mybatis的mapper映射文件
1概述
1.1应用架构
mybatis框架用于支持对关系数据库的操作,该体系的应用架构如下图所示:
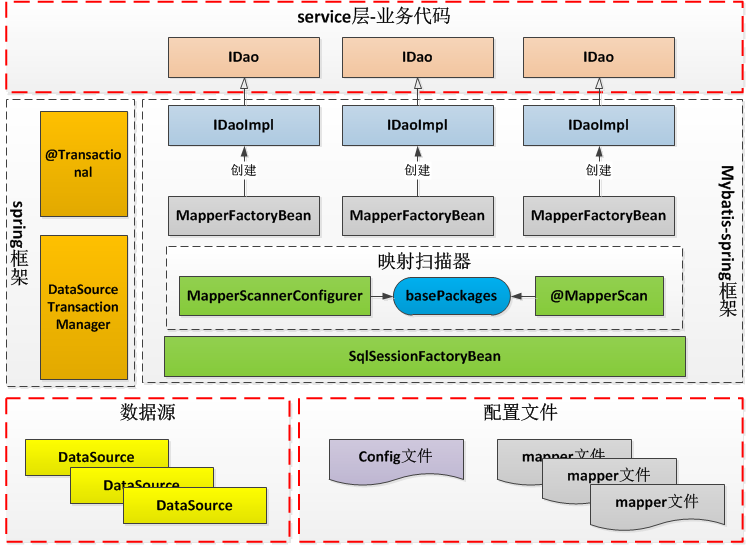
在mybatis框架体系中,主要的组件是:SqlSessionFactoryBean和MapperScannerConfigurer。SqlSessionFactoryBean类依赖外部注入的数据源:DataSource。并有两个属性:configLocation和mapperLocations。
ConfigLocation指定了mybatis配置文件的位置;mapperLocations指定了多个mapper映射文件的位置。
MapperSacannerConfigurer依赖SqlSessionFactoryBean,并根据basePackages属性指定的IDao接口类所在的包位置,自动扫描该包路径,为每个IDao类创建一个MapperFactoryBean类。MapperFactoryBean类会为它所对应的IDao接口类创建其具体的实现类实例,并将其注入到service层的业务代码中。
在Spring boot开发中,使用@MapperScan注解代替MapperScannerConfigurer类。它们的效果是一样的。
在使用mybatis框架实现数据库操作的时候,上图红色框部分的内容需要开发人员实现。
数据源是任何实现了javax.sql.datasource接口的类实例。例如:org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.datasource,该数据源对应单库单表操作;或者com.dangdang.ddframe.rdb.sharding.jdbc.core.datasource.ShardingDataSource,该数据源对用分库,分表操作。
IDao为数据操作接口,实现用户的数据操作逻辑。一般分为接口类和po类两部分。
配置文件分为:mybatis配置文件和mapper配置文件。mybatis配置文件主要用来设计po类的别名,方便对po类的引用;mapper配置文件用来管理SQL语句。
1.2主要开发要素
在mybatis开发中,涉及到主要开发要素是:dao接口类,mapper映射文件,以及po类。它们之间的关系如下:
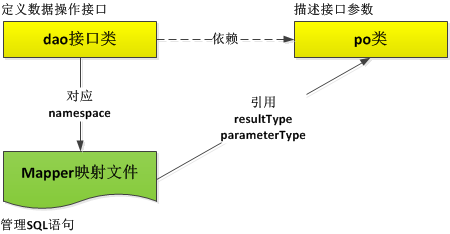
dao接口类中,定义了数据库操作的接口方法,主要包含增,删,改,查等接口方法;po类定义接口方法的参数,可使用po类保存查询结果,或者为insert,update方法提供数据集参数。操作数据库表的SQL语句保存在mapper映射文件中。mapper映射文件分别提供select,insert,update,delete xml元素,分别对应数据库的查询,插入,修改,删除操作。每一个xml元素通过id属性与dao接口类中的方法相互关联。
1.3 mapper文件的结构
mapper映射文件是xml格式的配置文件,由一系列具有层级关系的元素组成。并且通过元素的属性,这些元素之间具有关联关系。具体情况如下图所示:

在mapper映射文件中,主要包含如下配置元素:
- mapper元素。该元素是最顶层的配置元素,其属性namespace指向IDao类的全类型名,即:包路径+类名。在mapper元素下面,包含如下子元素:resultMap元素,select元素,insert元素,update元素,delete元素。
- resultMap元素。建立数据库表的列名与po类的数据字段之间的映射关系。当po类的数据字段与数据库表不一致的时候,或者承载复杂查询结果的时候,使用resultMap配置;
- select元素。用来维护select语句。
- insert元素。用来维护insert语句。
- update元素。用来维护update语句。
- delete元素。用来维护delete语句。
2 文件示例
在开发过程中,需要开发人员配置mapper映射文件,编写Idao类,以及Idao了所依赖的po类。具体示例如下:
2.1 mapper映射文件
mapper配置文件的示例如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org/DTD Mapper 3.0" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lifeng.demo.mybatis.dao.IUserDao"> <resultMap type="UserInfo" id="userData">
<id property="id" column="f_id" />
<result property="name" column="f_name" />
<result property="birth" column="f_birth" />
<result property="salary" column="f_salary" />
</resultMap> <!-- id要与接口方法名相同 -->
<!-- SQL语句中的参数名称(#{id}),要与java代码中的参数bean的数据字段相同,这里是UserInfo.id字段 -->
<!-- type属性可省略 -->
<insert id="insertUserInfoByBean">
insert into t_user (f_id,f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values (#{id},#{name},#{birth},#{salary})
</insert> <!-- @Param的参数必须与#{}中的参数一致 -->
<insert id="insertUserInfo">
insert into t_user (f_id,f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values (#{id},#{name},#{birth},#{salary})
</insert> <insert id="insertUserInfoByBatch">
