MySQL基准测试工具--sysbench
我们需要知道的是sysbench并不是一个压力测试工具,是一个基准测试工具。linux自带的版本比较低,我们需要自己安装sysbench。
[root@test2 ~]# sysbench --version
sysbench 0.4.
安装sysbench,sysbench的源码托管在GitHub上,下载源码:
unzip sysbench-master.zip #解压源码
yum -y install make automake libtool pkgconfig libaio-devel #下载依赖包
cd sysbench-master
sh autogen.sh
编译:
./configure --with-mysql-includes=/usr/local/mysql/include --with-mysql-libs=/usr/local/mysql/lib #根据安装的MySQL的位置,设置目录位置
make
make install 这样安装之后使用sysbench命令时会报错。
[root@test3 sysbench-master]# sysbench --version
sysbench: error while loading shared libraries: libmysqlclient.so.: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 解决办法:
在/etc/profile文件中加入一行:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/mysql/lib source /etc/profile
命令可以正常使用
[root@test3 sysbench-master]# sysbench --version
sysbench 1.1.
查看sysbench的一些帮助信息:
[root@test3 ~]# sysbench --help
Usage:
sysbench [options]... [testname] [command] Commands implemented by most tests: prepare run cleanup help General options:
--threads=N number of threads to use [] #线程的数量,默认是1
--events=N limit for total number of events [] #限制的最大事件数量,默认是0,不限制
--time=N limit for total execution time in seconds [] #整个测试执行的时间
--warmup-time=N #在进行基准测试多少秒之后启用统计信息--forced-shutdown=STRING #超过--time时间限制后,强制中断,默认是【off】
--thread-stack-size=SIZE size of stack per thread [64K]
--thread-init-timeout=N wait time in seconds for worker threads to initialize []
--rate=N average transactions rate. for unlimited rate []
--report-interval=N #打印出中间的信念,N表示每隔N秒打印一次,0表示禁用--report-checkpoints=[LIST,...] #转储完全统计信息并在指定时间点复位所有计数器,参数是逗号分隔值的列表,表示从必须执行报告检查点的测试开始所经过的时间(以秒为单位)。 默认情况下,报告检查点处于关闭状态[off]。--debug[=on|off] print more debugging info [off]
--validate[=on|off] #在可能情况下执行验证检查,默认是[off]
--help[=on|off] print help and exit [off]
--version[=on|off] print version and exit [off]
--config-file=FILENAME File containing command line options
--luajit-cmd=STRING perform LuaJIT control command. This option is equivalent to 'luajit -j'. See LuaJIT documentation for more information #上面是一些通用的配置信息,在具体测试某个测试时,会再详细说明参数设置
首先来进行IO测试
[root@test3 ~]# sysbench fileio help #查看IO测试的文档
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) fileio options:
--file-num=N number of files to create [] #文件的数量
--file-block-size=N block size to use in all IO operations [] #文件块的大小,如果要是针对INNODB的测试,可以设置为innodb_page_size的大小
--file-total-size=SIZE total size of files to create [2G] #文件的总大小
--file-test-mode=STRING test mode {seqwr【顺序写】, seqrewr【顺序读写】, seqrd【顺序读】, rndrd【随机读】, rndwr【随机写】, rndrw【随机读写】} #文件测试模式
--file-io-mode=STRING file operations mode {sync【同步】,async【异步】,mmap【map映射】} [默认为:sync] #文件的io模式
--file-async-backlog=N number of asynchronous operatons to queue per thread [] #打开文件时的选项,这是与API相关的参数。
--file-extra-flags=[LIST,...] #打开文件时的选项,这是与API相关的参数。可选有sync,dsync,direct。--file-fsync-freq=N #执行fsync函数的频率,fsync主要是同步磁盘文件,因为可能有系统和磁盘缓冲的关系。默认为100,如果为0表示不使用fsync。
--file-fsync-all[=on|off] #每执行完一次写操作,就执行一次fsync,默认未off。--file-fsync-end[=on|off] #在测试结束时,执行fsync,默认为on。--file-fsync-mode=STRING #文件同步函数的选择,同样是和API相关的参数,由于多个操作对fdatasync支持的不同,因此不建议使用fdatasync。默认为fsync。--file-merged-requests=N #尽可能合并此数量的io请求(0-不合并),默认为[0]。
--file-rw-ratio=N #测试时的读写比例,默认是2:1。
在使用sysbench进行测试的时候,通常分为三个步骤prepare,run,cleanup阶段。
第一步准备数据(prepare阶段):
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num= --file-total-size=50G prepare
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) files, 5242880Kb each, 51200Mb total
Creating files for the test...
