python数据结构之图论
本篇学习笔记内容为图的各项性质、图的表示方法、图ADT的python实现
图(Graph)
是数据结构和算法学中最强大的框架之一(或许没有之一)。图几乎可以用来表现所有类型的结构或系统,从交通网络到通信网络,从下棋游戏到最优流程,从任务分配到人际交互网络,图都有广阔的用武之地。
我们会把图视为一种由“顶点”组成的抽象网络,网络中的各顶点可以通过“边”实现彼此的连接,表示两顶点有关联。我们要知道最基础最基本的2个概念,顶点(vertex)和边(edge)。
G=(V,E)来表示图。经常用邻接矩阵或者邻接表来描述一副图。首先是链表、树与图的对比图:
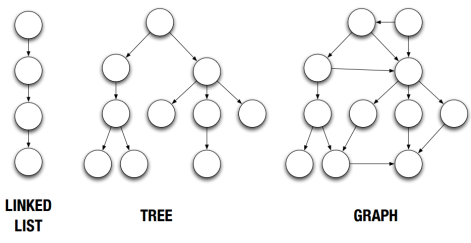
圆为顶点、线为边
图的术语

图 G 是顶点V 和边 E的集合
两个顶点之间:边
如果顶点 x 和 y 共享边,则它们相邻,或者它们是相邻的
无向图 :无向图中的一个边可以在任一方向上遍历
路径::通过边连接的顶点序列
周期:第一个和最后一个顶点相同的路径
入度::顶点的度数V是以V为端点的边数
出度: 顶点的出度v是以v为起点的边的数量
度:顶点的度数是其入度和出度的总和
图的ADT
数据成员 :
顶点 (vertex)
边缘 (edge)
操作 :
有多少顶点?
有多少个边缘?
添加一个新的顶点
添加一个新的边缘
获取所有邻居? (进出)
U,V连接吗?
反转所有边缘?
获取2跳邻居
图表示法:邻接矩阵

class Vertex:
def __init__(self, node):
self.id = node
# Mark all nodes unvisited
self.visited = False def addNeighbor(self, neighbor, G):
G.addEdge(self.id, neighbor) def getConnections(self, G):
return G.adjMatrix[self.id] def getVertexID(self):
return self.id def setVertexID(self, id):
self.id = id def setVisited(self):
self.visited = True def __str__(self):
return str(self.id) class Graph:
def __init__(self, numVertices=10, directed=False):
self.adjMatrix = [[None] * numVertices for _ in range(numVertices)]
self.numVertices = numVertices
self.vertices = []
self.directed = directed
for i in range(0, numVertices):
newVertex = Vertex(i)
self.vertices.append(newVertex) def addVertex(self, vtx, id): #增加点,这个function没有扩展功能
if 0 <= vtx < self.numVertices:
self.vertices[vtx].setVertexID(id) def getVertex(self, n):
for vertxin in range(0, self.numVertices):
if n == self.vertices[vertxin].getVertexID():
return vertxin
return None def addEdge(self, frm, to, cost=0): #返回全部连线/航线
#print("from",frm, self.getVertex(frm))
#print("to",to, self.getVertex(to))
if self.getVertex(frm) is not None and self.getVertex(to) is not None:
self.adjMatrix[self.getVertex(frm)][self.getVertex(to)] = cost
if not self.directed:
# For directed graph do not add this
self.adjMatrix[self.getVertex(to)][self.getVertex(frm)] = cost def getVertices(self):
vertices = []
for vertxin in range(0, self.numVertices):
vertices.append(self.vertices[vertxin].getVertexID())
return vertices def printMatrix(self):
for u in range(0, self.numVertices):
row = []
for v in range(0, self.numVertices):
row.append(str(self.adjMatrix[u][v]) if self.adjMatrix[u][v] is not None else '/')
print(row) def getEdges(self):
edges = []
for v in range(0, self.numVertices):
for u in range(0, self.numVertices):
if self.adjMatrix[u][v] is not None:
vid = self.vertices[v].getVertexID()
wid = self.vertices[u].getVertexID()
edges.append((vid, wid, self.adjMatrix[u][v]))
return edges def getNeighbors(self, n):
neighbors = []
for vertxin in range(0, self.numVertices):
if n == self.vertices[vertxin].getVertexID():
for neighbor in range(0, self.numVertices):
if (self.adjMatrix[vertxin][neighbor] is not None):
neighbors.append(self.vertices[neighbor].getVertexID())
return neighbors def isConnected(self, u, v):
