Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 5: Kd-Trees (98分)
题目地址:http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/kdtree.html
分析:
Brute-force implementation. 蛮力实现的方法比较简单,就是逐个遍历每个point进行比较,实现下述API就可以了,没有什么难度。

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.RectHV;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
/**
* @author evasean www.cnblogs.com/evasean/
*/
public class PointSET {
private TreeSet<Point2D> points;
public PointSET() {
// construct an empty set of points
points = new TreeSet<Point2D>();
} public boolean isEmpty() {
// is the set empty?
return points.isEmpty();
} public int size() {
// number of points in the set
return points.size();
} public void insert(Point2D p) {
// add the point to the set (if it is not already in the set)
if(p==null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
if(!points.contains(p))
points.add(p);
} public boolean contains(Point2D p) {
// does the set contain point p?
if(p==null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
return points.contains(p);
} public void draw() {
// draw all points to standard draw
for (Point2D p : points) {
p.draw();
}
StdDraw.show();
} public Iterable<Point2D> range(RectHV rect) {
// all points that are inside the rectangle (or on the boundary)
if(rect==null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("RectHV rect is not illegal!");
ArrayList<Point2D> list = new ArrayList<Point2D>();
for(Point2D point : points){
if(rect.contains(point)) list.add(point);
}
return list;
} public Point2D nearest(Point2D p) {
// a nearest neighbor in the set to point p; null if the set is empty
if(p==null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
if(points.size() == 0) return null;
double neareatDistance = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
Point2D nearest = null;
for(Point2D point : points){
double tmp = p.distanceTo(point);
if(Double.compare(neareatDistance, tmp) == 1){
neareatDistance = tmp;
nearest = point;
} }
return nearest;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
// unit testing of the methods (optional)
}
}
2d-tree implementation.
kd-tree插入时要交替以x坐标和y坐标作为判断依据,比如root节点处比较依据为x坐标,那么当要查找或插入一个新节点point时,比较root节点的x坐标和point的x坐标,如果后者比前者小,那么下一次要比较的就是root->left, 相反下一次要比较的就是root->right。进入下一层级之后,就要使用y坐标作为比较依据。示例如下图:
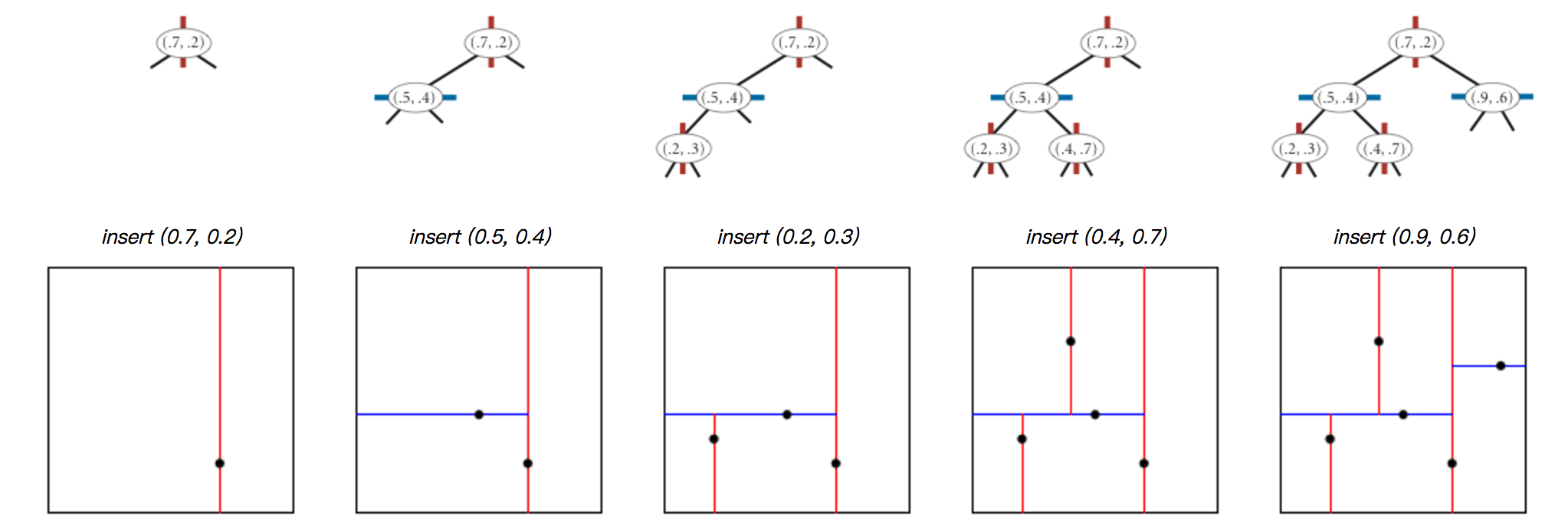
区域搜索:查找落在给定矩阵区域范围内的所有points。从root开始递归查找,如果给定的矩阵不与当前节点的相关矩阵相交,那么就没有必要继续查找该节点及其子树了。
最近节点搜索:查找与给定point距离最近的节点。从root开始递归查找其左右子树,如果给定节点point和已经查找到的最近节点的距离比该point与当前遍历节点的相关矩阵距离还近,那么就没必要遍历这个当前节点及其子树了。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Point2D;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.RectHV;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdDraw;
/**
* @author evasean www.cnblogs.com/evasean/
*/
public class KdTree {
private Node root;
private class Node {
private Point2D p;
/*
* 节点的value就是包含该节点的矩形空间 其左右子树的矩形空间,就是通过该节点进行水平切分或垂直切分的两个子空间
*/
private RectHV rect;
private Node left, right;
private int size;
