C++实现车轮轨迹
标题:车轮轴迹
栋栋每天骑自行车回家需要经过一条狭长的林荫道。道路由于年久失修,变得非常不平整。虽然栋栋每次都很颠簸,但他仍把骑车经过林荫道当成一种乐趣。
由于颠簸,栋栋骑车回家的路径是一条上下起伏的曲线,栋栋想知道,他回家的这条曲线的长度究竟是多长呢?更准确的,栋栋想知道从林荫道的起点到林荫道的终点,他的车前轮的轴(圆心)经过的路径的长度。
栋栋对路面进行了测量。他把道路简化成一条条长短不等的直线段,这些直线段首尾相连,且位于同一平面内。并在该平面内建立了一个直角坐标系,把所有线段的端点坐标都计算好。
假设栋栋的自行车在行进的过程中前轮一直是贴着路面前进的。
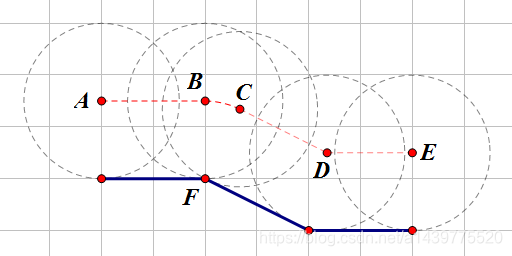
图1给出了一个简单的路面的例子,其中蓝色实线为路面,红色虚线为车轮轴经过的路径。在这个例子中,栋栋的前轮轴从A点出发,水平走到B点,然后绕着地面的F点到C点(绕出一个圆弧),再沿直线下坡到D点,最后水平走到E点,在这个图中地面的坐标依次为:(0, 0), (2, 0), (4, -1), (6, -1),前轮半径为1.50,前轮轴前进的距离依次为:
AB=2.0000;弧长BC=0.6955;CD=1.8820;DE=1.6459。
总长度为6.2233。
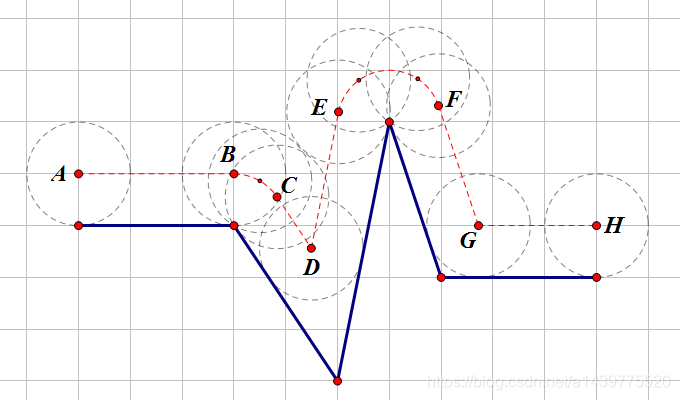
图2给出了一个较为复杂的路面的例子,在这个例子中,车轮在第一个下坡还没下完时(D点)就开始上坡了,之后在坡的顶点要从E绕一个较大的圆弧到F点。这个图中前轮的半径为1,每一段的长度依次为:
AB=3.0000;弧长BC=0.9828;CD=1.1913;DE=2.6848;弧长EF=2.6224; FG=2.4415;GH=2.2792。
总长度为15.2021。
现在给出了车轮的半径和路面的描述,请求出车轮轴轨迹的总长度。
输入的第一行包含一个整数n和一个实数r,用一个空格分隔,表示描述路面的坐标点数和车轮的半径。
接下来n行,每个包含两个实数,其中第i行的两个实数x[i], y[i]表示描述路面的第i个点的坐标。
路面定义为所有路面坐标点顺次连接起来的折线。给定的路面的一定满足以下性质:
*第一个坐标点一定是(0, 0);
*第一个点和第二个点的纵坐标相同;
*倒数第一个点和倒数第二个点的纵坐标相同;
*第一个点和第二个点的距离不少于车轮半径;
*倒数第一个点和倒数第二个点的的距离不少于车轮半径;
*后一个坐标点的横坐标大于前一个坐标点的横坐标,即对于所有的i,x[i+1]>x[i]。
输出一个实数,四舍五入保留两个小数,表示车轮轴经过的总长度。
你的结果必须和参考答案一模一样才能得分。数据保证答案精确值的小数点后第三位不是4或5。
【样例输入1】
4 1.50
0.00 0.00
2.00 0.00
4.00 -1.00
6.00 -1.00
【样例输出1】
6.22
【样例说明1】
这个样例对应图1。
【样例输入2】
6 1.00
0.00 0.00
3.00 0.00
5.00 -3.00
6.00 2.00
7.00 -1.00
10.00 -1.00
【样例输出2】
15.20
【样例说明2】
这个样例对应图2
【数据规模与约定】
对于20%的数据,n=4;
对于40%的数据,n≤10;
对于100%的数据,4≤n≤100,0.5≤r≤20.0,x[i] ≤2000.0,-2000.0≤y[i] ≤2000.0。
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 64M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意: main函数需要返回0
注意: 只使用ANSI C/ANSI C++ 标准,不要调用依赖于编译环境或操作系统的特殊函数。
注意: 所有依赖的函数必须明确地在源文件中 #include , 不能通过工程设置而省略常用头文件。
提交时,注意选择所期望的编译器类型(千万不要混淆c和cpp)。
锦囊
有20%的数据n=4,此时路面由两段水平线和一个坡组成,可以分为上坡和下坡讨论,可以推导出数学公式,这20%的分数比较好拿。
此题正确的做法是:对于每个条线段,将这条线段按车轮的半径平移到路面上方,然后在每个线段的端点画一个圆。由这些平移后的线段和圆组成的最上面的一条线就是车轮的路径,接下来需要算出这条线。
这条线是一条分段连续的线,每段或者是一条直线段,或者是一段圆弧。先求出所有直线段与直线段、直线段与圆、圆与圆的交点,并把所有的端点,所有圆的左右边界一起放入一个集合中,这个集合中的所有横坐标就是可能分段的坐标。按这个集合的坐标分段,每一段分别计算。每一段只需要找到最靠上方的线段/弧即可,最终将所有段的线段和弧的长度相加得到答案。
本题与几何关系较大,公式推导是一个麻烦之处。另外选手可能漏考虑一些情况而失分。本题对编程的要求较高,较容易写错,而且不好调试。
#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <vector>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int MAXN = 10000;const double PI = atan(1.0) * 4;const double EPS = 1e-10;class Point {public:double x, y;Point() {}Point(double x, double y) : x(x), y(y) {}Point operator - (const Point &r) const { return Point(x-r.x, y-r.y); }Point operator + (const Point &r) const { return Point(x+r.x, y+r.y); }Point &operator += (const Point &r) { x += r.x; y += r.y; return *this; }Point &operator *= (double m) { x *= m; y *= m; return *this; }Point pOfRotate(double angle) const {double cosA = cos(angle);double sinA = sin(angle);return Point(cosA*x-sinA*y, sinA*x+cosA*y);}Point pOfRotate90() const { return Point(-y, x); }double