Extra file open flags: (none)
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
Creating file test_file.
bytes written in 489.55 seconds (104.59 MiB/sec). #这里给出一个每秒写入的数据量104.59MB/s, 这里的写入是顺序写入的,表示磁盘的吞吐量为104.59MB/s。
【一般对顺序的读写称为吞吐量,对随机的IO使用IOPS来表示】
[root@test3 systext]# ll -h #文件大小为5个G
total 50G
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:30 test_file.0
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:31 test_file.1
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:32 test_file.2
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:32 test_file.3
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:33 test_file.4
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:34 test_file.5
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:35 test_file.6
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:36 test_file.7
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:36 test_file.8
-rw------- 1 root root 5.0G Nov 27 09:37 test_file.9
数据准备好之后,进行测试:
#这里进行随机读写测试
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num= --file-total-size=50G --file-block-size= --file-test-mode=rndrw --file-io-mode=sync --file-extra-flags=direct --time= --threads= --report-interval= run
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Running the test with following options: #设定的一些参数数值
Number of threads:
Report intermediate results every second(s)
Initializing random number generator from current time Extra file open flags: directio
files, 5GiB each
50GiB total file size
Block size 16KiB
Number of IO requests:
Read/Write ratio for combined random IO test: 1.50
Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each requests.
Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled.
Using synchronous I/O mode
Doing random r/w test
Initializing worker threads... Threads started! [ 10s ] reads: 3.24 MiB/s writes: 2.16 MiB/s fsyncs: 34.08/s latency (ms,%): 80.025 #每隔10s输出一次报告
[ 20s ] reads: 3.49 MiB/s writes: 2.32 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.70/s latency (ms,%): 73.135
[ 30s ] reads: 3.45 MiB/s writes: 2.29 MiB/s fsyncs: 37.00/s latency (ms,%): 75.817
[ 40s ] reads: 3.43 MiB/s writes: 2.29 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.00/s latency (ms,%): 75.817
[ 50s ] reads: 3.57 MiB/s writes: 2.38 MiB/s fsyncs: 37.40/s latency (ms,%): 73.135
[ 60s ] reads: 3.08 MiB/s writes: 2.06 MiB/s fsyncs: 32.30/s latency (ms,%): 86.002
[ 70s ] reads: 3.41 MiB/s writes: 2.27 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.40/s latency (ms,%): 75.817
[ 80s ] reads: 3.47 MiB/s writes: 2.31 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.20/s latency (ms,%): 73.135
[ 90s ] reads: 3.46 MiB/s writes: 2.31 MiB/s fsyncs: 36.20/s latency (ms,%): 77.194
[ 100s ] reads: 3.10 MiB/s writes: 2.07 MiB/s fsyncs: 33.50/s latency (ms,%): 75.817 Throughput:
read: IOPS=215.57 3.37 MiB/s (3.53 MB/s) #通常的机械磁盘随机IOPS也就是200多一点。
write: IOPS=143.72 2.25 MiB/s (2.35 MB/s) #随机写入的速度明显要低很多。
fsync: IOPS=37.13 Latency (ms):
min: 0.08
avg: 40.51
max: 1000.31
95th percentile: 77.19
sum: 1601329.71 #随机读大概是2.10M/s,文件块的大小为16KB,可以大概估计磁盘转速: 2.10*1024KB*60s/16KB=7560n/m, 大概就是7500转每分
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num= --file-total-size=50G --file-block-size= --file-test-mode=seqrd --file-io-mode=sync --file-extra-flags=direct --time= --threads= --report-interval= run
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Running the test with following options:
Number of threads:
Report intermediate results every second(s)
Initializing random number generator from current time Extra file open flags: directio
files, 5GiB each
50GiB total file size
Block size 16KiB
Periodic FSYNC enabled, calling fsync() each requests.
Calling fsync() at the end of test, Enabled.
