SIFT Learing records
花了一周的时间去读了一下SIFT的原论文,相关的一些视频还有文章,大体了解了其思想和步骤,在这里记录一下吧。
SIFT是一种提取图像中具有尺度不变性的关键点的算法。举个例子,一个鼠标,对其拍摄远端,近端两张照片,然后用SIFT分别提取这两张图片的关键点,然后计算特征点的描述符,用描述符进行匹配。类似的这些描述符也可以用于图像检索。

SIFT算法的步骤
构建高斯差分金字塔,寻找可能的关键点。
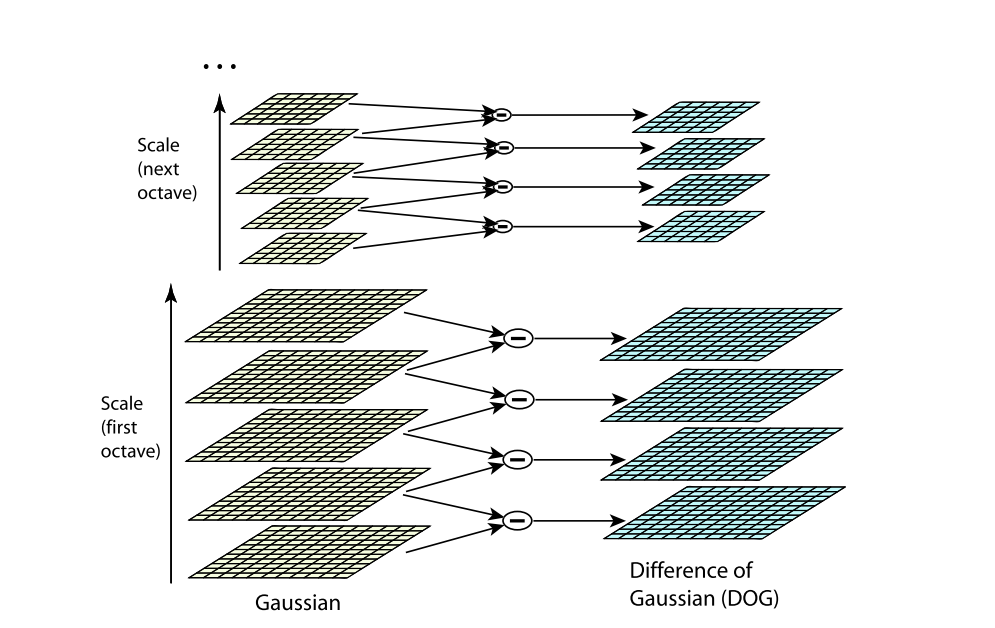
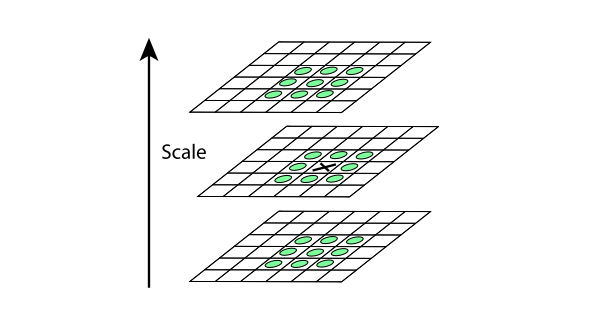
因为上一步找到的极值点都是离散的,不一定是真正的极值点,对此可以在检测到的极值点处做三元二阶泰勒展开,
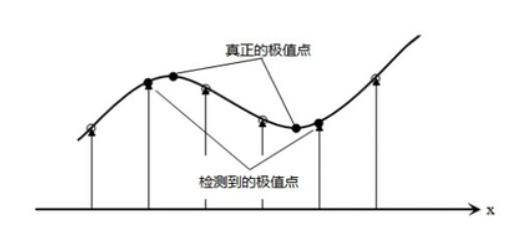
通过有限差分法求偏导,代入原方程,求导,并让方程等于零,我们可以得到极值点的偏移量为:
将(10)代入(9)可以得到对应的极值点:
同时舍去对比度低的点。
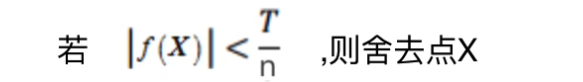
