Redis5源码解析-Sentinel
简单的概念就不解释。基于Redis5.0.5
从Sentinel主函数触发
在sentinel.c文件的最后面可以发现sentinelTimer函数,这个就是Sentinel的主函数,sentinel的各项功能检测都是在这里进行,循环调用。
void sentinelTimer(void) {
// 并判断是否需要进入 TITL 模式
sentinelCheckTiltCondition();
// 执行定期操作
// 比如 PING 实例、分析主服务器和从服务器的 INFO 命令
// 向其他监视相同主服务器的 发送问候信息
// 并接收其他 发来的问候信息
// 执行故障转移操作,等等
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters);
sentinelRunPendingScripts();
sentinelCollectTerminatedScripts();
sentinelKillTimedoutScripts();
/* We continuously change the frequency of the Redis "timer interrupt"
* in order to desynchronize every Sentinel from every other.
* This non-determinism avoids that Sentinels started at the same time
* exactly continue to stay synchronized asking to be voted at the
* same time again and again (resulting in nobody likely winning the
* election because of split brain voting). */
server.hz = CONFIG_DEFAULT_HZ + rand() % CONFIG_DEFAULT_HZ;
}
Sentinel主函数(sentinelTimer)由server.c中的serverCron()函数调用,serverCron()由server.c中initServer()调用,initServer()由整个Redis主函数调用,在server.c文件最后面。
由于sentinel的各项功能大部分都在sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters);中实现,我们主要分析这个函数。
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters)
从上面可以看到,函数传进去了一个sentinel.masters的参数,这就迁出第一个问题,sentinel.masters是什么东西,从何而来。
Ctrl+左键可以看到定义masters的地方,其存在于一个sentinelState的结构体中,这个结构体定义了整个sentinel的状态结构,一个sentinel就是只存在一个sentinelState的实例。
struct sentinelState {
char myid[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE+1]; /* sentinel ID. */
uint64_t current_epoch; /* Current epoch. */
dict *masters; /* Dictionary of master sentinelRedisInstances.
Key is the instance name, value is the
sentinelRedisInstance structure pointer. */
int tilt; /* Are we in TILT mode? */
int running_scripts; /* Number of scripts in execution right now. */
mstime_t tilt_start_time; /* When TITL started. */
mstime_t previous_time; /* Last time we ran the time handler. */
list *scripts_queue; /* Queue of user scripts to execute. */
char *announce_ip; /* IP addr that is gossiped to other sentinels if
not NULL. */
int announce_port; /* Port that is gossiped to other sentinels if
non zero. */
unsigned long simfailure_flags; /* Failures simulation. */
int deny_scripts_reconfig; /* Allow SENTINEL SET ... to change script
paths at runtime? */
} sentinel;
其中定义一个masters的字典,顺着这个关键点,我们引出第二个问题,sentinelState结构在哪里初始化,其中的masters字典中的数据结构是什么样子的。在redis的主函数里面,存在
/* We need to init sentinel right now as parsing the configuration file
* in sentinel mode will have the effect of populating the sentinel
* data structures with master nodes to monitor. */
if (server.sentinel_mode) {
initSentinelConfig();
initSentinel();
}
