机器学习实用案例解析(1) 使用R语言
简介
统计学一直在研究如何从数据中得到可解释的东西,而机器学习则关注如何将数据变成一些实用的东西。对两者做出如下对比更有助于理解“机器学习”这个术语:机器学习研究的内容是教给计算机一些知识,再让计算机利用这些知识完成其他的任务。相比之下,统计学则更倾向于开发一些工具来帮助人类认识世界,以便人类可以更加清晰地思考,从而做出更佳的决策。
在机器学习中,学习指的是采用一些算法来分析数据的基本结构,并且辨别其中的信号和噪声,从而提取出尽可能多的(或者尽可能合理的)信息的过程。在算法发现信号或者说模式之后,其余的所有东西都将被简单判断为噪声。因此,机器学习技术也称为模式识别算法。
观测数据、从中学习、自动化识别过程,这三个概念是机器学习的核心。
R最大的优势是:它是由统计学家们开发的。R最大的劣势是……它是由统计学家们开发的。——Bo Cowgill, Google公司
太过真实,哈哈哈,比如R在矩阵运算方面确实不如MATLAB方便。
R的基本数据类型是向量。在本质上,R语言里的所有的数据都是向量,尽管它们有不同的聚合和组织方式。
警告:正因其有所长,R也有短板——R并不能很好地处理大数据。尽管已有很多人在努力解决,但这仍然是一个严重的问题。然而,对于我们将要探讨的案例研究来说,这不是个问题。我们使用的数据集相对较小,要搭建的系统也都只是原型系统或概念验证模型。这个区别很重要,因为如果你要搭建Google或Facebook那样规模的企业级机器学习系统,选择R并不合适。事实上,像Google或Facebook这些公司通常把R作为“数据沙箱”,用于处理数据以及实验新的机器学习方法。如果某个实验有了成果,那么工程师就会把R中的相关功能用更适合的语言复现出来,比如C语言。
实现加载的两个函数是:library和require。两者之间存在细微差别,在本书中,主要差别是:后者会返回一个布尔值(TRUE或FALSE)来表示是否加载成功。
library(package) and require(package) both load the namespace of the package with name package and attach it on the search list. require is designed for use inside other functions; it returns FALSE and gives a warning (rather than an error as library() does by default) if the package does not exist. Both functions check and update the list of currently attached packages and do not reload a namespace which is already loaded.
> a<-require(tm)
载入需要的程辑包:tm
载入需要的程辑包:NLP
Warning messages:
1: 程辑包‘tm’是用R版本3.5.3 来建造的
2: 程辑包‘NLP’是用R版本3.5.2 来建造的
> a
[1] TRUE
UFO案例
数据读入
# Load libraries and data
library(ggplot2) # We'll use ggplot2 for all of our visualizations
library(plyr) # For data manipulation
library(scales) # We'll need to fix date formats in plots ufo <- read.delim("ufo_awesome.tsv",
sep = "\t",
stringsAsFactors = FALSE,
header = FALSE,
na.strings = "")
- read.delim: Reads a file in table format and creates a data frame from it, with cases corresponding to lines and variables to fields in the file.
Similarly, read.delim is for reading delimited files, defaulting to the TAB character for the delimiter.
在本例中,每一行的数据类型都是strings(字符串),但是所有read.*函数都默认把字符串转换为factor类型,因此,我们需要设置stringsAsFactors=FALSE来防止其转换。此外,这份数据第一行并没有表头,因此还需要把表头的参数设置为FALSE。最后,数据中有许多空元素,我们想把这些空元素设置为R中的特殊值N A,为此,我们显式地定义空字符串为na.string。
视察数据:
# Inspect the data frame
head(ufo)
我们可以赋予每一列更有意义的标签。给数据框每一列赋予有意义的名称很重要。这样一来,不管对自己还是其他人,代码和输出都有更强的可读性。
- names: Functions to get or set the names of an object.
names(ufo) <- c("DateOccurred", "DateReported",
"Location", "ShortDescription",
"Duration", "LongDescription")
无论何时,只要你操作数据框,尤其当数据是从外部数据源读入时,我们都推荐你手工查看一下数据。关于手工查看数据,两个比较好用的函数是head和tail。这两个函数会分别打印出数据框中的前六条和后六条数据记录。或者直接使用view查看全貌。
数据清理
日期清理
good.rows <- ifelse(nchar(ufo$DateOccurred) != 8 |
nchar(ufo$DateReported) != 8,
FALSE,
TRUE)
length(which(!good.rows))
## [1] 688
ufo <- ufo[good.rows, ] # Now we can convert the strings to Date objects and work with them properly
ufo$DateOccurred <- as.Date(ufo$DateOccurred, format = "%Y%m%d")
ufo$DateReported <- as.Date(ufo$DateReported, format = "%Y%m%d")
- ifelse(test, yes, no)
ifelse returns a value with the same shape as test which is filled with elements selected from either yes or no depending on whether the element of test is TRUE or FALSE.