Using synchronous I/O mode
Doing sequential read test
Initializing worker threads... Threads started! [ 10s ] reads: 98.88 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.020
[ 20s ] reads: 98.64 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.681
[ 30s ] reads: 93.24 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 2.913
[ 40s ] reads: 89.12 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 4.028
[ 50s ] reads: 93.17 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 4.487
[ 60s ] reads: 91.98 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 4.652
[ 70s ] reads: 97.08 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.425
[ 80s ] reads: 93.71 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.020
[ 90s ] reads: 94.63 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.304
[ 100s ] reads: 89.57 MiB/s writes: 0.00 MiB/s fsyncs: 0.00/s latency (ms,%): 3.364 Throughput:
read: IOPS=6016.01 94.00 MiB/s (98.57 MB/s)
write: IOPS=0.00 0.00 MiB/s (0.00 MB/s)
fsync: IOPS=0.00 Latency (ms):
min: 0.40
avg: 2.66
max: 687.00
95th percentile: 3.62
sum: 1599247.42 #测试结果可以看到顺序的读和随机读的差距还是超大的
顺序读的测试
可以更改--file-test-mode的模式,改变测试的模式。
测试阶段完成之后,需要进行最后的cleanup阶段,
[root@test3 systext]# sysbench fileio --file-num= --file-total-size= cleanup
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Removing test files...
[root@test3 systext]# ls
[root@test3 systext]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda3 29G .4G 20G % /
tmpfs .9G 44K .9G % /dev/shm
/dev/vda1 190M 30M 151M % /boot
/dev/vdb 100G 25G 76G % /data
cgroup_root .9G .9G % /cgroup
#看到磁盘空间已经释放
测试MySQL的OLTP
sysbench新版的用法和之前的旧版本有所不同,先来看测试数据库时的一些参数:
General database options:
--db-driver=STRING specifies database driver to use ('help' to get list of available drivers) [mysql] #指定数据库驱动,默认是mysql
--db-ps-mode=STRING prepared statements usage mode {auto, disable} [auto] #
--db-debug[=on|off] print database-specific debug information [off] #dubug模式
Compiled-in database drivers:
mysql - MySQL driver
mysql options:
--mysql-host=[LIST,...] MySQL server host [localhost]
--mysql-port=[LIST,...] MySQL server port []
--mysql-socket=[LIST,...] MySQL socket
--mysql-user=STRING MySQL user [sbtest]
--mysql-password=STRING MySQL password []
--mysql-db=STRING MySQL database name [sbtest] #数据库名字,默认是sbtest
--mysql-ssl[=on|off] use SSL connections, if available in the client library [off] #以下是ssl的连接测试
--mysql-ssl-key=STRING path name of the client private key file
--mysql-ssl-ca=STRING path name of the CA file
--mysql-ssl-cert=STRING path name of the client public key certificate file
--mysql-ssl-cipher=STRING use specific cipher for SSL connections []
--mysql-compression[=on|off] use compression, if available in the client library [off] #压缩测试
--mysql-debug[=on|off] trace all client library calls [off]
--mysql-ignore-errors=[LIST,...] list of errors to ignore, or "all" [,,] #忽略的错误
--mysql-dry-run[=on|off] Dry run, pretend that all MySQL client API calls are successful without executing them [off]
MySQL测试的lua脚本:
#因为是源码安装,索引目录在这里
[root@test3 lua]# pwd
/data/sysbench-master/src/lua
[root@test3 lua]# ls
bulk_insert.lua Makefile oltp_common.lua oltp_point_select.lua oltp_update_index.lua prime-test.lua
empty-test.lua Makefile.am oltp_delete.lua oltp_read_only.lua oltp_update_non_index.lua select_random_points.lua
internal Makefile.in oltp_insert.lua oltp_read_write.lua oltp_write_only.lua select_random_ranges.lua
#根据脚本的名字可以选择对应的基本
#查看某个lua脚本的用法
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench oltp_common.lua help
sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3) oltp_common.lua options:
--auto_inc[=on|off] Use AUTO_INCREMENT column as Primary Key (for MySQL), or its alternatives in other DBMS. When disabled, use client-generated IDs [on]
--create_secondary[=on|off] Create a secondary index in addition to the PRIMARY KEY [on]
--create_table_options=STRING Extra CREATE TABLE options []
--delete_inserts=N Number of DELETE/INSERT combinations per transaction [1]
--distinct_ranges=N Number of SELECT DISTINCT queries per transaction [1]