insert into t_user (f_id,f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values
<foreach collection="list" item="item" separator="," index="idx">
(#{idx},#{item.name},#{item.birth},#{item.salary})
</foreach>
</insert> <!--resultMap属性的值是 resultMap配置节id的值。当承载返回结果的java bean数据字段与数据库表字段格式不一致时,使用resultMap -->
<!-- 如果返回多行数据,会用list封装UserData -->
<select id="listUserInfo" resultMap="userData">
select * from t_user
</select> <select id="getUserCount" resultType="int">
select count(*) from
t_user
</select> <select id="listUserInfoToMap" resultType="map">
select * from
t_user
</select> <select id="getUserInfoById" resultMap="userData">
select * from t_user
where f_id = #{id}
</select> <select id="getUserInfoToMap" resultType="hashmap">
select * from t_user
where f_id=#{id}
</select> <delete id="deleteAll">
delete from t_user
</delete> <delete id="deleteUserInfoById">
delete from t_user where
id=#{id}
</delete> <update id="updateUserInfo">
update t_user set f_name =
#{name} where f_id =
#{id}
</update> </mapper>
2.2 po文件
po文件的示例如下:
package com.lifeng.demo.mybatis.dao.dto; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date; public class UserInfo implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 6730890636022435120L;
private int id;
private String name;
private Date birth;
private double salary; public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
} public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
} public double getSalary() {
return salary;
} public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("UserInfo = [");
builder.append("id:");
builder.append(this.id); builder.append(" name:");
builder.append(this.name); if (this.birth != null) {
builder.append(" birth:");
builder.append(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd").format(this.birth));
} builder.append(" salary:");
builder.append(this.salary); return builder.toString();
}
}
2.3 dao文件
Dao接口的示例如下:
package com.lifeng.demo.mybatis.dao; import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import com.lifeng.demo.mybatis.dao.dto.UserInfo; public interface IUserDao { List<UserInfo> listUserInfo(); int getUserCount(); UserInfo getUserInfoById(int Id); Map<String,Object> getUserInfoToMap(int id); @MapKey("f_id")
Map<BigInteger,Map<String,Object>> listUserInfoToMap(); int insertUserInfoByBean(UserInfo userInfo); int insertUserInfo(@Param("id") int id,@Param("name") String userName,@Param("birth") Date birthDay,@Param("salary") double salary); int insertUserInfoByBatch(List<UserInfo> ls); int updateUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo); int deleteUserInfoById(int Id); int deleteAll();
}
3 常用元素
3.1 resultMap
使用resultMap配置节,建立po类的数据字段与数据库表的列名之间的映射关系。当po类的数据字段与数据库表的列名不一致的时候,可使用该配置。 resultMap的代码示例如下:
