Spring IOC容器的初始化—(一)Resource定位
前言
上一篇博文“ Spring IOC是怎样启动的 ”中提到了refresh()方法,这个就是容器初始化的入口。容器初始化共有三个阶段:
第一阶段:Resource定位
第二阶段:BeanDefinition解析
第三阶段:BeanDefinition注册
这一篇我们讲第一阶段Resource定位。
阅读目录
- 1.XmlWebApplicationContext的继承体系图
- 2.refresh()方法
- 3.Resource组件
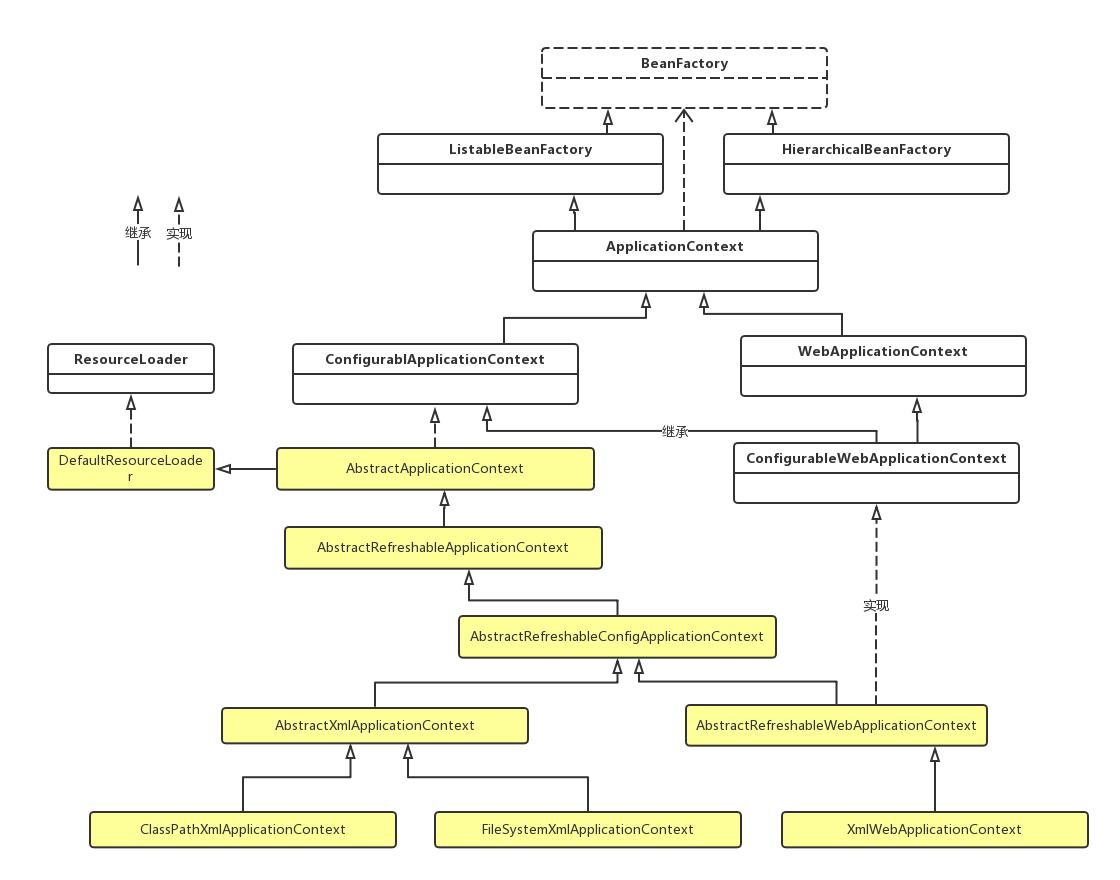
1. XmlWebApplicationContext的继承体系图
我们知道Spring IOC容器的默认实现类是XmlWebApplicationContext,下图是ApplicationContext的继承体系,至于BeanFactory的分支,以后再研究
BeanFactory or ApplicationContext?
