3451: Tyvj1953 Normal 点分治 FFT
国际惯例的题面: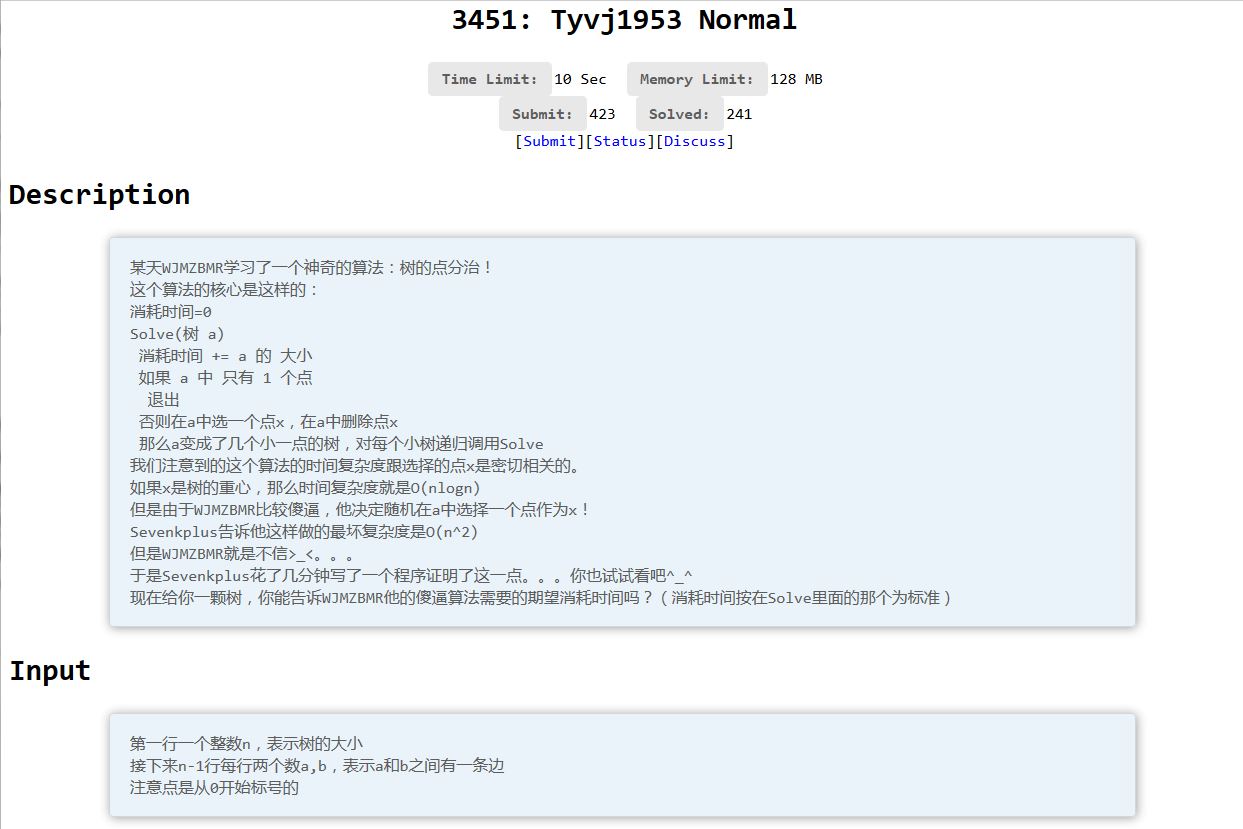
代价理解为重心和每个点这个点对的代价。根据期望的线性性,我们枚举每个点,计算会产生的ij点对的代价即可。
那么,i到j的链上,i必须是第一个被选择的点。
对于i来说,就是1/dis(i,j)。
所以答案就是sigma(i,j) 1/(dis(i,j)+1)。
然而这样计算是n^2的,考虑优化。
如果我们能计算出边长为某个数值的边的数量的话,是不是就能计算答案呢?
统计路径的题,一眼点分治。
考虑怎样计算,我们能dfs出每个子树中距离分治重心为x的点有多少个,然后我们枚举两个点让他们取去组成路径即可。
这显然是个卷积,FFT优化。我们补集转化,先计算全部方案,再减去本身对本身(两个点来自相同子树)的方案。
为什么这样算复杂度正确?因为当当前分治层数一定时,所有子树的最深点的深度总和是O(n)的,并且那个log还会更小。这样分析的话发现复杂度是O(nlog^2n)。
正常的二元关系计算方式是前缀和和当前的卷积贡献,为什么这次不能这样呢?
给你一棵扫把形的树,一半的点形成一条链,显然你会选择扫把的重心(一边是一堆叶子,一边是链)当做重心。
然后你发现链的那边长度为n/2,如果你对每个叶子都和链做一次卷积的话,恭喜你卡成n^2logn,不如暴力......
