[PY3]——内置数据结构(1)——列表及其常用操作
列表及其常用操作_xmind图
about列表
列表是一个序列,用于顺序存储数据
列表分为两种:ArrayList(用数组实现)、LinkedList(用链表实现)
定义与初始化
#list() 使用工厂函数list定义一个空列表 #[] 使用中括号定义一个空列表 #[1,2,3] 使用中括号定义有初始值的列表 #list(可迭代对象) 把可迭代对象转换为一个列表 In [1]: lst=list();print(lst)
[] In [2]: lst=[];print(lst)
[] In [3]: lst=[1,2,3];print(lst)
[1, 2, 3] In [4]: lst=list(range(1,10));print(lst)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
修改列表元素
# 直接使用索引操作即可 list[index]=new value In [2]: lst=[1,2,3,2,4,3,5] In [3]: lst[4]=3 In [4]: print(lst)
[1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5]
访问列表元素
1. list(index) 通过索引访问元素,索引规则为:
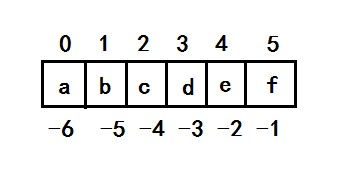
#索引从0开始
In [5]: print(lst[0])
1 #负数索引从-1开始
In [6]: print(lst[-1])
9
In [7]: print(lst[-2])
8 #当索引(正负都是)超出范围,会报错IndexError
In [6]: print(lst[10])
IndexError: list index out of range
2. index()
# index()主要用于查找列表中某个值的索引
In [3]:help(lst.index)
index(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present. In [3]: lst=[1,2,3,2,1] # 返回要查找的value的第一个索引
In [4]: lst.index(2)
Out[4]: 1 # start参数指定从哪个索引开始查找
In [5]: lst.index(2,2)
Out[5]: 3 # stop参数指定从到哪个索引结束,且[start,stop]的范围中不包含stop
# 当value不能在[start,stop]的范围查找到,则报错ValueError
In [6]: lst.index(2,2,3)
ValueError: 2 is not in list # 若想缺省start值,可将其设为0(start的默认值为0,stop的默认值为-1)
In [7]: lst.index(2,0,3)
Out[7]: 1 # start和stop可以是负索引,但总是从左往右查找
In [8]: lst.index(2,-4,-1)
Out[8]: 1
# 并且要注意:如果stop<start,就相当于在空列表中查找一个元素,则抛出ValueError
In [9]: lst.index(2,-1,-4)
ValueError: 2 is not in list
3. count()
# count()返回某个value值在列表中出现的次数
In [14]: help(lst.count)
Help on built-in function count:
count(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value In [15]: lst.count(2)
Out[15]: 2 In [16]: lst.count(10)
Out[16]: 0
添加列表元素
1. append() 用于在list末尾添加一个元素
# 原地修改list,返回结果为none
In [5]: help(lst.append)
Help on built-in function append:
append(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end In [1]: lst=[1,2,3,2,3,3,5] In [2]: lst.append(9) In [3]: print(lst)
[1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9]
2. insert() 用于在指定索引位置添加元素
# 原地修改list,返回结果为none
In [12]: help(lst.insert)
insert(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index In [13]: lst=[1,2,3,2,3,3,5,9] # 正数索引:实际是使得index位置上的元素为我们所添加的,后面的元素依次往后挪
In [14]: lst.insert(1,11);print(lst)
[1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9] In [15]: lst.insert(0,'a');print(lst)
['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9] # 负数索引:实际是在index的前一个位置添加元素
In [16]: lst.insert(-1,'-a');print(lst)
['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9] # 当index超出索引范围,正数索引会在最后一个位置添加元素
In [17]: lst.insert(100,'');print(lst)
['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9, ''] # 当index超出索引范围,负数索引会在第0个位置添加元素
In [18]: lst.insert(-100,'-100');print(lst)
['-100', 'a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9, ''] # 比较append和insert: append的时间复杂度是O(1):常数时间,效率和数据规模无关 insert的时间复杂度是O(n):线性时间,效率和数据规模有关
3. extend()
# extend的参数是一个可迭代对象,在list末尾添加此可迭代对象
#原地修改list,返回结果为none
In [1]: help(lst.extend)