--index_updates=N Number of UPDATE index queries per transaction [1]
--mysql_storage_engine=STRING Storage engine, if MySQL is used [innodb]
--non_index_updates=N Number of UPDATE non-index queries per transaction [1]
--order_ranges=N Number of SELECT ORDER BY queries per transaction [1]
--pgsql_variant=STRING Use this PostgreSQL variant when running with the PostgreSQL driver. The only currently supported variant is 'redshift'. When enabled, create_secondary is automatically disabled, and delete_inserts is set to 0
--point_selects=N Number of point SELECT queries per transaction [10]
--range_selects[=on|off] Enable/disable all range SELECT queries [on]
--range_size=N Range size for range SELECT queries [100]
--secondary[=on|off] Use a secondary index in place of the PRIMARY KEY [off]
--simple_ranges=N Number of simple range SELECT queries per transaction [1]
--skip_trx[=on|off] Don't start explicit transactions and execute all queries in the AUTOCOMMIT mode [off]
--sum_ranges=N Number of SELECT SUM() queries per transaction [1]
--table_size=N Number of rows per table [10000]
--tables=N Number of tables [1]
prepare阶段:
创建默认的测试库:
mysql> create database sbtest; #创建数据库
Query OK, row affected (0.11 sec) #准备数据,时间比较长,可以把table_size设置的小一点
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables= --table_size= --mysql-user=root --mysql-password= --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port= --mysql-db=sbtest prepare
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Creating table 'sbtest1'...
Inserting records into 'sbtest1'
Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest1'...
Creating table 'sbtest2'...
Inserting records into 'sbtest2'
Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest2'...
Creating table 'sbtest3'...
Inserting records into 'sbtest3'
Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest3'... #在MySQL shel1中查看数据
mysql> select count(*) from sbtest1;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10000000 |
+----------+
1 row in set (1.89 sec) mysql> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_sbtest |
+------------------+
| sbtest1 |
| sbtest2 |
| sbtest3 |
+------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
run阶段
选择一个合适的lua脚本进行测试:
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_point_select.lua --tables= --table_size= --mysql-user=root --mysql-password= --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port= --mysql-db=sbtest --threads= --time= --report-interval= run
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Running the test with following options:
Number of threads:
Report intermediate results every second(s)
Initializing random number generator from current time Initializing worker threads... Threads started! [ 5s ] thds: tps: 15037.47 qps: 15037.47 (r/w/o: 15037.47/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 41.10 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 10s ] thds: tps: 18767.43 qps: 18767.43 (r/w/o: 18767.43/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 46.63 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 15s ] thds: tps: 22463.68 qps: 22463.68 (r/w/o: 22463.68/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 40.37 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 20s ] thds: tps: 26848.42 qps: 26848.42 (r/w/o: 26848.42/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 28.67 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 25s ] thds: tps: 27005.57 qps: 27005.57 (r/w/o: 27005.57/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 15.00 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 30s ] thds: tps: 26965.62 qps: 26965.62 (r/w/o: 26965.62/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 1.82 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 35s ] thds: tps: 27626.74 qps: 27626.74 (r/w/o: 27626.74/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 40s ] thds: tps: 27244.27 qps: 27244.27 (r/w/o: 27244.27/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.33 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 45s ] thds: tps: 26522.56 qps: 26522.56 (r/w/o: 26522.56/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 1.