在这个两个函数中完成了对sentinel状态结构的初始化,但是其中并没有为sentinel.masters赋值的代码,这时应该可以想到,在sentinel的配置文件中定义了monitor监控的主服务器配置,我们随即找到sentinel读取配置文件的函数,果然在redis的主函数中找到在入配置文件函数
loadServerConfig(configfile, options);
loadServerConfig(configfile, options)–> loadServerConfigFromString(config), 其中对配置文件的各个部分进行解析,在匹配sentinel配置语句内发现为处理sentinel配置文件函数sentinelHandleConfiguration(argv+1,argc-1),这个函数就是sentinel配置文件分析器,在这里面终于找到了解析sentinel monitor 配置的语句。
if (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"monitor") && argc == 5) {
/* monitor <name> <host> <port> <quorum> */
int quorum = atoi(argv[4]);
if (quorum <= 0) return "Quorum must be 1 or greater.";
if (createSentinelRedisInstance(argv[1],SRI_MASTER,argv[2],
atoi(argv[3]),quorum,NULL) == NULL)
{
switch(errno) {
case EBUSY: return "Duplicated master name.";
case ENOENT: return "Can't resolve master instance hostname.";
case EINVAL: return "Invalid port number";
}
}
}
又转进createSentinelRedisInstance(argv[1],SRI_MASTER,argv[2],atoi(argv[3]),quorum,NULL)函数,这就是为sentinel.masters结构赋值的函数,其中主要定义了
- sentinelRedisInstance *ri;
- dict *table = NULL;
变量,接下来便看到
/* Make sure the entry is not duplicated. This may happen when the same
* name for a master is used multiple times inside the configuration or
* if we try to add multiple times a slave or sentinel with same ip/port
* to a master. */
if (flags & SRI_MASTER) table = sentinel.masters;
else if (flags & SRI_SLAVE) table = master->slaves;
else if (flags & SRI_SENTINEL) table = master->sentinels;
这个table指针指向了sentinel.masters,之后就肯定想的到修改table指针就可以直接修改sentinel.masters
/* Add into the right table. */
dictAdd(table, ri->name, ri);//将实例添加到适当的表中
可以看出,如果函数的实参flags == SRI_MASTER,就会创建一个 sentinelRedisInstance 结构,
并按照 /键sentinelRedisInstance.name /值sentinelRedisInstance的形式加入table字典,而table字典指向sentinel.masters字典,sentinel.masters存在于sentinelState结构体,一个sentinel只存在一个sentinelState实例,逻辑渐渐清晰,sentinelState中的sentinel.masters字典保存了所有的master实例。
既然看到这里,就引出第三个问题,createSentinelRedisInstance函数中的sentinelRedisInstance *ri;是什么? Sentinel 会为每个被监视的 Redis 实例创建相应的 sentinelRedisInstance 实例(被监视的实例可以是主服务器、从服务器、或者其他 Sentinel )。
现在我们把逻辑理一下,在createSentinelRedisInstance的形参中有两个重要的形参 int flags 和
sentinelRedisInstance *master
if (flags & SRI_MASTER) table = sentinel.masters;
else if (flags & SRI_SLAVE) table = master->slaves;
else if (flags & SRI_SENTINEL) table = master->sentinels;
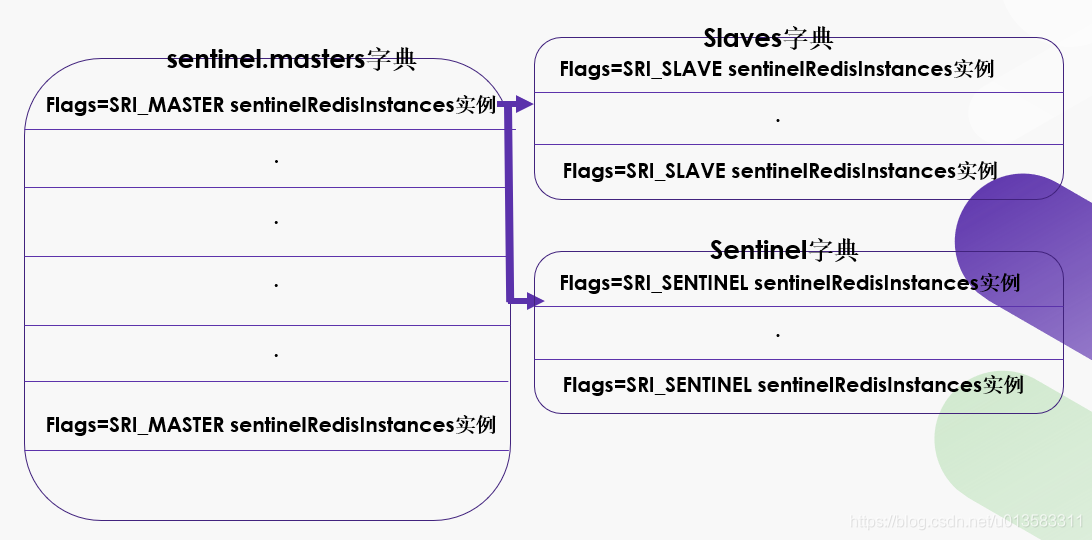
根据flags个标志不同,如果是SRI_MASTER,就创建一个flags = SRI_MASTER 的sentinelRedisInstance结构加入sentinel.masters中;如果是SRI_SLAVE, table指针就指向sentinel.masters的slaves变量,并创建slave实例加入sentinel.masters.slaves变量中;如果是SRI_SENTINEL,table指针就指向sentinel.masters的sentinels变量,并创建sentinel的sentinelRedisInstance实例加入sentinel.masters.slaves变量中。所以我们大概可以想到sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters)函数只要传进一个sentinel.masters变量就可以遍历所有的master,slave,sentinel实例。
