Spring源码加载BeanDefinition过程
本文主要讲解Spring加载xml配置文件的方式,跟踪加载BeanDefinition的全过程。
源码分析
源码的入口

ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“spring.xml”)用于加载CLASSPATH下的Spring配置文件,将配置文件传给构造函数,然后调用类内部的另外一个重载方法。

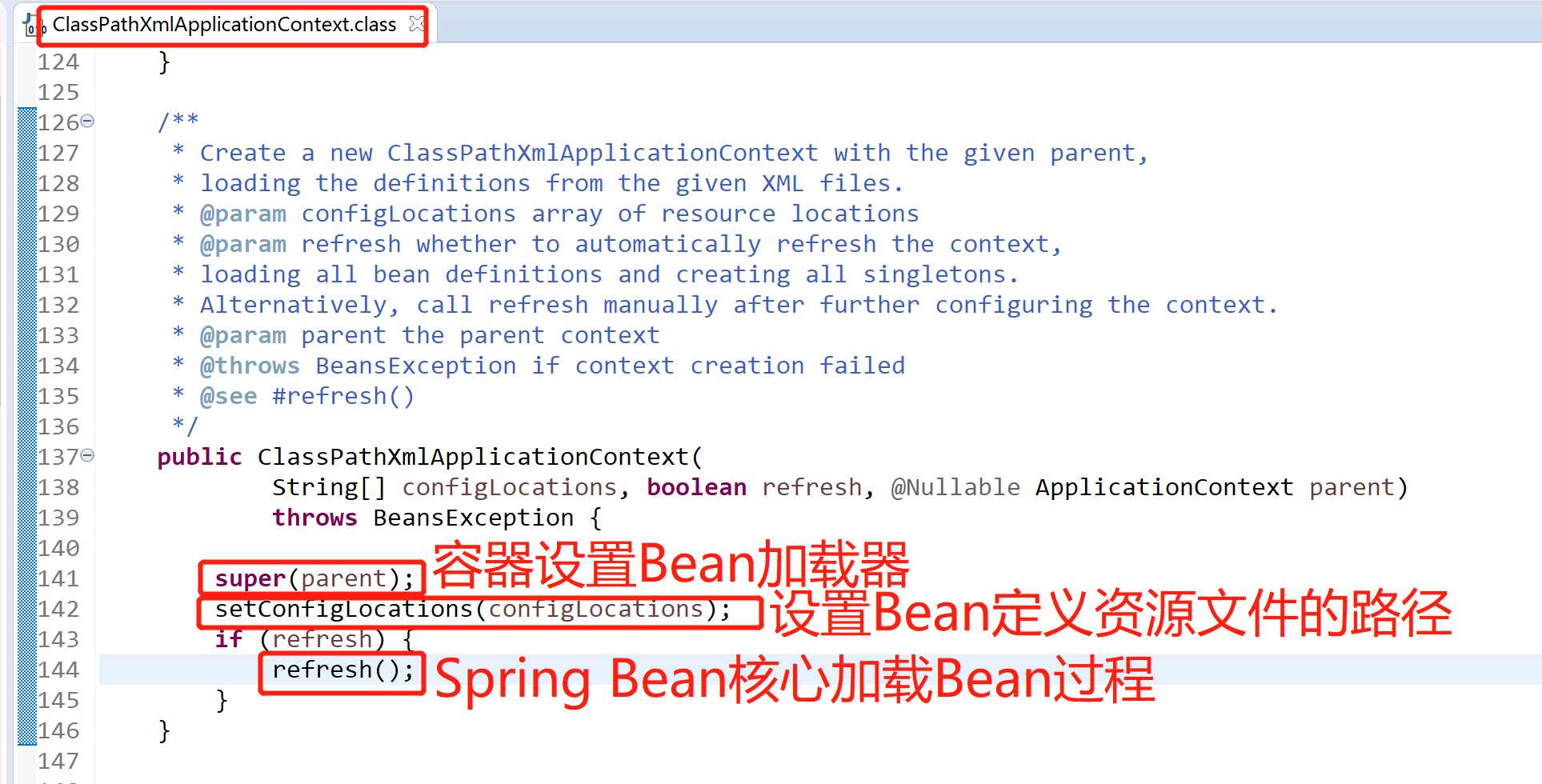
从构造函数中,可以看到一共做了3件事
super(parent)
super(parent)的作用是为容器设置Bean资源加载器,层层跟踪,可知实际是由其父类AbstractApplicationContext完成设置的,parent为null,setParent(parent)就不继续跟踪了,这里需要注意的是,该类继承了DefaultResourceLoader,所以该类也作为资源加载器
AbstractApplicationContext.java
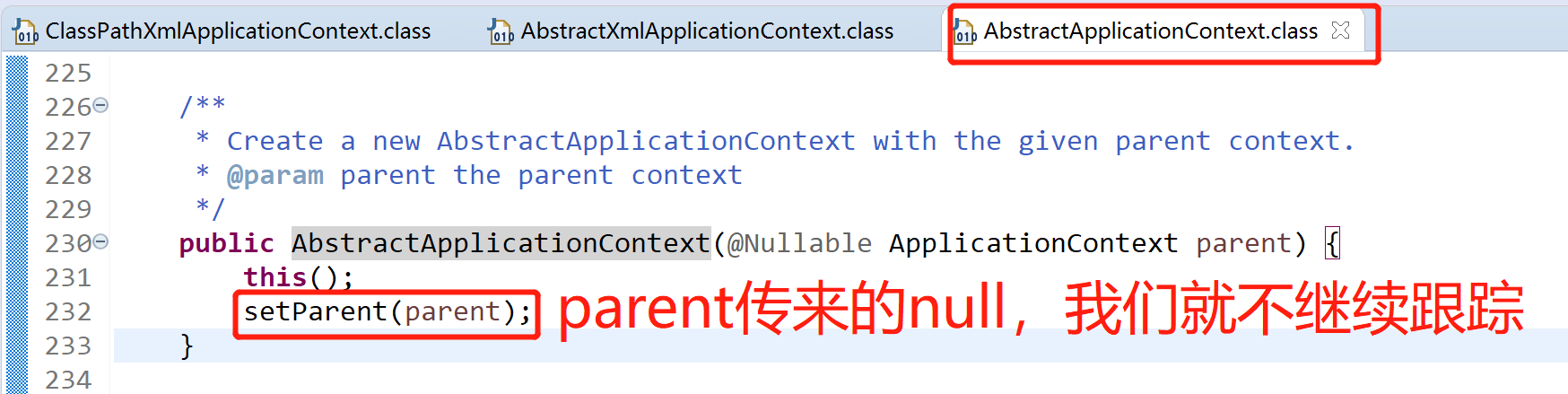
跟踪该类this()无参构造函数进去看看
AbstractApplicationContext.java

AbstractApplicationContext.java
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.java

setConfigLocations(configLocations)
设置Bean定义资源的路径,由其父类AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext完成,resolvePath解析路径,一直跟踪到底层是调用PropertyPlaceholderHelper的parseStringValue完成设置的

refresh()
这个就是整个Spring Bean加载的核心里面十二大步,用于刷新整个Spring上下文信息,定义了整个Spring上下文加载的流程。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//1、 Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); //创建DefaultListableBeanFactory(真正生产和管理bean的容器)
//加载BeanDefition并注册到BeanDefitionRegistry
//通过NamespaceHandler解析自定义标签的功能(比如:context标签、aop标签、tx标签)
//2、 Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); //3、 Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
//4、 Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //实例化并调用实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的Bean
//比如:PropertyPlaceHolderConfigurer(context:property-placeholer)
//就是此处被调用的,作用是替换掉BeanDefinition中的占位符(${})中的内容
//5、 Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //创建并注册BeanPostProcessor到BeanFactory中(Bean的后置处理器)
//比如:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(实现@Autowired注解功能)
// RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(实现@d注解功能)
//这些注册的BeanPostProcessor
//6、 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); //7、 Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); //8、 Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); //9、 Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); //10、 Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); //创建非懒加载方式的单例Bean实例(未设置属性)
//填充属性
//初始化实例(比如调用init-method方法)