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext都是实现IoC容器的基础接口。Application是BeanFactory的子接口,包含了BeanFactory的功能,同时增加了对Transactions和AOP的支持。所以官方更推荐开发者使用ApplicationContext及其子类实现IoC容器。特别地,Spring在实现时,大量使用ApplicationContext实现BeanPostProcessor extension point。
2.refresh()方法
我们追溯XmlWebApplicationContext的refresh()方法,依据继承体系图,追踪源码至AbastractApplicationContext的refresh()方法。
refresh()是一个模板方法,执行多个方法,而且提供了各(protected)方法的(默认)实现,其子类可以重写它们
模板方法模式:在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类(使用protected方法)可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。
refresh函数中调用了多个方法,这里先不详细讲解每一个方法,可以先通过英文注释大概了解各方法的作用。
AbastractApplicationContext的refresh()方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.//告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,bean定义资源文件的载入从子类的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动【重点】
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
这个refresh()方法就是SpringIOC 容器的初始化全过程。那么我们先关注obtainFreshBeanFactory()这个方法,因为这个方法里面会实现我们上述的Resource定位及载入解析和注册。
2.1 obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法完成了容器初始化的最重要最基础的功能,Bean定义资源的Resource定位、载入解析和注册。
AbstractApplicationContext的obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
这里使用了委派设计模式,obtainFreshBeanFactory()中调用了两个抽象方法,定义了obtainFreshBeanFactory的算法骨架,实际的行为交给其子类(AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext)实现。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory()方法
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) { //如果已经有容器,销 毁 容器中的bean,关闭容器 以保证在refresh之后使用的是新建立起来的IoC容器
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建IoC容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//对IOC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用载入Bean定义的方法,这里又使用了委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现调用子类容器
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
protected abstract void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException;
由于是web容器启动的,追溯源码,我们看到XmlWebApplicationContext实现了loadBeanDefinitions()方法。
XmlWebApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
上面的XMLBeanDefinitionReader我们先不理睬,后面BeanDefinition解析的时候会讲到这个类,我们直接看loadBeanDefinitions方法,这里是具体载入bean信息,那么要载入就要知道bean的定义文件在哪,所以Resource定位还要继续跟下去,来看这个方法的源码:
XmlWebApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader)方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
//获取ConfigLocations,也就是配置文件路径
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
看到这里大家还记得之前我们的web.xml里面配置的context-param吗?还记得我们的ContextLoader里面设置了wac.setConfigLocation(sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM))吗?这里我们就取到了xml的位置。但是这里我们并没有看到我们一直在说的Resource,那么继续看代码:经过了一次重载的方法,我们最终可以看到这个方法:
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//这里得到当前定义的ResourceLoader,默认的使用DefaultResourceLoader
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
//下面这堆是对Resource的路径模式进行解析(像我们在web.xml里面有可能使用通配符等),得到需要的Resource集合,这些Resource集合指向了我们定义好的BeanDefinition的信息,可以是多个文件。
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
try {
//将指定位置的Bean定义资源文件解析为Spring IoC容器封装的资源(Resource)
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL. 这里通过ResourceLoader来完成位置定位
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}
那么对于取得Resource的具体过程,((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location)这个方法大家点开看看就可以知道,是PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver中的实现的,它具体里面就是针对我们配置的是否以“classpath*:” 开头分别处理。对于resourceLoader.getResource(location)方法,具体是交给继承ResourceLoader的子类完成的。这里不再多述了。
总结一下,容器初始化各个父类方法调用,不然就更懵了!
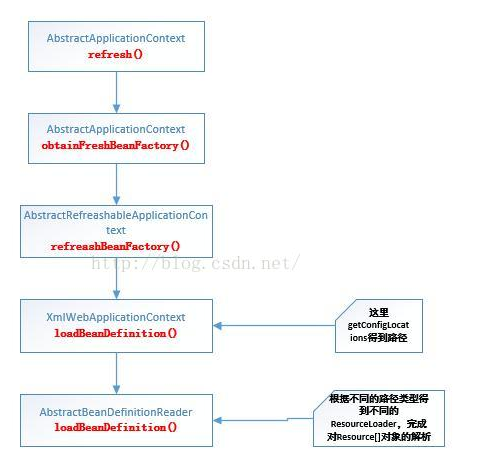
3.Resource组件
Resource组件与ResourceLoader组件一起工作,将字符串格式指示的资源解析为Resource对象。事实上ResourceLoader是Resource的工厂类, ResourceLoader的核心工作就是解析location。
location示例:”classpath:applicationContext.xml”,”classpath:applicationContext-.xml”,”file:/some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt”,"http://XX/resource/path/myTemplate.txt“ ResourceLoader根据所指示的前缀返回特定的Resource对象。看下Resource的结构图:
Spring IOC容器的初始化—(一)Resource定位的更多相关文章
- Spring IoC容器的初始化过程
Spring IoC容器的初始化包括 BeanDefinition的Resource定位.载入和注册 这三个基本的过程.IoC容器的初始化过程不包含Bean依赖注入的实现.Bean依赖的注入一般会发生 ...
