POJ 2528 区间染色,求染色数目,离散化
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 47905 | Accepted: 13903 |
Description
- Every candidate can place exactly one poster on the wall.
- All posters are of the same height equal to the height of the wall; the width of a poster can be any integer number of bytes (byte is the unit of length in Bytetown).
- The wall is divided into segments and the width of each segment is one byte.
- Each poster must completely cover a contiguous number of wall segments.
They have built a wall 10000000 bytes long (such that there is enough place for all candidates). When the electoral campaign was restarted, the candidates were placing their posters on the wall and their posters differed widely in width. Moreover, the candidates started placing their posters on wall segments already occupied by other posters. Everyone in Bytetown was curious whose posters will be visible (entirely or in part) on the last day before elections.
Your task is to find the number of visible posters when all the posters are placed given the information about posters' size, their place and order of placement on the electoral wall.
Input
Output
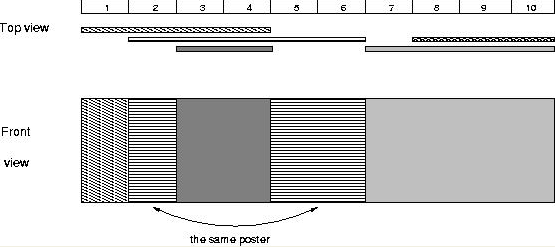
The picture below illustrates the case of the sample input.
Sample Input
1
5
1 4
2 6
8 10
3 4
7 10
Sample Output
4
Source
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
using namespace std; #define N 40005
#define ll root<<1
#define rr root<<1|1
#define mid (a[root].l+a[root].r)/2 int max(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y;}
int min(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y;}
int abs(int x,int y){return x<?-x:x;} int n;
int x[N];
int m; int bin_s(int key){
int l=, r=m-;
while(l<=r){
int mm=(l+r)/;
if(x[mm]==key) return mm;
if(x[mm]>key) r=mm-;
else if(x[mm]<key) l=mm+;
}
} struct Line{
int l, r;
}line[N]; struct node{
int l, r, val;
bool f;
}a[N*]; void build(int l,int r,int root){
a[root].l=l;
a[root].r=r;
a[root].val=-;
if(l==r) return;
build(l,mid,ll);
build(mid+,r,rr);
} void down(int root){
if(a[root].val>&&a[root].l!=a[root].r){
a[ll].val=a[rr].val=a[root].val;
a[root].val=-;
}
} void update(int l,int r,int val,int root){
if(a[root].val==val) return;
if(a[root].l==l&&a[root].r==r){
a[root].val=val;
return;
}
down(root);
if(r<=a[ll].r) update(l,r,val,ll);
else if(l>=a[rr].l) update(l,r,val,rr);
else{
update(l,mid,val,ll);
update(mid+,r,val,rr);
}
if(a[ll].val==a[rr].val&&a[ll].val>) a[root].val=a[ll].val;
} bool visited[N];
int ans; void query(int root){
if(a[root].val!=-&&!visited[a[root].val]) {
ans++;
visited[a[root].val]=true;
return;
}
if(a[root].l==a[root].r)return ;
down(root);
query(ll);
query(rr);
} void out(int root){
if(a[root].l==a[root].r) {
printf("%d ",a[root].val);
return;
}
down(root);
out(ll);
out(rr);
} main()
{
int t, i, j, k; cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&n);
k=;
for(i=;i<n;i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&line[i].l,&line[i].r);
x[++k]=line[i].l;
x[++k]=line[i].r;
}
sort(x+,x+k);
k=unique(x+,x+k+)-x;
m=k;
for(i=;i<k;i++){
if(x[i]-x[i-]>) x[m++]=x[i]-;
}
sort(x,x+m);
build(,m,);
for(i=;i<n;i++){
int l=bin_s(line[i].l);
int r=bin_s(line[i].r);
update(l,r,i+,); }
memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited));
ans=;
query();
printf("%d\n",ans);
//out(1);
}
}
POJ 2528 区间染色,求染色数目,离散化的更多相关文章
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化技巧
poj 2528 Mayor's posters 题目链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=2528 思路: 线段树+离散化技巧(这里的离散化需要注意一下啊,题目数据弱看不出来) ...
- zoj 1610 Count the Colors 【区间覆盖 求染色段】
Count the Colors Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Painting some colored segments on ...
- POJ - 2528 区间离散化,线段树区间修改,区间询问
这个题非常有意思的地方是,我们发现区间[1,4]和[5,8]是紧挨着的,因为这个的数代表的是一段区间,原本我们对于普通的离散, a[1]=1,a[2]=5,a[3]=6,a[4]=8;数组下标就是重新 ...
- poj 2528(区间改动+离散化)
题意:有一个黑板上贴海报.给出每一个海报在黑板上的覆盖区间为l r,问最后多少个海报是可见的. 题解:由于l r取值到1e7,肯定是要离散化的,但普通的离散化会出问题.比方[1,10],[1,4],[ ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters(线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters 转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/winddreams/article/details/38443761 [题目链接]Mayor's posters [ ...
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化 || hihocode #1079 离散化
Mayor's posters Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor‘s poster 线段树+离散化
给一块最大为10^8单位宽的墙面,贴poster,每个poster都会给出数据 a,b,表示该poster将从第a单位占据到b单位,新贴的poster会覆盖旧的,最多有10^4张poster,求最后贴 ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions:75394 Accepted: 21747 ...
- poj 2528 poster经典线段树+lazy+离散化
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; ; #def ...
随机推荐
- [转载] 为 Key-Value 数据库实现 MVCC 事务
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA5ODM5MDU3MA==&mid=400086920&idx=1&sn=b8174184059e2886 ...
- 没办法,还是要补一下js,回调函数(转载)
<html> <head> <title>回调函数(callback)</title> <script language="javasc ...
- 理解odbc
1.解决什么样的问题?不同的数据库产品,具有不同的特性,也就是方言.因此应用程序针对不同的数据库产品,编写不同的代码.如果换了一个数据库产品,还需要重新编写数据库交互部分,不具备扩展和移植.odbc对 ...
- .net连接access操作类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.We ...
- Python学习笔记2—内置函数
函数的使用 官方文档:https://docs.python.org/2/library/functions.html
- Hello,Akka
版权声明:转载时请以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息及本声明http://www.blogbus.com/dreamhead-logs/235916459.html 只要稍微了解过一些Scala, ...
- nginx日志分析手机使用频次
__author__ = 'similarface' from collections import defaultdict import glob ip = r"?P<ip>[ ...
- easyui 查询
<fieldset> <legend>查询</legend> <table style="width: 100%;"> <tr ...
- 生物信息 perl 脚本实战
索引 1.统计fasta.fa和fastq文件的长度,统计fastq的reads个数,单个reads长度,reads总长度:统计fasta文件中contig的个数,列出名称,单条的长度,以及总长度. ...
- Graph-tool简介 - wiki
graph-tool is a Python module for manipulation and statistical analysis of graphs[disambiguation nee ...