uidx = self.getVertex(u)
vidx = self.getVertex(v)
return self.adjMatrix[uidx][vidx] is not None def get2Hops(self, u): #转一次机可以到达哪里
neighbors = self.getNeighbors(u)
print(neighbors)
hopset = set()
for v in neighbors:
hops = self.getNeighbors(v)
hopset |= set(hops)
return list(hopset)
图表示法:邻接表
用邻接矩阵来表示,每一行表示一个节点与其他所有节点是否相连,但对于邻接表来说,一行只代表和他相连的节点:
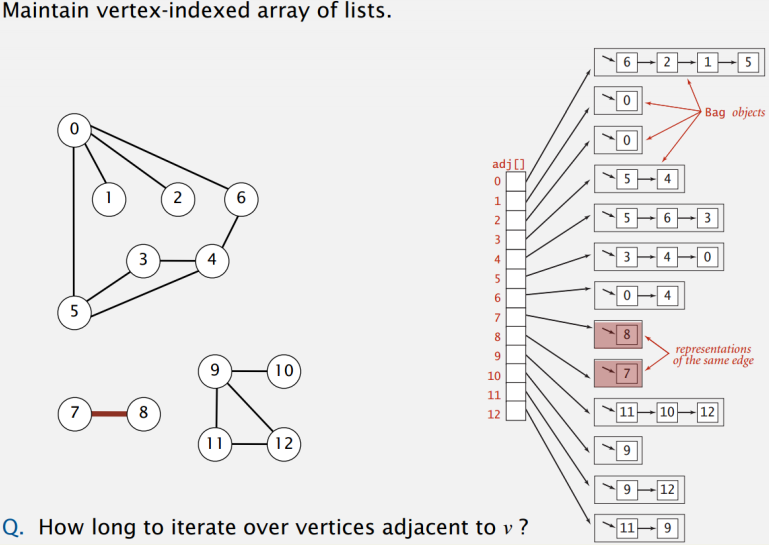
可见邻接表在空间上是更省资源的。
邻接表适合表示稀疏图,邻接矩阵适合表示稠密图。
import sys
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, node):
self.id = node
self.adjacent = {}
#为所有节点设置距离无穷大
self.distance = sys.maxsize
# 标记未访问的所有节点
self.visited = False
# Predecessor
self.previous = None def addNeighbor(self, neighbor, weight=0):
self.adjacent[neighbor] = weight # returns a list
def getConnections(self): # neighbor keys
return self.adjacent.keys() def getVertexID(self):
return self.id def getWeight(self, neighbor):
return self.adjacent[neighbor] def setDistance(self, dist):
self.distance = dist def getDistance(self):
return self.distance def setPrevious(self, prev):
self.previous = prev def setVisited(self):
self.visited = True def __str__(self):
return str(self.id) + ' adjacent: ' + str([x.id for x in self.adjacent]) def __lt__(self, other):
return self.distance < other.distance and self.id < other.id class Graph:
def __init__(self, directed=False):
# key is string, vertex id
# value is Vertex
self.vertDictionary = {}
self.numVertices = 0
self.directed = directed def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.vertDictionary.values()) def isDirected(self):
return self.directed def vectexCount(self):
return self.numVertices def addVertex(self, node):
self.numVertices = self.numVertices + 1
newVertex = Vertex(node)
self.vertDictionary[node] = newVertex
return newVertex def getVertex(self, n):
if n in self.vertDictionary:
return self.vertDictionary[n]
else:
return None def addEdge(self, frm, to, cost=0):
if frm not in self.vertDictionary:
self.addVertex(frm)
if to not in self.vertDictionary:
self.addVertex(to) self.vertDictionary[frm].addNeighbor(self.vertDictionary[to], cost)
if not self.directed:
# For directed graph do not add this
self.vertDictionary[to].addNeighbor(self.vertDictionary[frm], cost) def getVertices(self):
return self.vertDictionary.keys() def setPrevious(self, current):
self.previous = current def getPrevious(self, current):
return self.previous def getEdges(self):
edges = []
for key, currentVert in self.vertDictionary.items():
for nbr in currentVert.getConnections():
currentVertID = currentVert.getVertexID()
nbrID = nbr.getVertexID()
edges.append((currentVertID, nbrID, currentVert.getWeight(nbr))) # tuple
return edges def getNeighbors(self, v):
vertex = self.vertDictionary[v]
return vertex.getConnections()
学习资料参考:图论算法初步、python算法图论
python数据结构之图论的更多相关文章
- python数据结构与算法
最近忙着准备各种笔试的东西,主要看什么数据结构啊,算法啦,balahbalah啊,以前一直就没看过这些,就挑了本简单的<啊哈算法>入门,不过里面的数据结构和算法都是用C语言写的,而自己对p ...