- Spring IOC容器的初始化-(二)BeanDefinition的载入和解析
前言 1.在讲BeanDefinition的载入和解析之前,我们先来看看什么是BeanDefinition. Bean对象在Spring中是以BeanDefinition来描述的,也就是说在Sprin ...
- Spring IOC容器的初始化流程
IOC初始化流程 Resource定位:指对BeanDefinition的资源定位过程.Bean 可能定义在XML中,或者是一个注解,或者是其他形式.这些都被用Resource来定位, 读取Resou ...
- Spring IOC容器的初始化-(三)BeanDefinition的注册
---恢复内容开始--- 前言 在上一篇中有一处代码是BeanDefiniton注册的入口,我们回顾一下. 1.BeanDefiniton在IOC容器注册 首先我们回顾两点,1. 发起注册的地方:2. ...
- 03.Spring IoC 容器 - 初始化
基本概念 Spring IoC 容器的初始化过程在监听器 ContextLoaderListener 类中定义. 具体由该类的的 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationCo ...
- Spring IOC容器分析(4) -- bean创建获取完整流程
上节探讨了Spring IOC容器中getBean方法,下面我们将自行编写测试用例,深入跟踪分析bean对象创建过程. 测试环境创建 测试示例代码如下: package org.springframe ...
- JavaEE互联网轻量级框架整合开发(书籍)阅读笔记(6):Spring IOC容器学习(概念、作用、Bean生命周期)
一.IOC控制反转概念 控制反转(IOC)是一种通过描述(在Java中可以是XML或者是注解)并通过第三方去生产或获取特定对象的方式. 主动创建模式,责任在于开发者,而在被动模式下,责任归于Ioc容器 ...
- spring5源码分析系列(三)——IOC容器的初始化(一)
前言: IOC容器的初始化包括BeanDefinition的Resource定位.载入.注册三个基本过程. 本文以ApplicationContext为例讲解,XmlWebApplicationCon ...
- 04.Spring Ioc 容器 - 刷新
基本概念 Spring Ioc 容器被创建之后,接下来就是它的初始化过程了.该过程包含了配置.刷新两个步骤 . 刷新由 Spring 容器自己实现,具体发生在 ConfigurableApplicat ...
随机推荐
- No module named bz2
yum install bzip* python2.6 import bz2 python2.7 import bz2 error 解决:sudo cp /usr/lib64/python2.6/li ...
- Oracle数据库的数据导入导出
--备份数据库--数据库系统用户账号system/adminuser --查看oracle数据库的用户select * from all_users;--查看oracle数据库的版本号select * ...
- Rreact Native 常见错误总结
1.invariant violation:expected a component class,got[object object] 创建自定义组件首字母要大写,否则会报错. ...
- camera frame work v3 note
1 android_atomic_write(level, &gLogLevel); 原子写操作. 2 构造函数和onFirstRef onFirstRef 会在构造函数运行后执行,这个是在m ...
- HDU 5703
题意:给你一个数n,问将n分为正整数和的方案数.如n=3共四种,1 1 1 , 1 2 , 2 1 ,3 . 思路:隔板法,n个1,有n-1个空位,每个空位可以选择是否插入隔板,插入k(0<=k ...
- EF Code-First 学习之旅 数据库初始化
1.CreateDatabaseIfNotExists: 2.DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges: 3.DropCreateDatabaseAlways: 4.Custo ...
- Reverse Nodes In K Group,将链表每k个元素为一组进行反转---特例Swap Nodes in Pairs,成对儿反转
问题描述:1->2->3->4,假设k=2进行反转,得到2->1->4->3:k=3进行反转,得到3->2->1->4 算法思想:基本操作就是链表 ...
- linux下gzip压缩同样内容大小不一样
一份数据,两种传输方式进行收集. 一份数据:有多台数据采集节点或者多个数据源 两种方式:一种是从依次多个采集节点或者多个数据源将数据拷贝过来,合并为一个文件 另外一种是多个采集节点或者数据源同时向汇总 ...
- Pandas窗口函数
为了处理数字数据,Pandas提供了几个变体,如滚动,展开和指数移动窗口统计的权重. 其中包括总和,均值,中位数,方差,协方差,相关性等. 下来学习如何在DataFrame对象上应用上提及的每种方法. ...
- NumPy切片和索引
NumPy - 切片和索引 ndarray对象的内容可以通过索引或切片来访问和修改,就像 Python 的内置容器对象一样. 如前所述,ndarray对象中的元素遵循基于零的索引. 有三种可用的索引方 ...

