Spring框架系列(二)--装配和注入Bean
企业日常开发中,几乎都是Spring系的框架,无论是SSM、还是现在大火的SpringBoot,使用最大的目的就是简化开发
基本模块:
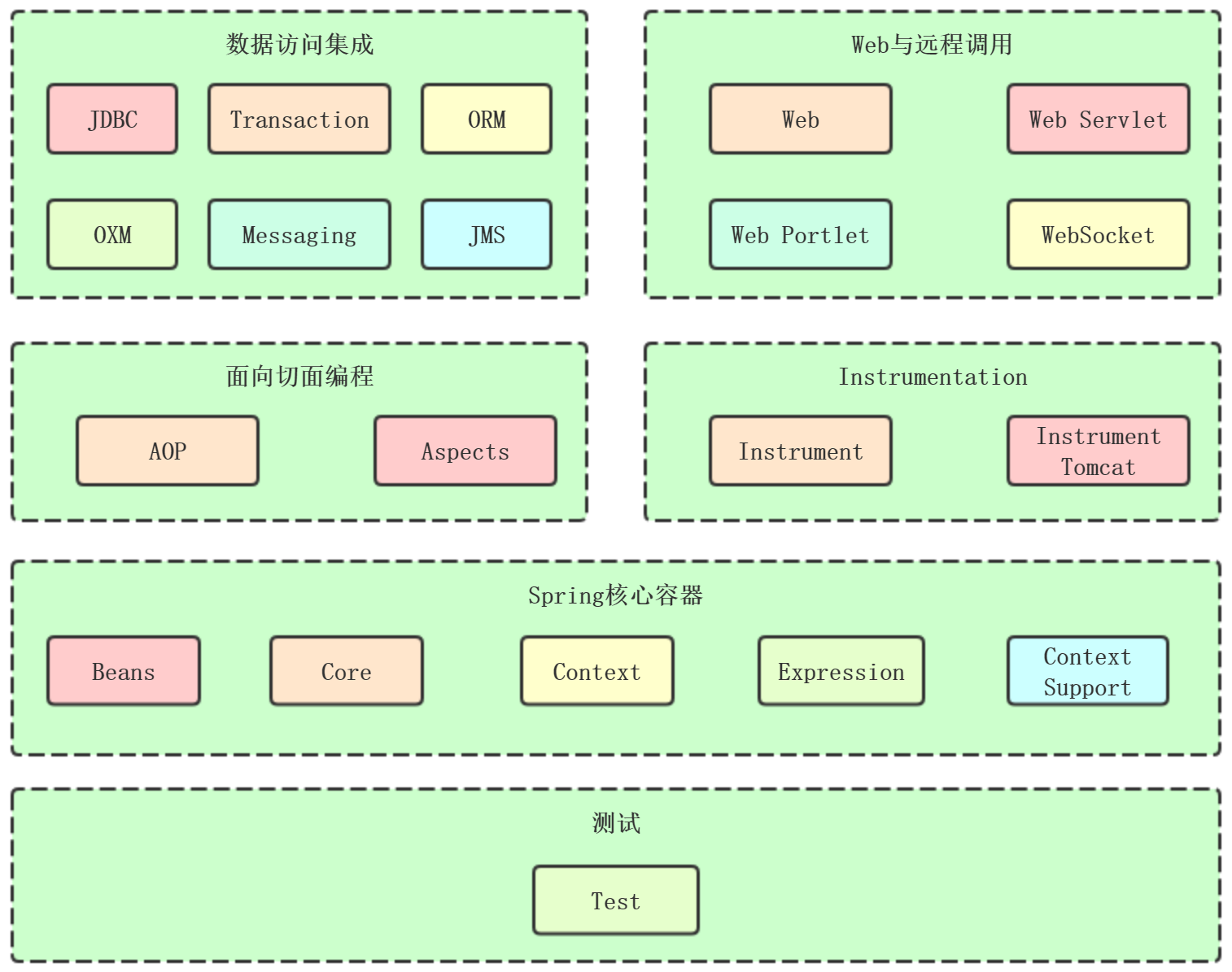
核心容器:Beans、Core、Context、SpEL
1. core和beans模块提供了整个框架最基础的部分,包括了IoC(控制反转)和Dependency Injection(依赖注入)。
2. Context建立在Core和Beans模块提供的基础之上:他提供了框架式访问对象的方式
3. core、beans、context构成了Spring的骨架
4. SpEL:提供了一种强大的用于在运行时操作对象的表达式语言
优点:
1、对象之间的依赖关系通过IOC容器进行管理,降低组件之间的耦合,不需要总是new一个对象
2、提供面向切面编程
3、功能丰富,Transaction、JDBC、WebSocket等
4、轻量级:大小和开销方面都是轻量级的
5、开放性很高,可以选择自己想要使用的功能
装配Bean
pojo的使用体现了非侵入式编程,通过DI进行装配
装配方式:
1、xml显式配置
2、java中显式配置
3、隐式的bean发现机制和自动装配
StudentDaoImpl.java
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("add");
}
@Override
public void del() {
System.out.println("del");
}
}
StudentServiceImpl.java
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { private StudentRepository studentResponstory; @Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("add");
} @Override
public void del() {
System.out.println("del");
}
}
1、xml显式配置
Spring最开始的配置方式,相比注解装配和java配置比较麻烦
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <beans>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.it.dao.impl.StudentDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.it.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl" >
<constructor-arg ref="studentDao" />
</bean>
</beans> </beans>
xml文件中首先要声明多个xml模式文件,这些xsd文件了配置spring xml元素
通过<bean>去配置,id如果省略的话,自动生成名称:"class内容"#0,可读性较差,一般主动声明,首字母要小写
2、自动化装配Bean
实现:
1、自动扫描@ComponentScan,自动发现应用上下文中所创建的 bean
2、自动装配@Autowired,自动满足 bean 之间的依赖
例如上面例子service和dao之间关系,dao上面都要通过@Component("StudentDao")声明是个组件,通过config的@ComponentScan去扫描(也可以
在xml配置扫描),通过@Autowired去自动注入
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { private StudentDao studentDao; @Override
public void add() {
studentDao.add();
} @Override
public void del() {
studentDao.del();
}
}
注入的方式一般有两种:
1、@Autowired,按类型注入,只能是当有且仅有一个匹配的Bean才可以,如果有多个,就需要和@Qualifier联合使用,确定唯一的实现类,相
比@Resource多一个required属性,如果等于false,即使没有发现这个bean,也不会抛出异常
2、@Resource,按名称注入,建议指明name值,@Resource(name="xxx"),这个注解是javax带有的,而不是Spring的注解
3、@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired)):基于lombok的注入,实际上通过构造器注入的方式,不需要为每个注入
