Spring Boot系列——Spring Boot如何启动
Spring Boot启动过程
上篇《Spring Boot系列——5分钟构建一个应用》介绍了如何快速创建一个Spring Boot项目并运行。虽然步骤少流程简单,为开发者省去了很多重复性的配置工作,但是其底层实现并没有这么简单。
这篇,我们就通过入口类TutorialApplication看看Spring Boot是如何启动的。
注解
写过Spring Boot都知道需要有一个入口类,就是本例子中的TutorialApplication,而这个类上面必不可上的需要有一个@SpringBootApplication注解。
点击进入该注解,我们可以发现其是一个复合注解,包括@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan。
/**
* Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more
* {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience
* annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration},
* {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
@SpringBootConfiguration
该注解底层其实就是@Configuration注解。熟悉Spring的发展里程碑就知道这是Java Config的配置形式。
通过该注解修饰,表示该类是一个配置类。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
该注解其实也是一个复合注解。
/**
* Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and
* configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually
* applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined. For example, if you
* have {@code tomcat-embedded.jar} on your classpath you are likely to want a
* {@link TomcatServletWebServerFactory} (unless you have defined your own
* {@link ServletWebServerFactory} bean).
* <p>
* When using {@link SpringBootApplication}, the auto-configuration of the context is
