信号量 sem_t 进程同步
sem_t分为有名和无名。有名的sem_t通过sem_open来创建, 而无名的sem_t通过sem_init的初始化。 用有名的sem_t来进程间同步是件很容易的事情,百度上一搜很多想相关的例子。
有名和无名的sem_t主要区别:
1. 效率:有名sem_t是放在文件,无名的sem_t是放在内存。
2.限制:有名的sem_t可以用来同步多线程,任意多进程。而无名的sem_t可以用来同步多线程,以及Fork出来的进程间的同步。
网上想关的例子很多,本文主要是测试一下用无名sem_t进程同步,比如你在使用nginx的时候,nginx会fork出很多works,如果在works间你希望能同步一些操作,那么这个时候就可以用它,注意下面API描述中的红色部分,明确说了需要放到共享内存(shared memory)。
Name
sem_init - initialize an unnamed semaphore
Synopsis #include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
Link with -pthread.
Description sem_init() initializes the unnamed semaphore at the address pointed to by sem. The value argument specifies the initial value for the semaphore.
The pshared argument indicates whether this semaphore is to be shared between the threads of a process, or between processes. If pshared has the value 0, then the semaphore is shared between the threads of a process, and should be located at some address that is visible to all threads (e.g., a global variable, or a variable allocated dynamically on the heap).
If pshared is nonzero, then the semaphore is shared between processes, and should be located in a region of shared memory (see shm_open(3), mmap(2), and shmget(2)). (Since a child created by fork(2) inherits its parent's memory mappings, it can also access the semaphore.) Any process that can access the shared memory region can operate on the semaphore using sem_post(3), sem_wait(3), etc. Initializing a semaphore that has already been initialized results in undefined behavior.
下面是一段简单的测试代码
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h> void *createSharedMemory(size_t size) {