//调用BeanPostProcessor(后置处理器)对实例bean进行后置处理
//11、 Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //12、 Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
总结:
- 方法加了个类锁,避免了多线程同时刷新Spring上下文。
- 锁的这个对象为this.startupShutdownMonitor,有两个好处
- refresh()方法和close()方法都使用了this.startupShutdownMonitor,保证了在调用refresh()方法的时候无法使用close()方法,反之亦然,避免了冲突
- 使用对象锁可以减少同步的范围,只对不能并发的代码块进行加锁,提高了整体代码的运行效率。
- refresh()函数是一个模板方法,执行多个方法,而且提供了各个protected方法(默认实现),其子类可以重写他们。
- 模板方法模式:在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类(protected方法)可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。
refresh()核心调用obtainFreshBeanFactory()
obtainFreshBeanFactory()函数调用,完成了容器初始化的最基础的功能,Bean定义资源的Resource定位、加载解析和注册
AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//使用的委派模式,调用2个抽象方法,定义了obtainFreshBeanFactory的算法骨架,实际的行为交给了子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext实现
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//若有容器,销毁容器中的bean,关闭容器,以此保证refresh()之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建IoC容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用加载bean定义的方法,使用了委派模式,在当前类中定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体实现交给子类
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}st
在这个方法中,先判断BeanFactory是否存在,若存在,则先销毁并关闭BeanFactory接着创建DefaultListableBeanFactory,并调用loadBeanDefinitions装在bean使用了委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现交给子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 为给定的bean工厂创建一个新的xmlbeanfinitionReader
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//使用此上下文的bean定义读取器配置
// 资源加载环境
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // 允许子类提供读取器的自定义初始化,然后继续实际加载bean定义
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
看下new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory)做了哪些工作,底层初始化了BeanDefinitionRegistry=BeanDefinitionRegistry也就是this.registry = registry
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Create new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory.
* @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry
*/
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Create a new AbstractBeanDefinitionReader for the given bean factory.