- nchar: nchar takes a character vector as an argument and returns a vector whose elements contain the sizes of the corresponding elements of x.
- nzchar is a fast way to find out if elements of a character vector are non-empty strings.
- as.Date: Functions to convert between character representations and objects of class "Date" representing calendar dates.
地址清理
get.location <- function(l)
{
split.location <- tryCatch(strsplit(l, ",")[[1]],
error = function(e) return(c(NA, NA)))
clean.location <- gsub("^ ","",split.location)
if (length(clean.location) > 2)
{
return(c(NA,NA))
}
else
{
return(clean.location)
}
} # We use 'lapply' to return a list with [City, State] vector as each element
city.state <- lapply(ufo$Location, get.location) # We use 'do.call' to collapse the list to an N-by-2 matrix
location.matrix <- do.call(rbind, city.state)
- lapply: lapply returns a list of the same length as X, each element of which is the result of applying FUN to the corresponding element of X.
分离州名和城市,example:
l <- "Iowa City, IA"
strsplit(l, ",")
## [[1]]
## [1] "Iowa City" " IA"
- strsplit: Split the elements of a character vector x into substrings according to the matches to substring split within them.
split.location <- tryCatch(strsplit(l, ",")[[1]], error = function(e) return(c(NA, NA)))
## [1] "Iowa City" " IA"
- tryCatch: These functions provide a mechanism for handling unusual conditions, including errors and warnings.
#正则表达式匹配替换,去掉开头的空格
clean.location <- gsub("^ ","",split.location)
clean.location
## [1] "Iowa City" "IA"
- do.call: constructs and executes a function call from a name or a function and a list of arguments to be passed to it.
我们会经常把lapply和do.call函数结合起来用于处理数据。
> head(location.matrix)
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "Iowa City" "IA"
[2,] "Milwaukee" "WI"
[3,] "Shelton" "WA"
[4,] "Columbia" "MO"
[5,] "Seattle" "WA"
[6,] "Brunswick County" "ND"
清除非美国数据:
ufo <- transform(ufo,
USCity = location.matrix[, 1],
USState = location.matrix[, 2],
stringsAsFactors = FALSE) ufo$USState <- state.abb[match(ufo$USState, state.abb)] ufo.us <- subset(ufo, !is.na(USState))
- transform: transform is a generic function, which—at least currently—only does anything useful with data frames. transform.default converts its first argument to a data frame if possible and calls transform.data.frame.
- state.abb state.area state.center state.division state.name state.region state.x77: Data sets related to the 50 states of the United States of America.