<resultMap type="UserInfo" id="userData">
<id property="id" column="f_id" />
<result property="name" column="f_name" />
<result property="birth" column="f_birth" />
<result property="salary" column="f_salary" />
</resultMap>
type属性执行po类的全类型名,即:包名+类名。如果在mybatis配置文件中,为po类建立了别名,那么type属性可以引用该别名。
id属性应该全局唯一,它被select元素的resultMap属性引用。
<id>子元素用来建立po数据字段与数据库表主键列之间的映射关系。
<result>子元素用来建立po数据字段与数据库表非主键列之间的映射关系。
property属性用来指定po类的数据字段名。例如:private String name;该定义中的name。
column属性用来指定数据库表的列名。
3.2 select
在mapper文件中,使用select元素来管理select语句。
3.2.1 返回单值
当查询结果返回一个单值的时候,其配置如下:
<select id="getUserCount" resultType="int">
select count(*) from t_user
</select>
使用resultType属性指定返回结果的数据类型,这里可以是java基本数据类型,如:int,String等。
在IDao类中,接口方法定义如下:
int getUserCount();
方法的返回值类型是int,与resultType的值对应;方法的名称是getUserCount与id属性的值对应。
3.2.2 返回单对象
单对象的含义是:查询结果包含多个数据列,但只有一行数据。可以使用javabean或者map来保存查询结果。
3.2.2.1通过javabean返回单对象
通过javabean返回查询结果的配置如下:
<select id="getUserInfoById" resultMap="userData">
select * from t_user
where f_id = #{id}
</select>
当po类的数据字段与数据库表的列名完全一致的时候,可使用resultType=po类全类型名,或po类别名 的方式指定查询结果的类型。
当po类的数据字段与数据库表的列名不一致的时候,需要定义resultMap映射。在这种情况下,使用resultMap属性,该属性的值与<resultMap>元素的id属性的值相同。
resultMap与resultType不能同时使用。
在IDao类中,接口方法的定义如下:
UserInfo getUserInfoById(int id)
返回值的类型是UserInfo,通过<resultMap>元素的配置,将该类型映射到userData。在<select>元素中,通过resultMap属性引用userData.
3.2.2.2通过map返回单对象
当查询结果是一个单对象,但是没有定义po类的时候,可使用map来承载查询结果。map的key是数据库表的列名,value是该列对应的值。mapper映射文件的配置如下:
<select id="getUserInfoToMap" resultType="hashmap">
select * from t_user where f_id=#{id}
</select>
resultType属性的值设定为hashmap,或者map即可。IDao类中,接口方法定义如下:
Map<String,Object> getUserInfoToMap(int id);
3.2.3返回数据集
数据集的含义是:包含多行数据,每行数据包含多列。
3.2.3.1通过list返回数据集
当查询结果返回一个数据集的时候,mybatis会将查询结果放入list中,然后返回。在这种情况下,resultTpye或者resultMap属性指定的是list列表元素的类型,而非集合本身。mapper映射文件的配置如下:
<select id="listUserInfo" resultMap="userData">
select * from t_user
</select>
resultMap或者resultType可以设定为java bean ,也可设定为map。该配置形式与返回单对象相同,其差别在IDao类中的接口方法定义:
list<UserInfo> listUserInfo();
在定义接口方法的时候,需要使用list包装单值对象的类型。
3.2.3.2通过map返回数据集
该方式需要与注解@MapKey配合使用。map的key是:数据库表中的任意一列,一般选具有索引性质的列,如:id,name等。value是:po类的引用,或者另外一个map的引用。mapper配置文件的内容如下:
<select id="listUserInfoToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
在IDao类中,接口方法的定义如下:
@MapKey("f_id")
Map<BigInteger,Map<String,Object>> listUserInfoToMap();
在上面的示例中,value的值是map类型。value的值也可以是po类。在使用po类的时候,mapper映射文件的配置如下:
<select id="listUserInfo" resultMap="userData">
select * from t_user
</select>
在IDao类中,接口方法定义如下:
@MapKey("id")
map<int,UserInfo> listUserInfo();
3.3结论
resultType使用汇总如下,resultType属性的值可以是如下情形:
1.基本数据类型,如:int,String等;
2.class数据类型,如:java bean,这里输入的是全类型名或者别名;
3.map数据类型。包括:单对象和集合两种;
4.集合数据类型,是集合元素的类型,而非集合本身。
resultMap的使用汇总如下:
