java:快速文件分割及合并
文件分割与合并是一个常见需求,比如:上传大文件时,可以先分割成小块,传到服务器后,再进行合并。很多高大上的分布式文件系统(比如:google的GFS、taobao的TFS)里,也是按block为单位,对文件进行分割或合并。
看下基本思路:
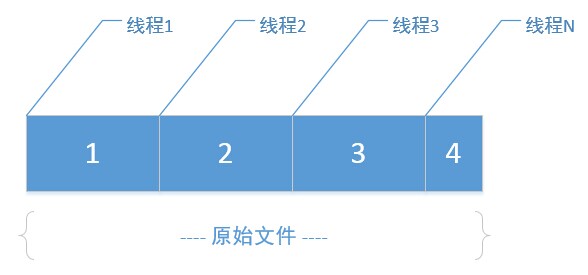
如果有一个大文件,指定分割大小后(比如:按1M切割)
step 1:
先根据原始文件大小、分割大小,算出最终分割的小文件数N
step 2:
在磁盘上创建这N个小文件
step 3:
开多个线程(线程数=分割文件数),每个线程里,利用RandomAccessFile的seek功能,将读取指针定位到原文件里每一段的段首位置,然后向后读取指定大小(即:分割块大小),最终写入对应的分割文件,因为多线程并行处理,各写各的小文件,速度相对还是比较快的。
合并时,把上面的思路逆向处理即可。
核心代码:
分割处理:
/**
* 拆分文件
* @param fileName 待拆分的完整文件名
* @param byteSize 按多少字节大小拆分
* @return 拆分后的文件名列表
* @throws IOException
*/
public List<String> splitBySize(String fileName, int byteSize)
throws IOException {
List<String> parts = new ArrayList<String>();
File file = new File(fileName);
int count = (int) Math.ceil(file.length() / (double) byteSize);
int countLen = (count + "").length();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(count,
count * 3, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(count * 2)); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String partFileName = file.getName() + "."
+ leftPad((i + 1) + "", countLen, '0') + ".part";
threadPool.execute(new SplitRunnable(byteSize, i * byteSize,
partFileName, file));
parts.add(partFileName);
}
return parts;
}
private class SplitRunnable implements Runnable {
int byteSize;
String partFileName;
File originFile;
int startPos;
public SplitRunnable(int byteSize, int startPos, String partFileName,
File originFile) {
this.startPos = startPos;
this.byteSize = byteSize;
this.partFileName = partFileName;
this.originFile = originFile;
}
public void run() {
RandomAccessFile rFile;
OutputStream os;
try {
rFile = new RandomAccessFile(originFile, "r");
byte[] b = new byte[byteSize];
rFile.seek(startPos);// 移动指针到每“段”开头
int s = rFile.read(b);
os = new FileOutputStream(partFileName);
os.write(b, 0, s);
os.flush();
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
合并处理:
/**
* 合并文件
*
* @param dirPath 拆分文件所在目录名
* @param partFileSuffix 拆分文件后缀名
* @param partFileSize 拆分文件的字节数大小
* @param mergeFileName 合并后的文件名
* @throws IOException
*/
public void mergePartFiles(String dirPath, String partFileSuffix,
int partFileSize, String mergeFileName) throws IOException {
ArrayList<File> partFiles = FileUtil.getDirFiles(dirPath,
partFileSuffix);
Collections.sort(partFiles, new FileComparator()); RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(mergeFileName,
"rw");
randomAccessFile.setLength(partFileSize * (partFiles.size() - 1)
+ partFiles.get(partFiles.size() - 1).length());
randomAccessFile.close(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
partFiles.size(), partFiles.size() * 3, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(partFiles.size() * 2)); for (int i = 0; i < partFiles.size(); i++) {
threadPool.execute(new MergeRunnable(i * partFileSize,
mergeFileName, partFiles.get(i)));
} }
private class MergeRunnable implements Runnable {
long startPos;
String mergeFileName;
File partFile;
public MergeRunnable(long startPos, String mergeFileName, File partFile) {
this.startPos = startPos;
this.mergeFileName = mergeFileName;
this.partFile = partFile;
}
public void run() {
RandomAccessFile rFile;
try {
rFile = new RandomAccessFile(mergeFileName, "rw");
rFile.seek(startPos);
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream(partFile);
byte[] b = new byte[fs.available()];
fs.read(b);
fs.close();
rFile.write(b);
rFile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
为了方便文件操作,把关于文件读写的功能,全封装到FileUtil类:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*; /**
* 文件处理辅助类
*
* @author yjmyzz@126.com
* @version 0.2
* @since 2014-11-17
*
*/
public class FileUtil { /**
* 当前目录路径
*/
public static String currentWorkDir = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "\\"; /**
* 左填充
*
* @param str
* @param length
* @param ch
* @return
*/
