IOS网络编程:HTTP
IOS网络编程:HTTP
HTTP定义了一种在服务器和客户端之间传递数据的途径。
URL定义了一种唯一标示资源在网络中位置的途径。
REQUESTS 和 RESPONSES: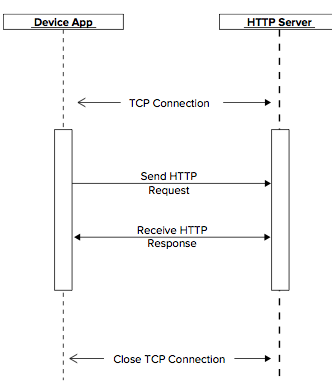
客户端先建立一个TCP连接,然后发送一个请求。服务器受到请求处理后发送一个响应向客户端传递数据。然后客户端可以继续发送请求或者关闭这个TCP连接。
HTTPS:
在TCP连接建立后,发送请求之前,需要建立一个一个SSL会话。
request方法和它们的用途
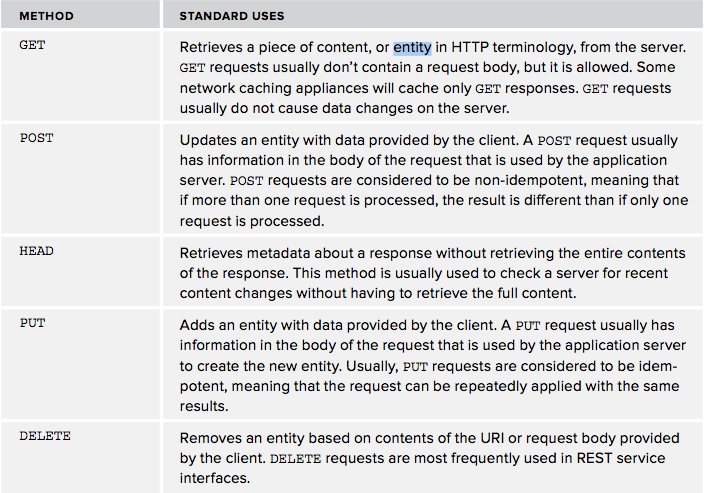
iOS的NSURLRequest和它的子类NSMutableURLRequest提供了建立HTTP请求的方法。
NSURLResponse 和 它的子类NSHTTPURLResponse 处理返回的数据。
URL:
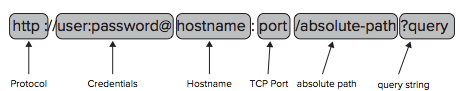
Protocol包括HTTP、FTP和file。
URL编码:
NSString *urlString = @"http://myhost.com?query=This is a question";
NSString *encoded = [urlString stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSURL用来管理URL。
IOS HTTP APIS:
涉及到下面一些类:
NSURL, NSURLRequest, NSURLConnection, 和 NSURLResponse.
1、NSURL
NSURL可以定义本地文件和网络文件
NSURL *url = [NSURL urlWithString:@"http://www.google.com"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
NSURL定义了很多访问器:

if (url.port == nil) {
NSLog(@"Port is nil");
} else {
NSLog(@"Port is not nil");
}

2、NSURLRequest
创建了NSURL后,就可以用NSURLRequest建立请求了:


NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString: @"https://gdata.youtube.com/feeds/api/standardfeeds/top_rated"];
if (url == nil) {
NSLog(@"Invalid URL"); return;
}
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url]; if (request == nil) {
NSLog(@"Invalid Request");
return;
}


NSMutableURLRequest是NSURLRequest 的子类,提供了改变请求的属性的方法:
NSURL *url = [NSURL urlWithString@"http://server.com/postme"];
NSMutableURLRequest *req = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
[req setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];
[req setHTTPBody:[@"Post body" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
如果你要发送一个图片或者视频,那么用需要用NSInputStream,它没有把数据全部加在到内存。
NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];
NSInputStream *inStream = [NSInputStream inputStreamWithFileAtPath:srcFilePath];
[request setHTTPBodyStream:inStream];
[request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];
3、NSURLConnection
提供了初始化、开始、和取消一个连接。
4、NSURLResponse
发送同步请求:


