CF 1131A,1131B,1131C,1131D,1131F(Round541 A,B,C,D,F)题解
A. Sea Battle
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In order to make the "Sea Battle" game more interesting, Boris decided to add a new ship type to it. The ship consists of two rectangles. The first rectangle has a width of w1w1 and a height of h1h1, while the second rectangle has a width of w2w2 and a height of h2h2, where w1≥w2w1≥w2. In this game, exactly one ship is used, made up of two rectangles. There are no other ships on the field.
The rectangles are placed on field in the following way:
- the second rectangle is on top the first rectangle;
- they are aligned to the left, i.e. their left sides are on the same line;
- the rectangles are adjacent to each other without a gap.
See the pictures in the notes: the first rectangle is colored red, the second rectangle is colored blue.
Formally, let's introduce a coordinate system. Then, the leftmost bottom cell of the first rectangle has coordinates (1,1)(1,1), the rightmost top cell of the first rectangle has coordinates (w1,h1)(w1,h1), the leftmost bottom cell of the second rectangle has coordinates (1,h1+1)(1,h1+1) and the rightmost top cell of the second rectangle has coordinates (w2,h1+h2)(w2,h1+h2).
After the ship is completely destroyed, all cells neighboring by side or a corner with the ship are marked. Of course, only cells, which don't belong to the ship are marked. On the pictures in the notes such cells are colored green.
Find out how many cells should be marked after the ship is destroyed. The field of the game is infinite in any direction.
Four lines contain integers w1,h1,w2w1,h1,w2 and h2h2 (1≤w1,h1,w2,h2≤1081≤w1,h1,w2,h2≤108, w1≥w2w1≥w2) — the width of the first rectangle, the height of the first rectangle, the width of the second rectangle and the height of the second rectangle. You can't rotate the rectangles.
Print exactly one integer — the number of cells, which should be marked after the ship is destroyed.
2 1 2 1
12
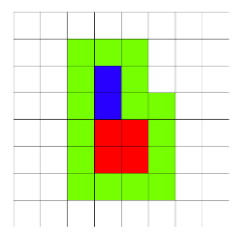
2 2 1 2
16
In the first example the field looks as follows (the first rectangle is red, the second rectangle is blue, green shows the marked squares):

In the second example the field looks as:
题解:题意就是让你求围绕两个矩形一周所占的方格数;答案就是不论上面的方格小于还是等于下面的方格的宽,都是2*(w1+2+h1+h2)
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
ll w1,h1,w2,h2,ans;
int main()
{
ans=;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&w1,&h1,&w2,&h2);
ans=*(w1+h1+h2+);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return ;
}
B. Draw!
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You still have partial information about the score during the historic football match. You are given a set of pairs (ai,bi)(ai,bi), indicating that at some point during the match the score was "aiai: bibi". It is known that if the current score is «xx:yy», then after the goal it will change to "x+1x+1:yy" or "xx:y+1y+1". What is the largest number of times a draw could appear on the scoreboard?
The pairs "aiai:bibi" are given in chronological order (time increases), but you are given score only for some moments of time. The last pair corresponds to the end of the match.
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤100001≤n≤10000) — the number of known moments in the match.
Each of the next nn lines contains integers aiai and bibi (0≤ai,bi≤1090≤ai,bi≤109), denoting the score of the match at that moment (that is, the number of goals by the first team and the number of goals by the second team).
All moments are given in chronological order, that is, sequences xixi and yjyj are non-decreasing. The last score denotes the final result of the match.
Print the maximum number of moments of time, during which the score was a draw. The starting moment of the match (with a score 0:0) is also counted.
3
2 0
3 1
3 4
2
3
0 0
0 0
0 0
1
1
5 4
5
In the example one of the possible score sequences leading to the maximum number of draws is as follows: 0:0, 1:0, 2:0, 2:1, 3:1, 3:2, 3:3, 3:4.
题解:给你两个人在比赛中某些时刻的得分比,让你判断最多有多少时刻,两个人的比分是相同的;
对两个时刻之间处理即可:现在的最小值-前一时刻的最大值,(如果前一时刻是比分不相同的,再加一)
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
ll x,y,cx,cy,ans;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
ans=;cx=cy=;
for(int i=;i<=n;++i)
{
cin>>x>>y;
ll L=max(cx,cy);
ll R=min(x,y);
if(R>=L)
{
if(cx==cy) ans+=(R-L);
else ans+=(R-L+);
}
cx=x;cy=y;
}
cout<<ans<<endl; return ;
}
C. Birthday
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Cowboy Vlad has a birthday today! There are nn children who came to the celebration. In order to greet Vlad, the children decided to form a circle around him. Among the children who came, there are both tall and low, so if they stand in a circle arbitrarily, it may turn out, that there is a tall and low child standing next to each other, and it will be difficult for them to hold hands. Therefore, children want to stand in a circle so that the maximum difference between the growth of two neighboring children would be minimal possible.