public static String leftPad(String str, int length, char ch) {
if (str.length() >= length) {
return str;
}
char[] chs = new char[length];
Arrays.fill(chs, ch);
char[] src = str.toCharArray();
System.arraycopy(src, 0, chs, length - src.length, src.length);
return new String(chs); } /**
* 删除文件
*
* @param fileName
* 待删除的完整文件名
* @return
*/
public static boolean delete(String fileName) {
boolean result = false;
File f = new File(fileName);
if (f.exists()) {
result = f.delete(); } else {
result = true;
}
return result;
} /***
* 递归获取指定目录下的所有的文件(不包括文件夹)
*
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList<File> getAllFiles(String dirPath) {
File dir = new File(dirPath); ArrayList<File> files = new ArrayList<File>(); if (dir.isDirectory()) {
File[] fileArr = dir.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < fileArr.length; i++) {
File f = fileArr[i];
if (f.isFile()) {
files.add(f);
} else {
files.addAll(getAllFiles(f.getPath()));
}
}
}
return files;
} /**
* 获取指定目录下的所有文件(不包括子文件夹)
*
* @param dirPath
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList<File> getDirFiles(String dirPath) {
File path = new File(dirPath);
File[] fileArr = path.listFiles();
ArrayList<File> files = new ArrayList<File>(); for (File f : fileArr) {
if (f.isFile()) {
files.add(f);
}
}
return files;
} /**
* 获取指定目录下特定文件后缀名的文件列表(不包括子文件夹)
*
* @param dirPath
* 目录路径
* @param suffix
* 文件后缀
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList<File> getDirFiles(String dirPath,
final String suffix) {
File path = new File(dirPath);
File[] fileArr = path.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
String lowerName = name.toLowerCase();
String lowerSuffix = suffix.toLowerCase();
if (lowerName.endsWith(lowerSuffix)) {
return true;
}
return false;
} });
ArrayList<File> files = new ArrayList<File>(); for (File f : fileArr) {
if (f.isFile()) {
files.add(f);
}
}
return files;
} /**
* 读取文件内容
*
* @param fileName
* 待读取的完整文件名
* @return 文件内容
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String read(String fileName) throws IOException {
File f = new File(fileName);
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream(f);
String result = null;
byte[] b = new byte[fs.available()];
fs.read(b);
fs.close();
result = new String(b);
return result;
} /**
* 写文件
*
* @param fileName
* 目标文件名
* @param fileContent
* 写入的内容
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static boolean write(String fileName, String fileContent)
throws IOException {
boolean result = false;
File f = new File(fileName);
FileOutputStream fs = new FileOutputStream(f);
byte[] b = fileContent.getBytes();
fs.write(b);
fs.flush();
fs.close();
result = true;
return result;
} /**
* 追加内容到指定文件
*
* @param fileName
* @param fileContent
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static boolean append(String fileName, String fileContent)
throws IOException {
boolean result = false;
File f = new File(fileName);
if (f.exists()) {
RandomAccessFile rFile = new RandomAccessFile(f, "rw");
byte[] b = fileContent.getBytes();
long originLen = f.length();
rFile.setLength(originLen + b.length);
rFile.seek(originLen);
rFile.write(b);
rFile.close();
}
result = true;
return result;
} /**
* 拆分文件
*
* @param fileName
* 待拆分的完整文件名
* @param byteSize
* 按多少字节大小拆分
* @return 拆分后的文件名列表
* @throws IOException
*/
public List<String> splitBySize(String fileName, int byteSize)
throws IOException {
List<String> parts = new ArrayList<String>();
File file = new File(fileName);
int count = (int) Math.ceil(file.length() / (double) byteSize);
int countLen = (count + "").length();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(count,
count * 3, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(count * 2)); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String partFileName = file.getName() + "."