该属性的值是:<resultMap>元素的id属性的值。只有当po数据字段与数据库表列名不一致的时候,才使用。
3.3 insert
在mybatis中,使用<insert>元素来管理insert语句。如果sql语句比较简单,可使用@Insert注解来代替mapper映射文件。
如果需要插入的数据字段比较多,可以使用po类封装这些数据字段,示例如下:
<insert id="insertUserInfoByBean" parameterType="UserInfo">
insert into t_user (f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values (#{name},#{birth},#{salary})
</insert>
IDao类的接口方法定义如下:
int insertUserInfoByBean(UserInfo userInfo);
<insert>元素的id属性值是IDao类接口方法的名称。
<insert>元素的parameterType属性值可以省略。其值是接口方法参数的类型。如果接口方法的参数是java bean,那么该值是全类型名(即:包名+类名),或者是类型的别名。
注意:在sql语句中,如:#{name},#{birth}等参数,其名称:name,birth,必须与接口参数UserInfo的数据字段一致。即:UserInfo的数据字段名称必须是name,birth。否则无法识别。
如果需要插叙的数据字段比较少,那么可以直接传递给参数到接口方法中,mapper映射文件的示例如下:
<insert id="insertUserInfo" >
insert into t_user (f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values (#{name},#{birth},#{salary})
</insert>
IDao接口类的定义如下:
int insertUserInfo(@Param("name") String userName,@Param("birth") Date birthDay,@Param("salary") double salary);
注解@Param用来指定接口方法的参数名与sql语句中的参数名之间的映射。@Param注解的参数,如:name,必须与sql语句中的参数,如:#{name}中的name 是完全一致的。
如果sql语句比较简单,可以使用注解来代替mapper映射文件,示例如下:
@Insert("{insert into t_user (f_name,f_birth,f_salary) values (#{name},#{birth},#{salary})}")
int insertUserInfo(@Param("name") String userName,@Param("birth") Date birthDay,@Param("salary") double salary);
3.4 update
<update>元素用来维护update类型的sql语句。如果该sql语句比较简单,可以使用@Update注解代替mapper映射文件。
3.5 delete
<delete>元素用来维护delete类型的sql语句。如果该sql语句比较简单,可以使用@Delete注解来代替mapper映射文件。
3.6 动态sql
使用动态sql来支持复杂的sql语句。在动态sql部分,包含如下xml元素:
if, choose, when, otherwise, trim, where, set, foreach。
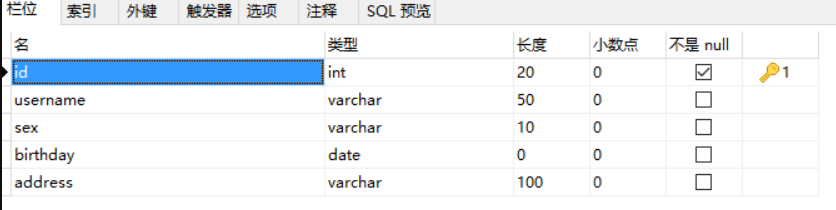
3.6.1示例表
以如下表结构示例动态sql:
3.6.2 if语句
根据 username 和 sex 来查询数据。如果username为空,那么将只根据sex来查询;反之只根据username来查询。首先不使用 动态SQL 来书写
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex"
resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
<!-- 这里和普通的sql 查询语句差不多,对于只有一个参数,后面的 #{id}表示占位符,里面不一定要写id,
写啥都可以,但是不要空着,如果有多个参数则必须写pojo类里面的属性 -->
select * from user where username=#{username} and sex=#{sex}
</select>
上面的查询语句,我们可以发现,如果 #{username} 为空,那么查询结果也是空,如何解决这个问题呢?使用 if 来判断
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user where
<if test="username != null">
username=#{username}
</if> <if test="username != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</select>
这样写我们可以看到,如果 sex 等于 null,那么查询语句为 select * from user where username=#{username},但是如果usename 为空呢?那么查询语句为 select * from user where and sex=#{sex},这是错误的 SQL 语句,如何解决呢?请看下面的 where 语句
3.6.3 if + where 语句
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="username != null">
username=#{username}
</if> <if test="username != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
3.6.3 if + set 语句
同理,上面的对于查询 SQL 语句包含 where 关键字,如果在进行更新操作的时候,含有 set 关键词,我们怎么处理呢?