* <p>If the passed-in bean factory does not only implement the BeanDefinitionRegistry
* interface but also the ResourceLoader interface, it will be used as default
* ResourceLoader as well. This will usually be the case for
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} implementations.
* <p>If given a plain BeanDefinitionRegistry, the default ResourceLoader will be a
* {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver}.
* <p>If the passed-in bean factory also implements {@link EnvironmentCapable} its
* environment will be used by this reader. Otherwise, the reader will initialize and
* use a {@link StandardEnvironment}. All ApplicationContext implementations are
* EnvironmentCapable, while normal BeanFactory implementations are not.
* @param registry the BeanFactory to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a BeanDefinitionRegistry
* @see #setResourceLoader
* @see #setEnvironment
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry; // Determine ResourceLoader to use.
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
} // Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
接着看AbstractXmlApplicationContext下的loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法,看最下面一行的loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader)
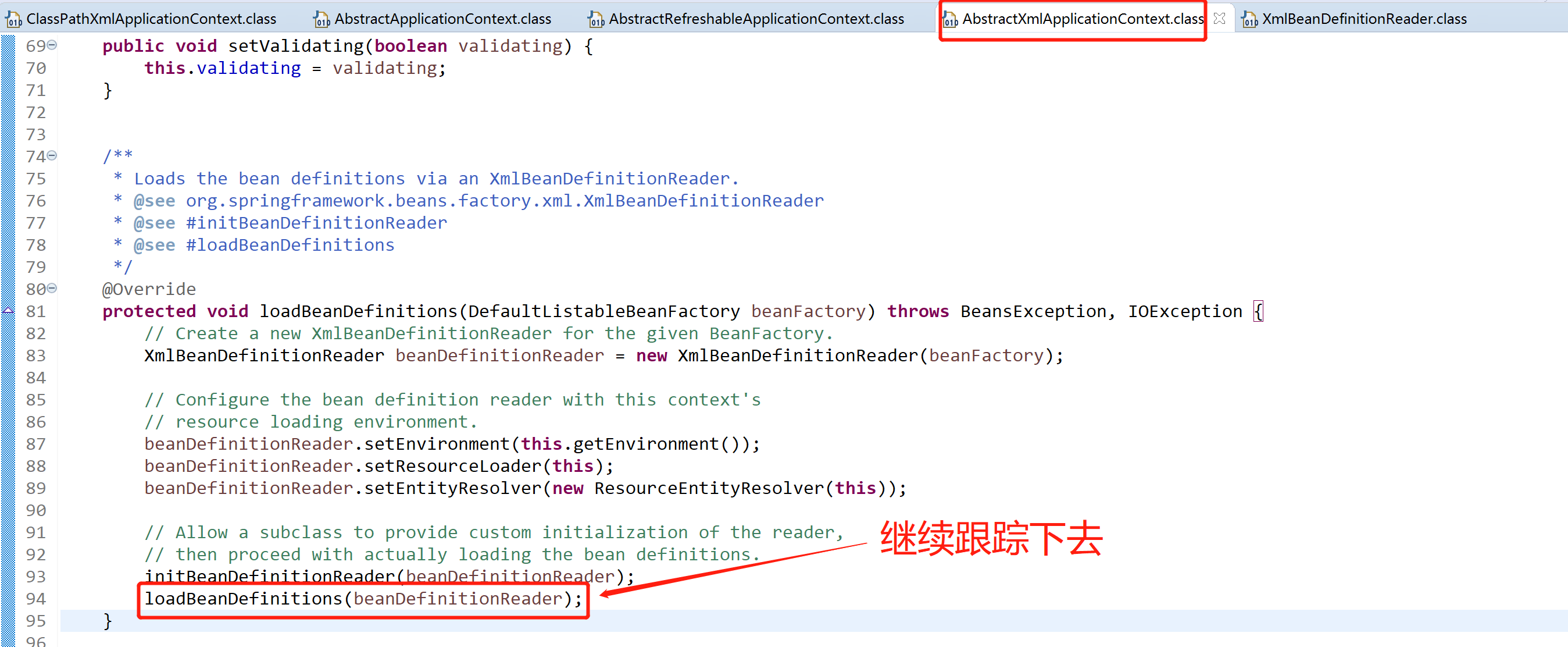
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
/**
* Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory}
* method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions.
* @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use
* @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors
* @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found
* @see #refreshBeanFactory
* @see #getConfigLocations
* @see #getResources
* @see #getResourcePatternResolver
*/
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
接着跟踪第一个reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources)
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
return counter;
}
开始循环加载loadBeanDefinitions,继续跟踪loadBeanDefinitions方法
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
继续跟踪loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
} Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