extend(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable In [1]: lst=[1,2,3] In [2]: lst.extend([4,5,6]);print(lst)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] In [3]: lst.extend(range(0,4));print(lst)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3]
4. + list的连接操作
# 连接操作不修改list本身,返回一个新的list
In [9]: lst=[1,2,3] In [10]: lst+[4,5,6]
Out[10]: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] In [11]: print(lst)
[1, 2, 3] In [12]: lst2=[4,5,6] In [13]: lst+lst2
Out[13]: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
删除列表元素
1. remove() 根据指定的value元素值删除元素,返回none
# 原地删除,返回为none
In [1]: help(lst.remove)
remove(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present. In [2]: lst=[0,1,2,3,2,4,5,6] # 删除list中值为4的元素
In [6]: lst.remove(4);print(lst)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 5, 6] # list中有两个相同的value时,删除第一个出现的
In [7]: lst.remove(2);print(lst)
[0, 1, 3, 2, 5, 6] # 当value不存在,则抛出ValueError
In [8]: lst.remove(10);print(lst)
ValueError: list.remove(x): x not in list
2. pop() 根据index索引删除元素,返回被删除的元素
In [10]: help(lst.pop)
pop(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. # pop()不指定索引时,随机删除列表的一个元素,直到list为空
In [36]: lst=[1,0,9,8,2,6,9] In [37]: lst.pop()
Out[37]: 9
In [38]: lst.pop()
Out[38]: 6
In [39]: lst.pop()
Out[39]: 2
In [40]: lst.pop()
Out[40]: 8
In [41]: lst.pop()
Out[41]: 9
In [42]: lst.pop()
Out[42]: 0
In [43]: lst.pop()
Out[43]: 1
In [44]: lst.pop()
IndexError: pop from empty list # pop(index)指定index时,删除该索引对应的值
In [45]: lst=[1,0,9,8,2,6,9] In [46]: lst.pop(0)
Out[46]: 1 In [47]: lst.pop(-1)
Out[47]: 9 # pop()和pop(index)比较:pop()传递index参数时,时间复杂度是O(n) 不传递index参数时,时间复杂度是O(1)
3. clear() 清空一个列表
In [16]: help(lst.clear)
clear(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L In [17]: print(lst)
[1, 2] In [18]: lst.clear() In [19]: print(lst)
[]
其他常用操作
1. len( )
# 求list长度
In [20]: lst=list(range(0,6)) In [21]: len(lst)
Out[21]: 6
2. reverse ( )
# 反转列表
In [23]: help(lst.reverse)
reverse(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* In [24]: print(lst)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] In [25]: lst.reverse() In [26]: print(lst)
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
3. sort( )
# 对列表排序
In [27]: help(lst.sort)
sort(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE* In [28]: lst=[1,2,3,2,7,8] In [29]: lst.sort() In [30]: print(lst) #默认为正序
[1, 2, 2, 3, 7, 8] In [31]: lst.sort(reverse=True);print(lst) #设置reverse=True为逆序
[8, 7, 3, 2, 2, 1] # key=None 实际是可以自定义的一个函数参数(python的函数可以作为函数参数使用)
keys=[('x',3),('z',6),('y',1)]
keys.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
print(keys)
[('x', 3), ('y', 1), ('z', 6)]
4. 拷贝
# 赋值操作‘=’是引用传递 也叫浅拷贝
In [32]: lst1=[0,1,2] In [33]: lst2=lst1 In [34]: print(lst2)
[0, 1, 2] In [35]: lst2[2]=3 In [36]: print(lst1,lst2) #浅拷贝是lst1跟着变了
[0, 1, 3] [0, 1, 3] # copy()是影子拷贝
In [37]: help(lst.copy)
copy(...) method of builtins.list instance
L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L def copy(lst): # copy()的实现
tmp = []
for i in lst:
tmp.append(i)
return tmp In [38]: lst1=[0,1,2] In [39]: lst2=lst1.copy() In [40]: print(lst2)
[0, 1, 2] In [41]: lst2[2]=3 In [42]: print(lst1,lst2)