Formally, let's number children from 11 to nn in a circle order, that is, for every ii child with number ii will stand next to the child with number i+1i+1, also the child with number 11 stands next to the child with number nn. Then we will call the discomfort of the circle the maximum absolute difference of heights of the children, who stand next to each other.
Please help children to find out how they should reorder themselves, so that the resulting discomfort is smallest possible.
The first line contains a single integer nn (2≤n≤1002≤n≤100) — the number of the children who came to the cowboy Vlad's birthday.
The second line contains integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤1091≤ai≤109) denoting heights of every child.
Print exactly nn integers — heights of the children in the order in which they should stand in a circle. You can start printing a circle with any child.
If there are multiple possible answers, print any of them.
5
2 1 1 3 2
1 2 3 2 1
3
30 10 20
10 20 30
In the first example, the discomfort of the circle is equal to 11, since the corresponding absolute differences are 11, 11, 11 and 00. Note, that sequences [2,3,2,1,1][2,3,2,1,1] and [3,2,1,1,2][3,2,1,1,2] form the same circles and differ only by the selection of the starting point.
In the second example, the discomfort of the circle is equal to 2020, since the absolute difference of 1010 and 3030 is equal to 2020.
题解:重新排列这些数,是其围城一个环相邻差值和最小;
分奇数位和偶数位分别放在两边;
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define clr(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a))
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,a[],b[];
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sort(a+,a++n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i&)
b[i/+]=a[i];
else b[n-i/+]=a[i];
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) printf("%d ",b[i]);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
D. Gourmet choice
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mr. Apple, a gourmet, works as editor-in-chief of a gastronomic periodical. He travels around the world, tasting new delights of famous chefs from the most fashionable restaurants. Mr. Apple has his own signature method of review — in each restaurant Mr. Apple orders two sets of dishes on two different days. All the dishes are different, because Mr. Apple doesn't like to eat the same food. For each pair of dishes from different days he remembers exactly which was better, or that they were of the same quality. After this the gourmet evaluates each dish with a positive integer.
Once, during a revision of a restaurant of Celtic medieval cuisine named «Poisson», that serves chestnut soup with fir, warm soda bread, spicy lemon pie and other folk food, Mr. Apple was very pleasantly surprised the gourmet with its variety of menu, and hence ordered too much. Now he's confused about evaluating dishes.
The gourmet tasted a set of nn dishes on the first day and a set of mm dishes on the second day. He made a table aa of size n×mn×m, in which he described his impressions. If, according to the expert, dish ii from the first set was better than dish jj from the second set, then aijaij is equal to ">", in the opposite case aijaij is equal to "<". Dishes also may be equally good, in this case aijaij is "=".
Now Mr. Apple wants you to help him to evaluate every dish. Since Mr. Apple is very strict, he will evaluate the dishes so that the maximal number used is as small as possible. But Mr. Apple also is very fair, so he never evaluates the dishes so that it goes against his feelings. In other words, if aijaij is "<", then the number assigned to dish ii from the first set should be less than the number of dish jj from the second set, if aijaij is ">", then it should be greater, and finally if aijaij is "=", then the numbers should be the same.
Help Mr. Apple to evaluate each dish from both sets so that it is consistent with his feelings, or determine that this is impossible.
The first line contains integers nn and mm (1≤n,m≤10001≤n,m≤1000) — the number of dishes in both days.
Each of the next nn lines contains a string of mm symbols. The jj-th symbol on ii-th line is aijaij. All strings consist only of "<", ">" and "=".
The first line of output should contain "Yes", if it's possible to do a correct evaluation for all the dishes, or "No" otherwise.
If case an answer exist, on the second line print nn integers — evaluations of dishes from the first set, and on the third line print mmintegers — evaluations of dishes from the second set.
3 4
>>>>
>>>>
>>>>
Yes
2 2 2
1 1 1 1
3 3
>>>
<<<
>>>
Yes
3 1 3
2 2 2
3 2
==
=<
==
No
In the first sample, all dishes of the first day are better than dishes of the second day. So, the highest score will be 22, for all dishes of the first day.
In the third sample, the table is contradictory — there is no possible evaluation of the dishes that satisfies it.