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 50s ] thds: tps: 26791.43 qps: 26791.43 (r/w/o: 26791.43/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 5.57 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 55s ] thds: tps: 27088.42 qps: 27088.42 (r/w/o: 27088.42/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 1.42 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 60s ] thds: tps: 28056.06 qps: 28056.06 (r/w/o: 28056.06/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.22 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 65s ] thds: tps: 27296.11 qps: 27296.11 (r/w/o: 27296.11/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.73 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 70s ] thds: tps: 28621.60 qps: 28621.60 (r/w/o: 28621.60/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.19 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 75s ] thds: tps: 28992.29 qps: 28992.29 (r/w/o: 28992.29/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.19 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 80s ] thds: tps: 28279.88 qps: 28279.88 (r/w/o: 28279.88/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 85s ] thds: tps: 28612.84 qps: 28612.84 (r/w/o: 28612.84/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 90s ] thds: tps: 28031.47 qps: 28031.47 (r/w/o: 28031.47/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 95s ] thds: tps: 28734.66 qps: 28734.66 (r/w/o: 28734.66/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 0.20 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
[ 100s ] thds: tps: 28767.20 qps: 28767.20 (r/w/o: 28767.20/0.00/0.00) lat (ms,%): 2.39 err/s: 0.00 reconn/s: 0.00
SQL statistics:
queries performed:
read: 2638920 #总的select数量
write:
other:
total:
transactions: (26382.71 per sec.) #TPS
queries: (26382.71 per sec.) #QPS
ignored errors: (0.00 per sec.) #忽略的错误
reconnects: (0.00 per sec.) #重新连接 Throughput:
events/s (eps): 26382.7081 #每秒的事件数,一般和TPS一样
time elapsed: .0246s #测试的总时间
total number of events: 2638920 #总的事件数,一般和TPS一样 Latency (ms):
min: 0.11 #最小响应时间
avg: 4.85 #平均响应时间
max: 649.29 #最大响应时间
95th percentile: 25.74 #95%的响应时间是这个数据
sum: 12796148.28 Threads fairness:
events (avg/stddev): 20616.5625/196.08
execution time (avg/stddev): 99.9699/0.00 #在这个测试中,可以看到TPS与QPS的大小基本一致,说明这个lua脚本中的一个查询一般就是一个事务!
我们一般关注的指标主要有:
- response time avg:平均响应时间(后面的95%的大小可以通过–percentile=98的方式去更改)。
- transactions:精确的说是这一项后面的TPS,但如果使用了–skip-trx=on,这项事务数为0,需要用total number of events去除以总时间,得到tps(其实还可以分为读tps和写tps)。
- queries:用它除以总时间,得到吞吐量QPS。
因为上面的TPS与QPS是一样的,因此只绘了TPS的图,如下:
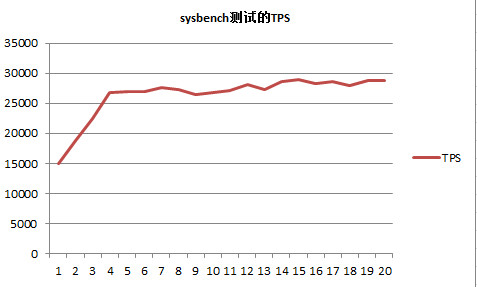
刚开始的时候有一个明显的上升,这时候是因为在bp中没有缓存数据,需要从磁盘中读数据,也就是预热阶段!
清理数据
[root@test3 lua]# sysbench /data/sysbench-master/src/lua/oltp_read_write.lua --tables= --table_size= --mysql-user=root --mysql-password= --mysql-host=10.0.102.214 --mysql-port= --mysql-db=sbtest cleanup
sysbench 1.1. (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.-beta3) Dropping table 'sbtest1'...
Dropping table 'sbtest2'...
Dropping table 'sbtest3'...
[root@test3 lua]#
sysbench除了以上的测试之外,还可以测试:
Compiled-in tests:
fileio - File I/O test
cpu - CPU performance test
memory - Memory functions speed test
threads - Threads subsystem performance test
mutex - Mutex performance test See 'sysbench <testname> help' for a list of options for each test
MySQL基准测试工具--sysbench的更多相关文章
- 详解MySQL基准测试和sysbench工具
前言 作为一名后台开发,对数据库进行基准测试,以掌握数据库的性能情况是非常必要的.本文介绍了MySQL基准测试的基本概念,以及使用sysbench对MySQL进行基准测试的详细方法. 文章有疏漏之处, ...
- 详解MySQL基准测试和sysbench工具(转)
前言 作为一名后台开发,对数据库进行基准测试,以掌握数据库的性能情况是非常必要的.本文介绍了MySQL基准测试的基本概念,以及使用sysbench对MySQL进行基准测试的详细方法. 文章有疏漏之处, ...
- 解MySQL基准测试和sysbench工具
前言 作为一名后台开发,对数据库进行基准测试,以掌握数据库的性能情况是非常必要的.本文介绍了MySQL基准测试的基本概念,以及使用sysbench对MySQL进行基准测试的详细方法. 文章有疏漏之处, ...
- MySQL性能压力基准测试工具sysbench
1.sysbench介绍 这里介绍一款MySQL数据库的压力测试软件sysbench,用它来进行基准测试. sysbench 是一个开源的.模块化的.跨平台的多线程性能测试工具, 可以用来进行CPU. ...
