How Kafka’s Storage Internals Work
In this post I’m going to help you understand how Kafka stores its data.
I’ve found understanding this useful when tuning Kafka’s performance and for context on what each broker configuration actually does. I was inspired by Kafka’s simplicity and used what I learned to start implementing Kafka in Golang.
So how does Kafka’s storage internals work?
Kafka’s storage unit is a partition
A partition is an ordered, immutable sequence of messages that are appended to. A partition cannot be split across multiple brokers or even multiple disks.
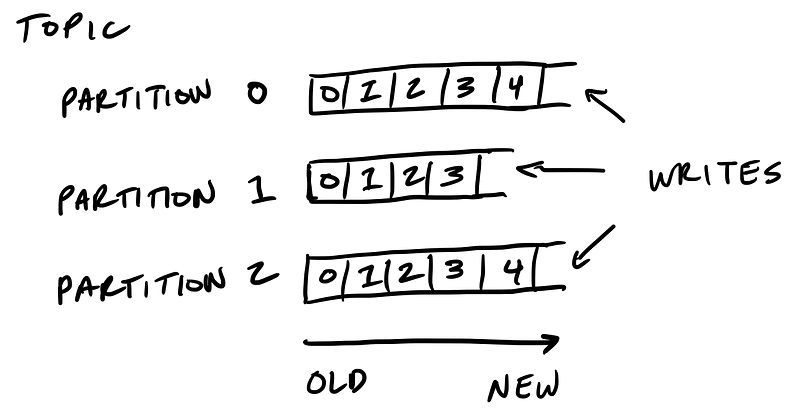
The retention policy governs how Kafka retains messages
You specify how much data or how long data should be retained, after which Kafka purges messages in-order—regardless of whether the message has been consumed.
Partitions are split into segments
So Kafka needs to regularly find the messages on disk that need purged. With a single very long file of a partition’s messages, this operation is slow and error prone. To fix that (and other problems we’ll see), the partition is split into segments.
When Kafka writes to a partition, it writes to a segment — the active segment. If the segment’s size limit is reached, a new segment is opened and that becomes the new active segment.
Segments are named by their base offset. The base offset of a segment is an offset greater than offsets in previous segments and less than or equal to offsets in that segment.
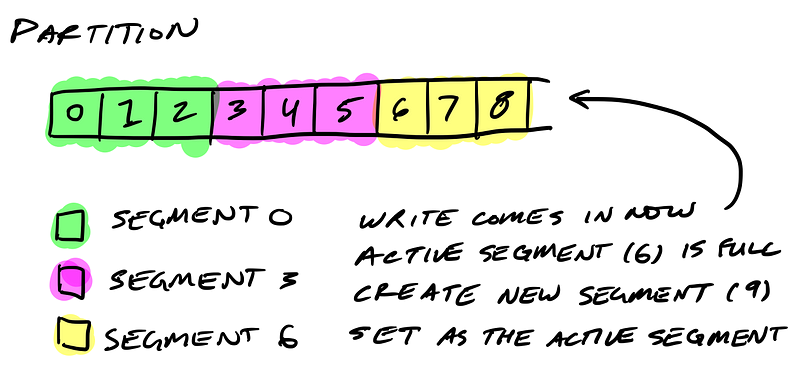
On disk a partition is a directory and each segment is an index file and a log file.
$ tree kafka | head -n 6
kafka
├── events-1
│ ├── 00000000003064504069.index
│ ├── 00000000003064504069.log
│ ├── 00000000003065011416.index
│ ├── 00000000003065011416.log
Segments logs are where messages are stored
Each message is its value, offset, timestamp, key, message size, compression codec, checksum, and version of the message format.
The data format on disk is exactly the same as what the broker receives from the producer over the network and sends to its consumers. This allows Kafka to efficiently transfer data with zero copy.
$ bin/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.DumpLogSegments --deep-iteration --print-data-log --files /data/kafka/events-1/00000000003065011416.log | head -n 4
Dumping /data/kafka/appusers-1/00000000003065011416.log
Starting offset: 3065011416
offset: 3065011416 position: 0 isvalid: true payloadsize: 2820 magic: 1 compresscodec: NoCompressionCodec crc: 811055132 payload: {"name": "Travis", msg: "Hey, what's up?"}
offset: 3065011417 position: 1779 isvalid: true payloadsize: 2244 magic: 1 compresscodec: NoCompressionCodec crc: 151590202 payload: {"name": "Wale", msg: "Starving."}
Segment indexes map message offsets to their position in the log
The segment index maps offsets to their message’s position in the segment log.
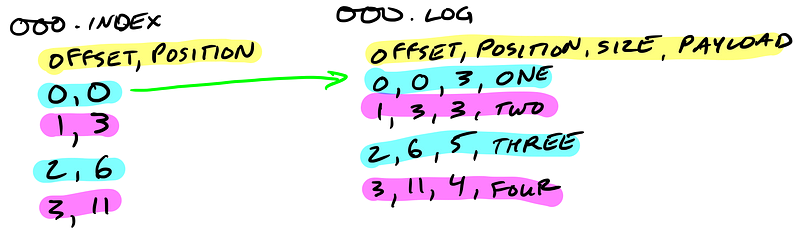
The index file is memory mapped, and the offset look up uses binary search to find the nearest offset less than or equal to the target offset.
The index file is made up of 8 byte entries, 4 bytes to store the offset relative to the base offset and 4 bytes to store the position. The offset is relative to the base offset so that only 4 bytes is needed to store the offset. For example: let’s say the base offset is 10000000000000000000, rather than having to store subsequent offsets 10000000000000000001 and 10000000000000000002 they are just 1 and 2.