同时仅仅舍去对比度低的点,是不够的,又使用了一个Heesian 矩阵 来消除边缘效应。
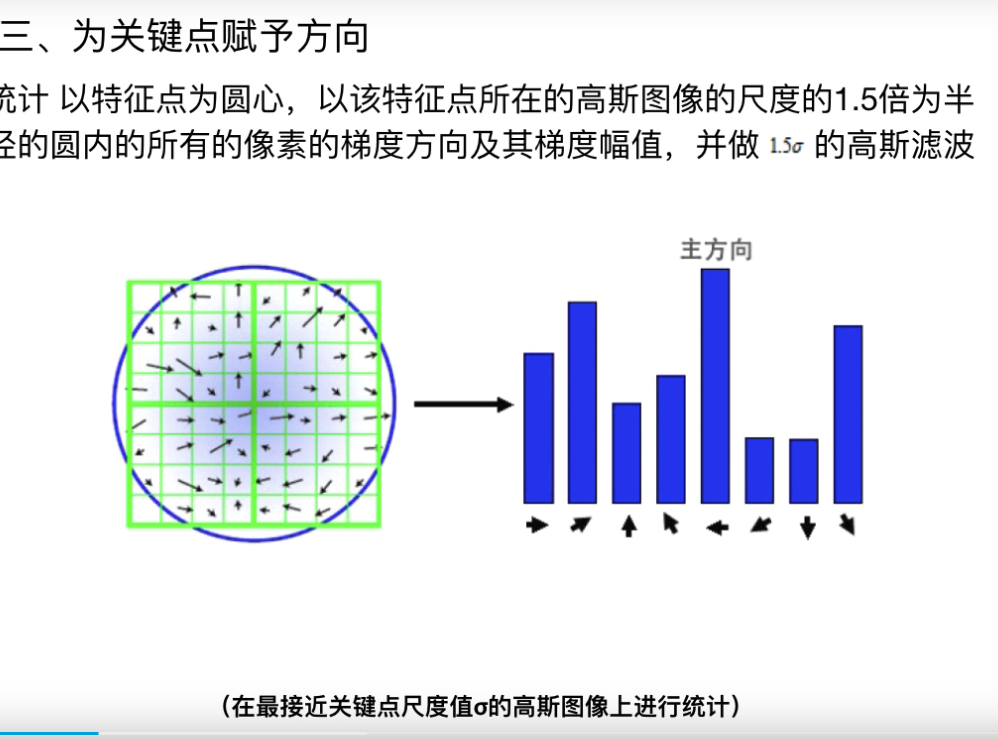
- 为关键点赋方向
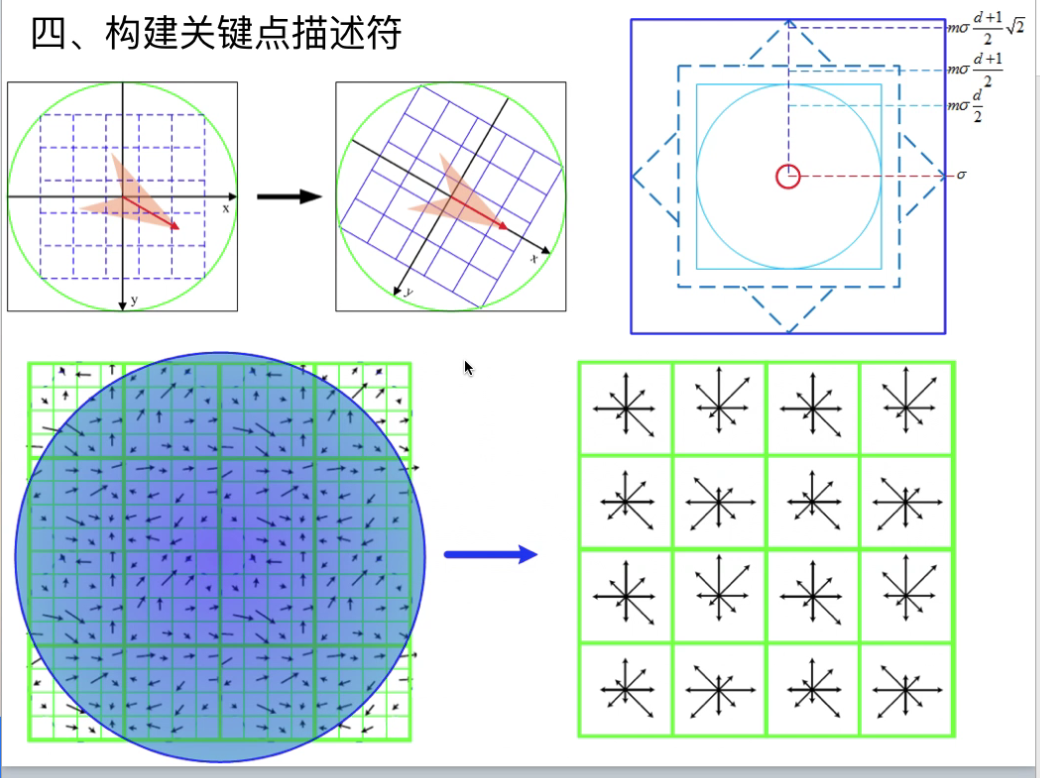
构建关键点描述符
通过我们上边步骤,每个特征点被分配了坐标位置、尺度和方向。在图像局部区域内,这些参数可以重复的用来描述局部二维坐标系统,因为这些参数具有不变性。
可以使用描述符进行关键点匹配。
小结
SIFI是真的难理解,刚开始去查阅了很多关于图像处理的基本知识,才能勉强理解每一步的作用。这个算法很经典,但是,整个研究过程真的挺难的,很多知识点论文中没有提到,论文本身又是英文写,读起来难免有些困难,限于自己目前的知识以及编程能力,仍有一些问题还没有想通,可能随着时间的推移,会有另一种层面的理解。
附录代码
from __future__ import print_function
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Code for Feature Matching with FLANN tutorial.')
