2、Spring的IOC标签介绍以及实例
一、Spring_ioc配置文件bean标签介绍
1、 bean标签
名称:bean
类型:标签
归属:beans标签
作用:定义spring中的资源,受此标签定义的资源将受到spring控制
格式:
<beans>
<bean/>
</beans>
基本属性:
<bean id="bean_id" name="beanName1,beanName2" class="ClassName"></bean>
基本属性解释:
id:bean的名称,通过id值获取bean
class:bean的类型
name:bean的名称,可以通过name值获取bean,用于多人配合时给bean起别名
2、 bean标签下scope属性
名称:scope
类型:属性
归属:bean标签
作用:定义bean的作用范围
格式:
<bean scope="singleton"></bean>
取值:
singleton:设定创建出的对象保存在spring容器中,是一个单例的对象
prototype:设定创建出的对象保存在spring容器中,是一个非单例的对象
request、session、application、websocket 设定创建出的对象放置在web容器对应的位置
演示scope标签
配置文件spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--演示scope的值为singleton是,单例创建对象-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" scope="singleton"></bean>
<!--演示scope的值为singleton是,单例创建对象-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" scope="prototype"></bean>
</beans>
测试scope=singleton属性
package com.why.controller;
import com.why.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author Laity
* @date 2021年11月16日 9:41
*/
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
}
}
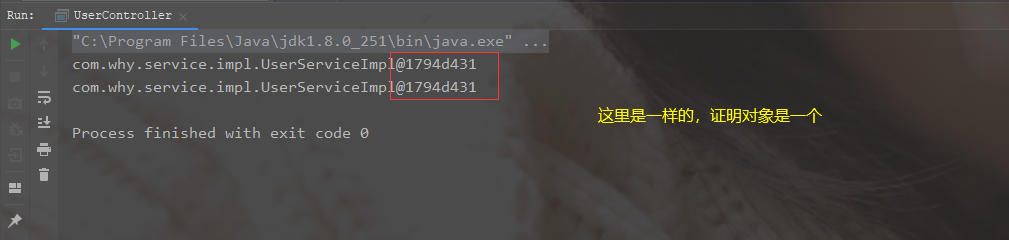
运行scope="singleton"时结果
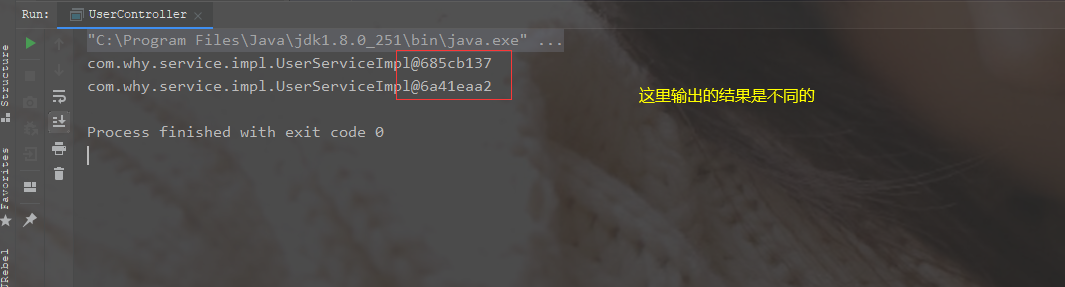
运行scope="prototype"时结果
3、 bean生命周期
名称:init-method,destroy-method
类型:属性
归属:bean标签
作用:定义bean对象在初始化或销毁时完成的工作
格式:
<bean init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy></bean>
取值:bean对应的类中对应的具体方法名
注意事项:
当scope=“singleton”时,spring容器中有且仅有一个对象,init方法在创建容器时仅执行一次
当scope=“prototype”时,spring容器要创建同一类型的多个对象,init方法在每个对象创建时均执行一次
当scope=“singleton”时,关闭容器会导致bean实例的销毁,调用destroy方法一次
当scope=“prototype”时,对象的销毁由垃圾回收机制gc()控制,destroy方法将不会被执行
测试生命周期
- 在业务层实现类创建两个类
package com.why.service.impl;
import com.why.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void saveUser() {
System.out.println("Hello,Spring............");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("bean初始化");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("bean销毁");
}
}
- 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--当前scope为singleton单例时-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
scope="singleton"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"
/>
</beans>
当配置文件中scope属性为singleton时:
- 测试代码
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
}
}

总结:当scope=“singleton”时,spring容器中有且仅有一个对象,init方法在创建容器时仅执行一次
当配置文件中scope属性为prototype时:
- 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--演示scope的值为singleton是,单例创建对象-->
<!-- <bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" scope="singleton"></bean>-->
<!-- <bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" scope="singleton"></bean>-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
scope="prototype"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"
/>
</beans>
- 测试代码
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
}
}
- 测试结果

总结:当scope=“prototype”时,spring容器要创建同一类型的多个对象,init方法在每个对象创建时均执行一次
思考:
为什么只有init方法运行,destory方法怎么没有运行?