Kafka wraps compressed messages together
Producers sending compressed messages will compress the batch together and send it as the payload of a wrapped message. And as before, the data on disk is exactly the same as what the broker receives from the producer over the network and sends to its consumers.

Let’s Review
Now you know how Kafka storage internals work:
- Partitions are Kafka’s storage unit
- Partitions are split into segments
- Segments are two files: its log and index
- Indexes map each offset to their message’s position in the log, they’re used to look up messages
- Indexes store offsets relative to its segment’s base offset
- Compressed message batches are wrapped together as the payload of a wrapper message
- The data stored on disk is the same as what the broker receives from the producer over the network and sends to its consumers
Implementing Kafka in Golang
I’m writing an implementation of Kafka in Golang, Jocko. So far I’ve implemented reading and writing to segments on a single broker and am working on making it distributed. Follow along and give me a hand.
How Kafka’s Storage Internals Work的更多相关文章
- Error when sending message to topic test with key: null, value: 2 bytes with error: (org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.ErrorLoggingCallback)
windows下使用kafka遇到这个问题: Error when sending message to topic test with key: null, value: 2 bytes with ...
- Kafka遇到30042ms has passed since batch creation plus linger time at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.FutureRecordMetadata.valueOrError(FutureRecordMetadata.java:94)
问题描述: 运行生产者线程的时候显示如下错误信息: Expiring 1 record(s) for XXX-0: 30042 ms has passed since batch creation p ...
- Kafka Offset Storage
1.概述 目前,Kafka 官网最新版[0.10.1.1],已默认将消费的 offset 迁入到了 Kafka 一个名为 __consumer_offsets 的Topic中.其实,早在 0.8.2. ...
- 《Pro SQL Server Internals, 2nd edition》的CHAPTER 1 Data Storage Internals中的Data Pages and Data Rows(翻译)
数据页和数据行 数据库中的空间被划分为逻辑8KB的页面.这些页面是以0开始的连续编号,并且可以通过指定文件ID和页号来引用它们.页面编号都是连续的,这样当SQL Server增长数据库文件时,从文件中 ...
- Kafka Internals: Consumers
Check out my last article, Kafka Internals: Topics and Partitions to learn about Kafka storage inter ...
- kafka学习指南(总结版)
版本介绍 从使用上来看,以0.9为分界线,0.9开始不再区分高级/低级消费者API. 从兼容性上来看,以0.8.x为分界线,0.8.x不兼容以前的版本. 总体拓扑架构 从上可知: 1.生产者不需要访问 ...
- Kafka官方文档V2.7
1.开始 1.1 简介 什么是事件流? 事件流相当于人体的中枢神经系统的数字化.它是 "永远在线 "世界的技术基础,在这个世界里,业务越来越多地被软件定义和自动化,软件的用户更是软 ...
- Kafka 消费者解析
一.消费者相关概念 1.1 消费组&消费者 消费者: 消费者从订阅的主题消费消息,消费消息的偏移量保存在Kafka的名字是__consumer_offsets的主题中 消费者还可以将⾃⼰的偏移 ...
- Kafka 0.9+Zookeeper3.4.6集群搭建、配置,新Client API的使用要点,高可用性测试,以及各种坑 (转载)
Kafka 0.9版本对java client的api做出了较大调整,本文主要总结了Kafka 0.9在集群搭建.高可用性.新API方面的相关过程和细节,以及本人在安装调试过程中踩出的各种坑. 关于K ...
随机推荐
- ACM/ICPC 之 简单DP-记忆化搜索与递推(POJ1088-滑雪)
递推型DP 将每个滑雪点都看作起点,从最低点开始逐个由四周递推出到达此点的最长路径的长度,由该点记下. 理论上,也可以将每一点都看作终点,由最高点开始计数,有兴趣可以试试. //经典DP-由高向低海拔 ...
- static 修饰内部类
static一般用来修饰成员变量或函数也修饰代码块,一般不能修饰类,但是可以修饰内部类,被修饰的内部类可以直接作为一个普通类来用,不需要创建一个外部类的实例,而普通内部类的引用需要创建一个外部类的实例 ...
- Java for LeetCode 209 Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Given an array of n positive integers and a positive integer s, find the minimal length of a subarra ...
- 【Android Studio错误】 If you are behind an HTTP proxy, please configure the proxy settings either in IDE or Gradle.
解决办法:以管理员身份运行cmd窗口,输入命令“netsh winsock reset” netsh winsock reset命令,作用是重置 Winsock 目录.如果一台机器上的Winsock协 ...
- UIWebView内嵌网页 Xcode7.0以后的用法
UIWebView* webPage=[[UIWebView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, screenWidth, screenHeight-64)]; ...
- 【编程题目】查找最小的 k 个元素
5.查找最小的 k 个元素(数组)题目:输入 n 个整数,输出其中最小的 k 个.例如输入 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 和 8 这 8 个数字,则最小的 4 个数字为 1,2,3 和 4. 算法里面学 ...
- 【gsl】生成随机数
来自:http://hsxqwanting.blog.163.com/blog/static/16945437201301042830815/ 使用GSL生成随机数时的三个步骤: (1)gsl_ ...
- JavaScript基础——实现循环
循环是多次执行同一段代码的一种手段.当你需要在一个数组或对象集上重复执行相同的任务时,这是非常有用的. JavaScript提供执行for和while循环的功能. 1.while循环 JavaScri ...
- 浅谈 switch和if
1.所有的switch 都可以用if 替换,但所有的if不一定能被switch替换 2.:switch case直接跳到对应的case值里面执行相应代码.而if语句会执行一条一条判断语句,直到匹配到对 ...
- AJAX 三级联动
新的封装类 <?php class DBDA { public $host="localhost";//服务器地址 public $uid="root"; ...