19.07.11
再看sentinel的运行过程。
第一个阶段:在Redis的主函数中调用initSentinelConfig();和initSentinel();函数主要完成对sentinelState实例sentinel的初始化。
第二个阶段:在Redis的主函数中调用loadServerConfig(configfile, options) -> loadServerConfigFromString(config) -> sentinelHandleConfiguration(argv+1,argc-1); 完成对sentinel配置文件的解析,在检测到 monitor, known-slave, known-sentinel配置时调用createSentinelRedisInstance()函数创建对应sentinelRedisInstance实例并根据known-slave、known-sentinel配置的master名字加入到对应相同名字的master sentinelRedisInstance实例结构中,不同的master sentinelRedisInstance实例加入sentinelState实例的masters字典中,最后形成上图所示的结构。
第三个阶段(在此循环)
在Redis主函数中调用initServer(),在函数内部向事件循环中注册timer事件回调(serverCron函数)、可以理解为循环执行serverCron函数,在serverCron函数内部执行sentinel主函数sentinelTimer()。
第三个又一阶段
sentinel主函数内部执行sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(sentinel.masters)函数,传入的实参是一个字典,遍历master字典,当遍历的实例标志为SRI_MASTER时再递归调用master的所有slave和sentinel,对所有实例执行调度操作。
void sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(dict *instances) {
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de;
sentinelRedisInstance *switch_to_promoted = NULL;
/* There are a number of things we need to perform against every master. */
di = dictGetIterator(instances);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
// 取出实例对应的实例结构
sentinelRedisInstance *ri = dictGetVal(de);
// 对所有实例执行调度操作,最主要的操作
sentinelHandleRedisInstance(ri);
if (ri->flags & SRI_MASTER) {
// 递归slave
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(ri->slaves);
// 递归sentinel
sentinelHandleDictOfRedisInstances(ri->sentinels);
// 故障master的所有从服务器都已经同步到新主服务器
if (ri->failover_state == SENTINEL_FAILOVER_STATE_UPDATE_CONFIG) {
// 把故障 masters 赋值给 witch_to_promoted执行下面的操作
switch_to_promoted = ri;
}
}
}
// 故障master存在
if (switch_to_promoted)
// 将故障master(已下线)从主服务器表格中移除,并使用新master代替它
sentinelFailoverSwitchToPromotedSlave(switch_to_promoted);
dictReleaseIterator(di);
}
第三个又一又一阶段
sentinelHandleRedisInstance(ri)函数对所有实例执行调度操作,
- 可能创建这个哨兵连向遍历实例 ri 的网路连接sentinelReconnectInstance(ri);
- 可能向实例发送 PING、 INFO 或者 PUBLISH 命令sentinelSendPeriodicCommands(ri);
- 检查实例是否主观下线sentinelCheckSubjectivelyDown(ri);
- 当遍历的sentinelRedisInstance实例为master时,判断其是否进入客观下线状态并执行相应的故障转移。
void sentinelHandleRedisInstance(sentinelRedisInstance *ri) {
/* ========== MONITORING HALF ============ */
/* Every kind of instance */
//可能创建这个哨兵连向遍历实例 ri 的网路连接sentinelReconnectInstance(ri);
sentinelReconnectInstance(ri);
//可能向实例发送 PING、 INFO 或者 PUBLISH 命令sentinelSendPeriodicCommands(ri);
sentinelSendPeriodicCommands(ri);
/* ============== ACTING HALF ============= */
/* We don't proceed with the acting half if we are in TILT mode.