length() const { return sqrt(x*x+y*y); }Point pOfNormal() const {double len = length();return Point(x/len, y/len);}double angle() const { return atan2(y, x); }};ostream & operator <<(ostream &os, const Point &v){os << "(" << v.x << "," << v.y << ")";return os;}class Segment;class Circle;class Seg {public:virtual double getLeft() const = 0;virtual double getRight() const = 0;virtual double getY(double x) const = 0;virtual double getLength(double x1, double x2) const = 0;virtual void intersect(Seg *r) const = 0;virtual void intersect(const Segment &v) const = 0;virtual void intersect(const Circle &v) const = 0;bool contains(double x) const { return x>=getLeft() && x<=getRight(); }virtual void acceptPrint(ostream &os) const = 0;};ostream & operator <<(ostream &os, const Seg &v){v.acceptPrint(os);return os;}Point intersectRet[4];int tIntersectRet;class Segment : public Seg {public:Point a, b;Segment &moveLeft(double dis){Point tmp = ((b-a).pOfRotate90().pOfNormal() *= dis);a += tmp;b += tmp;return *this;}virtual double getLeft() const { return a.x; }virtual double getRight() const { return b.x; }virtual double getY(double x) const {return (x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y)/(b.x-a.x)+a.y;}virtual double getLength(double x1, double x2) const {return (x2-x1) * (b-a).length() / (b.x-a.x);}virtual void intersect(Seg *r) const {r->intersect(*this);}virtual void intersect(const Segment &v) const {tIntersectRet = 0;double ang = (b-a).angle();Point c = (v.a-a).pOfRotate(-ang);Point d = (v.b-a).pOfRotate(-ang);// Bug//double di = b.length();double di = (b-a).length();if (!((c.y>0&&d.y<0) || (c.y<0&&d.y>0)))return ;double x = (d.x-c.x) * (-c.y) / (d.y-c.y) + c.x;if (x<0 || x>di)return ;Point ret = Point(x,0).pOfRotate(ang)+a;intersectRet[tIntersectRet++] = ret;}virtual void intersect(const Circle &v) const;virtual void acceptPrint(ostream &os) const {os << a << "-" << b;}};class Circle : public Seg {public:Point c;double r;virtual double getLeft() const { return c.x - r; }virtual double getRight() const { return c.x + r; }virtual double getY(double x) const {double y2 = r * r - (c.x - x) * (c.x - x);if (y2<0) y2 = 0;return c.y + sqrt(y2);}virtual double getLength(double x1, double x2) const {x1 -= c.x; x2 -= c.x;double a1 = Point(x1, sqrt(abs(r*r-x1*x1))).angle(), a2 = Point(x2, sqrt(abs(r*r-x2*x2))).angle();return (a1-a2) * r;}virtual void intersect(Seg *r) const {r->intersect(*this);}virtual void intersect(const Segment &v) const {tIntersectRet = 0;Point a = v.a - c;Point b = v.b - c;double ang = (b-a).angle();Point nA = a.pOfRotate(-ang);Point nB = b.pOfRotate(-ang);double y = nA.y;if (y>r || y<-r)return ;double x = sqrt(r*r - y*y);if (x>=nA.x && x<=nB.x)intersectRet[tIntersectRet++] = Point(x, y).pOfRotate(ang) + c;if (-x>=nA.x && -x<=nB.x)intersectRet[tIntersectRet++] = Point(-x, y).pOfRotate(ang) + c;}virtual