CF 672C 两个人捡瓶子 最短路与次短路思想
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
It was recycling day in Kekoland. To celebrate it Adil and Bera went to Central Perk where they can take bottles from the ground and put them into a recycling bin.
We can think Central Perk as coordinate plane. There are n bottles on the ground, the i-th bottle is located at position (xi, yi). Both Adil and Bera can carry only one bottle at once each.
For both Adil and Bera the process looks as follows:
- Choose to stop or to continue to collect bottles.
- If the choice was to continue then choose some bottle and walk towards it.
- Pick this bottle and walk to the recycling bin.
- Go to step 1.
Adil and Bera may move independently. They are allowed to pick bottles simultaneously, all bottles may be picked by any of the two, it's allowed that one of them stays still while the other one continues to pick bottles.
They want to organize the process such that the total distance they walk (the sum of distance walked by Adil and distance walked by Bera) is minimum possible. Of course, at the end all bottles should lie in the recycling bin.
First line of the input contains six integers ax, ay, bx, by, tx and ty(0 ≤ ax, ay, bx, by, tx, ty ≤ 109) — initial positions of Adil, Bera and recycling bin respectively.
The second line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of bottles on the ground.
Then follow n lines, each of them contains two integers xi and yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 109) — position of the i-th bottle.
It's guaranteed that positions of Adil, Bera, recycling bin and all bottles are distinct.
Print one real number — the minimum possible total distance Adil and Bera need to walk in order to put all bottles into recycling bin. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct if 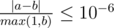 .
.
3 1 1 2 0 0 1 1
2 1
2 3
11.084259940083
5 0 4 2 2 0 5 2
3 0
5 5
3 5
3 3
33.121375178000
Consider the first sample.
Adil will use the following path:  .
.
Bera will use the following path:  .
.
Adil's path will be 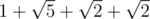 units long, while Bera's path will be
units long, while Bera's path will be 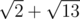 units long.
units long.
C题题意:二维平面上有n个(n<=10^5)点(xi,yi),有两个起点A(ax,ay)和B(bx,by),一个终点T(tx,ty)(0<=横纵坐标<=10^9)
可以从两个起点中的一个或两个出发,经过所有(xi,yi),且每到达一个(xi,yi)都要回到终点,问所有走过距离的最小值
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
#define MM(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a));
const double eps = 1e-;
const int inf =0x7f7f7f7f;
const double pi=acos(-);
const int maxn=+; struct point{
double x,y;
}p[maxn];
point a,b,o;
int a1,a2,b1,b2;
double l[maxn+],mina,minb,seca,secb,ca1,ca2,cb1,cb2; double dis(point a,point b)
{
return pow((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y),0.5);
} void solvea(int i)
{
if(l[i]-dis(a,p[i])>mina)
{
seca=mina;
ca2=ca1;
mina=l[i]-dis(a,p[i]);
ca1=i;
}
else if(l[i]-dis(a,p[i])>seca)
{
seca=l[i]-dis(a,p[i]);
ca2=i;
}
} void solveb(int i)
{
if(l[i]-dis(b,p[i])>minb)
{
secb=minb;
cb2=cb1;
minb=l[i]-dis(b,p[i]);
cb1=i;
}
else if(l[i]-dis(b,p[i])>secb)
{
secb=l[i]-dis(b,p[i]);
cb2=i;
}
} int main()
{
while(~scanf("%lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf",&a.x,&a.y,&b.x,&b.y,&o.x,&o.y))
{
mina=minb=seca=secb=-1e20;
ca1=,ca2=,cb1=,cb2=;
int n;double ans=; scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
l[i]=dis(p[i],o);
ans+=*l[i];
solvea(i);
solveb(i);
} if(ca1!=cb1)
{
if(mina<||minb<)
ans-=max(mina,minb);//刚开始没有加这句就wa了,因为即使两人最优的瓶子不是同
//一个,却可能存在其中有人的收益为负的情况,这种情况下就应该取两者中收益较大的一个(满足至少一个,可以///只有一个)
else
ans-=mina+minb;
}
else
{
if(mina<||minb<)
ans-=max(mina,minb);
else
{
if(mina+max(secb,0.0)>minb+max(seca,0.0))
ans-=mina+max(secb,0.0);
else ans-=minb+max(seca,0.0);
}
}
printf("%.16f\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
分析:用图论里的最短路和次短路的思想记录下最短路和次短路就好,,其实写的有点挫,可以直接用pair<double,int>再sort排序就好,,最关键的是,,要分情况讨论,因为两个人至少有一个要去捡,也就是说可以只有一个,所以应分情况讨论,错误点见代码
CF 672C 两个人捡瓶子 最短路与次短路思想的更多相关文章
- 最短路和次短路问题,dijkstra算法
/* *题目大意: *在一个有向图中,求从s到t两个点之间的最短路和比最短路长1的次短路的条数之和; * *算法思想: *用A*求第K短路,目测会超时,直接在dijkstra算法上求次短路; ...
