Codeforces Fix a Tree
Fix a Tree
time limit per test2 seconds
A tree is an undirected connected graph without cycles.
Let's consider a rooted undirected tree with n vertices, numbered 1 through n. There are many ways to represent such a tree. One way is to create an array with n integers p1, p2, ..., pn, where pi denotes a parent of vertex i (here, for convenience a root is considered its own parent).

For this rooted tree the array p is [2, 3, 3, 2].
Given a sequence p1, p2, ..., pn, one is able to restore a tree:
There must be exactly one index r that pr = r. A vertex r is a root of the tree.
For all other n - 1 vertices i, there is an edge between vertex i and vertex pi.
A sequence p1, p2, ..., pn is called valid if the described procedure generates some (any) rooted tree. For example, for n = 3 sequences (1,2,2), (2,3,1) and (2,1,3) are not valid.
You are given a sequence a1, a2, ..., an, not necessarily valid. Your task is to change the minimum number of elements, in order to get a valid sequence. Print the minimum number of changes and an example of a valid sequence after that number of changes. If there are many valid sequences achievable in the minimum number of changes, print any of them.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ n).
Output
In the first line print the minimum number of elements to change, in order to get a valid sequence.
In the second line, print any valid sequence possible to get from (a1, a2, ..., an) in the minimum number of changes. If there are many such sequences, any of them will be accepted.
Examples
input
4
2 3 3 4
output
1
2 3 4 4
input
5
3 2 2 5 3
output
0
3 2 2 5 3
input
8
2 3 5 4 1 6 6 7
output
2
2 3 7 8 1 6 6 7
Note
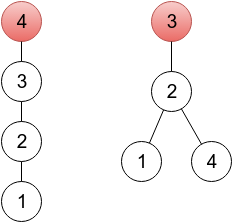
In the first sample, it's enough to change one element. In the provided output, a sequence represents a tree rooted in a vertex 4 (because p4 = 4), which you can see on the left drawing below. One of other correct solutions would be a sequence 2 3 3 2, representing a tree rooted in vertex 3 (right drawing below). On both drawings, roots are painted red.
In the second sample, the given sequence is already valid.
大概意思是:
给出 n 个结点的父亲,问至少修改多少个结点的父亲,能使整张图变成
一棵树(根的父亲为自己),要求输出任一方案。
其中 1 ≤ n ≤ 200000。
我的想法是你先按最小生成树的方法生成树,然后找一个点为根节点,有现成的就用,没有就选一个。
然后把每棵树都连起来就成了一棵新的树了。。。
写完以后很开心的发现1A了。。然后去看了看题解。。。
别人的方法是:
思考环和链的答案
图的各个弱连通块是环 + 内向树,或者树/环。
先用拓扑排序把内向树消掉
剩下来的是一些环,每个环随便选一个结点当根,然后再把所有的根连
在一起。
答案是环数-(是否存在自环)
其实我也没怎么看懂,我觉得道理应该差不多吧
```c++
include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
int n, root, tot, fa[maxn], ini[maxn];
bool flag[maxn];
set s;
set::iterator iter;
inline int read()
{
int s = 0, w = 1; char ch = getchar();
while(ch <= '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch == '-') w = -1; ch = getchar();}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') s = s * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return s * w;
}
int find(int t){return t == fa[t] ? t : fa[t] = find(fa[t]);}
int main()
{
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ini[i] = read(), fa[i] = i;
for(int A, B, i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
A = find(i); B = find(ini[i]); if(A == B) continue;
fa[A] = B; flag[i] = true;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){s.insert(find(fa[i])); if(i == ini[i]) root = i;}
for(iter = s.begin(); iter != s.end(); ++iter) tot++;
if(!root){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(flag[i]) continue;
root = i; tot++; flag[i] = true; ini[i] = i; break;
}
}
printf("%d\n", tot - 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(flag[i]) printf("%d ", ini[i]);
else printf("%d ", root);
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Fix a Tree的更多相关文章
- Problem - D - Codeforces Fix a Tree
Problem - D - Codeforces Fix a Tree 看完第一名的代码,顿然醒悟... 我可以把所有单独的点全部当成线,那么只有线和环. 如果全是线的话,直接线的条数-1,便是操作 ...
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree —— 并查集
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/699/problem/D D. Fix a Tree time limit per test 2 seconds memory ...
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) 698B Fix a Tree
D. Fix a Tree time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes A tree is an und ...
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2)D. Fix a Tree(并查集)
D. Fix a Tree time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Fix a Tree
Fix a Tree A tree is an undirected connected graph without cycles. Let's consider a rooted undirecte ...
- Codeforces 699D Fix a Tree 并查集
原题:http://codeforces.com/contest/699/problem/D 题目中所描述的从属关系,可以看作是一个一个块,可以用并查集来维护这个森林.这些从属关系中会有两种环,第一种 ...
- 【并查集】【模拟】Codeforces 698B & 699D Fix a Tree
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/698/B http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/699/D ...
- 【codeforces 698B】 Fix a Tree
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/698/B 题解: 还是比较简单的.因为每个节点只有一个父亲,可以直接建反图,保证出现的环中只有一条路径. ...
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 1) B. Fix a Tree 树的拆环
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/698/B题意:告诉你n个节点当前的父节点,修改最少的点的父节点使之变成一棵有根树.思路:拆环.题解:htt ...
随机推荐
- centos7安装rabbitmq简单方式
1,安装rabbitmq前要准备的基础环境 yum install build-essential openssl openssl-devel unixODBC unixODBC-devel make ...
- KVC、KVO 理解
参考经典链接: https://www.jianshu.com/p/f8198ca5e682 https://www.jianshu.com/p/be80318115a7 一. KVC 1.KVC介绍 ...
- nginx下TP3.2访问页面总是404
这是我测试onethink用的配置 可以参考一下 server { listen 80; server_name onethink.dev www.onethink.dev; root /vagran ...
- 6层PCB设计技巧和步骤
6层PCB设计技巧和步骤 一.原理图的编辑 6层板由于PCB板中可以有两层地,所以可以将模拟地和数字地分开.对于统一地还是分开地,涉及到电磁干扰中信号的最小回流路径问题,绘制完原理图,别忘检查错误和 ...
- C Primer Plus 学习 第四章
字符串与格式化输入/输出 函数 strlen() 关键字 const 利用#define 和 const创建符号常量 #include <stdio.h> #include <str ...
- Sass字符运算
在 Sass 中可以通过加法符号“+”来对字符串进行连接.例如: $content: "Hello" + "" + "Sass!"; .bo ...
- Hibernate性能提升
1.大数据量批量插入造成Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError 内存溢出异常 正常插入: session.sav ...
- golang接口
接口是方法的集合,接口不需要考虑类型的属性是否一致,只需要考虑类型是否实现了接口的方法. 比如接口不需要考虑例二中的类型student和employee的属性,都可以传入接口,只需要他们实现了接口中的 ...
- vue 防止xss攻击
1.在终端引入xss,命令: npm install xss --save 2.在vue的页面进行引入 import xss from 'xss' 测试 <p v-html="test ...
- Properties工具类学习
Properties类学习 1.定义 Properties,java.utils包下的一个工具类,主要用于读取Java的配置文件.各种语言都有自己所支持的配置文件,配置文件中很多变量是经常变动的. 这 ...