其实destory是有运行的,但是由于程序结束的太快虚拟机以及关闭了,来不及打印,所以就没有显示了。
我们可以通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的close()方法在程序结束之前强制关闭容器,这样就可以看到destroy方法的打印了。
- 修改配置文件(scope = singleton)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
scope="singleton"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"
/>
</beans>
- 测试
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
context.close();
}
}
- 结果
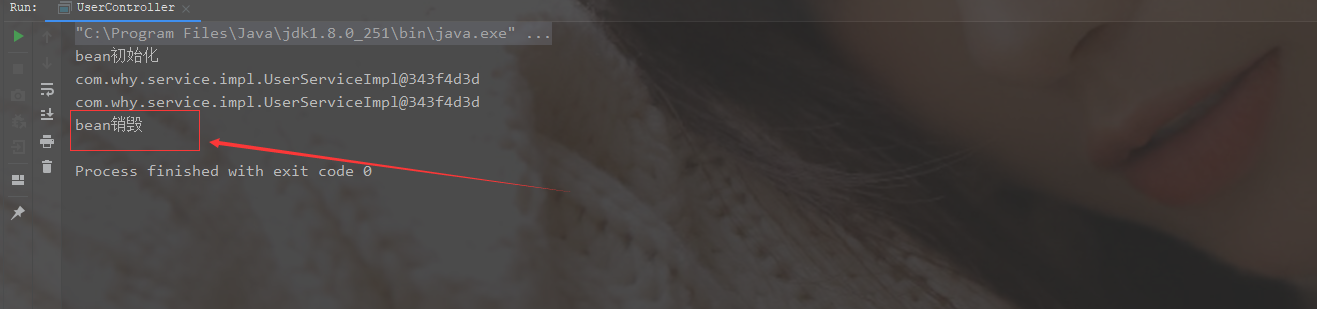
当scope=“singleton”时,关闭容器会导致bean实例的销毁,调用destroy方法一次
- 修改配置文件(scope = prototype)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
scope="prototype"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"
/>
</beans>
- 测试代码
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
UserService userService1 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
System.out.println(userService1);
context.close();
}
}
- 运行结果
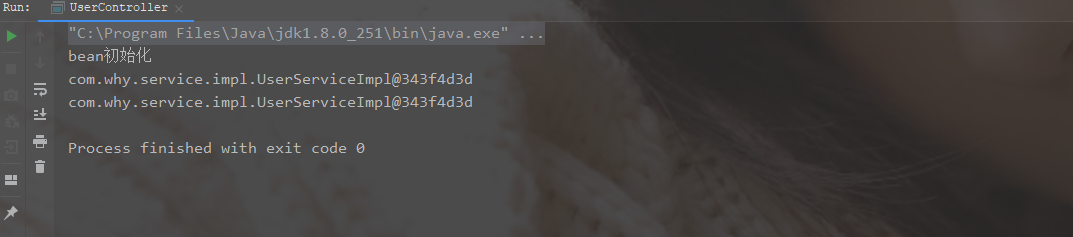
当scope=“prototype”时,对象的销毁由垃圾回收机制gc()控制,destroy方法将不会被执行
4、 bean对象创建方式
(1) factory-bean
名称:factory-bean
类型:属性
归属:bean标签
作用:定义bean对象创建方式,使用静态工厂的形式创建bean,兼容早期遗留系统的升级工作
格式:
<bean class="FactoryClassName" factory-method="factoryMethodName"></bean>
取值:工厂bean中用于获取对象的静态方法名
注意事项:
class属性必须配置成静态工厂的类名
(2)factory-bean,factory-method
名称:factory-bean,factory-method
类型:属性
归属:bean标签
作用:定义bean对象创建方式,使用实例工厂的形式创建bean,兼容早期遗留系统的升级工作
格式:
<bean factory-bean="factoryBeanId" factory-method="factoryMethodName"></bean>
取值:工厂bean中用于获取对象的实例方法名
注意事项:
使用实例工厂创建bean首先需要将实例工厂配置bean,交由spring进行管理
factory-bean是实例工厂的beanId
4.1 配置静态工厂创建bean
- 创建工厂类(工厂方法为静态方法)
package com.why.factory;
/**
* @author Laity
* @date 2021年11月17日 9:45
*/
public class UserServiceFactory {
public static UserService getService(){