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 -->
<update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
update user u
<set>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
u.username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
u.sex = #{sex}
</if>
</set> where id=#{id}
</update>
这样写,如果第一个条件 username 为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.sex=? where id=? ; 如果第一个条件不为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.username = ? ,u.sex = ? where id=?
3.6.4 choose(when,otherwise) 语句
有时候,我们不想用到所有的查询条件,只想选择其中的一个,查询条件有一个满足即可,使用 choose 标签可以解决此类问题,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句
<select id="selectUserByChoose" resultType="com.ys.po.User" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id !='' and id != null">
id=#{id}
</when>
<when test="username !='' and username != null">
and username=#{username}
</when>
<otherwise>
and sex=#{sex}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
也就是说,这里我们有三个条件,id,username,sex,只能选择一个作为查询条件
如果 id 不为空,那么查询语句为:select * from user where id=?
如果 id 为空,那么看username 是否为空,如果不为空,那么语句为 select * from user where username=?;
如果 username 为空,那么查询语句为 select * from user where sex=?
3.6.5 trim语句
trim标记是一个格式化的标记,可以完成set或者是where标记的功能
①、用 trim 改写上面第二点的 if+where 语句
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<!-- <where>
<if test="username != null">
username=#{username}
</if> <if test="username != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</where> -->
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or">
<if test="username != null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
<if test="sex != null">
and sex=#{sex}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
prefix:前缀;prefixoverride:去掉第一个and或者是or。
②、用 trim 改写上面第三点的 if+set 语句
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 -->
<update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
update user u
<!-- <set>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
u.username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
u.sex = #{sex}
</if>
</set> -->
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
u.username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
u.sex = #{sex},
</if>
</trim> where id=#{id}
</update>
suffix:后缀
suffixoverride:去掉最后一个逗号(也可以是其他的标记,就像是上面前缀中的and一样)
3.6.6 SQL片段
有时候可能某个 sql 语句我们用的特别多,为了增加代码的重用性,简化代码,我们需要将这些代码抽取出来,然后使用时直接调用。
比如:假如我们需要经常根据用户名和性别来进行联合查询,那么我们就把这个代码抽取出来,如下:
<!-- 定义 sql 片段 -->
<sql id="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
AND username = #{username}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
AND sex = #{sex}
</if>
</sql>
引用 sql 片段
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or">
<!-- 引用 sql 片段,如果refid 指定的不在本文件中,那么需要在前面加上 namespace -->
<include refid="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL"></include>
<!-- 在这里还可以引用其他的 sql 片段 -->
</trim>
</select>
注意:①、最好基于 单表来定义 sql 片段,提高片段的可重用性
②、在 sql 片段中不要包括 where
3.6.7 foreach语句
需求:我们需要查询 user 表中 id 分别为1,2,3的用户
sql语句:select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
①、建立一个 UserVo 类,里面封装一个 List<Integer> ids 的属性
package com.ys.vo;
import java.util.List;
public class UserVo {
//封装多个用户的id
private List<Integer> ids;
public List<Integer> getIds() {
return ids;
}
public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
}
②、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<where>
<!--
collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性。该属性的值有三种:list,array,map,根据传入的集合类型而设定该值。
item:每次遍历生成的对象
index:当前迭代的次数
open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串
close:结束时拼接的字符串
separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串
select * from user where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3)
-->
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or">
id=#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
③、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User">
select * from user
<where>
<!--
collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性.该属性的值有三种:list,array,map,根据传入的集合类型而设定该值。
item:每次遍历生成的对象
index:当前迭代的次数
open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串
close:结束时拼接的字符串
separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串
select * from user where 1=1 and id in (1,2,3)
-->
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="and id in (" close=") " separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
mybatis的mapper映射文件的更多相关文章
- Mybatis系列全解(五):全网最全!详解Mybatis的Mapper映射文件
封面:洛小汐 作者:潘潘 若不是生活所迫,谁愿意背负一身才华. 前言 上节我们介绍了 < Mybatis系列全解(四):全网最全!Mybatis配置文件 XML 全貌详解 >,内容很详细( ...