的Bean书写@Autowired,只需要写在class的上面。而且对于某些IDE不识别的Bean,会爆红,例如MyBatis的Mapper注入,这种方式不会爆红。
@Autowired
public AddressServiceImpl(ModelMapper modelMapper, SupportAddressRepository supportAddressRepository) {
this.modelMapper = modelMapper;
this.supportAddressRepository = supportAddressRepository;
}
Bean注入/创建方式
1、XML配置
Student.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student { private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
1.1)属性注入,也就是setter注入
需要生成属性的set方法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <beans>
<bean id="student" class="com.it.entity.Student">
<property name="id" value="1001" />
<property name="name" value="sam" />
<property name="age" value="25" />
</bean> </beans> </beans>
1.2)构造器注入
School.java
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class School {
private Student student;
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <beans>
<bean id="student" class="com.it.entity.Student" />
<bean id="school" class="com.it.entity.School" >
<constructor-arg name="student" ref="student" />
</bean>
</beans> </beans>
1.3)工厂方法注入:静态工厂和实例工厂
School.java
public class School {
public Teacher createTeacher() {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setId(1001);
teacher.setName("sam");
return teacher;
}
public static Teacher createTeacher1() {
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
return teacher;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <beans> <bean id="school" class="com.it.entity.School" />
<bean factory-bean="school" factory-method="createTeacher" /> <bean id="school1" class="com.it.entity.School" factory-method="createTeacher1"/>
</beans> </beans>
2、基于Java类的bean定义
在任何一个配置类中通过@Bean实现创建Bean,适用于外部引用jar包
@Bean
public Gson gson() {
return new Gson();
}
此时就可以通过@Autowired装配
3、基于注解
@Component:当对组件的层次难以定位的时候使用这个注解
@Controller:表示控制层的组件
@Service:表示业务逻辑层的组件
@Repository:表示数据访问层的组件
基于注解也是项目中使用最多的,只有在引用外部jar包才会采用第二种方式,尽量避免XML配置
Spring框架系列(二)--装配和注入Bean的更多相关文章
- Spring框架系列(8) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之Bean实例化(生命周期,循环依赖等)
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:以及Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的:容器中存放的是Bean的定义即Be ...