- python数据结构与算法——链表
具体的数据结构可以参考下面的这两篇博客: python 数据结构之单链表的实现: http://www.cnblogs.com/yupeng/p/3413763.html python 数据结构之双向 ...
- python数据结构之图的实现
python数据结构之图的实现,官方有一篇文章介绍,http://www.python.org/doc/essays/graphs.html 下面简要的介绍下: 比如有这么一张图: A -> B ...
- Python数据结构与算法--List和Dictionaries
Lists 当实现 list 的数据结构的时候Python 的设计者有很多的选择. 每一个选择都有可能影响着 list 操作执行的快慢. 当然他们也试图优化一些不常见的操作. 但是当权衡的时候,它们还 ...
- Python数据结构与算法--算法分析
在计算机科学中,算法分析(Analysis of algorithm)是分析执行一个给定算法需要消耗的计算资源数量(例如计算时间,存储器使用等)的过程.算法的效率或复杂度在理论上表示为一个函数.其定义 ...
- SDUT 2141 【TEST】数据结构实验图论一:基于邻接矩阵的广度优先搜索遍历
数据结构实验图论一:基于邻接矩阵的广度优先搜索遍历 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536KB Submit Statistic Discuss Problem ...
- Python数据结构与循环语句
# Python数据结构与循环语句: 首先编程是一项技能,类似跑步,期初不必在意细节,能使用起来就行,等学的游刃有余了再回过头来关注细节问题也不迟. 关于买书: 学会python之后,才需要买书 ...
- python数据结构之栈与队列
python数据结构之栈与队列 用list实现堆栈stack 堆栈:后进先出 如何进?用append 如何出?用pop() >>> >>> stack = [3, ...
- python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历)
python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历.中序遍历和后序遍历) 树 树是\(n\)(\(n\ge 0\))个结点的有限集.在任意一棵非空树中,有且只有一个根结点. 二叉树是有限个元素的集合,该集合或 ...
随机推荐
- MySql事务select for update及数据的一致性处理讲解
MySQL中的事务,默认是自动提交的,即autocommit = 1: 但是这样的话,在某些情形中就会出现问题:比如: 如果你想一次性插入了1000条数据,mysql会commit1000次的, 如果 ...
- too many open files
压测遇到这个问题,每次都查,记录一下: 系统分配文件数太少,临时修改方案: ulimit -n 2048 永久配置: vim /etc/security/limits.conf 底部配置: # End ...
- java InputStream和OutputStream
InputStream类型 类 功能 构造器参数 如何使用 ByteArrayInputStream 允许将内存的缓冲区当做InputStreams使用 缓冲区,字节将从中取出 作为一种数据源:将其与 ...
- FilenameFilter总结
一.FilenameFilter介绍 java.io.FilenameFilter是文件名过滤器,用来过滤不符合规格的文件名,并返回合格的文件: 一般地: (1)String[] fs = f.l ...
- fresco xml配置属性不起作用
在xml中配置加载等待图标,不起作用. 正确的如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <Line ...
- React Native 项目整合 CodePush 全然指南
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/y4x5M0nivSrJaY3X92c/article/details/81976844 作者 | 钱 ...
- java导出json格式文件
生成json文件代码: import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.Writer; public class Crea ...
- 获取linux服务进程号
ps -ef | grep "服务名" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}' # ps -ef|grep "被查询的 ...
- adb shell命令行
d: cd D:\software\adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030\sdk\platform-tools ————————> sdk的路径 adb shell s ...
- MapReduce处理HBase出错:XXX.jar is not a valid DFS filename
原因:Hadoop文件系统没有检查路径时没有区分是本地windows系统还是Hadoop集群文件系统 解决: 只需将Map和Reduce的init方法最后一个参数(boolean addDepend ...