private boolean xCoordinate; // 标识该节点是否是以x坐标垂直切分 public Node(Point2D point, RectHV rect, int size, boolean xCoordinate) {
this.p = point;
this.rect = rect;
this.size = size;
this.xCoordinate = xCoordinate;
}
} public KdTree() {
// construct an empty set of points
} public boolean isEmpty() {
// is the set empty?
return size() == 0;
} public int size() {
// number of points in the set
return size(root);
} private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
else
return x.size;
} public void insert(Point2D p) {
// add the point to the set (if it is not already in the set)
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
if (root == null)
root = new Node(p, new RectHV(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0), 1, true);
else
insert(root, p);
// System.out.println("size="+root.size);
} private void insert(Node x, Point2D p) {
if (x.xCoordinate == true) { // x的切分标志是x坐标
int cmp = Double.compare(p.x(), x.p.x());
if (cmp == -1) {
if (x.left != null)
insert(x.left, p);
else {
RectHV parent = x.rect;
// 将节点x的矩形空间进行垂直切分后的左侧部分
double newXmin = parent.xmin();
double newYmin = parent.ymin();
double newXmax = x.p.x();
double newYmax = parent.ymax();
x.left = new Node(p, new RectHV(newXmin, newYmin, newXmax, newYmax), 1, false);
}
} else if (cmp == 1) {
if (x.right != null)
insert(x.right, p);
else {
RectHV parent = x.rect;
// 将节点x的矩形空间进行垂直切分后的右侧部分
double newXmin = x.p.x();
double newYmin = parent.ymin();
double newXmax = parent.xmax();
double newYmax = parent.ymax();
x.right = new Node(p, new RectHV(newXmin, newYmin, newXmax, newYmax), 1, false);
}
} else { // x.key.x() 与 p.x() 相等
int cmp2 = Double.compare(p.y(), x.p.y());
if (cmp2 == -1) {
if (x.left != null)
insert(x.left, p);
else {
x.left = new Node(p, x.rect, 1, false);
}
} else if (cmp2 == 1) {
if (x.right != null)
insert(x.right, p);
else {
x.right = new Node(p, x.rect, 1, false);
}
}
}
} else { // x的切分标志是y坐标
int cmp = Double.compare(p.y(), x.p.y());
if (cmp == -1) {
if (x.left != null)
insert(x.left, p);
else {
RectHV parent = x.rect;
// 将节点x的矩形空间进行垂直切分后的左侧部分
double newXmin = parent.xmin();
double newYmin = parent.ymin();
double newXmax = parent.xmax();
double newYmax = x.p.y();
x.left = new Node(p, new RectHV(newXmin, newYmin, newXmax, newYmax), 1, true);
}
} else if (cmp == 1) {
if (x.right != null)
insert(x.right, p);
else {
RectHV parent = x.rect;
// 将节点x的矩形空间进行垂直切分后的左侧部分
double newXmin = parent.xmin();
double newYmin = x.p.y();
double newXmax = parent.xmax();
double newYmax = parent.ymax();
x.right = new Node(p, new RectHV(newXmin, newYmin, newXmax, newYmax), 1, true);
}
} else { // x.key.y() 与 p.y()相等
int cmp2 = Double.compare(p.x(), x.p.x());
if (cmp2 == -1) {
if (x.left != null)
insert(x.left, p);
else {
x.left = new Node(p, x.rect, 1, true);
}
} else if (cmp2 == 1) {
if (x.right != null)
insert(x.right, p);
else {
x.right = new Node(p, x.rect, 1, true);
}
}
}
}
x.size = 1 + size(x.left) + size(x.right);
} public boolean contains(Point2D p) {
// does the set contain point p?