* automatically enabled and adding this annotation has therefore no additional effect.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration tries to be as intelligent as possible and will back-away as you
* define more of your own configuration. You can always manually {@link #exclude()} any
* configuration that you never want to apply (use {@link #excludeName()} if you don't
* have access to them). You can also exclude them via the
* {@code spring.autoconfigure.exclude} property. Auto-configuration is always applied
* after user-defined beans have been registered.
* <p>
* The package of the class that is annotated with {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration},
* usually via {@code @SpringBootApplication}, has specific significance and is often used
* as a 'default'. For example, it will be used when scanning for {@code @Entity} classes.
* It is generally recommended that you place {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} (if you're
* not using {@code @SpringBootApplication}) in a root package so that all sub-packages
* and classes can be searched.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration classes are regular Spring {@link Configuration} beans. They are
* located using the {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} mechanism (keyed against this class).
* Generally auto-configuration beans are {@link Conditional @Conditional} beans (most
* often using {@link ConditionalOnClass @ConditionalOnClass} and
* {@link ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnMissingBean} annotations).
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @see ConditionalOnBean
* @see ConditionalOnMissingBean
* @see ConditionalOnClass
* @see AutoConfigureAfter
* @see SpringBootApplication
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
其实现也是通过类似@Import的方式注入AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,并借助该类将所有符合条件的Configuration注解修饰的配置类加载到Spring Boot容器中。从classpath中搜索所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,将其中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration对应配置项通过反射的形式实例化为标注了@Configuration和javaconfig形式的IOC容器配置类,然后汇总为一个并加载到ioc容器中。
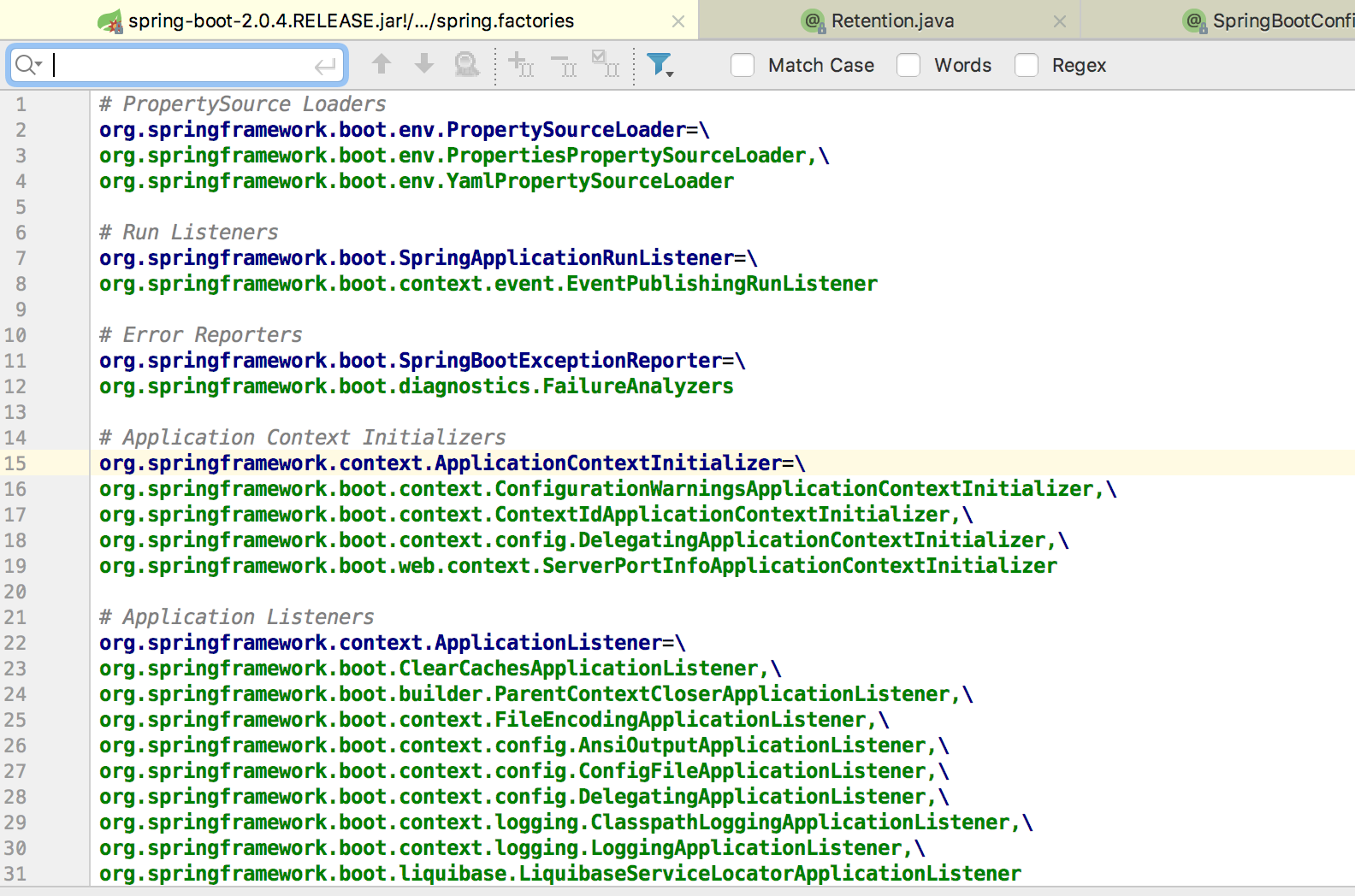
@ComponentScan
这个注解就不需要多介绍了吧,其作用自动扫描加载符合条件的bean。
SpringApplication
从项目的入口第一个碰到的就是SpringApplication类。
@SpringBootApplication
public class TutorialApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TutorialApplication.class, args);
}
}
进入该类的静态方法run,可以看到其在构造SpringApplication对象