- subset: Return subsets of vectors, matrices or data frames which meet conditions.
ufo.us <- subset(ufo.us, DateOccurred >= as.Date("1990-01-01"))
new.hist <- ggplot(ufo.us, aes(x = DateOccurred)) +
geom_histogram(aes(fill='white', color='red')) +
scale_fill_manual(values=c('white'='white'), guide="none") +
scale_color_manual(values=c('red'='red'), guide="none") +
scale_x_date(breaks = "50 years")
ggsave(plot = new.hist,
filename = "new_hist.bmp",
height = 6,
width = 8)
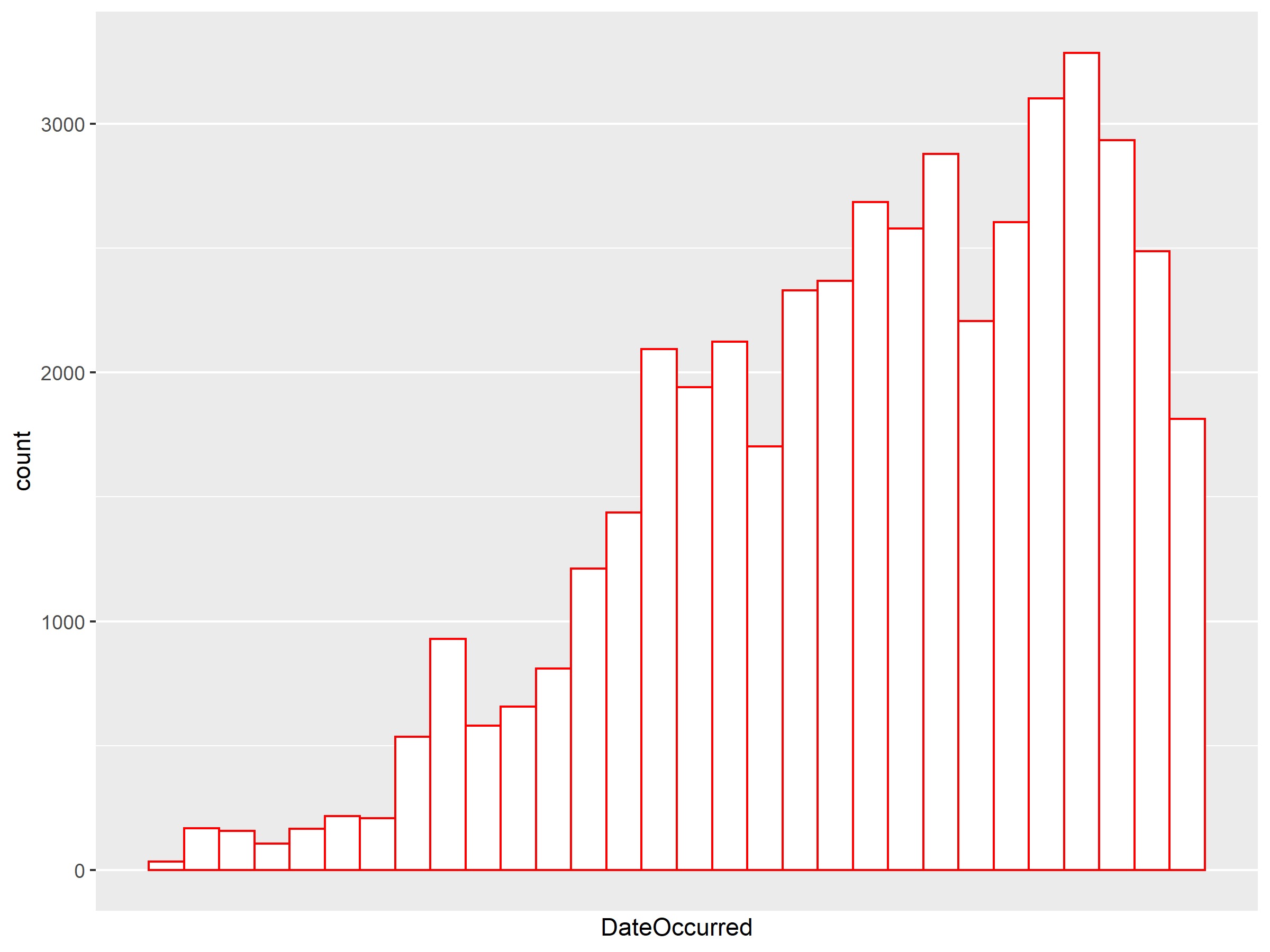
绘图
按照州和月份统计数据
ufo.us$YearMonth <- strftime(ufo.us$DateOccurred, format = "%Y-%m") sightings.counts <- ddply(ufo.us, .(USState,YearMonth), nrow)
- strftime: Functions to convert between character representations and objects of classes "POSIXlt" and "POSIXct" representing calendar dates and times.
- ddply: For each subset of a data frame, apply function then combine results into a data frame. To apply a function for each row, use adply with .margins set to 1.
数据整理
#补全月份
date.range <- seq.Date(from = min(ufo.us$DateOccurred),
to = max(ufo.us$DateOccurred),
by = "month")
date.strings <- strftime(date.range, "%Y-%m")
#将州添加进去
states.dates <- lapply(state.abb, function(s) cbind(s, date.strings))
states.dates <- data.frame(do.call(rbind, states.dates),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
#按照前两列标识进行合并,没有记录则记为NA
all.sightings <- merge(states.dates,
sightings.counts,
by.x = c("s", "date.strings"),
by.y = c("USState", "YearMonth"),
all = TRUE)
#添加列名,NA转0,转化日期格式,州名转换为因子型
names(all.sightings) <- c("State", "YearMonth", "Sightings")
all.sightings$Sightings[is.na(all.sightings$Sightings)] <- 0
all.sightings$YearMonth <- as.Date(rep(date.range, length(state.abb)))
all.sightings$State <- as.factor(all.sightings$State)
- merge: Merge two data frames by common columns or row names, or do other versions of database join operations.
绘图
state.plot <- ggplot(all.sightings, aes(x = YearMonth,y = Sightings)) +
geom_line(aes(color = "darkblue")) +
facet_wrap(~State, nrow = 10, ncol = 5) +
theme_bw() +
scale_color_manual(values = c("darkblue" = "darkblue"), guide = "none") +
scale_x_date(breaks = "5 years", labels = date_format('%Y')) +
xlab("Years") +
ylab("Number of Sightings") +
ggtitle("Number of UFO sightings by Month-Year and U.S. State (1990-2010)") # Save the plot as a PDF
ggsave(plot = state.plot,
filename = "ufo_sightings.bmp",
width = 14,
height = 8.5)

We can alse create a new graph where the number of signtings is normailzed by the state population.