void *addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_ANON | MAP_SHARED, -, );
if (addr == MAP_FAILED) {
return NULL;
}
return addr;
} void freeSharedMemory(void *addr, size_t size)
{
if (munmap(addr, size) == -) {
printf("munmap(%p, %d) failed", addr, (int)size);
}
} int main(int argc, char *argv[] ) { sem_t* mutex_share = createSharedMemory(sizeof(sem_t));
sem_t mutex_not_share;
if (mutex_share == NULL) {
printf("creat share memory error\n");
return ;
}
if( sem_init(mutex_share,,) < || sem_init(&mutex_not_share,,) < ) {
printf("semaphore initilization\n");
return ;
}
if (fork() == ) {
sem_wait(&mutex_not_share);
for(int j = ;j<;j++) {
printf("mutex_not_share child j = %d\n", j);
usleep();
}
sem_post(&mutex_not_share); sem_wait(mutex_share);
for (int i = ;i<;i++) {
printf("mutex_share child i = %d\n", i);
usleep();
}
sem_post(mutex_share); }
else {
sem_wait(&mutex_not_share);
for(int j = ;j<;j++) {
printf("mutex_not_share parent j = %d\n", j);
usleep();
}
sem_post(&mutex_not_share);
sem_wait(mutex_share);
for (int i = ;i<;i++) {
printf("mutex_share parent i = %d\n", i);
usleep();
}
sem_post(mutex_share);
}
freeSharedMemory(mutex_share,sizeof(sem_t));
return ;
}
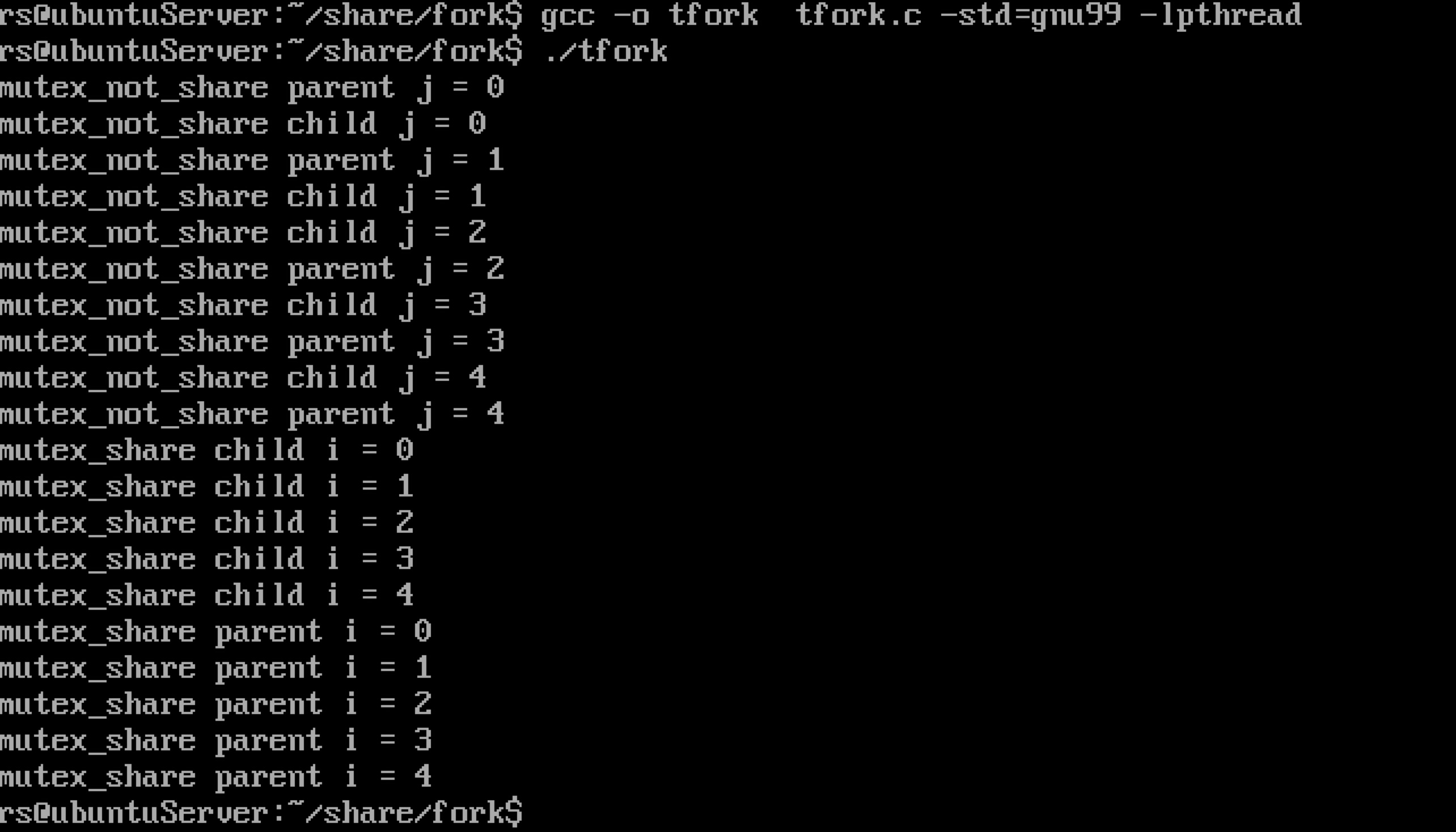
运行结果可以看出,如果没有放到共享内存,就算将pshared设置为1,也起不了作用。
信号量 sem_t 进程同步的更多相关文章
- 信号量进程同步,王明学learn
信号量进程同步 一组并发进程进行互相合作.互相等待,使得各进程按一定的顺序执行的过程称为进程间的同步. 信号量在进程同步时初始值为:0 信号量在进程互斥时初始值为:大于0的 本章节主要使用信号量,使的 ...
- system V信号量和Posix信号量
一.函数上的区别 信号量有两种实现:传统的System V信号量和新的POSIX信号量.它们所提供的函数很容易被区分:对于所有System V信号量函数,在它们的名字里面没有下划线.例如,应该是sem ...