- (NSArray *) doSyncRequest:(NSString *)urlString {
// make the NSURL object from the string
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
// Create the request object with a 30 second timeout and a cache policy to always retrieve the
// feed regardless of cachability.
NSURLRequest *request =
[NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url
cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData
timeoutInterval:30.0];
// Send the request and wait for a response
NSHTTPURLResponse *response;
NSError *error;
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:request
returningResponse:&response
error:&error];
// check for an error
if (error != nil) {
NSLog(@"Error on load = %@", [error localizedDescription]);
return nil;
}
// check the HTTP status
if ([response isKindOfClass:[NSHTTPURLResponse class]]) {
NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) {
return nil;
}
NSLog(@"Headers: %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]);
}
// Parse the data returned into an NSDictionary
NSDictionary *dictionary =
[XMLReader dictionaryForXMLData:data
error:&error];
// Dump the dictionary to the log file
NSLog(@"feed = %@", dictionary);
NSArray *entries =[self getEntriesArray:dictionary];
// return the list if items from the feed.
return entries;
}


Queued Asynchronous Requests:


- (void) doQueuedRequest:(NSString *)urlString delegate:(id)delegate {
// make the NSURL object
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
// create the request object with a no cache policy and a 30 second timeout.
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData timeoutInterval:30.0];
// If the queue doesn't exist, create one.
if (queue == nil) {
queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init];
}
// send the request and specify the code to execute when the request completes or fails.
[NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request
queue:queue
completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response,
NSData *data,
NSError *error) {
if (error != nil) {
NSLog(@"Error on load = %@", [error localizedDescription]);
} else {
// check the HTTP status
if ([response isKindOfClass:[NSHTTPURLResponse class]]) {
NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) {
return;
}
NSLog(@"Headers: %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]);
}
// parse the results and make a dictionary
NSDictionary *dictionary =
[XMLReader dictionaryForXMLData:data
error:&error];
NSLog(@"feed = %@", dictionary);
// get the dictionary entries.
NSArray *entries =[self getEntriesArray:dictionary];
// call the delegate
if ([delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(setVideos:)]) {
[delegate performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setVideos:)
withObject:entries
waitUntilDone:YES];
}
}
}];
}


Asynchronous Requests:


#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#define kDownloadComplete @"downloadComplete"
@class DownloadProgressView;
@interface AsyncDownloader : NSObject <NSURLConnectionDelegate> {
// The number of bytes that need to be downloaded
long long downloadSize;
// the total amount downloaded thus far
long long totalDownloaded;
}
// A reference to the progress view to show the user how things are progressing
@property (assign) DownloadProgressView *progressView;
// The target MP4 file
@property (strong) NSString *targetFile;
// The original URL to download. Due to redirects the actual content may come from another URL
@property (strong) NSString *srcURL;
// The open file to which the content is written
@property (strong) NSFileHandle *outputHandle;
// The name of the temp file to which the content is streamed. This file is moved to the target file when
// the download is complete
@property (strong) NSString *tempFile;
@property (strong) NSURLConnection *conn;
// instructs the class to start the download.
- (void) start;
@end