利用currentResources.add(encodedResource)用set判断,如果重复加载资源就抛出异常,继续跟踪doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #doLoadDocument
* @see #registerBeanDefinitions
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)将xml解析成org.w3c.dom,具体底层如何实现,自行跟踪,主要看registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
/**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
继续跟踪documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource))
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/**
* This implementation parses bean definitions according to the "spring-beans" XSD
* (or DTD, historically).
* <p>Opens a DOM Document; then initializes the default settings
* specified at the {@code <beans/>} level; then parses the contained bean definitions.
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
继续跟踪doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
//初始化bean默认的解析器BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
} preProcessXml(root);
//解析dom
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent;
}
createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent)初始化bean默认的解析器,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate开始解析dom,前面各有一个预留的空方法,方便以后版本扩展,继续跟踪parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
获取节点的命名空间,判断是不是spring默认的,是的话就执行parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate),不是的话,就执行delegate.parseCustomElement(root),跟踪parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { //import
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { //alias
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { //bean
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { //beans
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
标签分别是import、alias、bean、beans,至此BeanDefinition加载完成,这就是refresh()方法中的
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
Spring源码加载BeanDefinition过程的更多相关文章
- Spring源码加载过程图解(一)
最近看了一下Spring源码加载的简装版本,为了更好的理解,所以在绘图的基础上,进行了一些总结.(图画是为了理解和便于记忆Spring架构) Spring的核心是IOC(控制反转)和AOP(面向切面编 ...
- 【学习底层原理系列】重读spring源码3-加载beanDefinition的方法obtainFreshBeanFactory
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法概述 定义BeanFactory,并加载以下两种bean的定义,装配到BeanFactory: 1.配置文件中定义的bean 2.通过<con ...
