python模块subprocess学习
当我们想要调用系统命令,可以使用os,commands还有subprocess模块整理如下:
os模块:
1. os.system 输出命令结果到屏幕、返回命令执行状态。
>>> os.system('ls')
1 2 nginx.conf.bak nginx.conf.default
0
>>> os.system('ls -l')
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 525 Oct 19 16:50 1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 Oct 19 16:51 2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2260 Jul 7 12:00 nginx.conf.bak
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 22 20:53 nginx.conf.default
0
>>>
2. os.popen("dir").read() 会保存命令的执行结果输出,返回的是 file read 的对象,对其进行读取 read() 的操作可以看到执行的输出。
>>> os.popen("dir").read()
'1 2 nginx.conf.bak nginx.conf.default\n'
commands模块:(py2.7、3.6版本已经没了)
1. commands.getstatusoutput 模块返回元组 only support Linux。
>>> commands.getstatusoutput('ls')
(0, '1\n2\nnginx.conf.bak\nnginx.conf.default')
Subprocess 模块:
subprocess一个更好用的模块,并且可以用Popen的类进行来创建进程,并与进程进行复杂的交互手册介绍如下:
This module intends to replace several other, older modules and functions, such as: os.system、os.spawn*、os.popen*、popen2.*、commands.*
subprocess被用来替换一些老的模块和函数,如:os.system、os.spawn*、os.popen*、popen2.*、commands.*。可见,subprocess是被推荐使用的模块。
使用 subprocess模块,启动子进程的推荐方式是使用下面的便利功能。当这些还不能满足需求时,就需要使用底层的Popen
1. subprocess.call
示例代码:
语法:subprocess.call(args, *, stdin=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, shell=False)
语义:运行由args指定的命令,直到命令结束后,返回返回码的属性值。
WARNING: 使用 shell=True 是一种安全保护机制。
NOTE: 在使用这个函数时,不要使用 stdout=PIPE 或 stderr=PIPE 参数,不然会导致子进程输出的死锁。
使用了shell=True这个参数。这个时候,我们使用一整个字符串,而不是一个表来运行子进程。Python将先运行一个shell,再用这个shell来解释这整个字符串。
>>> subprocess.call(['ls','-l'])
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 525 Oct 19 16:50 1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 Oct 19 16:51 2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2260 Jul 7 12:00 nginx.conf.bak
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 22 20:53 nginx.conf.default
0 >>> subprocess.call('ls',shell=True)
1 2 nginx.conf.bak nginx.conf.default
0
2. subprocess.check_call 这个函数在py2.5中引入。
示例代码:
语法: subprocess.check_call(args, *, stdin=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, shell=False)
语义:运行由args指定的命令,直到命令执行完成。如果返回码为零,则返回。否则,抛出 CalledProcessError异常。CalledProcessError对象包含有返回码的属性值。
WARNING: 使用 shell=True 是一种安全机制。
NOTE: 不要在这个函数中使用 stdout=PIPE 或 stderr=PIPE, 否则会造成子进程死锁。如果需要使用管道,可以在 communicate()方法中使用Popen.
>>> subprocess.check_call(['ls','-l'])
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 525 Oct 19 16:50 1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 Oct 19 16:51 2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2260 Jul 7 12:00 nginx.conf.bak
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 22 20:53 nginx.conf.default
0
>>> subprocess.check_call('ls -l',shell=True)
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 525 Oct 19 16:50 1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 323 Oct 19 16:51 2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2260 Jul 7 12:00 nginx.conf.bak
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 22 20:53 nginx.conf.default
0
>>>
3. subprocess.check_output 这个函数在py2.7中引入。
示例代码:
语法: subprocess.check_output(args, *, stdin=None, stderr=None, shell=False, universal_newlines=False)
语义:运行args定义的命令,并返回一个字符串表示的输出值。如果返回码为非零,则抛出 CalledProcessError异常。
WARNING: 使用 shell=True 是一种安全机制。
NOTE: 不要在这个函数中使用 stdout=PIPE 或 stderr=PIPE, 否则会造成子进程死锁。如果需要使用管道,可以在 communicate()方法中使用Popen.
>>> subprocess.check_output(["echo","Hello World!"])
b'Hello World!\n'
>>> subprocess.check_output("exit 1", shell=True)
Traceback (most recent call last):
.
.
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command 'exit 1' returned non-zero exit status 1.