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
const int maxn=;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double pi = acos(-1.0); int tim[maxn]; namespace FFT {
struct Complex {
double r,i;
friend Complex operator + (const Complex &a,const Complex &b) { return (Complex){a.r+b.r,a.i+b.i}; }
friend Complex operator - (const Complex &a,const Complex &b) { return (Complex){a.r-b.r,a.i-b.i}; }
friend Complex operator * (const Complex &a,const Complex &b) { return (Complex){a.r*b.r-a.i*b.i,a.r*b.i+a.i*b.r}; }
}cp[maxn];
inline void FFT(Complex* dst,int n,int tpe) {
for(int i=,j=;i<n;i++) {
if( i < j ) std::swap(dst[i],dst[j]);
for(int t=n>>;(j^=t)<t;t>>=) ;
}
for(int len=;len<=n;len<<=) {
const int h = len >> ;
const Complex per = (Complex){cos(pi*tpe/h),sin(pi*tpe/h)};
for(int st=;st<n;st+=len) {
Complex w = (Complex){1.0,0.0};
for(int pos=;pos<h;pos++) {
const Complex u = dst[st+pos] , v = dst[st+pos+h] * w;
dst[st+pos] = u + v , dst[st+pos+h] = u - v , w = w * per;
}
}
}
if( !~tpe ) for(int i=;i<n;i++) dst[i].r /= n;
}
inline void mul(int* dst,int n) {
int len = ;
while( len <= ( n << ) ) len <<= ;
for(int i=;i<len;i++) cp[i] = (Complex){(double)dst[i],0.0};
FFT(cp,len,);
for(int i=;i<len;i++) cp[i] = cp[i] * cp[i];
FFT(cp,len,-);
for(int i=;i<len;i++) dst[i] = (int)(cp[i].r+0.5);
}
} namespace Tree {
int s[maxn],t[maxn<<],nxt[maxn<<];
int siz[maxn],mxs[maxn],ban[maxn];
int su[maxn],tp[maxn]; inline void addedge(int from,int to) {
static int cnt = ;
t[++cnt] = to , nxt[cnt] = s[from] , s[from] = cnt;
}
inline void findroot(int pos,int fa,const int &fs,int &rt) {
siz[pos] = , mxs[pos] = ;
for(int at=s[pos];at;at=nxt[at]) if( t[at] != fa && !ban[t[at]] ) findroot(t[at],pos,fs,rt) , siz[pos] += siz[t[at]] , mxs[pos] = std::max( mxs[pos] , siz[t[at]] );
if( ( mxs[pos] = std::max( mxs[pos] , fs - siz[pos]) ) <= mxs[rt] ) rt = pos;
}
inline void dfs(int pos,int fa,int dep,int &mxd) {
mxd = std::max( mxd , dep ) , ++tp[dep];
for(int at=s[pos];at;at=nxt[at]) if( t[at] != fa && !ban[t[at]] ) dfs(t[at],pos,dep+,mxd);
}
inline void solve(int pos,int fs) {
int root = , mxd = , ths ;
*mxs = inf, findroot(pos,-,fs,root) , ban[root] = ;
for(int at=s[root];at;at=nxt[at]) if( !ban[t[at]]) {
ths = , dfs(t[at],root,,ths) , mxd = std::max( mxd , ths );
for(int i=;i<=ths;i++) su[i] += tp[i];
FFT::mul(tp,ths);
for(int i=;i<=ths<<;i++) tim[i] -= tp[i];
memset(tp,,sizeof(int)*(ths<<|));
}
++*su , FFT::mul(su,mxd);
for(int i=;i<=mxd<<;i++) tim[i] += su[i];
memset(su,,sizeof(int)*(mxd<<|));
for(int at=s[root];at;at=nxt[at]) if( !ban[t[at]] ) solve(t[at],siz[t[at]]<siz[root]?siz[t[at]]:fs-siz[root]);
}
} int main() {
static int n;
static long double ans;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=,a,b;i<n;i++) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b) , ++a , ++b , Tree::addedge(a,b) , Tree::addedge(b,a);
Tree::solve(,n) , ans = n;
for(int i=;i<=n<<;i++) ans += (long double) tim[i] / ( i + );
printf("%0.4Lf\n",ans);
return ;
}
ここでこのまま
即使在这里就这样
僕が消えてしまっても 誰も知らずに
我消失不见了 谁也不会知道吧
明日が来るのだろう
明天依然会来临吧
わずか 世界のひとかけらに過ぎない
我仅仅是 这个世界的微小碎屑
ひとりを夜が包む
夜晚怀抱孤独的身影
3451: Tyvj1953 Normal 点分治 FFT的更多相关文章
- BZOJ 3451: Tyvj1953 Normal 点分治+FFT
根据期望的线性性,我们算出每个点期望被计算次数,然后进行累加. 考虑点 $x$ 对点 $y$ 产生了贡献,那么说明 $(x,y)$ 之间的点中 $x$ 是第一个被删除的. 这个期望就是 $\frac{ ...