* TILT happens when we find something odd with the time, like a
* sudden change in the clock. */
* //// 如果 Sentinel 处于 TILT 模式,那么不执行故障检测。
if (sentinel.tilt) {
if (mstime()-sentinel.tilt_start_time < SENTINEL_TILT_PERIOD) return;
sentinel.tilt = 0;
sentinelEvent(LL_WARNING,"-tilt",NULL,"#tilt mode exited");
}
/* Every kind of instance */
/* 检测实体是否主观断线 */
sentinelCheckSubjectivelyDown(ri);
/* Masters and slaves */
if (ri->flags & (SRI_MASTER|SRI_SLAVE)) {
/* Nothing so far. */
}
/* Only masters */
if (ri->flags & SRI_MASTER) {
/* Only masters 检查其是否进入客观下线状态*/
sentinelCheckObjectivelyDown(ri);
// 检查其是满足故障转移的条件,满足条件时设置其故障转移标志位等待开始。
// master->failover_state = SENTINEL_FAILOVER_STATE_WAIT_START;
if (sentinelStartFailoverIfNeeded(ri))
// 向master的其他sentinel发送异步命令 SENTINEL is-master-down-by-addr
// 以获得允许达到法定人数的回复,就是请求其他哨兵投票。
sentinelAskMasterStateToOtherSentinels(ri,SENTINEL_ASK_FORCED);
// 根据master故障转移标志的不同执行对应的操作,到这里代表可以进行故障转移
sentinelFailoverStateMachine(ri);
// 这个函数跟上上面那个函数一样,但传入的标志不同,这是给那些不需要故障转移的master使用。
sentinelAskMasterStateToOtherSentinels(ri,SENTINEL_NO_FLAGS);
}
}
第三个又一又二阶段
由于在修改添加自定义配置时需要用到配置重写,在sentinel的各个阶段都有可能发生配置重写sentinelFlushConfig();sentinel的自动配置重写也是在这里运行,在添加自定义sentinel配置之后要在这个函数中加入相关重写函数,要不然会被刷掉
第三个又二阶段
判断这个sentinel需要执行操作
- 判断是否需要进入 TITL 模式sentinelCheckTiltCondition();
- 运行等待执行的脚本sentinelRunPendingScripts();
- 清理已执行完毕的脚本,并重试出错的脚本sentinelCollectTerminatedScripts();
- 杀死运行超时的脚本sentinelKillTimedoutScripts();
- server.hz = CONFIG_DEFAULT_HZ + rand() % CONFIG_DEFAULT_HZ;是为了防止哨兵同时启动同时请求对方投票造成没有哨兵可以成为领导者。split brain voting
第四个阶段
在Redis主函数initServer();的下面还有一个sentinelIsRunning();函数,这个函数在 Sentinel 准备就绪,可以执行操作时执行,为这个哨兵创建唯一的ID并刷新在硬盘上面,为每一个master生成 +monitor sentinelEvent事件。
Redis5源码解析-Sentinel的更多相关文章
- Raft协议实战之Redis Sentinel的选举Leader源码解析
这可能是我看过的写的最详细的关于redis 选举的文章了, 原文链接 Raft协议是用来解决分布式系统一致性问题的协议,在很长一段时间,Paxos被认为是解决分布式系统一致性的代名词.但是Paxos难 ...
- Sentinel源码解析四(流控策略和流控效果)
引言 在分析Sentinel的上一篇文章中,我们知道了它是基于滑动窗口做的流量统计,那么在当我们能够根据流量统计算法拿到流量的实时数据后,下一步要做的事情自然就是基于这些数据做流控.在介绍Sentin ...
- Sentinel源码解析二(Slot总览)
写在前面 本文继续来分析Sentinel的源码,上篇文章对Sentinel的调用过程做了深入分析,主要涉及到了两个概念:插槽链和Node节点.那么接下来我们就根据插槽链的调用关系来依次分析每个插槽(s ...
