Introduction to TensorFlow
Lecture note 1: Introduction to TensorFlow
Why TensorFlow
TensorFlow was originally created by researchers at Google as a single infrastructure for machine learning in both production and research. Later, an implementation of it was open sourced under the Apache 2.0 License in November 2015. On the Tensorflow website, we see:
"TensorFlow™ is an open source software library for
numerical computation using data flow graphs."
Note that only the implementation of TensorFlow that we see on GitHub is open-source. Google maintains its own internal version. It's said that Google did it because of the complicated relationships TensorFlow has with its other internal tools, not because Google is "hoarding good stuff". For the rest of this course, when we say TensorFlow, we are referring to the open source implementation.
The next key phrase we see is that TensorFlow is a "software library for Machine Intelligence". In the past year, it seems like every week, a company or another released their own deep learning library. For a non-exhaustive list of current deep learning libraries, please visit this link.
Given the plethora of these libraries, why did we choose Tensorflow to teach in this class? For a framework to be useful in production, it needs to be efficient, scalable, and maintainable. For research, the framework needs to have flexible operations that can be combined in novel ways. Alternative frameworks are either flexible enough for research but less scalable, such as Chainer and PyTorch, or scalable but less flexible, such as Caffe and MXNet. TensorFlow is both flexible and scalable, allowing users to streamline from research into production.
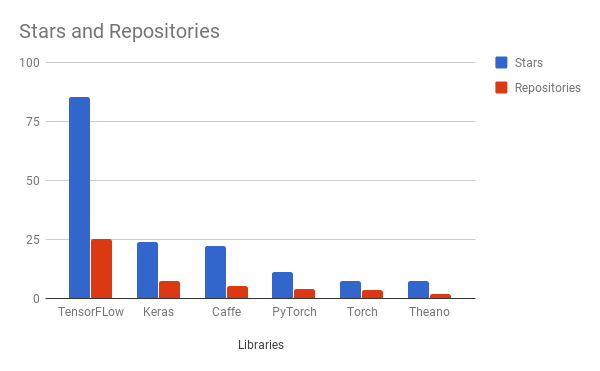
This unique position allowed TensorFlow to grow quickly. It's currently being used by big companies such as Google, OpenAI, NVIDIA, Intel, SAP, eBay, Airbus, Uber, Airbnb, Snap, Dropbox and startups alike. By the number of stars and related repositories on GitHub as of Jan 11, 2018, TensorFlow is by far the most popular machine learning library with more than 85.4k stars and 25.3k related repositories, twice as much as the total stars and related repositories of Caffe, PyTorch, Torch, and Theano combined. It's said that the rise of TensorFlow is the reason why the support for Theano was discontinued in September 2017.
 Demand for TensorFlow learning materials also surpasses that of any other framework.
Demand for TensorFlow learning materials also surpasses that of any other framework.

In summary, we chose TensorFlow because:
- Python API
- Portability: deploy computation to one or more CPUs or GPUs in a desktop, server, or mobile device with a single API
- Flexibility: from Raspberry Pi, Android, Windows, iOS, Linux to server farms
- Visualization (TensorBoard is da bomb)
- Save and restore models, graphs
- Auto-differentiation autodiff (no more taking derivatives by hand. Yay)
- Large community (~300k commits, ~85k repositories)
- Awesome projects already using TensorFlow
Some cool projects using Tensorflow
1. WaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio (DeepMind, 2016)
2. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks (Esteva, Kuprel, et al., Nature 2017)

3. Magenta (Google)
Use machine learning to create compelling art and music. Their projects are really fun! For example, please check out Draw Together with a Neural Network.