- myql基准测试工具Sysbench
一.Sysbench介绍 SysBench是一个模块化的.跨平台.多线程基准测试工具,主要用于评估测试各种不同系统参数下的数据库负载情况.它主要包括以下几种方式的测试: 1.cpu性能 2.磁盘io性 ...
- MySQL 常用工具sysbench/fio/tpcc等测试
为什么要压力测试采购新设备,评估新设备性能开发新项目,评估数据库容量新系统上线前,预估/模拟数据库负载更换数据库版本,评估性能变化 关注指标 CPU %wait,%user,%sys 内存 只内存读 ...
- MySQL基准测试工具
一.基准测试 基准测试(benchmark)是针对系统设计的一种压力测试. 基准测试是简化了的压力测试. 1.1 常见指标 TPS QPS 响应时间 并发量 1.2 收集与分析数据脚本 收集数据的sh ...
- mysql基准测试工具tpcc-mysql安装、使用、结果解读
TPCC是专门针对联机交易处理系统(OLTP系统)的规范,一般情况下我们也把这类系统称为业务处理系统,tpcc-mysql是percona基于TPC-C(下面简写成TPCC)衍生出来的产品,专用于My ...
- mysql基准测试与sysbench工具
一.基准测试简介 1.什么是基准测试 数据库的基准测试是对数据库的性能指标进行定量的.可复现的.可对比的测试. 基准测试与压力测试 基准测试可以理解为针对系统的一种压力测试.但基准测试不关心业务逻辑 ...
随机推荐
- PyQt4布局管理——绝对定位方式
PyQt4中的布局管理器 布局管理器是编程中重要的一部分.所谓布局管理器是指我们在窗口中安排部件位置的方法.布局管理器有两种工作方式:绝对定位方式(absolute positioning)和布局类别 ...
- Mybaits中的update
<update id="update" parameterType="Currency"> UPDATE YZ_SECURITIES_CURRENC ...
- poj_1037 动态规划+字典序第k大
题目大意 给定n个数字,规定一种 cute 排序:序列中的数字大小为严格的波浪形,即 a[0] > a[1] < a[2] > a[3] < .... 或者 a[0] < ...
- java基础---->FilenameFilter之文件过滤
FilenameFilter用于对列表中文件名的过滤,今天我们就开始java中FilenameFilter的学习.好多年了,你一直在我的伤口中幽居,我放下过天地,却从未放下过你,我生命中的千山万水,任 ...
- 教主泡嫦娥[有趣的dp状态设计]
P1342 教主泡嫦娥 时间: 1000ms / 空间: 131072KiB / Java类名: Main 背景 2012年12月21日下午3点14分35秒,全世界各国的总统以及领导人都已经汇聚在中国 ...
- 微信小游戏5.2.2 在子项目中使用EUI制作排行榜报错 wx.getFileSystemManager not function
本来想子项目(开放数据域)想使用EUI来制作排行榜. 原5.1.11的时候是ok的.在5.2.2中,使用assetsmananger而不是res,则会报错wx.getFileSystemManager ...
- 交换机工作原理、MAC地址表、路由器工作原理详解
一:MAC地址表详解 说到MAC地址表,就不得不说一下交换机的工作原理了,因为交换机是根据MAC地址表转发数据帧的.在交换机中有一张记录着局域网主机MAC地址与交换机接口的对应关系的表,交换机就是根据 ...
- 玩转Javascript 给JS写测试
给js写测试已经不是什么稀奇的事情了,最近项目里用了jasmine和JsTestDriver两种js测试框架.JsTestDriver易于与持续构建系统相集成并能够在多个浏览器上运行测试轻松实现TDD ...
- Oracle表的维护(字段,重命名表名)
案例:银行里建的开卡信息 字段 字段类型 Id Number name Varchar2(64) sex Char2() birth Date money Number(10,2) 创建银行卡表 cr ...
- Python爬虫基础(二)urllib2库的get与post方法
urllib2默认只支持HTTP/HTTPS的GET和POST方法 一.Get方式 GET请求一般用于我们向服务器获取数据,比如说,我们用百度搜索,在百度搜索框中搜索“秦时明月”,拿到地址栏里有效ur ...