[0, 1, 2] [0, 1, 3] In [43]: lst1=[0,[1,2,3],9] In [44]: lst2=lst1.copy() In [47]: print(lst2)
[0, [1, 2, 3], 9] In [49]: lst2[1][1]=5 In [50]: print(lst2)
[0, [1, 5, 3], 9] In [51]: print(lst1)
[0, [1, 5, 3], 9] # deepcopy()深拷贝
In [52]: lst1=[0,[1,2,3],9] In [53]: import copy In [54]: lst2=copy.deepcopy(lst1) In [55]: print(lst2)
[0, [1, 2, 3], 9] In [56]: lst2[1][1]=5 In [57]: print(lst2)
[0, [1, 5, 3], 9] In [58]: print(lst1)
[0, [1, 2, 3], 9]
5. 复制一个列表
lst=[1,2,3]
copy_lst=lst[:] print(copy_lst)
[1, 2, 3]
[PY3]——内置数据结构(1)——列表及其常用操作的更多相关文章
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(6)——集合及其常用操作
集合及其常用操作Xmind图 集合的定义 # set( ) # {0,1,2} //注意不能用空的大括号来定义集合 # set(可迭代对象) In [1]: s=set();type ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(7)——字典及其常用操作
字典及其常用操作Xmind图 关于字典 字典是一种key-value结构 字典是无序的 字典的定义 # {}大括号可以直接定义一个空字典 In [1]: d={};type(d) Out[1]: di ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(3)——字符串及其常用操作
字符串及其常用操作xmind图 字符串的定义 1. 单引号/双引号 In [1]: s1='hello world' In [2]: s1="hello world" 2. 三对单 ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(2)——元组及其常用操作
定义和初始化 #tuple() 使用工厂函数tuple定义一个空元组 #() 使用圆括号定义一个空元组 #(1,2,3) 使用圆括号定义有初始值的元组 #tuple(可迭代对象) 把可迭代对象转换为一 ...
- Python基础语法-内置数据结构之列表
列表的一些特点: 列表是最常用的线性数据结构 list是一系列元素的有序组合 list是可变的 列表的操作, 增:append.extend.insert 删:clear.pop.remove 改:r ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(9)——线性结构与切片/命名切片slice()
线性结构的总结 列表list 元组tuple 字符串str bytes bytearray的共同点: 都是顺序存储.顺序访问的: 都是可迭代对象: 都可以通过索引访问 线性结构的特征: 可迭代 ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(8)——解构与封装
### 解构的理解与用法 ### 解构是python很有特色的一个功能,被很多语言借鉴(例如ES6) # 元素按照顺序赋值给变量 In [31]: lst=list(range(5)) In [32] ...
- Python内置数据结构之列表list
1. Python的数据类型简介 数据结构是以某种方式(如通过编号)组合起来的数据元素(如数.字符乃至其他数据结构)集合.在Python中,最基本的数据结构为序列(sequence). Python内 ...
- [PY3]——内置数据结构(5)——字符串编码
py2和py3中关于字符串的最大区别? python2中只有 unicode类型 而python3中有 string bytes两种类型 关于string和bytes的区分? 1.str是文本序列.b ...
随机推荐
- Hibernate 零配置之Annotation注解
JPA规范推荐使用Annotation来管理实体类与数据表之间的映射关系,从而避免同时维护两份文件(Java 实体类 和 XML 映射文件),将映射信息(写在Annotation中)与实体类集中在一起 ...
- Azure静态公网ip自助反解
Linux下安装az工具,并登陆 az login 执行 az network public-ip update --resource-group ip所在资源组名称 --name ip对应资源名称 ...
- easyui - using
using 是 easyloader.load 简写 using('calendar', function() { alert("加载calendar成功 ...
- brew安装指定版本boost
brew 如何安装指定版本的boost brew uninstall boost brew install boost@1.57 brew link boost@1.57 --force --over ...
- Spring Boot 学习系列(06)—采用log4j2记录日志
此文已由作者易国强授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. 为什么选择log4j2 log4j2相比于log4j1.x和logback来说,具有更快的执行速度.同时也支 ...
- django系列6--Ajax05 请求头ContentType, 使用Ajax上传文件
一.请求头ContentType ContentType指的是请求体的编码类型,常见的类型共有三种: 1.application/x-www-form-urlencoded 这应该是最常见的 POST ...
- cnVCL的安装
cnVCL是cnpack组件中的不可视组件库,里面包含很多有用的组件,网址:http://www.cnpack.org/showdetail.php?id=739&lang=zh-cn 安装步 ...
- 循环语句(循环for与while等)
1.1for循环 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=" ...
- “全栈2019”Java第九十三章:内部类应用场景(迭代器设计模式)
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java第 ...
- Java几个基本概念
To xj 编译:test.java->test.class反编译:test.class->test.java打jar包:test.class->test.jar打war包:test ...