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
return contains(root, p);
} private boolean contains(Node x, Point2D p) {
if(x == null ) return false;
if (x.p.equals(p))
return true;
else {
if(x.xCoordinate == true){
int cmp = Double.compare(p.x(), x.p.x());
if(cmp == -1) return contains(x.left,p);
else if(cmp == 1 ) return contains(x.right,p);
else{
int cmp2 = Double.compare(p.y(), x.p.y());
if(cmp2 == -1) return contains(x.left,p);
else if(cmp2 == 1 ) return contains(x.right,p);
else return true;
}
}else{
int cmp = Double.compare(p.y(), x.p.y());
if(cmp == -1) return contains(x.left,p);
else if(cmp == 1 ) return contains(x.right,p);
else{
int cmp2 = Double.compare(p.x(), x.p.x());
if(cmp2 == -1) return contains(x.left,p);
else if(cmp2 == 1 ) return contains(x.right,p);
else return true;
}
}
}
} public void draw() {
// draw all points to standard draw
StdDraw.setXscale(0, 1);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, 1);
draw(root);
} private void draw(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return;
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLACK);
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.01);
x.p.draw();
if (x.xCoordinate == true) {
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED);
StdDraw.setPenRadius();
Point2D start = new Point2D(x.p.x(), x.rect.ymin());
Point2D end = new Point2D(x.p.x(), x.rect.ymax());
start.drawTo(end);
} else {
StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE);
StdDraw.setPenRadius();
Point2D start = new Point2D(x.rect.xmin(), x.p.y());
Point2D end = new Point2D(x.rect.xmax(), x.p.y());
start.drawTo(end);
}
draw(x.left);
draw(x.right);
} public Iterable<Point2D> range(RectHV rect) {
// all points that are inside the rectangle (or on the boundary)
if (rect == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("RectHV rect is not illegal!");
if (root != null)
return range(root, rect);
else
return new ArrayList<Point2D>();
} private ArrayList<Point2D> range(Node x, RectHV rect) {
ArrayList<Point2D> points = new ArrayList<Point2D>();
if (x.rect.intersects(rect)) {
if (rect.contains(x.p))
points.add(x.p);
if (x.left != null)
points.addAll(range(x.left, rect));
if (x.right != null)
points.addAll(range(x.right, rect));
}
return points;
} public Point2D nearest(Point2D p) {
// a nearest neighbor in the set to point p; null if the set is empty
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Point2D p is not illegal!");
if (root != null)
return nearest(root, p, root.p);
return null;
} /**
* 作业提交提示nearest的时间复杂度偏高,导致作业只有98分,我觉得这样写比较清晰明了,就懒得继续优化
* @param x
* @param p
* @param currNearPoint
* @return
*/
private Point2D nearest(Node x, Point2D p, Point2D currNearPoint) {
if(x.p.equals(p)) return x.p;
double currMinDistance = currNearPoint.distanceTo(p);
if (Double.compare(x.rect.distanceTo(p), currMinDistance) >= 0)
return currNearPoint;
else {
double distance = x.p.distanceTo(p);
if (Double.compare(x.p.distanceTo(p), currMinDistance) == -1) {
currNearPoint = x.p;
currMinDistance = distance;
}
if (x.left != null)
currNearPoint = nearest(x.left, p, currNearPoint);
if (x.right != null)
currNearPoint = nearest(x.right, p, currNearPoint);
}
return currNearPoint;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
// unit testing of the methods (optional)
}
}
Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 5: Kd-Trees (98分)的更多相关文章
- Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 1: Percolation(100分)
题目来源http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/percolation.html 作业分为两部分:建立模型和仿真实验. 最关键的部分就是建 ...
- Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recognition (100分)
题目原文详见http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/collinear.html 程序的主要目的是寻找n个points中的line seg ...
- Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 4: 8 Puzzle (100分)
题目原文:http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/8puzzle.html 题目要求:设计一个程序解决8 puzzle问题以及该问题的推广 ...
- Coursera Algorithms Programming Assignment 2: Deque and Randomized Queue (100分)
作业原文:http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/queues.html 这次作业与第一周作业相比,稍微简单一些.有三个编程练习:双端队列 ...
- Algorithms : Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recognition
Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recognition 1.题目重述 原题目:Programming Assignment 3: Pattern Recogniti ...
- Algorithms: Design and Analysis, Part 1 - Programming Assignment #1
自我总结: 1.编程的思维不够,虽然分析有哪些需要的函数,但是不能比较好的汇总整合 2.写代码能力,容易挫败感,经常有bug,很烦心,耐心不够好 题目: In this programming ass ...
- Coursera课程 Programming Languages, Part A 总结
Coursera CSE341: Programming Languages 感谢华盛顿大学 Dan Grossman 老师 以及 Coursera . 碎言碎语 这只是 Programming La ...
- 课程一(Neural Networks and Deep Learning),第三周(Shallow neural networks)—— 3.Programming Assignment : Planar data classification with a hidden layer
Planar data classification with a hidden layer Welcome to the second programming exercise of the dee ...
- Programming Assignment 4: Boggle
编程作业四 作业链接:Boggle & Checklist 我的代码:BoggleSolver.java 问题简介 Boggle 是一个文字游戏,有 16 个每面都有字母的骰子,开始随机将它们 ...
随机推荐
- HDU多校Round 5
Solved:3 rank:71 E. Everything Has Changed #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const ...
- HDU5834 Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree (树形DP)
题意:一棵树有点权和边权 从每个点出发 走过一条边要花费边权同时可以获得点权 边走几次就算几次花费 点权最多算一次 问每个点能获得的最大价值 题解:好吧 这才叫树形DP入门题 dp[i][0]表示从i ...
- vue v-model 的注意点
在使用表单元素 input 的 v-model 指令时,碰到一个问题: 如上图,修改 input 的内容,以便随时显示:但显示时明显慢一步. <template> <div> ...
- 返回通知&异常通知&环绕通知
[返回通知] LoggingAspect.java: @Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { /* * 在方法正常执行后执行的通知叫返回通知 * ...
- Java基础学习总结(88)——线程创建与终止、互斥、通信、本地变量
线程创建与终止 线程创建 Thread类与 Runnable 接口的关系 public interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); ...
- - > 听学姐讲那过去的故事——打代码的小女孩
童话故事 不知道大家有没有看过 天冷极了,下着雪,又快黑了.这是一年的最后一天——大年夜.在这又冷又黑的晚上,一个乖巧的小女孩在机房里调试程序.她从家里出来的时候还穿着一件外套,但是有什么用呢?那是 ...
- ojdbc.jar
Oracle的jdbc驱动是ojdbc.jar 文件,那么mysql的jdbc驱动是什么呢? 匿名 | 浏览 689 次 发布于2015-06-07 02:06 最佳答案 MySQL的JDBC ...
- Weblogic补丁升级操作手冊
1.查看Weblogic版本号 方法一 [weblogic@Weblogic201 ~]$ cd /home/weblogic/Oracle/Middleware/wlserver_10.3/serv ...
- php 生成订单号
最近在练手一个订单提交的小项目,需要用到生成订单号,网上找了下,觉得这个最好. function build_order_no(){ return date('Ymd').substr(implode ...
- _deque实现
/* deque是一种双向开口的连续线性空间,可以在头尾两端分别做元素的插入和删除操作 常用接口:back(), front(), push_back(), pop_back(), push_fron ...