- 【BZOJ3451】Tyvj1953 Normal 点分治+FFT+期望
[BZOJ3451]Tyvj1953 Normal Description 某天WJMZBMR学习了一个神奇的算法:树的点分治!这个算法的核心是这样的:消耗时间=0Solve(树 a) 消耗时间 += ...
- 【BZOJ3451】Tyvj1953 Normal - 点分治+FFT
题目来源:NOI2019模拟测试赛(七) 非原题面,题意有略微区别 题意: 吐槽: 心态崩了. 好不容易场上想出一题正解,写了三个小时结果写了个假的点分治,卡成$O(n^2)$ 我退役吧. 题解: 原 ...
- [BZOJ3451][Tyvj1953]Normal(点分治+FFT)
https://www.cnblogs.com/GXZlegend/p/8611948.html #include<cmath> #include<cstdio> #inclu ...
- bzoj 3451: Tyvj1953 Normal [fft 点分治 期望]
3451: Tyvj1953 Normal 题意: N 个点的树,点分治时等概率地随机选点,代价为当前连通块的顶点数量,求代价的期望值 百年难遇的点分治一遍AC!!! 今天又去翻了一下<具体数学 ...
- [BZOJ3451]Normal(点分治+FFT)
[BZOJ3451]Normal(点分治+FFT) 题面 给你一棵 n个点的树,对这棵树进行随机点分治,每次随机一个点作为分治中心.定义消耗时间为每层分治的子树大小之和,求消耗时间的期望. 分析 根据 ...
- BZOJ3451 Tyvj1953 Normal 点分治 多项式 FFT
原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/BZOJ3451.html 题目传送门 - BZOJ3451 题意 给定一棵有 $n$ 个节点的树,在树上随机点分 ...
- BZOJ3451: Tyvj1953 Normal
题解: 好神的一道题.蒟蒻只能膜拜题解. 考虑a对b的贡献,如果a是a-b路径上第一个删除的点,那么给b贡献1. 所以转化之后就是求sigma(1/dist(i,j)),orz!!! 如果不是分母的话 ...
- 【bzoj3451】Tyvj1953 Normal 期望+树的点分治+FFT
题目描述 给你一棵 $n$ 个点的树,对这棵树进行随机点分治,每次随机一个点作为分治中心.定义消耗时间为每层分治的子树大小之和,求消耗时间的期望. 输入 第一行一个整数n,表示树的大小接下来n-1行每 ...
随机推荐
- 矩阵的SVD分解
转自 http://blog.csdn.net/zhongkejingwang/article/details/43053513(实在受不了CSDN的广告) 在网上看到有很多文章介绍SVD的,讲的也都 ...
- K-means聚类算法原理和C++实现
给定训练集$\{x^{(1)},...,x^{(m)}\}$,想把这些样本分成不同的子集,即聚类,$x^{(i)}\in\mathbb{R^{n}}$,但是这是个无标签数据集,也就是说我们再聚类的时候 ...
- 命令行command line 使用 http proxy的设置方法 Setting Up HTTP Proxy in Terminal
Step 1: Install Shadowsocks Client Shadowsocks is an open-source proxy project to help people visit ...
- 利用grub从ubuntu找回windows启动项
在 /boot/grub/grub.cfg 中添加: menuentry "Windows 10" --class windows --class os { insmod ntfs ...
- genstr.py
#!/usr/bin/python #-*- coding:utf-8 –*- import os import sys import re import shutil import xlrd imp ...
- 『转载』hadoop 1.X到2.X的变化
表1新旧hadoop脚本/变量/位置变化表 改变项 原框架中 新框架中(Yarn) 备注 配置文件位置 ${hadoop_home_dir}/conf ${hadoop_home_dir}/etc/h ...
- as 插件GsonFormat用法(json字符串快速生成javabean)
GsonFormat 主要用于使用Gson库将JSONObject格式的String 解析成实体,该插件可以加快开发进度,使用非常方便,效率高. 插件地址:https://plugins.jetbra ...
- 红包外挂史及AccessibilityService分析与防御
最近在做一个有趣的外挂的小玩意,前提我们要了解一个重要的类AccessibilityService 转载请注明出处:https://lizhaoxuan.github.io 前言 提起Accessib ...
- TCP/IP、Http大纲
TPC/IP协议是传输层协议,主要解决数据如何在网络中传输,而HTTP是应用层协议,主要解决如何包装数据.关于TCP/IP和HTTP协议的关系,网络有一段比较容易理解的介绍:“我们在传输数据时,可以只 ...
- selenium自动化测试多条数据选择第一条
如果我们测试时在一个页面中存在多条数据元素名称一致但是我们要选择第一条? 示意图: 方法一 driver.find_element_by_css_selector('.article-list/div ...