void intersect(const Circle &v) const {tIntersectRet = 0;Point p = v.c - c;double d = p.length();if (d > r + v.r || d==0)return ;double x = (r*r - v.r*v.r + d*d) / (2*d);if (x <= r){double y = sqrt(abs(r*r - x*x));double ang = p.angle();intersectRet[tIntersectRet++] = Point(x,y).pOfRotate(ang) + c;intersectRet[tIntersectRet++] = Point(x,-y).pOfRotate(ang) + c;}}virtual void acceptPrint(ostream &os) const {os << c << "," << r;}};void Segment::intersect(const Circle &v) const {v.intersect(*this);}int n;Point inps[MAXN];vector<Seg *> segs;vector<double> spes;double radius = 1;void input(){scanf("%d%lf", &n, &radius);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){double x, y;scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);inps[i] = Point(x, y);}}void process(){segs.clear();spes.clear();for (int i = 1; i + 1 < n; ++i){Circle *tmp = new Circle;tmp->c = inps[i];tmp->r = radius;segs.push_back(tmp);}for (int i = 0; i + 1 < n; ++i){Segment *tmp = new Segment;tmp->a = inps[i];tmp->b = inps[i+1];tmp->moveLeft(radius);segs.push_back(tmp);}for (int i = 0; i < (int)segs.size(); ++i){spes.push_back(segs[i]->getLeft());spes.push_back(segs[i]->getRight());}for (int i = 0; i < (int)segs.size(); ++i){for (int j = i+1; j < (int)segs.size(); ++j){segs[i]->intersect(segs[j]);if (tIntersectRet > 0){for (int id = 0; id < tIntersectRet; ++id){//cout << *segs[i] << " " << *segs[j] << " : " << intersectRet[id] << endl;spes.push_back(intersectRet[id].x);}}}}sort(spes.begin(), spes.end());double pre = spes[0];const double NONE = 1e30;double preEnd = NONE;double totalLen = 0;for (int i = 1; i < (int)spes.size(); ++i){if (spes[i]-pre < EPS)continue;double cur = (pre+spes[i]) / 2;//cout << "Processing " << cur << " from " << pre << " to " << spes[i] << endl;if (cur>=inps[0].x && cur<=inps[n-1].x){double MY = -NONE;int who;for (int j = 0; j < (int)segs.size(); ++j){if (!segs[j]->contains(cur))continue;double y = segs[j]->getY(cur);if (y > MY){MY = y;who = j;}}if (preEnd != NONE){double LY = segs[who]->getY(pre);//cout << "Drop info " << *segs[who] << " " << "[" << pre << "]" << endl;totalLen += abs(preEnd-LY);//cout << "Pre drop = " << abs(preEnd-LY) << " from " << preEnd << " to " << LY << endl;}double len = segs[who]->getLength(pre, spes[i]);if (len < 0)printf("Error!\n");//cout << "Curlen = " << len << " from " << pre << " to " << spes[i] << endl;totalLen += len;preEnd = segs[who]->getY(spes[i]);}pre = spes[i];}printf("%0.2lf\n", totalLen);for (int i = 0; i < (int)segs.size(); ++i)delete segs[i];segs.clear();}int main(){input();process();return 0;}
C++实现车轮轨迹的更多相关文章
- Unity Standard Assets 简介之 Vehicles
这篇介绍载具资源包Vehicles. 主要包含Aircraft(飞行器)和Car(车辆)两部分,两个文件夹里分别有AircraftGuidelines.txt和CarGuidelines.txt对相关 ...
- MATLAB中绘制质点轨迹动图并保存成GIF
工作需要在MATLAB中绘制质点轨迹并保存成GIF以便展示. 绘制质点轨迹动图可用comet和comet3命令,使用例子如下: t = 0:.01:2*pi;x = cos(2*t).*(cos(t) ...