如果要捕捉结果中的标准错误,使用 stderr=subprocess.STDOUT参数:
>>> subprocess.check_output("ls non_existent_file; exit 0",stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,shell=True)
b'ls: cannot access non_existent_file: No such file or directory\n'
4. subprocess.PIPE : 使用Popen时,用于 stdin, stdout和stderr参数的特殊值,表示打开连接标准流的管道。
5. subprocess.STDOUT: 使用Popen时,用于 stderr 参数的特殊值,表示将标准错误重定向到标准输出的同一个句柄。
6. subprocess.CalledProcessError : 当由 check_call()或 check_output()运行的进程返回非零状态值时抛出的异常。
7. returncode: 子进程的退出状态。
8. cmd :子进程执行的命令。
9. output : 如果check_output()抛出异常时,子进程的输出值。否则,没有这个值。
Popen
subprocess中更底层的进程创建和管理可以通过Popen类实现。它提供了更多的灵活性,程序员通过它能处理更多复杂的情况。
语法:class subprocess.Popen(args, bufsize=0, executable=None, stdin=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, preexec_fn=None, close_fds=False, shell=False, cwd=None, env=None,universal_newlines=False, startupinfo=None, creationflags=0)
语义:在新进程中执行一个子程序。在Unix中,这个类使用 类似于 os.execvp()方式来执行子程序。在Windows中,这个类使用Windows的 CreateProcess()函数来执行子程序。
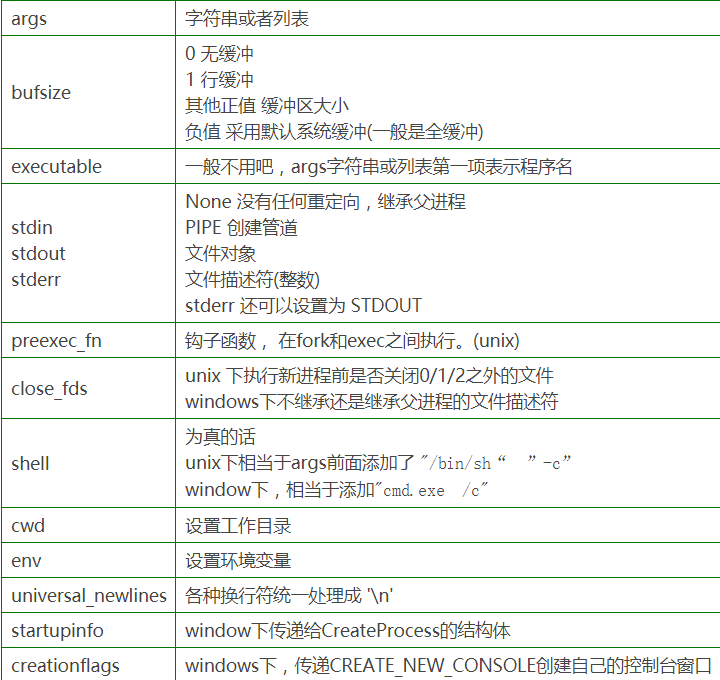
常用参数
1. args 所有的函数都需要这个参数,并且它是一个字符串,或者是程序的参数序列。提供一个参数序列是更推荐的方式,因为这样能允许模块接收空格 或 引号中的参数。如果传递的是单个字符串,要么 shell=True, 或要么字符串就程序名字,并且不能带参数。
2. stdin,stdout,stderr指定了执行程序的标准输入,标准输出和标准错误的文件句柄。它们的值可以是PIPE, 一个存在的文件描述符(正整数),一个存在的文件对象,或 None.PIPE 表示创建一个连接子进程的新管道。默认值 为 None, 表示不做重定向。子进程的文件句柄可以从父进程中继承得到。
另外,stderr可以设置值为 STDOUT,表示子进程的错误数据可以和标准输出是同一个文件句柄。当stdout 或 stderr的值为管道 并且 universal_newlines的值为真时,对于以 ‘U'模式参数打开的新行,所有行的结束都会转换成'\n'。
3.shell的值为 True, 则指定的命令行会通过shell来执行。如果你使用Python来作为流程控制,那这样的设置会很有用,因为它提供了绝大多数的系统shell命令且可以很方便地使用shell的各种功能,如 shell 管道,文件名通配符,环境变量扩展,以及用户目录扩展符 ~。但是,需要注意的是,Python 提供了类似shell功能的实现。执行不受信任来源的shell命令会是一个严重的安全问题。基于这一点,shell=True 是不建议的.