//
// AsyncDownloader.m
// VideoDownloader
//
// Created by Jack Cox on 4/7/12.
//
// #import "AsyncDownloader.h"
#import "DownloadProgressView.h" @implementation AsyncDownloader @synthesize targetFile;
@synthesize srcURL;
@synthesize outputHandle;
@synthesize tempFile;
@synthesize progressView;
@synthesize conn; - (void) start {
NSLog(@"Starting to download %@", srcURL); // create the URL
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:srcURL]; // Create the request
NSURLRequest *request = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:url]; // create the connection with the target request and this class as the delegate
self.conn =
[NSURLConnection connectionWithRequest:request
delegate:self]; // start the connection
[self.conn start];
} /**
* Creates a UUID to use as the temporary file name during the download
*/
- (NSString *)createUUID
{
CFUUIDRef uuidRef = CFUUIDCreate(NULL);
CFStringRef uuidStringRef = CFUUIDCreateString(NULL, uuidRef);
CFRelease(uuidRef);
NSString *uuid = [NSString stringWithString:(__bridge NSString *)
uuidStringRef];
CFRelease(uuidStringRef);
return uuid;
}
#pragma mark NSURLConnectionDelegate methods
/**
* This delegate method is called when the NSURLConnection gets a 300 series response that indicates
* that the request needs to be redirected. It is implemented here to display any redirects that might
* occur. This method is optional. If omitted the client will follow all redirects.
**/
- (NSURLRequest *)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
willSendRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
redirectResponse:(NSURLResponse *)redirectResponse { // Dump debugging information
NSLog(@"Redirect request for %@ redirecting to %@", srcURL, request.URL);
NSLog(@"All headers = %@",
[(NSHTTPURLResponse*) redirectResponse allHeaderFields]); // Follow the redirect
return request;
} /**
* This delegate method is called when the NSURLConnection connects to the server. It contains the
* NSURLResponse object with the headers returned by the server. This method may be called multiple times.
* Therefore, it is important to reset the data on each call. Do not assume that it is the first call
* of this method.
**/
- (void) connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response {
NSLog(@"Received response from request to url %@", srcURL); NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response;
NSLog(@"All headers = %@", [httpResponse allHeaderFields]); if (httpResponse.statusCode != 200) {// something went wrong, abort the whole thing
// reset the download counts
if (downloadSize != 0L) {
[progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize];
[progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded];
}
[connection cancel];
return;
} NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; // If we have a temp file already, close it and delete it
if (self.tempFile != nil) {
[self.outputHandle closeFile]; NSError *error;
[fm removeItemAtPath:self.tempFile error:&error];
} // remove any pre-existing target file
NSError *error;
[fm removeItemAtPath:targetFile error:&error]; // get the temporary directory name and make a temp file name
NSString *tempDir = NSTemporaryDirectory();
self.tempFile = [tempDir stringByAppendingPathComponent:[self createUUID]];
NSLog(@"Writing content to %@", self.tempFile); // create and open the temporary file
[fm createFileAtPath:self.tempFile contents:nil attributes:nil];
self.outputHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:self.tempFile]; // prime the download progress view
NSString *contentLengthString = [[httpResponse allHeaderFields] objectForKey:@"Content-length"];
// reset the download counts
if (downloadSize != 0L) {
[progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize];
[progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded];
}
downloadSize = [contentLengthString longLongValue];
totalDownloaded = 0L; [progressView addAmountToDownload:downloadSize];
}
/**
* This delegate method is called for each chunk of data received from the server. The chunk size
* is dependent on the network type and the server configuration.
*/
