HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)
Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 9283 Accepted Submission(s):
4193
either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the
left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the
vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are
preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees
T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r
followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in
preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the
vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in
inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the
vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we
visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of
a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.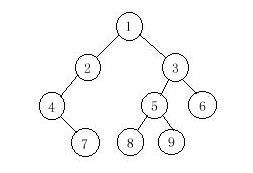
of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of
vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the
preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always
correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
corresponding postorder sequence.
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
- #include<iostream>
- #include <cstring>
- #include <string>
- #include <algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- typedef struct tree
- {
- int v;
- tree *l, *r;
- };
- tree *root;
- tree *build(int *a, int *b, int n)//函数不能少了*
- {
- tree *s;
- int i;
- for (i = ; i <= n; i++)
- {
- if (a[] == b[i])
- {
- s = (tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));//开辟空间
- s->v = b[i];
- s->l = build(a+, b, i-);
- s->r = build(a + i, b + i, n - i );
- return s;//要记得返回
- }
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- void postorder(tree *ro)
- {
- if (ro == NULL) return;
- postorder(ro->l);
- postorder(ro->r);
- if (ro == root)
- {
- printf("%d\n", ro->v);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("%d ", ro->v);
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n, a[], b[];
- while (cin>>n)
- {
- int i;
- for (i = ; i <=n; i++)
- {
- cin >> a[i];
- }
- for (i = ; i <= n; i++)
- {
- cin >> b[i];
- }
- root = build(a, b, n);
- postorder(root);
- }
- return ;
- }
另一种不建树的方法
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cstring>
- #include <algorithm>
- #define maxn 1111
- int n, pre[maxn], in[maxn], post[maxn], id[maxn], res;//pre表示前序遍历序列,in表示中序遍历序列
- void print(int a, int b, int c, int d)//a,b,c,d分别表示前序和中序遍历序列的起点和终点
- {
- int i = id[pre[a]];//根节点
- int j = i - c;//中序遍历序列的左子树
- int k = d - i;//中序遍历序列的右子树
- if (j) print(a + , a + j, c, i - );//左子树非空则递归左子树
- if (k) print(a + j + , b, i + , d);//右子树非空则递归右子树
- post[res++] = pre[a];
- }
- int main()
- {
- while (~scanf("%d", &n))
- {
- res = ;
- for (int i = ; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &pre[i]);
- for (int i = ; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &in[i]), id[in[i]] = i;
- print(, n - , , n - );
- for (int i = ; i<n; i++)
- printf("%d%c", post[i], i == n - ? '\n' : ' ');
- }
- return ;
- }
- #include <stdio.h>
- static int pre[];
- static int mid[];
- /**
- 每次处理数组中的一个小块
- 特点:先序和后序遍历任意子树都是连续的块
- **/
- void post(int pre_index, int mid_index, int size, int is_root)
- {
- if (!size) {
- return;
- }
- if (size == )
- {
- //打印先序
- printf("%d ", pre[pre_index]);
- return;
- }
- //每个(子)树根的位置
- int root;
- //找到根节点
- for (root = ; root < size && pre[pre_index] !=
- mid[mid_index + root]; root++);
- //处理根的左边
- post(pre_index + , mid_index, root, );
- //处理根的右边
- post(pre_index + root + , mid_index + root + ,
- size - root - , );
- //是否是总根,打印根(相对)
- is_root ? printf("%d\n", pre[pre_index]) :
- printf("%d ", pre[pre_index]);
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n, i;
- n = ;
- while (~scanf("%d", &n))
- {
- for (i = ; i < n; i++)
- scanf("%d", &pre[i]);
- for (i = ; i < n; i++)
- scanf("%d", &mid[i]);
- post(, , n, );
- }
- return ;
- }
HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)的更多相关文章
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals 前序遍历和中序推后序
题链;http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (J ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals (二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树)
题目地址:HDU 1710 已知二叉树先序和中序求后序. #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int a[1001], cnt; ty ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树遍历)
传送门 Description A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root ...
- 【二叉树】hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 [题意] 给定一棵二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出后序遍历 [思路] 根据前序遍历和中序遍历递归建树,再后续遍历输出 m ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
题意:给出一颗二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出其后续遍历 首先知道中序遍历是左子树根右子树递归遍历的,所以只要找到根节点,就能够拆分出左右子树 前序遍历是按照根左子树右子树递归遍历的,那么可以找出这颗 ...
- hdu 1701 (Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树前序中序推后序)
Binary Tree Traversals T ...
- PAT 甲级 1020 Tree Traversals (25 分)(二叉树已知后序和中序建树求层序)
1020 Tree Traversals (25 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integ ...
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
随机推荐
- [kata](5kyu) 约瑟夫战死排序(排列)
之前一直不懂,今天百度了下,发下kyu是级别的意思,dan是段的意思,级别数值越小越强,段数数值越大越强. 原题 https://www.codewars.com/kata/josephus-per ...
- TCGA下载神器--TCGAbiolinks
http://bioconductor.org/packages/devel/bioc/vignettes/TCGAbiolinks/inst/doc/tcgaBiolinks.html#gdcque ...
- android 官方demo地址
android官方demo地址都放在了github上:https://github.com/googlesamples
- ng-grid
请查看官网:http://angular-ui.github.io/ui-grid/ 简单的使用: 总的来说我们 1.需要引入ng-grid-1.3.2.js 2.在html页面需要加入 class ...
- EK算法复杂度分析
引理: EK算法每次增广使所有顶点$v\in V-\{s,t\}$到$s$的最短距离$d[v]$增大. 采用反证法, 假设存在一个点$v\in V-\{s,t\}$, 使得$d'[v]< d[v ...
- 在小红家里面,有n组开关,触摸每个开关,可以使得一组灯泡点亮。
package april; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; /** * * @ClassName: Class_9 * @ ...
- ES6学习笔记(一)——扩展运算符和解构赋值
前言 随着前端工程化的快速推进,在项目中使用ES6甚至更高的ES7等最近特性早已不是什么新鲜事.之前还觉得既然浏览器支持有限,那了解一下能看懂就好,然而仅仅了解还是不够的,现在放眼望去,那些成熟框架的 ...
- activity+fragment+listview+adapter+bean在同一个类中的套路
1.xml activity_main.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><FrameLay ...
- 关于CMD/DOS中的短文件名规则
最近在制作一个批处理的过程中发现一个很郁闷的问题,就是有些时候搜索到的结果不是我们想要的
- promise的基础知识
promise 相当于异步操作结果的占位符 它不会去订阅一个事件,也不会传递一个回调函数给目标函数,而是让函数返回一个promise,例如: let promise = readFile('a.txt ...