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
进入SpringApplication构造方法,可以看到
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
主要做了如下几件事:
- 加载Source,这里只有只有Application
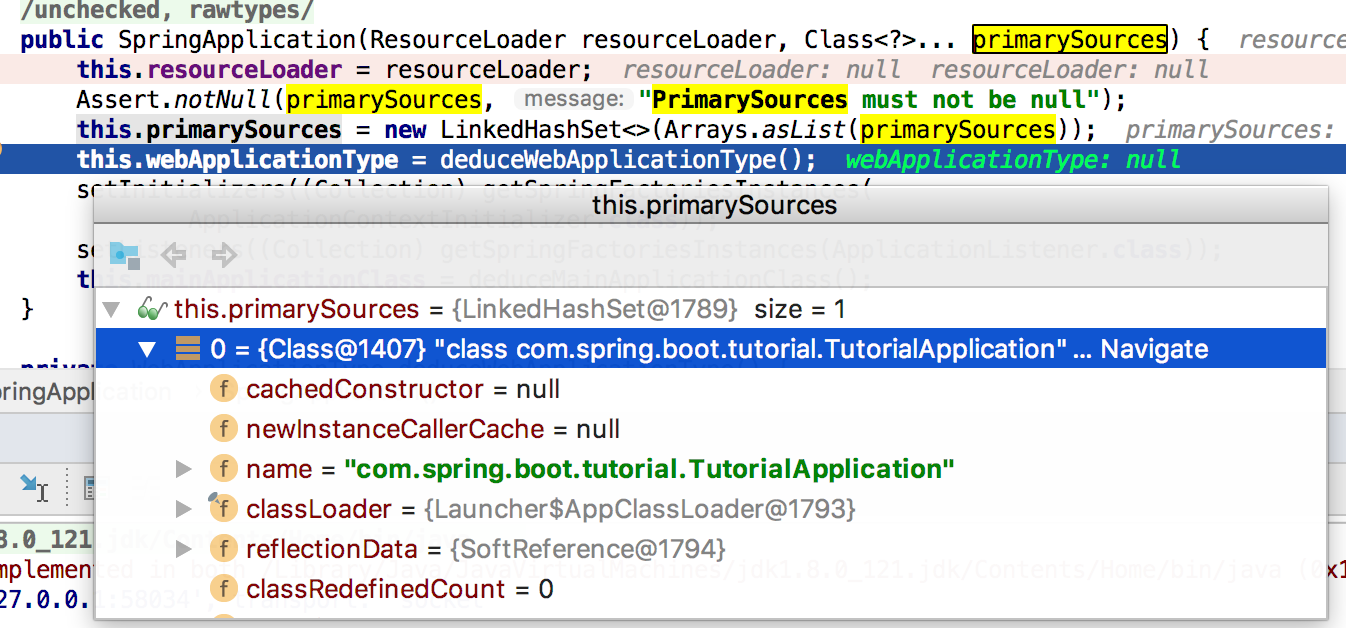
推断WebApplicationType,该枚举有三种类型NONE、SERVLET、REACTIVE。
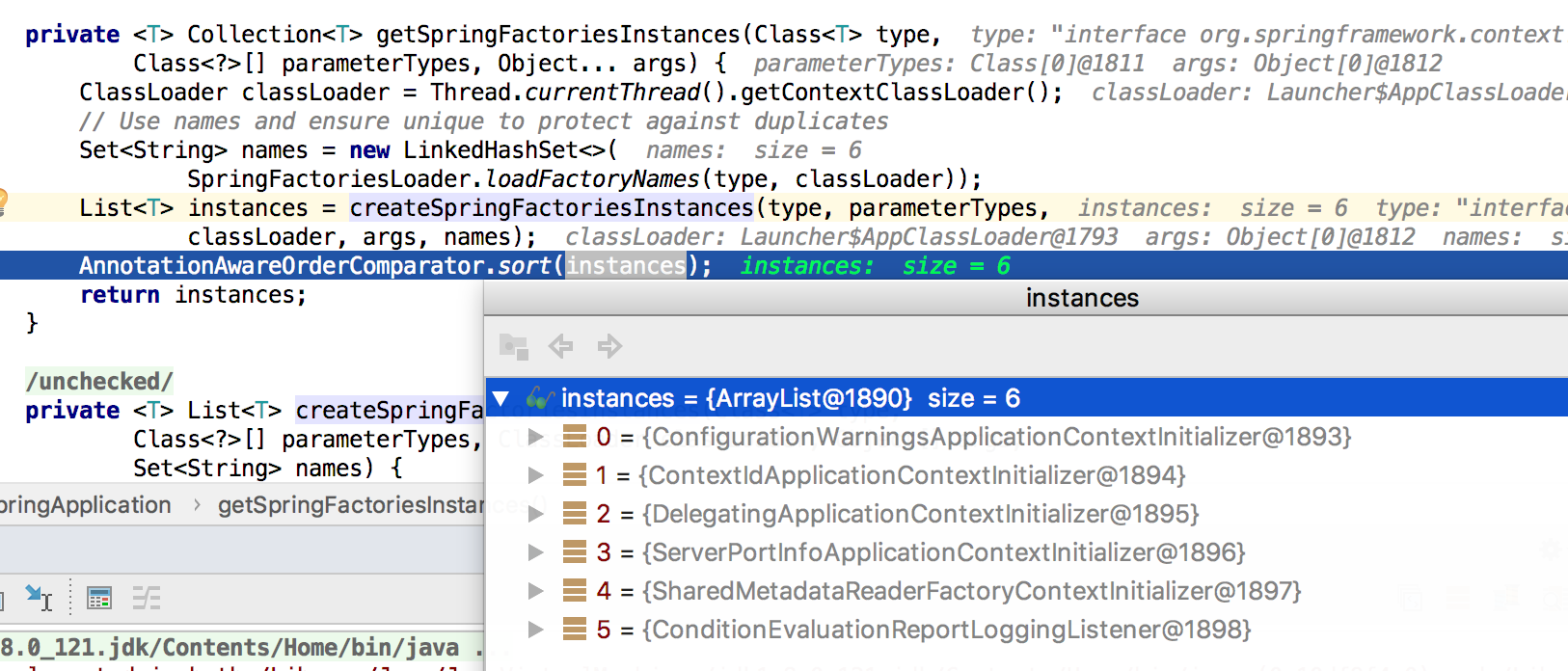
设置初始化器变量setInitializers,初始化后得到6个初始化变量,这些类在上面提到的spring.factories中可以找到
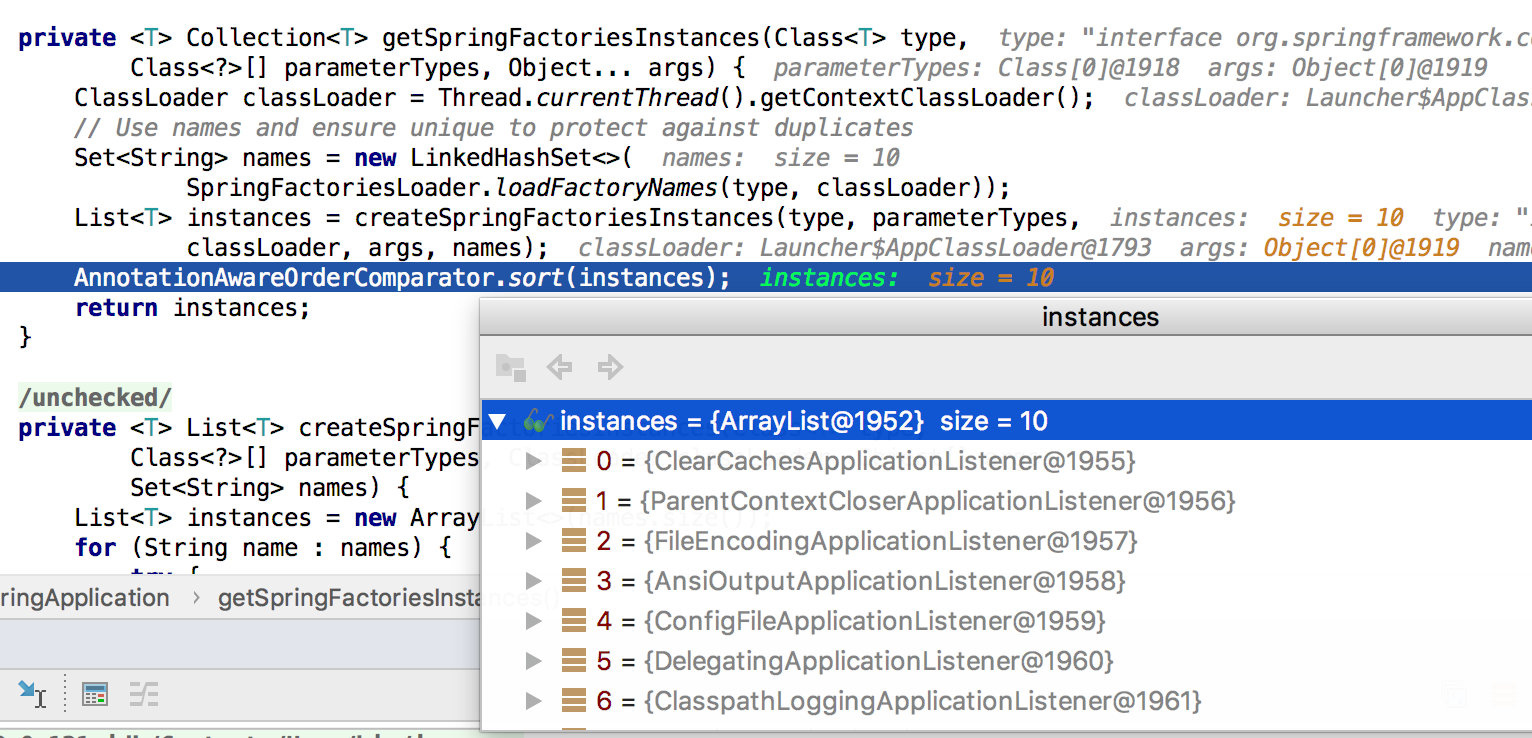
- 设置监听器,与上面setInitializers实现类似,最终得到如下10个listeners
- 最后推断带有main函数的所在类,即入口类,这里就是TutorialApplication
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
run方法
看完SpringApplication是如何初始化后,我们来看下这个后面的run方法具体做了哪些事。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
StopWatch,这是一个spring-core中的工具类,用来给程序运行计时(对于经常遇到需要计算某方法或接口耗时的场景,这个比System.currentTimeMillis好用)
configureHeadlessProperty配置,设置系统属性 java.awt.headless,这里设置为 true,表示运行在服务器端,在没有显示器和鼠标键盘的模式下工作,模拟输入输出设备功能。
遍历listeners并启动
封装入参args为AppliationArguments对象
打印banner(就是我们启动时看到的spring标识)
后面就是初始化上下文并加载上下文,具体实现就不进去看了
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!如果您想持续关注我的文章,请扫描二维码,关注JackieZheng的微信公众号,我会将我的文章推送给您,并和您一起分享我日常阅读过的优质文章。

Spring Boot系列——Spring Boot如何启动的更多相关文章
- Spring基础系列-Spring事务不生效的问题与循环依赖问题
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/9476550.html 一.提出问题 不知道你是否遇到过这样的情况,在ssm框架中开发we ...