Below are some more examples of real world projects using TensorFlow, according to Google Research Blog, 2016:
- Australian marine biologists are using TensorFlow to find sea cows in tens of thousands of hi-res photos to better understand their populations, which are under threat of extinction.
- An enterprising Japanese cucumber farmer trained a model with TensorFlow to sort cucumbers by size, shape, and other characteristics.
- Radiologists have adapted TensorFlow to identify signs of Parkinson's disease in medical scans.
- Data scientists in the Bay Area have rigged up TensorFlow and the Raspberry Pi to keep track of the Caltrain.
I hope that after this class, you'd be able to use TensorFlow to work on super cool projects like that!
High level APIs on top of TensorFlow
There are many high level APIs built on top of TensorFlow. Some of the most popular APIs included Keras, TFLearn, and Sonnet. These high-level APIs allow for faster experimentation -- you can call a complex neural network models in a few lines of code. The APIs have attracted a sizeable number of users. You should definitely check them out, and we might briefly go over these high-level APIs in class if time permits.
However, the primary purpose of TensorFlow is not to provide out-of-the-box machine learning solutions. Instead, TensorFlow provides an extensive suite of functions and classes that allow users to define models from scratch. This is more complicated, but offers much more flexibility. You can build almost any architecture you can think of in TensorFlow.
Resources
We won't be using any textbook for this class. The library is changing so fast that it's hard for any book to keep up. We will be using mainly lecture notes and lecture slides. There are several resources that you might want to refer to become fluent in TensorFlow.
TensorFlowofficial sample models
StackOverflow should be your first port of call should you run into any problem with TensorFlow
There are also several introductory books on TensorFlow.
- Aurélien Géron's Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow (O'Reilly, March 2017)
- François Chollet's Deep Learning with Python (Manning Publications, November 2017)
- Nishant Shukla's Machine Learning with TensorFlow (Manning Publications, January 2018)
- Lieder et al.'s Learning TensorFlow A Guide to Building Deep Learning Systems (O'Reilly, August 2017)
TensorFlow Basics
The first thing we need to understand about TensorFlow is its computation graph approach. Any TensorFlow program consists of two phases:
Phase 1: assemble a graph
Phase 2: use a session to execute operations in the graph.
Note that this might change in the future with TensorFlow's eager mode, currently experimental.
It's best to explain this with graphs. Please refer to 4)to learn about TensorFlow's computation graph approach, tensors, subgraphs, and sessions.
Introduction to TensorFlow的更多相关文章
- [TensorFlow] Introduction to TensorFlow Datasets and Estimators
Datasets and Estimators are two key TensorFlow features you should use: Datasets: The best practice ...
- 吴恩达课后习题第二课第三周:TensorFlow Introduction
目录 第二课第三周:TensorFlow Introduction Introduction to TensorFlow 1 - Packages 1.1 - Checking TensorFlow ...
- 谷歌发布 TensorFlow Lite [官方网站,文档]
机器学习社区:http://tensorflow123.com/ 简介 TensorFlow Lite TensorFlow Lite 是 TensorFlow 针对移动和嵌入式设备的轻量级解决方案. ...
- TensorFlow 中文资源全集,官方网站,安装教程,入门教程,实战项目,学习路径。
Awesome-TensorFlow-Chinese TensorFlow 中文资源全集,学习路径推荐: 官方网站,初步了解. 安装教程,安装之后跑起来. 入门教程,简单的模型学习和运行. 实战项目, ...
- TensorFlow tutorial
代码示例来自https://github.com/aymericdamien/TensorFlow-Examples tensorflow先定义运算图,在run的时候才会进行真正的运算. run之前需 ...
- 5个最好的TensorFlow网络课程
1. Introduction to TensorFlow for Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning This c ...
- (zhuan) Building Convolutional Neural Networks with Tensorflow
Ahmet Taspinar Home About Contact Building Convolutional Neural Networks with Tensorflow Posted on a ...
- TensorFlow数据读取方式:Dataset API
英文详细版参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/jins-note/p/10243716.html Dataset API是TensorFlow 1.3版本中引入的一个新的模块,主要服 ...
- Awesome TensorFlow
Awesome TensorFlow A curated list of awesome TensorFlow experiments, libraries, and projects. Inspi ...
随机推荐
- Java 链式写法
Java链式写法,子类继承父类的属性,也可以返回子类的对象,只是需要重写基类的Set方法 public class MyLS { public static void main(String[] ar ...
- P3953 逛公园(dp,最短路)
P3953 逛公园 题目描述 策策同学特别喜欢逛公园.公园可以看成一张NN个点MM条边构成的有向图,且没有 自环和重边.其中1号点是公园的入口,NN号点是公园的出口,每条边有一个非负权值, 代表策策经 ...
- mybatis时间查询小技巧
网上大多数使用mybatis查询的时候都是把时间转换成Date使用的,其实这里时可以直接使用String的,比如 <if test="startTime != null and st ...
- Oracle 助记
title: Oracle 助记 Nothing is impossible! 基础操作 $ sqlplus name/pssword; # 登录数据库 $ create user username ...
- [POI2013]POL-Polarization
题目描述 Everyone knew it would only be a matter of time. So what? Faced for years on, a peril becomes t ...
- Linux用户、用户组权限管理详解
Linux用户管理三个重要文件详解: Linux登陆需要用户名.密码./etc/passwd 文件保存用户名.登录Linux时,Linux 先查找 /etc/passwd 文件中是否有这个用户名,没有 ...
- JS在即将离开当前页面(刷新或关闭)时触发事件
// onbeforeunload 事件在即将离开当前页面(刷新或关闭)时触发 window.onbeforeunload = function () { return /^\#\/ipinfo/.t ...
- CF540C Ice Cave
思路: 搜索. 加回溯会超时,不加回溯就过了,不是很理解. 实现: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace ...
- Android基础TOP5_1:AutoCompleteTextView自动补全文本框
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools= ...
- glassfish中新建数据源(创建数据库连接池)
1.浏览器输入:http://localhost:4848 登录glassfish域管理控制台,默认的用户名和密码是amin和adminadmin.(也可以通过NetBeans的服务选项卡--服务器- ...