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data {
// figure out how many bytes in this chunk
totalDownloaded+=[data length]; // Uncomment if you want a packet by packet log of the bytes received.
NSLog(@"Received %lld of %lld (%f%%) bytes of data for URL %@",
totalDownloaded,
downloadSize,
((double)totalDownloaded/(double)downloadSize)*100.0,
srcURL); // inform the progress view that data is downloaded
[progressView addAmountDownloaded:[data length]]; // save the bytes received
[self.outputHandle writeData:data];
} /**
* This delegate methodis called if the connection cannot be established to the server.
* The error object will have a description of the error
**/
- (void)connection:(NSURLConnection *)connection
didFailWithError:(NSError *)error {
NSLog(@"Load failed with error %@",
[error localizedDescription]); NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; // If we have a temp file already, close it and delete it
if (self.tempFile != nil) {
[self.outputHandle closeFile]; NSError *error;
[fm removeItemAtPath:self.tempFile error:&error];
} // reset the progress view
if (downloadSize != 0L) {
[progressView addAmountToDownload:-downloadSize];
[progressView addAmountDownloaded:-totalDownloaded];
}
} /**
* This delegate method is called when the data load is complete. The delegate will be released
* following this call
**/
- (void)connectionDidFinishLoading:(NSURLConnection *)connection {
// close the file
[self.outputHandle closeFile]; // Move the file to the target location
NSFileManager *fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSError *error;
[fm moveItemAtPath:self.tempFile
toPath:self.targetFile
error:&error]; // Notify any concerned classes that the download is complete
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]
postNotificationName:kDownloadComplete
object:nil
userInfo:nil];
}
@end
IOS网络编程:HTTP的更多相关文章
- iOS网络编程模型
iOS网络编程层次结构也分为三层: Cocoa层:NSURL,Bonjour,Game Kit,WebKit Core Foundation层:基于 C 的 CFNetwork 和 CFNetServ ...
- IOS网络编程——第三方类库
IOS网络编程——第三方类库 目录 概述 ASIHttpRequest AFNetworking 其他 概述 ASIHttpRequest AFNetworking 其他
- iOS网络编程笔记——Socket编程
一.什么是Socket通信: Socket是网络上的两个程序,通过一个双向的通信连接,实现数据的交换.这个双向连路的一端称为socket.socket通常用来实现客户方和服务方的连接.socket是T ...
- 浅谈iOS网络编程之一入门
计算机网络,基本上可以抽象是端的通信.实际在通讯中会用到不同的设备,不同的硬件中,为了能友好的传输信息,那么建立一套规范就十分必要了.先来了解一些基本概念 了解网络中传输的都是二进制数据流. 2.了 ...
- iOS 网络编程:socket
@import url(http://i.cnblogs.com/Load.ashx?type=style&file=SyntaxHighlighter.css);@import url(/c ...
- iOS 网络编程模式总结
IOS 可以采用三类api 接口进行网络编程,根据抽象层次从低到高分别为socket方式.stream方式.url 方式. 一 .socket 方式 IOS 提供的socket 方式的网络编程接口为C ...
- ios网络编程(入门级别)-- 基础知识
在学习ios的过程中,停留在UI控件很长时间,现在正在逐步的接触当中!!!!!!在这个过程中,小编学到了一些关于网络编程知识,并且有感而发,在此分享一下: 关于网络请求的重要性我想不用多说了吧!!!对 ...
- iOS 网络编程(HTTP协议)
HTTP协议的概念HTTP协议,Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (超文本传输协议)是用于从万维网服务器传送超文本到本地浏览器的传输协议,HTTP是一个应用层协议,由请求和响应 ...
- 从socket开始讲IOS网络编程
home list tags talk user rss Mac&iOS Socket 大纲 一.Socket简介 二.BSD Socket编程准备 1.地址 2.端口 3.网络字节序 4.半 ...
随机推荐
- java读取图片的(尺寸、拍摄日期、标记)等EXIF信息
1.metadata-extractor是 处理图片EXIF信息的开源项目,最新代码及下载地址:https://github.com/drewnoakes/metadata-extractor 2.本 ...
- OBJ解析
OBJ文件是Alias|Wavefront公司为它的一套基于工作站的3D建模和动画软件"Advanced Visualizer"开发的一种标准3D模型文件格式,很适合用于3D软件模 ...
- IOS开发中 RunLoop,RunTime
1.Objective-C中的函数调用 对于C语言,函数调用是由编译器直接转化完成的,在编译时程序就开始查找要执行的函数(C语言函数调用原理).而在OC中,我们将函数调用称为消息发送.在编译时程序不查 ...
- mysqldump 定时任务 执行后备份的文件为空
#!/bin/bash mysql_host="127.0.0.1" mysql_user="root" mysql_passwd="******** ...
- linux调度器系列
http://blog.csdn.net/wudongxu/article/category/791519
- 亿图图示专家v7.7破解版
软件简介 亿图图示专家是一款综合矢量绘制软件,新颖小巧,功能强大,可以很方便的绘制各种专业的流程图.组织结构图.网络拓扑图.思维导图.商业图表.科学设计图等.轻轻松松绘制各种专业流程图,网络图,思维导 ...
- freemarker if..else.. 的使用
FreeMarker是一款模板引擎,今天在做Pad端的时候正好用到,用法非常简单: 在xml配置页面的文件中,直接使用 <#if 1=1> //条件成立要显示的内容 </#if> ...
- JAVA正则忽略大小写
java正则表达式: (?i)abc 表示abc都忽略大小写 a(?i)bc 表示bc忽略大小写 a((?i)b)c 表示只有b忽略大小写 也可以用Pattern.compile(re ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记18:List集合特有的ListIterator迭代器
1. ListIterator(列表迭代器): ListIterator listIterator():List集合特有的迭代器 2. 代码示例: package cn.itcast_04; impo ...
- media query
accepted Another useful media feature is device-aspect-ratio. Note that the iPhone 5 does not have a ...