题解:题目就是给你n和m个数,给出这n和m个数的大小关系,让你求,最小有多少种数;
n和m映射到1~n+m这些数中;
对于"=",我们用并查集将他们缩点;
然后对">"和"<"进行建边,跑拓扑排序即可;
然后dp[i]:表示第i个数大小;
dp[e[x].to]=max(dp[e[x].to],dp[x]+1);
最后依次输出即可;
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define clr(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a))
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N=2e3+,M=2e6+;
struct data{
int to,next;
} e[M];
int head[N],cnt,dp[N],x,tot,n,m;
int q[N],t,w,fa[N],ans[N],in[N];
char mp[N/][N/];
int find(int x){ return x==fa[x]?x:fa[x]=find(fa[x]); }
void ins(int u,int v)
{
e[++cnt].to=v;
e[cnt].next=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
in[v]++;//入度
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;++i) scanf("%s",mp[i]+);
for(int i=;i<=n+m;++i) fa[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<=n;++i) for(int j=;j<=m;++j) if(mp[i][j]=='=') fa[find(i)]=find(n+j);//缩点
for(int i=;i<=n;++i) for(int j=;j<=m;++j)
{
if(mp[i][j]=='>') ins(find(n+j),find(i));
else if(mp[i][j]=='<') ins(find(i),find(n+j));
} for(int i=;i<=n+m;++i) if(find(i)==i) tot++;
for(int i=;i<=n+m;++i) if(!in[i]&&find(i)==i) q[w++]=i,dp[i]=;
while(t!=w)//拓扑
{
x=q[t++];
for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next)
{
dp[e[i].to]=max(dp[e[i].to],dp[x]+);
if(--in[e[i].to]==) q[w++]=e[i].to;
}
}
if(t!=tot) { puts("No");return ;}
else
{
puts("Yes");
for(int i=;i<=n;++i) printf("%d%c",dp[find(i)],i==n?'\n':' ');
for(int i=;i<=m;++i) printf("%d%c",dp[find(i+n)],i==m?'\n':' ');
}
return ;
}
F. Asya And Kittens
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Asya loves animals very much. Recently, she purchased nn kittens, enumerated them from 11 and nn and then put them into the cage. The cage consists of one row of nn cells, enumerated with integers from 11 to nn from left to right. Adjacent cells had a partially transparent partition wall between them, hence there were n−1n−1 partitions originally. Initially, each cell contained exactly one kitten with some number.
Observing the kittens, Asya noticed, that they are very friendly and often a pair of kittens in neighboring cells wants to play together. So Asya started to remove partitions between neighboring cells. In particular, on the day ii, Asya:
- Noticed, that the kittens xixi and yiyi, located in neighboring cells want to play together.
- Removed the partition between these two cells, efficiently creating a single cell, having all kittens from two original cells.
Since Asya has never putted partitions back, after n−1n−1 days the cage contained a single cell, having all kittens.
For every day, Asya remembers numbers of kittens xixi and yiyi, who wanted to play together, however she doesn't remember how she placed kittens in the cage in the beginning. Please help her and find any possible initial arrangement of the kittens into nn cells.
The first line contains a single integer nn (2≤n≤1500002≤n≤150000) — the number of kittens.
Each of the following n−1n−1 lines contains integers xixi and yiyi (1≤xi,yi≤n1≤xi,yi≤n, xi≠yixi≠yi) — indices of kittens, which got together due to the border removal on the corresponding day.
It's guaranteed, that the kittens xixi and yiyi were in the different cells before this day.
For every cell from 11 to nn print a single integer — the index of the kitten from 11 to nn, who was originally in it.
All printed integers must be distinct.
It's guaranteed, that there is at least one answer possible. In case there are multiple possible answers, print any of them.
5
1 4
2 5
3 1
4 5
3 1 4 2 5
The answer for the example contains one of several possible initial arrangements of the kittens.
The picture below shows how the cells were united for this initial arrangement. Note, that the kittens who wanted to play together on each day were indeed in adjacent cells.

题解:题意就是一些人站成一排,然后n-1个关系,x,y:表示x和y想玩;
让你给出他们初始的顺序;
并查集,用g[i]表示i块最左边的人,每次合并块,保证相对位置即可;
参考代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define clr(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a))
#define ll long long
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=2e5+;
int n,fa[maxn],r[maxn],g[maxn],x,y;
int find(int x){return x==fa[x]? x:fa[x]=find(fa[x]);}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;++i) fa[i]=i,r[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<n;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int fx=find(x),fy=find(y);
g[r[fx]]=fy;r[fx]=r[fy];fa[fy]=fx;
}
for(int i=find();i;i=g[i]) printf("%d ",i);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
参考代码:
CF 1131A,1131B,1131C,1131D,1131F(Round541 A,B,C,D,F)题解的更多相关文章
- CF 1132A,1132B,1132C,1132D,1132E,1132F(Round 61 A,B,C,D,E,F)题解
A.Regular bracket sequence A string is called bracket sequence if it does not contain any characters ...