+ leftPad((i + 1) + "", countLen, '0') + ".part";
threadPool.execute(new SplitRunnable(byteSize, i * byteSize,
partFileName, file));
parts.add(partFileName);
}
return parts;
} /**
* 合并文件
*
* @param dirPath
* 拆分文件所在目录名
* @param partFileSuffix
* 拆分文件后缀名
* @param partFileSize
* 拆分文件的字节数大小
* @param mergeFileName
* 合并后的文件名
* @throws IOException
*/
public void mergePartFiles(String dirPath, String partFileSuffix,
int partFileSize, String mergeFileName) throws IOException {
ArrayList<File> partFiles = FileUtil.getDirFiles(dirPath,
partFileSuffix);
Collections.sort(partFiles, new FileComparator()); RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(mergeFileName,
"rw");
randomAccessFile.setLength(partFileSize * (partFiles.size() - 1)
+ partFiles.get(partFiles.size() - 1).length());
randomAccessFile.close(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
partFiles.size(), partFiles.size() * 3, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(partFiles.size() * 2)); for (int i = 0; i < partFiles.size(); i++) {
threadPool.execute(new MergeRunnable(i * partFileSize,
mergeFileName, partFiles.get(i)));
} } /**
* 根据文件名,比较文件
*
* @author yjmyzz@126.com
*
*/
private class FileComparator implements Comparator<File> {
public int compare(File o1, File o2) {
return o1.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(o2.getName());
}
} /**
* 分割处理Runnable
*
* @author yjmyzz@126.com
*
*/
private class SplitRunnable implements Runnable {
int byteSize;
String partFileName;
File originFile;
int startPos; public SplitRunnable(int byteSize, int startPos, String partFileName,
File originFile) {
this.startPos = startPos;
this.byteSize = byteSize;
this.partFileName = partFileName;
this.originFile = originFile;
} public void run() {
RandomAccessFile rFile;
OutputStream os;
try {
rFile = new RandomAccessFile(originFile, "r");
byte[] b = new byte[byteSize];
rFile.seek(startPos);// 移动指针到每“段”开头
int s = rFile.read(b);
os = new FileOutputStream(partFileName);
os.write(b, 0, s);
os.flush();
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} /**
* 合并处理Runnable
*
* @author yjmyzz@126.com
*
*/
private class MergeRunnable implements Runnable {
long startPos;
String mergeFileName;
File partFile; public MergeRunnable(long startPos, String mergeFileName, File partFile) {
this.startPos = startPos;
this.mergeFileName = mergeFileName;
this.partFile = partFile;
} public void run() {
RandomAccessFile rFile;
try {
rFile = new RandomAccessFile(mergeFileName, "rw");
rFile.seek(startPos);
FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream(partFile);
byte[] b = new byte[fs.available()];
fs.read(b);
fs.close();
rFile.write(b);
rFile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} }
单元测试:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.junit.Test;
public class FileTest {
@Test
public void writeFile() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println(FileUtil.currentWorkDir);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
long originFileSize = 1024 * 1024 * 100;// 100M
int blockFileSize = 1024 * 1024 * 15;// 15M
// 生成一个大文件
for (int i = 0; i < originFileSize; i++) {
sb.append("A");
}
String fileName = FileUtil.currentWorkDir + "origin.myfile";
System.out.println(fileName);
System.out.println(FileUtil.write(fileName, sb.toString()));
// 追加内容
sb.setLength(0);
sb.append("0123456789");
FileUtil.append(fileName, sb.toString());
FileUtil fileUtil = new FileUtil();
// 将origin.myfile拆分
fileUtil.splitBySize(fileName, blockFileSize);
Thread.sleep(10000);// 稍等10秒,等前面的小文件全都写完
// 合并成新文件
fileUtil.mergePartFiles(FileUtil.currentWorkDir, ".part",
blockFileSize, FileUtil.currentWorkDir + "new.myfile");
}
}

java:快速文件分割及合并的更多相关文章
- (转)java:快速文件分割及合并
文件分割与合并是一个常见需求,比如:上传大文件时,可以先分割成小块,传到服务器后,再进行合并.很多高大上的分布式文件系统(比如:google的GFS.taobao的TFS)里,也是按block为单位, ...