- Linux 多线程信号量同步
PV原子操作 P操作: 如果有可用的资源(信号量值>0),则此操作所在的进程占用一个资源(此时信号量值减1,进入临界区代码); 如果没有可用的资源(信号量值=0),则此操作所在的进程被阻塞直到系 ...
- [转]一个简单的Linux多线程例子 带你洞悉互斥量 信号量 条件变量编程
一个简单的Linux多线程例子 带你洞悉互斥量 信号量 条件变量编程 希望此文能给初学多线程编程的朋友带来帮助,也希望牛人多多指出错误. 另外感谢以下链接的作者给予,给我的学习带来了很大帮助 http ...
- 关于Linux下进程间使用共享内存和信号量通信的时的编译问题
今天在编译一个使用信号量实现进程同步时,出现了库函数不存在的问题.如下图 编译结果实际上是说,没include相应的头文件,或是头文件不存在(即系统不支持该库函数) 但我man shm_open是可以 ...
- 线程间同步之 semaphore(信号量)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuqilin/archive/2011/10/16/2214429.html semaphore 可用于进程间同步也可用于同一个进程间的线程同 ...
- Linux多线程实践(5) --Posix信号量与互斥量解决生产者消费者问题
Posix信号量 Posix 信号量 有名信号量 无名信号量 sem_open sem_init sem_close sem_destroy sem_unlink sem_wait sem_post ...
- linux POSIX 信号量介绍
信号量一.什么是信号量信号量的使用主要是用来保护共享资源,使得资源在一个时刻只有一个进程(线程)使用.多线程可以同时运行多个线程函数完成功能,但是对于共享数据如果不加以锁定,随意改变共享数据的值会发生 ...
- Linux多线程--使用信号量同步线程【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/ljianhui/article/details/10813469 信号量.同步这些名词在进程间通信时就已经说过,在这里它们的意思是相同的,只不过 ...
随机推荐
- ActionScript 3.0数组操作
var arr:Array=new Array();arr=["a","b","c"]; //赋初值,注意这里的即使单个字符赋值使用的是& ...
- maven配置信息查询
如何在pom.xml配置一个jar相关信息(如groupId,artifactId,version),请参考以下网址(在对应的搜索框中输入jar包名): http://mvnrepository.co ...
- STUCTS LABLE ‘S BENEFIT
{LJ?Dragon}[注]Struts标签的三个好处 RELATED LINKS 0.UTF-8 有无BOM的区别 UTF-8 BOM 06. 几款网页数据抓取软件 SOFTWARE_INTRODU ...
- Android使用DOM生成和输出XML格式数据
Android使用DOM生成和输出XML格式数据 本文主要简单解说怎样使用DOM生成和输出XML数据. 1. 生成和输出XML数据 代码及凝视例如以下: try { DocumentBuilderFa ...
- [Angular 2] NgNonBindable
If you want to print someting like {{content}} on the html, using ng-non-bindable directive: <div ...
- PHP安全编程:跨站脚本攻击的防御(转)
跨站脚本攻击是众所周知的攻击方式之一.所有平台上的Web应用都深受其扰,PHP应用也不例外. 所有有输入的应用都面临着风险.Webmail,论坛,留言本,甚至是Blog.事实上,大多数Web应用提供输 ...
- 使用 Java 配置进行 Spring bean 管理--转
概述 众所周知,Spring 框架是控制反转 (IOC) 或依赖性注入 (DI) 模式的推动因素,而这种推动是通过基于容器的配置实现的.过去,Spring 允许开发人员使用基于 XML 的配置,通过利 ...
- checkbox 删除
先创建del.php文件: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http ...
- display:inline、block、inline-block的区别(转)
display:block就是将元素显示为块级元素. block元素的特点是: 总是在新行上开始: 高度,行高以及顶和底边距都可控制: 宽度缺省是它的容器的100%,除非设定一个宽度 <div& ...
- Mysql 中is null 和 =null 的区别
在mysql中,筛选非空的时候经常会用到is not null和!=null,这两种方法单从字面上来看感觉是差不多的,其实如 果去运行一下试试的话差别会很大! 为什么会出现这种情况呢? null 表示 ...