- xml 文件不给提示(以mybatis 的 mapper映射文件为例)
在xxx.xml 映射文件的头部可以看到 如下: (mybatis generate 自动生成) <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DT ...
- Mybatis将mapper映射文件配置到recources下
关于为什么要将Mybatis的mappers.xml文件配置到resources目录下的粗浅看法: (1).使文件目录更加清晰.resources文件目录下通常为配置文件,所以将Mappers.xml ...
- Mybatis学习系列(二)Mapper映射文件
Mapper映射文件,作用是用来配置SQL映射语句,根据不同的SQL语句性质,使用不同的标签,mapper文件中常用的标签有<iselect>.<insert>.<upd ...
- MyBatis 体系结构、根配置文件、Mapper映射文件
一.MyBatis的体系结构 1.SqlSessionFactory对象 SqlSessionFactory对象是MyBatis的管理核心,它是单个数据库映射关系经过编译后的内存镜像,是创建SqlSe ...
- 深入浅出Mybatis系列(八)---mapper映射文件配置之select、resultMap
上篇<深入浅出Mybatis系列(七)---mapper映射文件配置之insert.update.delete>介绍了insert.update.delete的用法,本篇将介绍select ...
- 深入浅出Mybatis系列(七)---mapper映射文件配置之insert、update、delete
上篇文章<深入浅出Mybatis系列(六)---objectFactory.plugins.mappers简介与配置>简单地给mybatis的配置画上了一个句号.那么从本篇文章开始,将会介 ...
- 深入浅出Mybatis系列(八)---mapper映射文件配置之select、resultMap good
上篇<深入浅出Mybatis系列(七)---mapper映射文件配置之insert.update.delete>介绍了insert.update.delete的用法,本篇将介绍select ...
- IDEA maven项目下测试mybatis例子,使用mappper class或package引入mapper映射文件,总是报错Invalid bound statement(所有配置完全正确)
困扰几个小时,终于查到解决办法及原因(可以直接到最后看解决方案) 环境就是用IDEA搭建的maven项目,主要jar包引入配置如下 <dependencies> <dependenc ...
随机推荐
- golang实现RSA加密解密
非对称加密示意图: 在此可以看到,非对称加密是通过两个密钥(公钥-私钥)来实现对数据的加密和解密的.公钥用于加密,私钥用于解密. RSA公钥和私钥生成: package main import ( & ...
- 微服务之Nacos配置中心源码解析(二)
Nacos配置中心源码解析 源码入口 ConfigFactory.createConfigService ConfigService configService = NacosFactory.crea ...
- smbfs
Hi I tried to mount a network share (smbfs) but it complains about the lack of kernel support. To so ...
- three.js之正投影摄像机与透视投影摄像机的区别
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- 第1章 python入门
1.1 python的出生与应用 python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum).1989年的圣诞节期间,吉多·范罗苏姆(中文名字:龟叔)为了在阿姆斯特丹打发时间,决心开 ...
- Ubuntu 18.04 启动太慢不能忍
检查谁在搞鬼 $ systemd-analyze blame 结果 39.828s plymouth-quit-wait.service 39.311s apt-daily.service 30.93 ...
- 使用select异步IO实现socketserver服务器 源码剖析
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_ #这是一个echo server,客户端消息,服务端回复相同的消息 import select, socket, sys, queue # Create a T ...
- hdf5文件、tqdm模块、nunique、read_csv、sort_values、astype、fillna
pandas.DataFrame.to_hdf(self, path_or_buf, key, **kwargs): Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) ,to add an ...
- monkeyrunner录制和回放功能
脚本录制 网上先是搜索了一下,说是SDK--tools目录下有monkey_recorder.py和monkey_playback.py的脚本,但是我的没有找到所以可以自己编辑个脚本保存即可~ 先编辑 ...
- Java一棵树之001线程
一.理解浓缩 线程是计算机cpu调度的最小的单位,并且jvm中的线程和机器中的线程是一一对应的,在现代编程中,很多时候为了充分利用机器资源而使用多线程,当然很多时候工作中并未使用线程,还是根据场景来选 ...