- Spring源码-加载和IOC部分
源代码和注释放在了github上,包括加载过程的注释和getBean部分的 地址: https://github.com/lvxingzhi/spring-framework-4.3.9-note.g ...
- Spring 源码学习——注册 BeanDefinition
BeanFactory BeanFactory 是 Spring IoC 容器的具体实现,是 Spring 容器的核心接口. DefaultListableBeanFactory XmlBeanFac ...
- 框架源码系列七:Spring源码学习之BeanDefinition源码学习(BeanDefinition、Annotation 方式配置的BeanDefinition的解析)
一.BeanDefinition 1. bean定义都定义了什么? 2.BeanDefinition的继承体系 父类: AttributeAccessor: 可以在xml的bean定义里面加上DTD ...
- spring源码分析之初始化过程
1.org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 一个ServletContextListener,web容器启动监听器 1.1内有成员C ...
- Spring 源码(9)Spring Bean的创建过程的前期准备
回顾总结 到目前为止,Spring源码中AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法的已经解读到第11个方法finishBeanFactoryInitialization, ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(二)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(一)文末中已经提出loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory)的重要性,本文将以此为切入点继续分析. ...
- Spring 源码学习系列
前言 Spring框架之于 JavaEE 程序员来说,犹如锄头之于农民.Java 程序员每天都要使用Spring框架,Spring框架也确实是个可手的工具. 最初使用Spring的时候,我们需要配置m ...
随机推荐
- thinkphp 获取前端传递过来的参数
thinkphp 获取前端传递过来的参数 use think\facade\Request; // 获取当前请求的name变量 Request::param('name'); // 获取当前请求的所有 ...
- nyoj 26-孪生素数问题(打表)
26-孪生素数问题 内存限制:64MB 时间限制:3000ms Special Judge: No accepted:10 submit:43 题目描述: 写一个程序,找出给出素数范围内的所有孪生素数 ...
- 函数指针和成员函数指针有什么不同,反汇编带看清成员函数指针的本尊(gcc@x64平台)
函数指针是什么,可能会答指向函数的指针. 成员函数指针是什么,答指向成员函数的指针. 成员函数指针和函数指针有什么不同? 虚函数指针和非虚成员函数指针有什么不同? 你真正了解成员函数指针了吗? 本篇带 ...
- Docker从入门到实践(4-1)
使用 Docker 镜像 在之前的介绍中,我们知道镜像是 Docker 的三大组件之一. Docker 运行容器前需要本地存在对应的镜像,如果本地不存在该镜像,Docker 会从镜像仓库下载该镜像. ...
- 达梦关键字(如:XML,EXCHANGE,DOMAIN,link等)配置忽略
背景:在使用达梦数据库时,查询SQL中涉及XML,EXCHANGE,DOMAIN,link字段,在达梦中是关键字,SQL报关键词不能使用的错误. 解决办法: 配置达梦安装文件E:\MyJava\dmd ...
- Android中常见的设计模式
前言: Android开发的设计模式,基本设计思想源于java的设计模式,java的设计模式有N多种,据不完全统计,迄今为止,网络出现最频繁的大概有23种.Java只是一门开发语言,学会并掌握这门语言 ...
- 2019年12月1日Linux开发手记
配置ubuntu摄像头: 1.设置→添加→usb控制器→兼容usb3.0 2.虚拟机→可移动设备→web camera→连接(断开主机) 3.查看是否配置成功,打开终端,输入: susb ls /de ...
- 国内开源C# WPF控件库Panuon.UI.Silver推荐
国内优秀的WPF开源控件库,Panuon.UI的优化版本.一个漂亮的.使用样式与附加属性的WPF UI控件库,值得向大家推荐使用与学习. 今天站长(Dotnet9,站长网址:https://dotne ...
- 【JavaEE】之MyBatis动态SQL
动态SQL就是在SQL语句中添加一些标签,以完成某些逻辑.通常用到的动态SQL标签有<if>.<choose>.<where>.<trim>.<s ...
- 英语口语考试资料Family
I Love my family 12 years ago, I was born in a happy family, there was a gentle father, a beautif ...