- CF 1130A 1130B 1130C1129A1 1129A2 1129B(Round542A B C D1 D2 E)题解
A : Be Positive 题目地址:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1130/A 题解:让你求是否满足一个d使得数列长为n的a数组的每个数除以 ...
- B. Lost Number【CF交互题 暴力】
B. Lost Number[CF交互题 暴力] This is an interactive problem. Remember to flush your output while communi ...
- C可变参数的函数
我们实现一个简单的printf函数(可变参数) #include <stdio.h> #include <stdarg.h> void myprintf(const char ...
- ASP.Net中实现上传过程中将文本文件转换成PDF的方法
iTextSharp是一个常用的PDF库,我们可以使用它来创建.修改PDF文件或对PDF文件进行一些其他额外的操作.本文讲述了如何在上传过程中将文本文件转换成PDF的方法. 基本工作 在开始之前,我们 ...
- vim 使用
vim有三种模式:输入模式,命令模式,底行模式,使用esc进入命令模式,在命令模式下按英文的冒号,进入底行模式:命令行模式下按i进入输入模式.vim编辑文件是将文件内容复制到缓冲区显示在屏幕上. vi ...
- jquery-jsrender使用
JsRender是一款基于jQuery的JavaScript模版引擎 特点: · 简单直观 · 功能强大 · 可扩展的 · 快如闪电 jsrender使用比较简单,本文简单结束一些常用的 使用过程 ...
- yii php 图片上传与生成缩略图
今天需要做图片上传与生成缩略图的功能,把代码进行记录如下: html 视图 ($pic_action_url = $this->createAbsoluteUrl('h ...
- 学习linux内核时常碰到的汇编指令(1)
转载:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4be6adec01007xvg.html 80X86 汇编指令符号大全 +.-.*./∶算术运算符. &∶宏处理操作符. ...
随机推荐
- [LC]88题 Merge Sorted Array (合并两个有序数组 )
①英文题目 Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array. N ...
- vue开发之跨域请求,请求头not allowed by Access-Control-Allow-Headers,后端cookie session值取不到(二)
原因:你本地的请求ajax的get和post请求:如果你的请求头内放一些可用验证数据Token的时候就会存在跨域请求这是浏览器所不允许的问题: 方案一:后台的接口请求模式都写成jsonp请求,前端去调 ...
- 02. JVM运行机制
JVM运行机制 JVM启动流程 JVM基本结构 内存模型 编译和解释运行的概念 一.JVM启动流程
- hdu 2255 奔小康赚大钱 (KM)
奔小康赚大钱Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- ecryptfs
ecryptfs是一种加密文件系统.该文件系统的内容在传输和储存时以密文形式存在.只有在mount时用密钥解密才能得到明文.利用这个特性,我们可以用他来对软件镜像中的部分敏感文件系统进行加密,然后打包 ...
- Flex利用JavaScript执行cmd命令
Flex: //注册js事件 protected function init():void { ExternalInterfa ...
- PowerMock学习(七)之Mock Constructor的使用
前言 我们在编码的时候,总习惯在构造器中传参数,那么在powermock中是怎么模拟带参数构造的呢,这并不难. 模拟场景 我们先模拟这样一个场景,通过dao中的传入一个是布尔类型(是否加载)和一个枚举 ...
- ES6扩展运算符...
对象的扩展运算符理解对象的扩展运算符其实很简单,只要记住一句话就可以: 对象中的扩展运算符(...)用于取出参数对象中的所有可遍历属性,拷贝到当前对象之中 let bar = { a: 1, b: 2 ...
- python 面向对象的基本概念(未完待续)
面向对象编程简称OOP(Object-oriented-programming),是一种程序设计思想. 面向过程编程(如C语言)指一件事该怎么做,面向对象编程(如Java.python)指一件事该让谁 ...
- Java并发之synchronized关键字和Lock接口
欢迎点赞阅读,一同学习交流,有疑问请留言 . GitHub上也有开源 JavaHouse,欢迎star 引用 当开发过程中,我们遇到并发问题.怎么解决? 一种解决方式,简单粗暴:上锁.将千军万马都给拦 ...