- SQL Server 游标运用:鼠标轨迹字符串分割
一.本文所涉及的内容(Contents) 本文所涉及的内容(Contents) 背景(Contexts) 游标模板(Cursor Template) 鼠标轨迹字符串分割SQL脚本实现(SQL Code ...
- javascript运动系列第六篇——轨迹和投掷
× 目录 [1]运动轨迹 [2]拖拽轨迹 [3]投掷 前面的话 一般地,不同的运动形式会产生不同的轨迹.但仅凭肉眼去识别运动轨迹,其实并不是很直观.因此,在页面中显示运动轨迹,是一个重要的问题.物体初 ...
- PHP 使用 debug_print_backtrace() 或 debug_backtrace() 打印栈轨迹
<?php /* 使用debug_print_backtrace() 或 debug_backtrace() 打印栈轨迹 */ function fun1() { print "Hel ...
- 物联网应用中实时定位与轨迹回放的解决方案 – Redis的典型运用(转载)
物联网应用中实时定位与轨迹回放的解决方案 – Redis的典型运用(转载) 2015年11月14日| by: nbboy| Category: 系统设计, 缓存设计, 高性能系统 摘要 ...
- 【OpenGL(SharpGL)】支持任意相机可平移缩放的轨迹球实现
[OpenGL(SharpGL)]支持任意相机可平移缩放的轨迹球 (本文PDF版在这里.) 在3D程序中,轨迹球(ArcBall)可以让你只用鼠标来控制模型(旋转),便于观察.在这里(http://w ...
- Java基础-继承-编写一个Java应用程序,设计一个汽车类Vehicle,包含的属性有车轮个数 wheels和车重weight。小车类Car是Vehicle的子类,其中包含的属性有载人数 loader。卡车类Truck是Car类的子类,其中包含的属性有载重量payload。每个 类都有构造方法和输出相关数据的方法。最后,写一个测试类来测试这些类的功 能。
#29.编写一个Java应用程序,设计一个汽车类Vehicle,包含的属性有车轮个数 wheels和车重weight.小车类Car是Vehicle的子类,其中包含的属性有载人数 loader.卡车类T ...
- arcgis android 图上记录gps轨迹
原文 arcgis android 图上记录gps轨迹 public class MainActivity extends Activity { MapView mMapView; Location ...
随机推荐
- flink入门学习
Flink学习笔记 一.简介 1.定义: 针对流数据和批数据的分布式处理引擎.它主要是由 Java 代码实现.. 2.应用场景: 流数据:把所有任务当成流来处理,处理观察和分析连续事件产生的数 ...
- 【跟我一起读 linux 源码 01】boot
计算机启动流程在我的上一个学习计划<自制操作系统>系列中,已经从完全不知道,过渡到了现在的了如指掌了,虽然有些夸张,但整个大体流程已经像过电影一样在我脑海里了,所以在看 linux 源码的 ...
- python --集合set的学习
集合是一个无序的不重复的元素序列,一般我们使用set(value)函数来创建集合. 如下: 定义以及添加元素,以及注意点如下: 再如下:
- leetcode 第184场周赛第一题(数组中的字符串匹配)
一.函数的运用 1,strstr(a,b); 判断b是否为a的子串,如果是,返回从b的开头开始到a的结尾 如“abcdefgh” “de” 返回“defgh”: 如果不是子串,返回NULL: 2,me ...
- Java注解的定义和使用
注解也叫元数据,一种代码级别的说明.是jdk1.5后产生的一个特性,与类.接口.枚举同一个档次,他可以在包.类.字段.方法.局部变量.方法参数等的前面,用来对这些元素进行说明.注释: <!--m ...
- JavaScript和TypeScript的区别和联系
转载自:http://web.jobbole.com/93618/?utm_source=group.jobbole.com&utm_medium=relatedArticles JavaSc ...
- 第三篇:ASR(Automatic Speech Recognition)语音识别
ASR(Automatic Speech Recognition)语音识别: 百度语音--语音识别--python SDK文档: https://ai.baidu.com/docs#/ASR-Onli ...
- SecureCRT VBscript连接指定端口和波特率
crt.Session.Connect "/Serial COM2 /BAUD 38400" 其它可用选项参考: crt.session.connect options https ...
- Java switch case语句
switch case 语句判断一个变量与一系列值中某个值是否相等,每个值称为一个分支. switch case 语句语法格式如下: switch(expression){ case value : ...
- UVALive 3295
题目大意:见刘汝佳<算法竞赛入门经典——训练指南>P173 解题思路: 每一个合法的三角形的三个顶点都不在同一直线上,那么问题其实就是在求所有不全在同一直线上的三点的组合数. 我们可以利用 ...