- UESTC30-最短路-Floyd最短路、spfa+链式前向星建图
最短路 Time Limit: 3000/1000MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535KB (Java/Others) 在每年的校赛里,所有进入决赛的同 ...
- hdu1688(dijkstra求最短路和次短路)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1688 题意:第k短路,这里要求的是第1短路(即最短路),第2短路(即次短路),以及路径条数,最后如果最 ...
- POJ 3463 Sightseeing 【最短路与次短路】
题目 Tour operator Your Personal Holiday organises guided bus trips across the Benelux. Every day the ...
- POJ - 3463 Sightseeing 最短路计数+次短路计数
F - Sightseeing 传送门: POJ - 3463 分析 一句话题意:给你一个有向图,可能有重边,让你求从s到t最短路的条数,如果次短路的长度比最短路的长度多1,那么在加上次短路的条数. ...
- poj 3463 Sightseeing( 最短路与次短路)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3463 Sightseeing Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissio ...
- POJ---3463 Sightseeing 记录最短路和次短路的条数
Sightseeing Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 9247 Accepted: 3242 Descr ...
- CF 672C Recycling Bottles[最优次优 贪心]
C. Recycling Bottles time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- CF 586B 起点到终点的最短路和次短路之和
起点是右下角 终点是左上角 每次数据都是两行的点 输入n 表示有n列 接下来来的2行是 列与列之间的距离 最后一行是 行之间的距离 枚举就行 Sample test(s) input 41 ...
随机推荐
- Hadoop三种架构介绍及搭建
apache hadoop三种架构介绍(standAlone,伪分布,分布式环境介绍以及安装) hadoop 文档 http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/ 1.StandAlo ...
- Storm消费Kafka提交集群运行
1.创建拓扑,配置KafkaSpout.Bolt KafkaTopologyBasic.java: package org.mort.storm.kafka; import org.apache.ka ...
- 在Ubuntu上安装Spark
1.下载spark2.4.3 使用用户的hadoop的版本,解压并放到/usr/local下并改名为spark目录 2.设置spark目录为本用户所有 3.设置环境变量 (1)#~/.bashrc e ...
- NOIP2017普及组比赛总结
期中考总结&NOIP2017总结 2017年11月11日,我第二次参加NOIP普及组复赛.上一年,我的得分是250分,只拿到了二等奖.我便把目标定为拿到一等奖,考到300分以上. 早上8点多, ...
- 最短meeting路线(树的直径)--牛客第四场(meeting)
题意: 给你一棵树,树上有些点是有人的,问你选一个点,最短的(最远的那个人的距离)是多少. 思路: 其实就是树的直径,两遍dfs,dfs第二遍的时候遇到人就更新直径就行了,ans是/2,奇数的话+1. ...
- C# 面向对象8 值类型和引用类型
值类型和引用类型 概念 示意图: 1.值类型,在栈中开辟一块空间,存储 2.引用类型,在堆中开辟一块空间,存储数据,然在栈中开辟一块空间存储堆中的数据的地址
- git 常用命令语句(个人笔记)
切换账户 git config user.name xxxxx 查看用户名 ex: git config user.name tongjiaojiao git config user.e ...
- js 控制加载|移除 script 与 link 文件
js 加载 script 文件 /** * 加载 script 文件 * @param src */ function loadScript(src) { var addSign = true; va ...
- django 中实现文件下载的3种方式
方法一:使用HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse def file_down(request): file=open('/hom ...
- 微信支付成功没有回调遇到的坑 onBridgeReady getBrandWCPayRequest wx.chooseWXPay
最近在调微信支付,遇到一个问题,就是支付成功回调不执行的. 遇到的问题就是 苹果手机 支付成功没有进到回调函数里,但是支付的时候,点击取消支付是可以进到回调函数里的. 安卓手机测试一切正常! ...