System.out.println("对象是静态工厂创建的");
//返回需要创建的对象
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
}
- 修改配置文件(spring.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.why.factory.UserServiceFactory" factory-method="getService"/>
</beans>
- 测试
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
}
}
- 结果
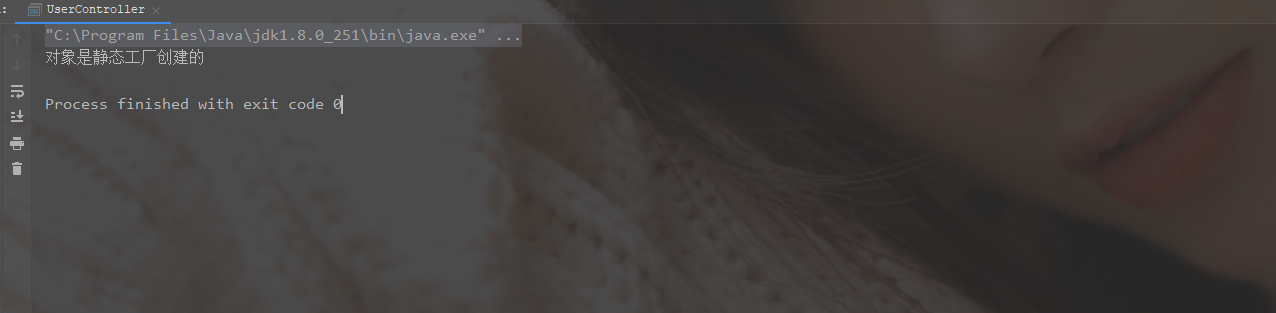
4.2 实例工厂创建bean
- 创建工厂类(工厂方法非静态方法)
public class UserServiceFactory {
public UserService getService(){
System.out.println("对象是实例化工厂创建的");
//返回需要实例化的对象
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
}
- 修改配置文件(spring.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="factoryBean" class="com.why.factory.UserServiceFactory" />
<bean id="userService" factory-bean="factoryBean" factory-method="getService"/>
</beans>
- 测试
public class UserController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
/*
通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值(id标识唯一的bean)
*/
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.saveUser();
}
}
- 结果
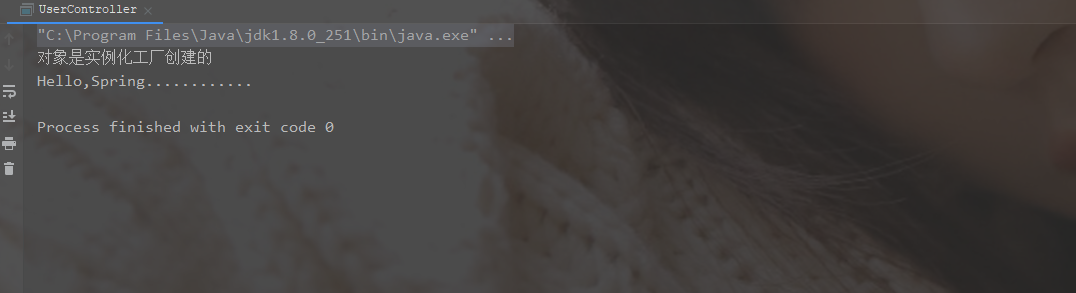
4.3 Spring三种创建bean的方式比较
方式一: bean标签创建,当各个bean的业务逻辑相互比较独立的时候或者和外 界关联较少的时候可以使用。
方式二: 利用静态factory方法创建,可以统一管理各个bean的创建,如各个bean在创建之前需要 相同的初始化处理,则可用这个factory方法险进行统一的处理等等。
方式三: 利用实例化factory方法创建,即将factory方法也作为了业务bean来控制,1可用于集成 其他框架的bean创建管理方法,2能够使bean和factory的角色互换。
开发中,项目一般使用第一种方式实例化bean,交给spring托管,使用时直接拿来使用即可,另外两种了解即可。
2、Spring的IOC标签介绍以及实例的更多相关文章
- 【死磕 Spring】----- IOC 之解析 bean 标签:开启解析进程
原文出自:http://cmsblogs.com import 标签解析完毕了,再看 Spring 中最复杂也是最重要的标签 bean 标签的解析过程. 在方法 parseDefaultElement ...
- Spring框架IOC和AOP介绍
说明:本文部分内容参考其他优秀博客后结合自己实战例子改编如下 Spring框架是个轻量级的Java EE框架.所谓轻量级,是指不依赖于容器就能运行的.Struts.Hibernate也是轻量级的. 轻 ...
