虚拟机: 2.安装ssh 在ubuntu虚拟机上安装ssh server: sudo apt-g ...
- MingW-v4.8.0+EDE-v13.04 配置使用C语言图形库
From: http://www.cnblogs.com/killerlegend/p/3946768.html Author:KillerLegend Date:2014.8.30 MingW的配置 ...
- HDU 2509 基础Anti-SG NIM
如果我们规定当局面中所有的单一游戏的SG值为0时,游戏结束,则先手必胜当且仅当:(1)游戏的SG!=0 && 存在单一游戏的SG>1:(2)游戏的SG==0 && ...
- 使用 git 托管代码
1. 下载安装好 git 客户端 2. 找一个家代码托管平台 我用 coding.net,注册个账号,建一个空项目 然后打开安装好的 git bash 客户端,使用 git clone 命令克隆下远程 ...
- 第10月第4天 Mac g++ sfml opendir
1. g++ OpenGL.cpp -I/Users/temp/Downloads/SFML-2.4.2-osx-clang/include -L/usr/local/lib -framework O ...
- 第6月第10天 svn checkout sqlite3
1. http://www.cnblogs.com/xuling/p/5602036.html 2. http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26819733/article/details/ ...
- sqlserver2008R2数据库自动备份脚本
CREATE proc [dbo].[usp_autoBackupDB] @dbname sysname=null --要备份的数据库名,不指定即为全部备份 ,)='d:\' --备份目录路径 ,)= ...
- 以python代码解释fork系统调用
import os print('Process (%s) start...' % os.getpid()) # Only works on Unix/Linux/Mac: pid = os.fork ...