- Spring框架(3)---IOC装配Bean(注解方式)
IOC装配Bean(注解方式) 上面一遍文章讲了通过xml来装配Bean,那么这篇来讲注解方式来讲装配Bean对象 注解方式需要在原先的基础上重新配置环境: (1)Component标签举例 1:导入 ...
- 使用spring框架,用xml方式进行bean装配出现“The fully qualified name of the bean's class, except if it serves...”
使用spring框架,用xml方式进行bean装配出现“The fully qualified name of the bean's class, except if it serves...”. 原 ...
- Spring框架系列(3) - 深入浅出Spring核心之控制反转(IOC)
在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了IoC的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些IoC相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读IOC的含义以及IOC的使用方式.@pd ...
- Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC体系结构设计
在对IoC有了初步的认知后,我们开始对IOC的实现原理进行深入理解.本文将帮助你站在设计者的角度去看IOC最顶层的结构设计.@pdai Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解 ...
- Spring框架系列(7) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的. ...
- Spring框架系列之AOP思想
微信公众号:compassblog 欢迎关注.转发,互相学习,共同进步! 有任何问题,请后台留言联系! 1.AOP概述 (1).什么是 AOP AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Progra ...
- Spring框架系列(2) - Spring简单例子引入Spring要点
上文中我们简单介绍了Spring和Spring Framework的组件,那么这些Spring Framework组件是如何配合工作的呢?本文主要承接上文,向你展示Spring Framework组件 ...
- Spring框架系列(9) - Spring AOP实现原理详解之AOP切面的实现
前文,我们分析了Spring IOC的初始化过程和Bean的生命周期等,而Spring AOP也是基于IOC的Bean加载来实现的.本文主要介绍Spring AOP原理解析的切面实现过程(将切面类的所 ...
随机推荐
- 三分钟迁移Spring boot工程到Serverless
前言 Spring Boot已成为当今最流行的Java后端开发框架,典型的应用方式是在云上购买一台虚拟机,每天24小时在上面运行Java程序,在这种情况下,用户必须维护自己的虚拟机环境,而且按照包月包 ...
- Linux操作系统改动PATH的方法
1. 暂时改动: 使用export.比如#export PATH=$PATH:/etc/apache/bin 2. 针对用户的改动: vi ~/.bash_profile 增加:export PATH ...
- react 开发过程中的总结/归纳
1.点击元素,获取绑定该事件的父级元素,使用 e.currentTarget.e.target 获取的是,出发该事件的元素,该元素有可能是所绑定事件的元素的子元素. 2.使用 react router ...
- Java String常见问题
一.怎样推断两个String是否相等??使用"=="还是使用"equals()"? 对String来说."=="是用来推断两个字符串(对象) ...
- beego1---beego,bee环境配置
1.配置环境变量GOPATH(代码路径,先在里面建立src,pkg,bin3个目录),GOROOT:go安装的目录,go安装目录下的bin目录放到Path环境变量. 安装完bee工具之后,bee 可执 ...
- go09---defer
package main /* defer 类似其它语言中的析构函数,在函数体执行结束后 按照调用顺序的相反顺序逐个执行,先进后出, 即使函数发生严重错误也会执行,资源清理文件关闭, 支持匿名函数的调 ...
- java获取本周 上周的所有日期
1 根据当前日期获得所在周的日期区间(周一和周日日期) public String getTimeInterval(Date date) { Calendar cal = Calendar.getIn ...
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'urlparse'
这是2.x转3.x问题 2.x写法: from urlparse import urlparse 3.x写法: from urllib.parse import urlparse 问题解决.
- Java 泛型 五:泛型与数组
简介 上一篇文章介绍了泛型的基本用法以及类型擦除的问题,现在来看看泛型和数组的关系.数组相比于Java 类库中的容器类是比较特殊的,主要体现在三个方面: 数组创建后大小便固定,但效率更高 数组能追踪它 ...
- Java 泛型 三
一.泛型初衷 Java集合不会知道我们需要用它来保存什么类型的对象,所以他们把集合设计成能保存任何类型的对象,只要就具有很好的通用性.但这样做也带来两个问题: –集合对元素类型没有任何限制,这样可能引 ...