- spring boot系列--spring security (基于数据库)登录和权限控制
先说一下AuthConfig.java Spring Security的主要配置文件之一 AuthConfig 1 @Configuration 2 @EnableWebSecurity 3 publ ...
- Spring Boot 系列教程16-数据国际化
internationalization(i18n) 国际化(internationalization)是设计和制造容易适应不同区域要求的产品的一种方式. 它要求从产品中抽离所有地域语言,国家/地区和 ...
- Spring Boot 系列教程15-页面国际化
internationalization(i18n) 国际化(internationalization)是设计和制造容易适应不同区域要求的产品的一种方式. 它要求从产品中抽离所有地域语言,国家/地区和 ...
- Spring Boot 系列教程7-EasyUI-datagrid
jQueryEasyUI jQuery EasyUI是一组基于jQuery的UI插件集合体,而jQuery EasyUI的目标就是帮助web开发者更轻松的打造出功能丰富并且美观的UI界面.开发者不需要 ...
- spring boot系列01--快速构建spring boot项目
最近的项目用spring boot 框架 借此学习了一下 这里做一下总结记录 非常便利的一个框架 它的优缺点我就不在这背书了 想了解的可以自行度娘谷歌 说一下要写什么吧 其实还真不是很清楚,只是想记录 ...
- Spring Boot系列(一) Spring Boot准备知识
本文是学习 Spring Boot 的一些准备知识. Spring Web MVC Spring Web MVC 的两个Context 如下图所示, 基于 Servlet 的 Spring Web M ...
- Spring Boot系列——如何集成Log4j2
上篇<Spring Boot系列--日志配置>介绍了Spring Boot如何进行日志配置,日志系统用的是Spring Boot默认的LogBack. 事实上,除了使用默认的LogBack ...
- Spring Boot系列(三):Spring Boot整合Mybatis源码解析
一.Mybatis回顾 1.MyBatis介绍 Mybatis是一个半ORM框架,它使用简单的 XML 或注解用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJOs(普通的Java 对象)映射成数据库中的记 ...
随机推荐
- openstack学习-创建一台云主机(七)
一.创建基础环境 1.检查网络是否正常 [root@linux-node1 ~]# openstack network agent list +---------------------------- ...
- python常用内建模块--collections
1.namedtuple #namedtuple是一个函数,它用来创建一个自定义的tuple对象,并且规定了tuple元素的个数,并可以用属性而不是索引来引用tuple的某个元素.#这样一来,我们用n ...
- Codeforces Round #310 (Div. 2)
Problem A: 题目大意:给你一个由0,1组成的字符串,如果有相邻的0和1要消去,问你最后还剩几个字符. 写的时候不想看题意直接看样例,结果我以为是1在前0在后才行,交上去错了..后来仔细 看了 ...
- MSF《构建之法》阅读笔记5
第七章 MSF MSF是一种软件开发方法,MSF原则包括1推动信息共享和沟通,2为共同的远景而工作,3充分授权和信任,4各司其职,对项目共同负责,5交付增量的价值,6保持敏捷,预期和适应变化,7投资质 ...
- Queuing HDU2604
一道递推题目 得到递推关系为 f[n]=f[n-1]+f[n-3]+f[n-4]; 用普通的枚举算法会超时 所以要用矩阵快速幂来加速 转化为矩阵即为: +1 0 1 1 F(N-1) F ...
- Tr A HDU1575
矩阵基本算法 #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int n; struct matrix { int m[15][15]; }ans,base; ...
- format 用法及对齐
空格填充: 元素填充(这里是2):
- Codeforces 862B (二分图染色)
<题目链接> 题目大意: 给出一个有n个点的二分图和n-1条边,问现在最多可以添加多少条边使得这个图中不存在自环,重边,并且此图还是一个二分图. 解题分析: 此题不难想到,假设二分图点集数 ...
- Flutter中打造多行列列表GridView组件的使用
GridView组件.一个可滚动的二维空间数组. 在使用无限加载滚动列表的时候,最先使用的还是ListView组件.但若是要一行显示2列或者更多列的滚动列表,GridView组件更为方便.如下 在向服 ...
- sass和less
一.相同点 sass和less具有变量.作用域.混合.嵌套.继承.运算符.颜色函数.导入和注释等基本特性,而且以“变量”.“混合”.“嵌套”.“继承”和“颜色函数”为五大基本特性. sass和less ...