parser.add_argument('--input1', help='Path to input image 1.', default='mu.jpg')
parser.add_argument('--input2', help='Path to input image 2.', default='mo.jpg')
args = parser.parse_args()
img_object = cv.imread(args.input2)
img_scene = cv.imread(args.input1)
if img_object is None or img_scene is None:
print('Could not open or find the images!')
exit(0)
#-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector, compute the descriptors
minHessian = 400
detector = cv.xfeatures2d_SURF.create(hessianThreshold=minHessian)
keypoints_obj, descriptors_obj = detector.detectAndCompute(img_object, None)
keypoints_scene, descriptors_scene = detector.detectAndCompute(img_scene, None)
#-- Step 2: Matching descriptor vectors with a FLANN based matcher
# Since SURF is a floating-point descriptor NORM_L2 is used
matcher = cv.DescriptorMatcher_create(cv.DescriptorMatcher_FLANNBASED)
knn_matches = matcher.knnMatch(descriptors_obj, descriptors_scene, 2)
#-- Filter matches using the Lowe's ratio test
ratio_thresh = 0.5
good_matches = []
for m,n in knn_matches:
if m.distance < ratio_thresh * n.distance:
good_matches.append(m)
#-- Draw matches
img_matches = np.empty((max(img_object.shape[0], img_scene.shape[0]), img_object.shape[1]+img_scene.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
cv.drawMatches(img_object, keypoints_obj, img_scene, keypoints_scene, good_matches, img_matches, flags=cv.DrawMatchesFlags_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS)
#-- Localize the object
obj = np.empty((len(good_matches),2), dtype=np.float32)
scene = np.empty((len(good_matches),2), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(len(good_matches)):
#-- Get the keypoints from the good matches
obj[i,0] = keypoints_obj[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt[0]
obj[i,1] = keypoints_obj[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt[1]
scene[i,0] = keypoints_scene[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt[0]
scene[i,1] = keypoints_scene[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt[1]
H, _ = cv.findHomography(obj, scene, cv.RANSAC)
#-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
obj_corners = np.empty((4,1,2), dtype=np.float32)
obj_corners[0,0,0] = 0
obj_corners[0,0,1] = 0
obj_corners[1,0,0] = img_object.shape[1]
obj_corners[1,0,1] = 0
obj_corners[2,0,0] = img_object.shape[1]
obj_corners[2,0,1] = img_object.shape[0]
obj_corners[3,0,0] = 0
obj_corners[3,0,1] = img_object.shape[0]
scene_corners = cv.perspectiveTransform(obj_corners, H)
#-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
cv.line(img_matches, (int(scene_corners[0,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[0,0,1])),\
(int(scene_corners[1,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[1,0,1])), (0,255,0), 4)
cv.line(img_matches, (int(scene_corners[1,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[1,0,1])),\
(int(scene_corners[2,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[2,0,1])), (0,255,0), 4)
cv.line(img_matches, (int(scene_corners[2,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[2,0,1])),\
(int(scene_corners[3,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[3,0,1])), (0,255,0), 4)
cv.line(img_matches, (int(scene_corners[3,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[3,0,1])),\
(int(scene_corners[0,0,0] + img_object.shape[1]), int(scene_corners[0,0,1])), (0,255,0), 4)
#-- Show detected matches
cv.namedWindow("Good Matches & Object detection", 0)
cv.resizeWindow("Good Matches & Object detection", 1024, 1024)
cv.imshow('Good Matches & Object detection', img_matches)
cv.waitKey()
SIFT Learing records的更多相关文章
- 【特征匹配】SIFT原理之KD树+BBF算法解析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/47606159 继上一篇中已经介绍了SIFT原理与C源代码剖析,最后得到了一系列 ...