- JAVA IO分析三:IO总结&文件分割与合并实例
时间飞逝,马上就要到2018年了,今天我们将要学习的是IO流学习的最后一节,即总结回顾前面所学,并学习一个案例用于前面所学的实际操作,下面我们就开始本节的学习: 一.原理与概念 一.概念流:流动 .流 ...
- c语言文件分割与合并
一.综述 c语言操作文件通过文件指针FILE*,每个要操作的文件必须打开然后才能读写. 注意事项: @1分割与合并文件最好使用二进制模式即"rb"或"wb",这 ...
- java 大文件分割与组装
不多说,直接上代码 1 import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; im ...
- PDF文件分割和合并
今天自己用C#实现了下PDF文件的分割和合并,大家可以试用一下. 代码和使用说明在这里:https://github.com/cserspring/pdf_split_merge 有什么意见,大家可以 ...
- python学习——大文件分割与合并
在平常的生活中,我们会遇到下面这样的情况: 你下载了一个比较大型的游戏(假设有10G),现在想跟你的同学一起玩,你需要把这个游戏拷贝给他. 然后现在有一个问题是文件太大(我们不考虑你有移动硬盘什么的情 ...
- delphi 文件分割与合并
流的使用分割与合并文件的函数 unit Unit1; interface uses Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, ...
- java文件分割及合并
分割设置好分割数量,根据源文件大小来把数据散到子文件中代码如下; package word; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; ...
- Java IO 流 -- 随机读取和写入流 RandomAccessFile (文件分割和合并)
RandomAccessFile 相对其它流多了一个seek() 方法指定指针的偏移量. 1.指定起始位置读取剩余内容 public static void test01() throws IOExc ...
随机推荐
- php并发编程相关扩展
Stream:PHP内核提供的socket封装Sockets:对底层Socket API的封装Libevent:对libevent库的封装Event:基于Libevent更高级的封装,提供了面向对象接 ...
- WPF学习之路(五) 实例:写字板(续)
WordPad 2.0 上一期实现了一虽然建议但是功能比较全面的Wordpad程序,但是程序代码略显繁琐,这一期更新改进版. MainWindows.xaml 添加 <Window.Comman ...
- ORA-00030: User session ID does not exist.
同事在Toad里面执行SQL语句时,突然无线网络中断了,让我检查一下具体情况,如下所示(有些信息,用xxx替换,因为是在处理那些历史归档数据,使用的一个特殊用户,所以可以用下面SQL找到对应的会话信息 ...
- Sql Server之旅——第十三站 对锁的初步认识
终于这个系列快结束了,马上又要过年了,没什么心情写博客...作为一个开发人员,锁机制也是我们程序员必须掌握的东西,很久之前 在学习锁的时候,都是教科书上怎么说,然后我怎么背,缺少一个工具让我们眼见为实 ...
- 简单的 http 服务器
HttpUtils: package org.windwant.httpserver; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAd ...
- js 求时间差
var date1=new Date(); //开始时间 var date2=new Date(); //结束时间 var date3=date2.getTime()-date1.getTim ...
- Windows自动关机命令
winxp中自带了自动关机功能,在开始→运行中使用SHUTDOWN命令 1. 延迟关机关机 shutdown -s -t 120 -s为关机:-t为时间,以秒为单位,120表示2分钟 表示两分钟后关机 ...
- JSP与Servelt的区别
相同点: 两者都是服务端的技术,而JSP本质上就是Servelt: 都可以处理来自客户端的请求,都可以对请求作出响应: 都可以生成HTML页面返回. 不同点: 在实际开发中,对JSP编程成响应的HTM ...
- sql server 常见错误代码15000 - 15999含义解析
错误 15000 - 15999 SQL Server 2008 R2 其他版本 错误 严重性 是否记录事件 说明(消息正文) 15001 16 否 对象 '%ls' 不存在或不是此操作的有效对象. ...
- MongoDB Sharding、库、collection设计学习汇总
sharding设计须考虑的几个因素 Sharding Key的选择 在片键的选择上,最好是能够在字段中选择混合型的片键,大范围的递增健.和随机分布的健组合,如按月份递增.按用户名 ...