- Spring中IoC的入门实例
Spring中IoC的入门实例 Spring的模块化是很强的,各个功能模块都是独立的,我们可以选择的使用.这一章先从Spring的IoC开始.所谓IoC就是一个用XML来定义生成对象的模式,我们看看如 ...
- 死磕Spring之IoC篇 - 解析自定义标签(XML 文件)
该系列文章是本人在学习 Spring 的过程中总结下来的,里面涉及到相关源码,可能对读者不太友好,请结合我的源码注释 Spring 源码分析 GitHub 地址 进行阅读 Spring 版本:5.1. ...
- 【死磕 Spring】—– IOC 之解析Bean:解析 import 标签
原文出自:http://cmsblogs.com 在博客[死磕Spring]----- IOC 之 注册 BeanDefinition中分析到,Spring 中有两种解析 Bean 的方式.如果根节点 ...
- SpringMVC系列(十五)Spring MVC与Spring整合时实例被创建两次的解决方案以及Spring 的 IOC 容器和 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器的关系
一.Spring MVC与Spring整合时实例被创建两次的解决方案 1.问题产生的原因 Spring MVC的配置文件和Spring的配置文件里面都使用了扫描注解<context:compon ...
- Spring IoC控制反转创建实例
Spring IoC控制反转创建实例写一个配置文件beans.xml,配置文件的约束可以访问:完整链接:https://repo.spring.io/libs-release-local/org/sp ...
- Spring之IoC详解(非原创)
文章大纲 一.Spring介绍二.Spring的IoC实战三.IoC常见注解总结四.项目源码及参考资料下载五.参考文章 一.Spring介绍 1. 什么是Spring Spring是分层的Java ...
- Spring之IOC原理及代码详解
一.什么是IOC 引用 Spring 官方原文:This chapter covers the Spring Framework implementation of the Inversion of ...
随机推荐
- C++概述及知识点总结
经过一段时间的学习,以前从没有接触过C++这个高逼格的语言的小白,逐渐对C++有了更深的了解和认识,C++是c语言的升级版,Bjarne Stroustrup在剑桥大学计算机中心工作.他使用过Simu ...
- 从零搭建vue3.0项目架构(附带代码、步骤详解)
前言: GitHub上我开源了vue-cli.vue-cli3两个库,文章末尾会附上GitHub仓库地址.这次把2.0的重新写了一遍,优化了一下.然后按照2.0的功能和代码,按照vue3.0的语法,完 ...
- myeclipse重写快捷键
shift+alt+s 点击Override/Implments methods
- [loj3333]混合物
假设选择的调味瓶为$k_{1}<k_{2}<...<k_{s}$,即判定是否存在正有理数解$\{x_{1},x_{2},...,x_{s}\}$,满足$$(\sum_{i=1}^{s ...
- [loj2091]小星星
(分别用$E_{T}$和$E_{G}$表示树和图的边集) 简单分析,可以发现题目即求排列$p_{i}$的数量,满足$\forall (x,y)\in E_{T},(p_{x},p_{y})\in E_ ...
- CF1368F Lamps on a Circle
思考我们一定有最后一个状态是空着的灯是按照一个间隔\(k\) 只要将原来\(n\)个灯,每\(k\)个分一组,强制将最后一盏灯不选,并且第n盏灯不选,需要注意的是某一组一定会被第二个人全部关掉,那么可 ...
- 各种多项式操作的 n^2 递推
zszz,使用 NTT 可以在 \(\mathcal O(n\log n)\) 的时间内求出两个多项式的卷积.以及一个多项式的 \(\text{inv},\ln,\exp,\text{sqrt}\) ...
- Codeforces 626G - Raffles(贪心+堆)
题面传送门 考虑对于固定的彩票池 \(i\),我们假设现在押了 \(x\) 张彩票.利用差分的思想,从 \(x\) 张彩票变为 \(x+1\) 张时,期望的变化量 \(\Delta E=\dfrac{ ...
- pcm.x代码分析
简介 运行说明 pcm 监控结果可以分为核心.socket 和系统三部分.在核心监控部分,结果包括如下内容: • EXEC • IPC:每 CPU 周期指令数 • FREQ:普通CPU频率系数 • A ...
- Hermite WENO 重构格式
Hermite WENO 单元重构 本文主要介绍采用 Hermite WENO 重构方法作为斜率限制器应用于二维或高维单元中. 1.简介[1] ENO格式最早由 Harten 等[2]提出,ENO格式 ...