机器学习实用案例解析(1) 使用R语言的更多相关文章
- 机器学习(一) 从一个R语言案例学线性回归
写在前面的话 按照正常的顺序,本文应该先讲一些线性回归的基本概念,比如什么叫线性回归,线性回规的常用解法等.但既然本文名为<从一个R语言案例学会线性回归>,那就更重视如何使用R语言去解决线 ...
- 机器学习算法基础(Python和R语言实现)
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2015/08/common-machine-learning-algorithms/?spm=5176.100239.blo ...
- R语言学习笔记-机器学习1-3章
在折腾完爬虫还有一些感兴趣的内容后,我最近在看用R语言进行简单机器学习的知识,主要参考了<机器学习-实用案例解析>这本书. 这本书是目前市面少有的,纯粹以R语言为基础讲解的机器学习知识,书 ...
- R语言:用简单的文本处理方法优化我们的读书体验
博客总目录:http://www.cnblogs.com/weibaar/p/4507801.html 前言 延续之前的用R语言读琅琊榜小说,继续讲一下利用R语言做一些简单的文本处理.分词的事情.其实 ...
- 主成分分析(PCA)原理及R语言实现
原理: 主成分分析 - stanford 主成分分析法 - 智库 主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis)原理 主成分分析及R语言案例 - 文库 主成分分析法的原理应用及 ...
- R+openNLP︱openNLP的六大可实现功能及其在R语言中的应用
每每以为攀得众山小,可.每每又切实来到起点,大牛们,缓缓脚步来俺笔记葩分享一下吧,please~ --------------------------- openNLP是NLP中比较好的开源工具,R语 ...
- 主成分分析(PCA)原理及R语言实现 | dimension reduction降维
如果你的职业定位是数据分析师/计算生物学家,那么不懂PCA.t-SNE的原理就说不过去了吧.跑通软件没什么了不起的,网上那么多教程,copy一下就会.关键是要懂其数学原理,理解算法的假设,适合解决什么 ...
- R语言使用tryCatch进行简单的错误处理
最近在看<机器学习:实用案例解析>,做邮件过滤器的时候,参考书中的代码读取邮件文件进行分类器训练,在读取过程中会出现下面的错误: seq.default(which(text == & ...
- 大数据时代的精准数据挖掘——使用R语言
老师简介: Gino老师,即将步入不惑之年,早年获得名校数学与应用数学专业学士和统计学专业硕士,有海外学习和工作的经历,近二十年来一直进行着数据分析的理论和实践,数学.统计和计算机功底强悍. 曾在某一 ...
随机推荐
- 陈天奇XGBoost文章解读(未完成)
这个是我下载的原文在看,然后结合一些网上的资料学习,先贴一个网上的资料. 终于有人说清楚了XGBoost算法 XGBoost阅读之Weighted quantile sketch XGBoost论文翻 ...
- Longest Increasing Subsequence (Medium)
第一次做题思路201511092250 1.采用map存储,key为nums[i],value为以nums[i]为结尾的最大递增子序列的长度 2.采用map里面的lower_bounder函数直接找出 ...
- Xpath 入门教程
准备xml 文档 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <bookstore> <book ...
- Hell World:)
第一次弄博客是在2017年春节,自己弄了个域名,租了个小小的VPS,装好了wordpress,挑了一套模板,就这样上线了,可惜wordpress实在不是一个适合写字的地方,插件.主题令人眼花缭乱,慢慢 ...
- linux在线书籍
<Linux就该这么学-刘遄>https://www.linuxprobe.com/
- 2016年3月13日 FXStreet首席分析师:欧元/美元下周走势展望
FX168讯 欧元/美元在经历周初沉闷的走势之后,最终在欧洲央行出台一系列措施促进通货膨胀和经济增长之后怒涨至近一个月最高位.欧洲央行决议公布之前,投资者预期存款利率将下调10至15个基点,并可能进一 ...
- (六)mybatis-spring集成完整版
mybatis-spring集成完整版 一.项目整体 mybatis接口层.mapper层 Service层 Test调用测试 二.自动生成代码-mybatis generator 主要修改: 接口. ...
- Python爬虫-selenium的使用(2)
使用selenium打开chrome浏览器百度进行搜索 12345678910111213141516171819202122232425 from selenium import webdriver ...
- Spring Boot 鉴权之—— JWT 鉴权
第一:什么是JWT鉴权 1. JWT即JSON Web Tokens,是为了在网络应用环境间传递声明而执行的一种基于JSON的开放标准((RFC 7519),他可以用来安全的传递信息,因为传递的信息是 ...
- web端手机方向传感器闲谈
因为工作需要,这段时间接触的手机传感器比较多.总体来说,市场上的传感器表现参差不齐.IPhone在传感器表现方面卓越,而安卓由于什么机型都有,则显得差强人意. 首先还是说说怎么在web端调用手机传感器 ...