- Sentinel源码解析一(流程总览)
引言 Sentinel作为ali开源的一款轻量级流控框架,主要以流量为切入点,从流量控制.熔断降级.系统负载保护等多个维度来帮助用户保护服务的稳定性.相比于Hystrix,Sentinel的设计更加简 ...
- tinyxml源码解析(中)
转载于:http://www.cnblogs.com/marchtea/archive/2012/11/20/2766756.html 前言: 之前趁着这段时间比较空闲,也因为听闻tinyxml大名, ...
- 4.Sentinel源码分析— Sentinel是如何做到降级的?
各位中秋节快乐啊,我觉得在这个月圆之夜有必要写一篇源码解析,以表示我内心的高兴~ Sentinel源码解析系列: 1.Sentinel源码分析-FlowRuleManager加载规则做了什么? 2. ...
- 5.Sentinel源码分析—Sentinel如何实现自适应限流?
Sentinel源码解析系列: 1.Sentinel源码分析-FlowRuleManager加载规则做了什么? 2. Sentinel源码分析-Sentinel是如何进行流量统计的? 3. Senti ...
- 6.Sentinel源码分析—Sentinel是如何动态加载配置限流的?
Sentinel源码解析系列: 1.Sentinel源码分析-FlowRuleManager加载规则做了什么? 2. Sentinel源码分析-Sentinel是如何进行流量统计的? 3. Senti ...
- 7.Sentinel源码分析—Sentinel是怎么和控制台通信的?
这里会介绍: Sentinel会使用多线程的方式实现一个类Reactor的IO模型 Sentinel会使用心跳检测来观察控制台是否正常 Sentinel源码解析系列: 1.Sentinel源码分析-F ...
随机推荐
- Android 禁止Edittext弹出系统软键盘 的几种方法
第一种方法:在XML文件下添加: android:focusable="true" android:focusableInTouchMode="true" 第二 ...
- Spring boot 梳理 - SpringApplication
简单启动方式 public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MySpringConfiguration.class, a ...
- 使用maven开发javaweb项目
想重新学习一下java web的知识,之前也学习过一些但是也没有用在开发中所以也忘的七七八八了,因为从事Android开发免不了要与服务器打交道,有时候想自己写一个小DEMO需要服务器的时候感觉真是很 ...
- 【ASP.NET基础--MVC】MVC视图基础语法学习
初步接触.net MVC的视图语法,很多东西都不太熟悉,感觉跟之前的aspx以及html都有一些区别,最近看别人的代码,一边看一边研究,现把学到的东西在这里记录一下,以便日后翻阅. 第一部分:基础知识 ...
- MongoDB 学习笔记之 索引
索引: db.media.createIndex({"Tracklist": 1}) 1表示升序 -1表示降序 我们要着重看一下对数组创建索引的情况. 构建一个集合:db.medi ...
- 每个新手程序员都必须知道的Python技巧
当下,Python 比以往的任何时候都更加流行,人们每天都在实践着 Python 是多么的强大且易用. 我从事 Python 编程已经有几年时间了,但是最近6个月才是全职的.下面列举的这些事情,是我最 ...
- package.json详解
1.概念 Node.js项目遵循模块化的架构,当我们创建了一个Node.js项目,意味着创建了一个模块,这个模块的描述文件,被称为package.json 亦即:模块的描述文件 = package.j ...
- pycharm导入自己写的包的时候,不能识别模块的解决办法
今天用写selenium脚本的时候导入自己统计目录下的模块时,出错,明明存在但是报错说模块不存在,找了半天终于找到解决方案,顺便记录一下吧 pycharm不会将当前文件目录自动加入自己的sourse_ ...
- 02-25 scikit-learn库之决策树
目录 scikit-learn库之决策树 一.DecisionTreeClassifier 1.1 使用场景 1.2 代码 1.3 参数详解 1.4 属性 1.5 方法 二.DecisionTreeR ...
- Qt+VC2010+glew环境安装配置
Qt的源码及预编译安装包在 Qt Archive下载,http://download.qt.io/archive/qt/, 目前最新的是Qt5,其中和Qt4不同的是,Qt5多了个QOpenGLWidg ...