- RobHess的SIFT代码解析之kd树
平台:win10 x64 +VS 2015专业版 +opencv-2.4.11 + gtk_-bundle_2.24.10_win32 主要参考:1.代码:RobHess的SIFT源码:SIFT+KD ...
- sift特征
已经有很多博客已经将sift特征提取算法解释的很清楚了,我只是记录一些我不明白的地方,并且记录几个理解sift特征比较好的博客. 1. http://aishack.in/tutorials/sift ...
- sift特征源码
先贴上我对Opencv3.1中sift源码的注释吧,虽然还有很多没看懂.先从detectAndCompute看起 void SIFT_Impl::detectAndCompute(InputArray ...
- opencv中的SIFT,SURF,ORB,FAST 特征描叙算子比较
opencv中的SIFT,SURF,ORB,FAST 特征描叙算子比较 参考: http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=1aDYAJBCrrK-uk2w3sSNai7h52x_ ...
- 特征描述算子-sift
特征描述算子-sift http://boche.github.io/download/sift/Introduction%20to%20SIFT.pdf
- SIFT特征详解
1.SIFT概述 SIFT的全称是Scale Invariant Feature Transform,尺度不变特征变换,由加拿大教授David G.Lowe提出的.SIFT特征对旋转.尺度缩放.亮度变 ...
- mysql slow query---pt-query-digest----db structure consistency,monitor table records before and after transaction.
将数据库脚本纳入版本管理是很必要的,尤其对于需要在客户那里部署升级的系统. 对于Python Django等框架,由于数据库是通过Model生成的,因此框架本身包括数据库升级工具,并通过代码版本间接管 ...
- SIFT中的尺度空间和传统图像金字塔
SIFT中的尺度空间和传统图像金字塔 http://www.zhizhihu.com/html/y2010/2146.html 最近自己混淆了好多概念,一边弄明白的同时,也做了一些记录,分享一下.最近 ...
随机推荐
- 【LeetCode】129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 题目地址:https://leetcode.com/pr ...
- LeetCode1237找出给定方程的正整数解
题目 给定方程f和值z,找出给定方程f(x,y)=z的正整数解x,y.f(x,y)关于x.y都是严格单调的. 题目保证 f(x, y) == z 的解处于 1 <= x, y <= 100 ...
- Joseph(hdu1443)
Joseph Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Sub ...
- Docker 与 K8S学习笔记(四)—— Dockerfile的编写
在上一篇中我们简单介绍了Docker镜像的获取与使用,其中在镜像制作中提到在实际使用中一定要用Dockerfile方式去创建镜像而不要用docker commit方式,那么我们该如何编写Dockerf ...
- STC8A,STC8G,STC8H系列的IRC内部振荡源频率调节
从STC15开始, 宏晶就在内置RC震荡源(内置时脉, 宏晶称之为IRC)这条路上越走越远. STC15这一代仅仅是"有", 精度和漂移差强人意. 从STC8开始对IRC的调节就越 ...
- 「AHOI2013」 差异
知识点: SA,线段树,单调栈 原题面 Loj Luogu 题意简述 给定一长度为 \(n\) 的字符串 \(S\),令 \(T_i\) 表示从第 \(i\) 个字符开始的后缀,求: \[\sum_{ ...
- NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
目录 概 主要内容 positional encoding 额外的细节 代码 Mildenhall B., Srinivasan P. P., Tancik M., Barron J. T., Ram ...
- Uncovering the Limits of Adversarial Training against Norm-Bounded Adversarial Examples
Uncovering the Limits of Adversarial Training against Norm-Bounded Adversarial Examples 目录 概 主要内容 实验 ...
- OAuth2.0的定义
1. 什么是OAuth2.0 * 用于REST/APIs的代理授权框架(delegated authorization) * 基于令牌Token的授权,在无需暴露用户密码的情况下,使应用能获取对用户数 ...
- SpringBoot 中拦截器的简介及使用方式
拦截器简介 拦截器通常通过动态代理的方式来执行. 拦截器的生命周期由IoC容器管理,可以通过注入等方式来获取其他Bean的实例,使用更方便. 拦截器配置使用方式 实现拦截器接口: import jav ...