Popen常用参数:
popen对象:
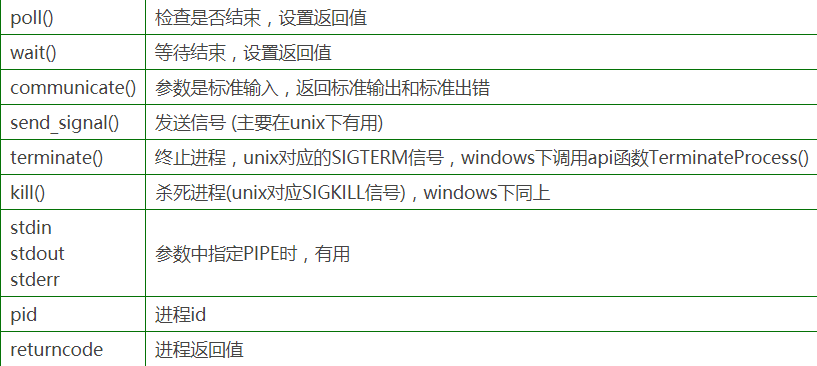
示例代码:
>>> subprocess.Popen('env', env={'test':'123', 'testtext':'zzz'})
test=123
<subprocess.Popen object at 0x7fb4254b5090>
testtext=zzz
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("ifconfig | grep 172",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> res.stdout.read()
b' inet 172.17.22.212 netmask 255.255.240.0 broadcast 172.17.31.255\n'
>>> res.stderr.read()
b''
在后面将要学习进程间通讯的时候,会更新笔记
结论:通过使用subprocess模块,我们可以运行外部程序。这极大的拓展了Python的功能。可以从Python中直接调用该应用(而不是完全依赖Python),并将应用的结果输出给Python,并让Python继续处理。
参考资料:
http://docs.python.org/library/subprocess.htcml
http://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0324/
http://blog.csdn.net/dbzhang800/article/details/6879239
python模块subprocess学习的更多相关文章
- Python中subprocess学习
subprocess的目的就是启动一个新的进程并且与之通信. subprocess模块中只定义了一个类: Popen.可以使用Popen来创建进程,并与进程进行复杂的交互.它的构造函数如下: subp ...
- Python基础篇【第6篇】: Python模块subprocess
subprocess Python中可以执行shell命令的相关模块和函数有: os.system os.spawn* os.popen* --废弃 popen2.* ...
- Python模块subprocess小记
转自:http://www.oschina.net/question/234345_52660 熟悉了Qt的QProcess以后,再回头来看python的subprocess总算不觉得像以前那么恐怖了 ...
- python模块的学习
# time 模块 import time print(time.time()) #当前的时间挫 #time.sleep(3) #休息3秒钟,这3秒cpu不工作的 print(time.gmtime( ...
- 【转】Python模块subprocess
subprocess 早期的Python版本中,我们主要是通过os.system().os.popen().read()等函数.commands模块来执行命令行指令的,从Python 2.4开始官方文 ...
- Python模块subprocess
subprocess的常用用法 """ Description: Author:Nod Date: Record: #-------------------------- ...
- Python模块——subprocess
subprocess模块 通过Python去执行一条系统命令或脚本. 三种执行命令的方法 subprocess.run(*popenargs, input=None, timeout=None, ch ...
- Python模块-subprocess模块
Run()方法 >>> a = subprocess.run(['df','-h']) 文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点 udev 468M 0 468M 0% /dev ...
- python模块:调用系统命令模块subprocess等
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/46972171 Python经常被称作"胶水语言",因为它能够轻易地操作其他程序,轻 ...
随机推荐
- C#,Winform 文件的导入导出 File
1.导入 导入对话框:OpenFileDialog private void sbtnsb_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { try { OpenFileDial ...
- 解决连接mysql报错1130
最近在服务器上部署好的应用突然间连接不上mysql数据库,报错“ERROR 1130: Host xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is not allowed to connect to this M ...
- matlab怎么选取excel的特定列构成数组
例如:
- activeMQ 讲解及实战
#### 软件架构项目中需要用到activeMQ 下载地址:http://activemq.apache.org/download.html #### 安装教程需要安装jdk环境activeMQ免安装 ...
- WPF对某控件添加右键属性
代码创建右键属性 ContextMenu cm = new ContextMenu(); MenuItem mi = new MenuItem(); mi.Header = "打开此文件所有 ...
- hdu 1688 Sightseeing (最短路径)
Sightseeing Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- Elasticsearch Query DSL备忘(1)(Constant score query和Bool Query)
Query DSL (Domain Specific Language),基于json的查询方式 1.Constant score query,常量分值查询,目的就是返回指定的score,一般都结合f ...
- BZOJ5290 & 洛谷4438:[HNOI/AHOI2018]道路——题解
https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=5290 https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4438 的确 ...
- ZOJ1081:Points Within——题解
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=1081 题目大意:给定一个点数为 n 的多边形,点按照顺序给出,再给出 m ...
- mysql语句及执行计划
数据库链接: mysql -uroot -p <!--数据库连接-->mysql -h10.0.0.100 -uuser -passwordshow databases <!--查看 ...
